SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Centre for Airborne Systems (CABS) has officially begun the hunt for a cutting-edge Mission System for the highly anticipated Airborne Early Warning and Control System MK-1A (AEW&CS). This upgraded version of India’s current Netra Mk1 AEW&CS promises to bolster the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) aerial surveillance and command capabilities.
The MK-1A aims to significantly modernize the existing system, phasing out several imported components. Gone will be the reliance on foreign ground-based Data Links, ground-based & airborne terminals, and even Electronic Intelligence (ELINT) and Radar Warning Receiver (RWR) systems. This ambitious project marks a major step towards indigenous defence production and technological self-reliance.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s supersonic cruise missile, the BrahMos, is gaining steam in the international arms market, with a second Southeast Asian country close to sealing a deal and promising negotiations with three more nations. This marks a significant step for India’s defence exports and its ambitions to become a major defence technology supplier.
Following the landmark deal with the Philippines, the second Southeast Asian nation is on the verge of joining the BrahMos club. While specifics remain confidential, sources believe the contract could be finalized later this year, boosting India’s strategic presence in the region. Talks with another Southeast Asian country are also progressing, potentially expanding BrahMos’ footprint in the vital Indo-Pacific.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

In a significant stride in India’s aerospace capabilities, the first of the newly constructed LCA-Tejas Mk1A fighter jets is poised to enter the crucial phase of its assembly process. Anticipated to initiate its first taxi trials by the middle of the upcoming month, the aircraft is set to undergo a series of flights by late February, marking a pivotal milestone in its journey towards operational readiness.
Following the taxi trials, the aircraft will embark on a series of flights in late February. By the end of March, it’s expected to have completed all necessary pre-delivery trials, paving the way for customer-mandated sorties to begin.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
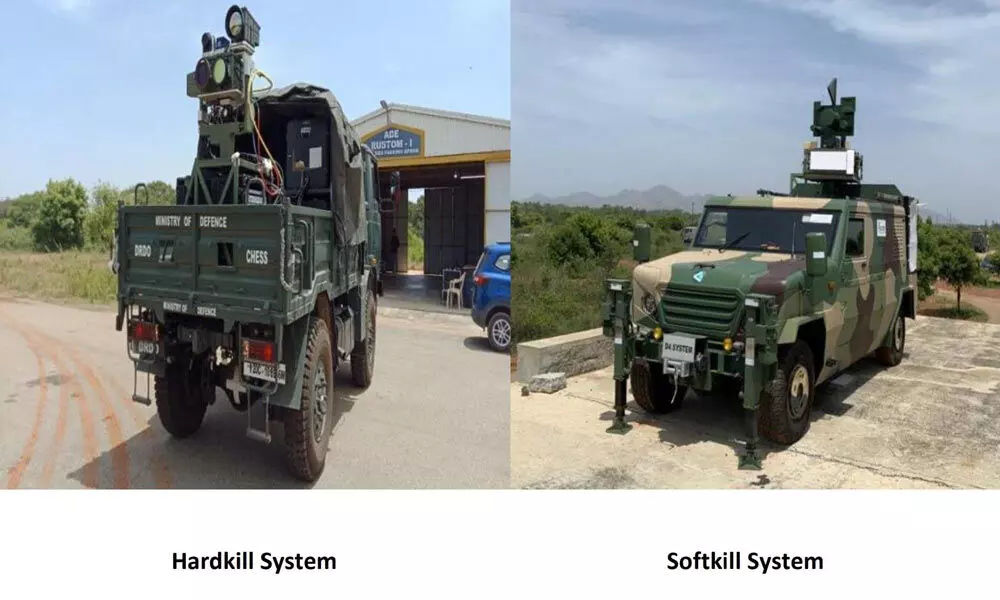

In a significant leap towards bolstering national security, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully developed indigenous counter-drone technology. This cutting-edge system, capable of detecting, soft kill, and hard kill responses against various types of drones, has already undergone successful demonstrations for armed services and internal security agencies.
The technology’s transfer to Bharat Electronics Limited, Bengaluru, for production marks a pivotal moment in India’s quest for self-reliance in defense capabilities. Additionally, four more Indian firms have been granted the Transfer of Technology for the production of anti-drone systems, amplifying the reach and impact of this groundbreaking innovation.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
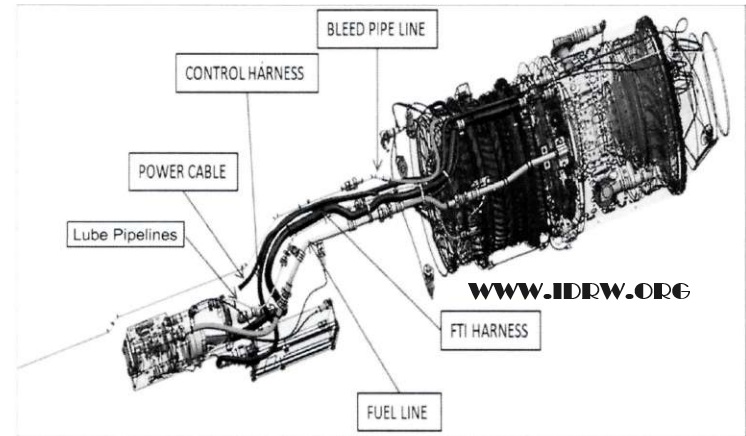
The Defence Research and Development Organization’s (DRDO) Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) has recently issued a tender that signifies a significant stride in India’s pursuit of cutting-edge technology. The tender calls for the development of manufacturing, assembly, and engine integration technologies, along with the manufacturing of engine hardware and the supply of 20 units of assembled Advanced Turbo Gas Generator (ATGG) Engines, including spares.
The key objective of the tender issued by GTRE is to invite Indian industry partners to participate in the development, manufacturing, and supply of ATGG Engines. This includes the creation of technologies for efficient manufacturing processes, assembly techniques, and integration methods. The tender outlines a timeline of 30 months for the Indian industry partner to deliver 20 units of assembled ATGG Engines along with necessary spares.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is gearing up for a major boost in its domestic fighter jet capabilities, planning to acquire an additional 97 Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk1A aircraft on top of the 83 already ordered in 2021. This ambitious acquisition plan signifies a strong commitment to indigenous fighter development and promises to significantly shape the IAF’s future fleet composition.
The initial batch of 83 Tejas Mk1A jets, with deliveries starting in February 2024, will primarily replace ageing MiG-21 squadrons scheduled for retirement by 2025. This phased acquisition allows for a smooth transition and ensures no gaps in aerial defence capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
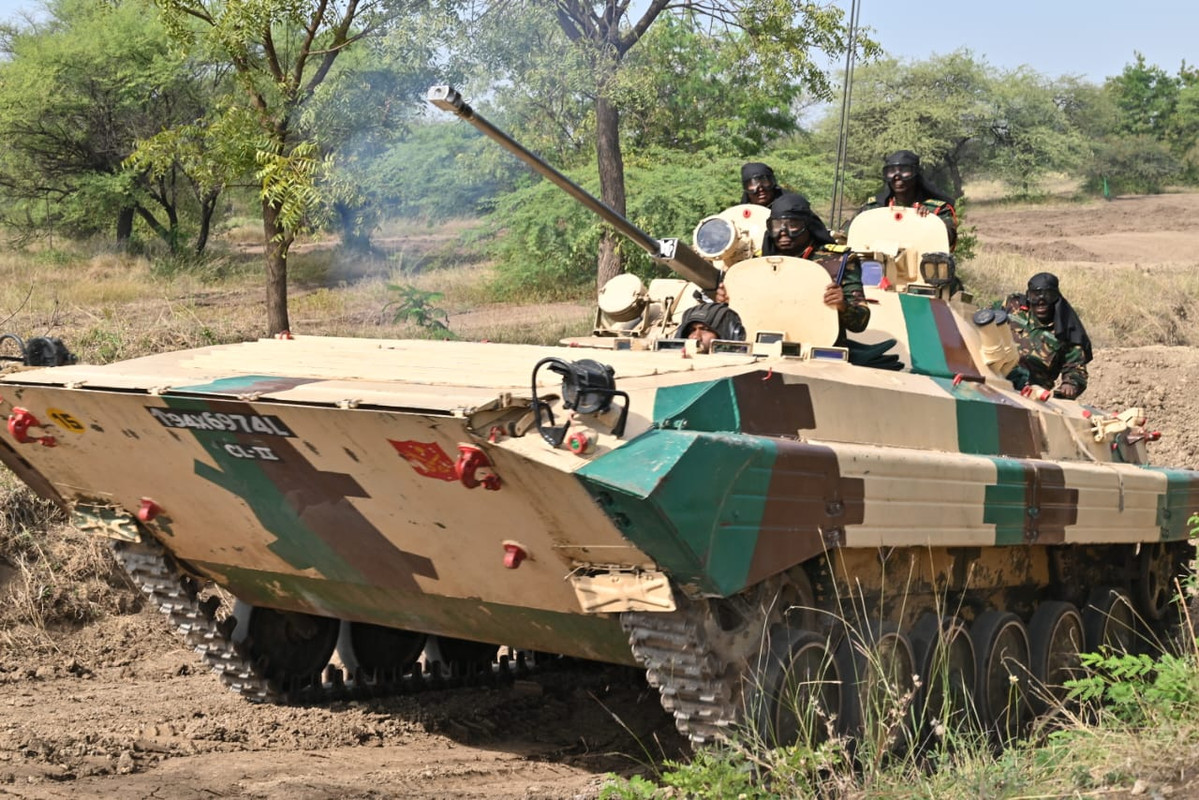

India and Tanzania’s military ties are heating up, with defence equipment sales talks ramping up and armoured vehicles taking centre stage. General Jacob John Mkunda, Tanzania’s Chief of Defence Force, made a strategic visit to India’s Mechanised Infantry School in Ahmednagar last month, where he witnessed demonstrations of two key contenders: the Indian-made BMP-II Infantry Combat Vehicle and the DRDO’s WhAP 8×8 Amphibious Wheeled Armoured Vehicle.
Tanzania’s military faces the challenge of ageing Soviet-era Armoured vehicles like the BTR-152 and BRDM-2. Modernization is a crucial goal, and Indian options seem to be gaining traction. The BMP-II, a Russian design manufactured in India under license, offers proven firepower and infantry support capabilities. Meanwhile, the WhAP 8×8, a domestically developed amphibious vehicle, boasts impressive manoeuvrability and all-terrain prowess, perfect for Tanzania’s diverse landscape.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

The fate of DRDO’s Tapas Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) program has taken an interesting turn. While funding for its production has been diverted to the newer Archer-NG program, the Tapas story is far from over. DRDO’s Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) will continue to refine the airframe, utilizing its potential for both engine testing and future platform development.
Tapas, originally known as Rustom-II, has been a significant player in India’s UAV journey. It has achieved several milestones, including successful flights at 28,000 ft and 18 hours endurance, demonstrating its capability for surveillance and intelligence gathering missions. While not without its challenges, Tapas has paved the way for advancements in indigenous UAV design and technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
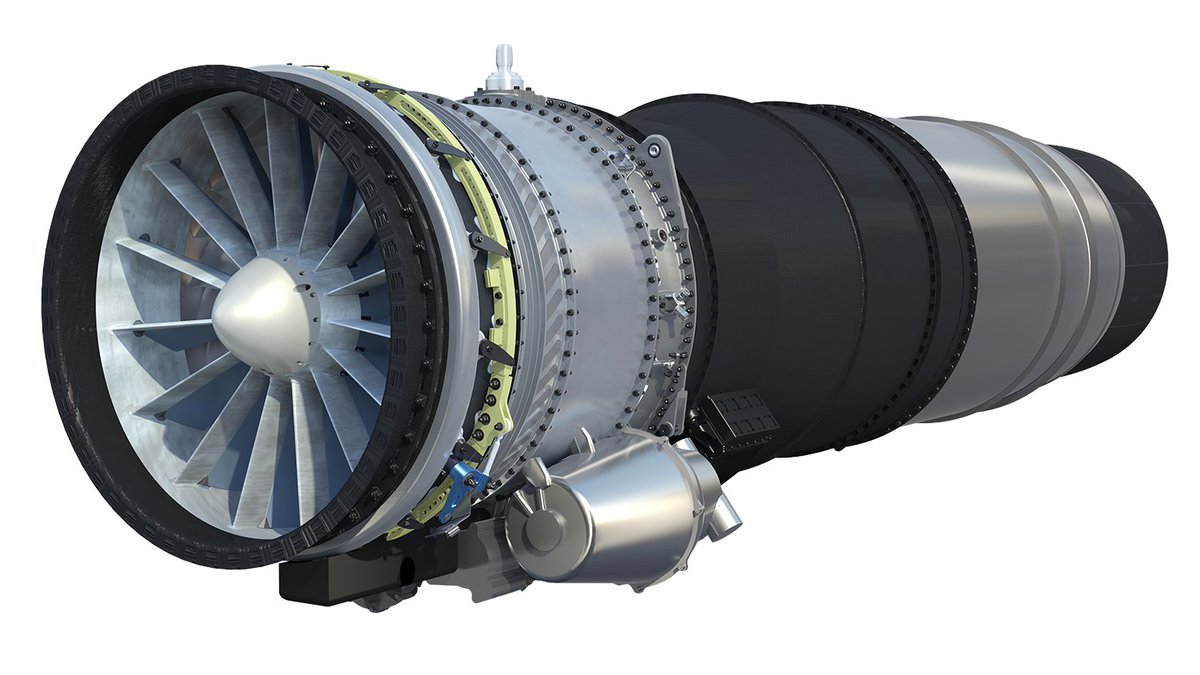

As India’s quest for a fifth-generation fighter jet gathers momentum, Rolls-Royce has thrown down a gauntlet with an audacious offer. The British engine giant has proposed co-developing a “Clean-Slate” new engine for India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, promising complete intellectual property (IP) transfer and operationalization within a flat decade.
This offer comes at a pivotal moment, coinciding with Indian Defence Minister Rajnath Singh’s upcoming two-day visit to the UK, aimed at strengthening strategic and security ties. With India’s indigenous Kaveri engine project facing delays, Rolls-Royce’s proposal presents a potentially attractive alternative.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a recent visit by India’s External Affairs Minister, S. Jaishankar, to Russia last month, Russia reiterated its offer to supply the AL-41F-1S (article 117S) aircraft engine for India’s Sukhoi-30MKI fleet. The AL-41F-1S is a modular two-shaft turbofan engine equipped with thrust vector control and integrated digital control systems.
Currently, the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) Su-30MKI fleet is powered by the AL-31FP (122.6 kN) engine. However, in a significant development, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has recently received approval for the upgrade of the Sukhoi-30MKI, where 84 Su-30s from the first batch will undergo a comprehensive transformation. The upgrade includes the installation of all-new avionics and an Indian-developed Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) Radar. Over 50 major subsystems will be replaced by indigenous systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
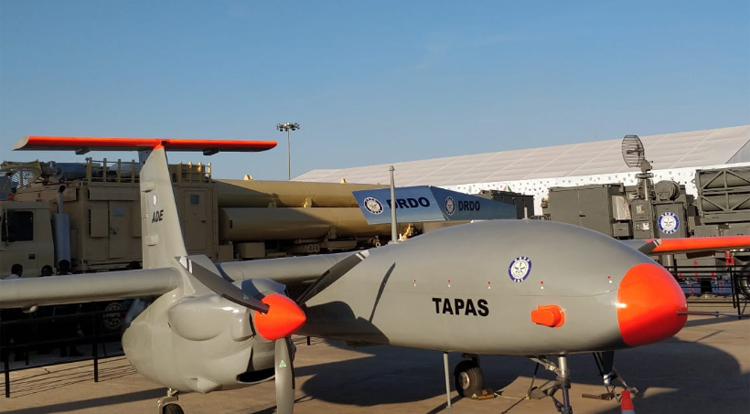

India’s endeavour into the development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) has been marked by ambitious projects such as the Rustom-II (Tapas), designed to be a medium-altitude long-endurance (MALE) UAV. However, recent reports suggest that this ambitious venture might never see production due to a myriad of challenges faced by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) in meeting the Preliminary Staff Qualitative Requirements (PSQR) standards.
One of the major stumbling blocks for the Rustom-II (Tapas) program was its failure to meet the Preliminary Staff Qualitative Requirement (PSQR) requirements. The UAV was expected to reach an altitude of 30,000 feet and demonstrate a flight time of 20 hours. Regrettably, the vehicle fell short of these benchmarks, leading to reconsideration of its viability for production.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Bangalore-based drone startup NewSpace Research and Technologies (NRT) is making waves with its innovative Combat Cloud platform, designed for data fusion and distribution within drone swarms. This cutting-edge technology, part of NRT’s Fused Teaming with Unmanned Rapid Effects (FUTURE) initiative, promises to revolutionize battlefield communication and decision-making.
Imagine a network where authorized drones, each a node, seamlessly share and analyze critical data. This is the essence of Combat Cloud. Each drone acts as a sensor and processor, contributing to a shared intelligence picture that empowers faster command and control (C2), quicker OODA loop closure (Observe, Orient, Decide, Act), and intelligent decision-making at the edge of the battlefield.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Marking a historic milestone, the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Naval trainer prototype NP5 has successfully completed a series of landings and take-offs from India’s first domestically built aircraft carrier, INS Vikrant. This achievement, showcased in the recent DRDO Year-End Review 2023, signifies a major leap forward in India’s quest for self-reliance in naval aviation.
NP5, which made its maiden flight last August, was initially planned to undergo trials on both INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant. Its successful operation on Vikrant demonstrates the aircraft’s adaptability and robustness, paving the way for its seamless integration into the Indian Navy’s carrier operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
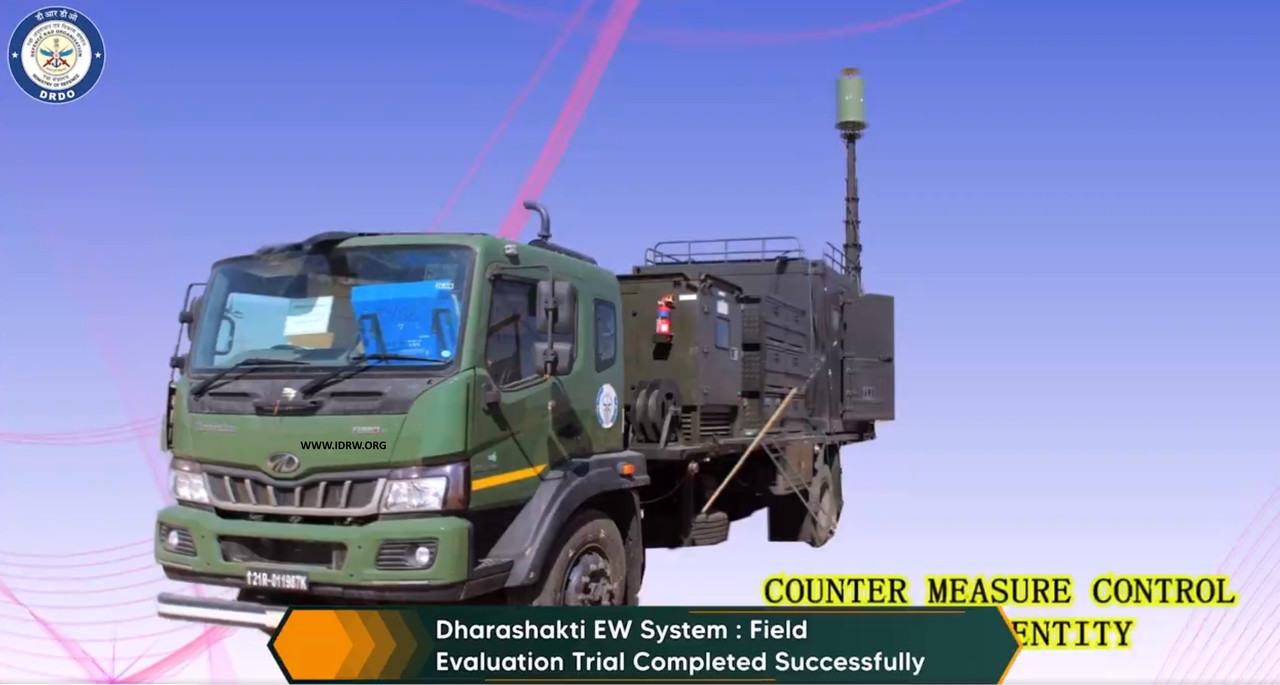

In a significant leap forward, the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) concluded 2023 on a high note, confirming the successful completion of Field Evaluation Trials for the Dharashakti Electronic Warfare (EW) System. This state-of-the-art system encompasses a comprehensive array of entities designed to address Control, Counter Measures, Jamming, Reconnaissance, and Direction Finding in diverse terrains such as deserts and plains.
The Dharashakti EW System boasts an intricate configuration comprising multiple entities, each serving a specific purpose in enhancing the electronic warfare capabilities. The key components include the Control Center Entity, Counter Measure Control Entity, Jammer UAV Entity, Reconnaissance and Direction Finding Station Radar, Jammer and High Band Entity, Jammer Interceptor Mobile Entity, and Jammer Station Very Ultra High Frequency Entity.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
Amidst whispers and speculation, India’s indigenous Archer-NG, a Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), is poised to take flight. Developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) of DRDO, the Archer-NG promises to strengthen India’s aerial surveillance and strike capabilities.
Contrary to speculation, the Archer-NG is not a licensed variant of the Israeli Heron MkII. While it draws inspiration from existing technologies, it marks a significant leap forward in indigenous design and development. In fact, the project leverages the extensive expertise gained through the Tapas program, a crucial stepping stone in India’s UAV development journey.
Continue reading