Idrw Team
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG
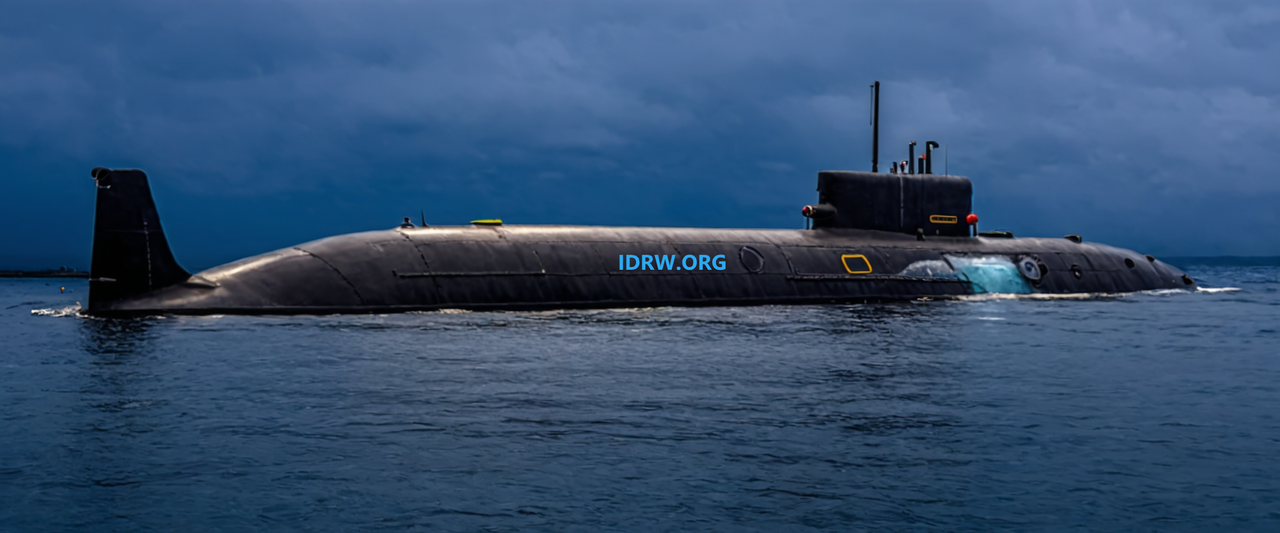

India has quietly achieved another significant milestone in its strategic defense capabilities by launching its fourth nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN), codenamed S4 (Star), according to a recent report from Hindustan Times. The submarine was launched on October 16, 2024, a day after Defence Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated the Very Low-Frequency (VLF) Naval Station, underscoring India’s growing naval prowess.
The S4 (Star) is a sister ship of INS Aridhaman (S4), part of India’s second generation of SSBNs, designed to improve upon the capabilities of the Arihant-class submarines. With a displacement of approximately 7,000 tons, S4 (Star) is 1,000 tons heavier than the earlier Arihant-class submarines, offering more space for enhanced capabilities, including a larger missile payload.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Earlier this month, the Supreme Court of India dismissed a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) that sought to halt the export of Indian defense equipment to Israel, citing allegations of war crimes by Tel Aviv in Gaza. The court’s refusal to intervene was rooted in the fact that foreign policy is not within its jurisdiction, deferring the matter to the executive. However, the issue raised by the PIL transcends Israel and touches on a broader debate critical to India’s aspirations to become a major defense exporter.
The question of whether a country should regulate its defence exports based on the actions of its buyers in global conflicts is a normative one. It requires India to balance its moral standing with its strategic and economic ambitions in the global defence market. This debate has gained importance as India seeks to transition from one of the world’s largest arms importers to a competitive exporter of weapons and military systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
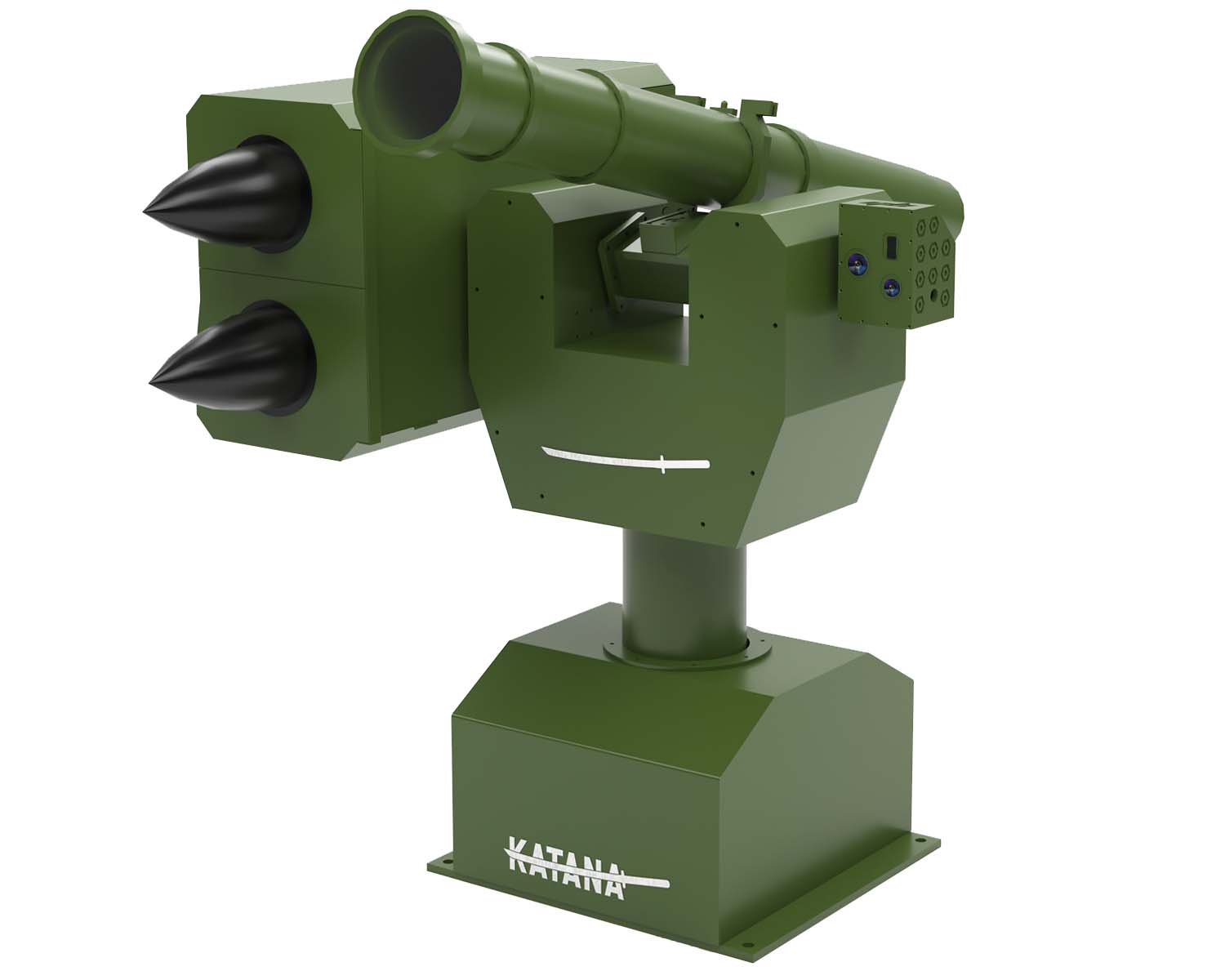

Indian robotics and AI company Gridbots has developed a state-of-the-art autonomous weapon station named KATANA, designed to enhance the situational awareness and defensive capabilities of homeland security units and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs). The KATANA Autonomous Weapon Station represents a major technological leap, integrating advanced AI systems to track, lock onto, and eliminate multiple threats in seconds, providing a fully autonomous defense solution.
KATANA’s integration of AI and deep learning technologies sets it apart from traditional weapon stations. The system’s AI not only tracks and identifies targets but also learns from previous engagements, allowing it to become more efficient over time. This capability ensures that KATANA can detect, identify, and neutralize threats faster and more accurately than systems relying solely on manual operation.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
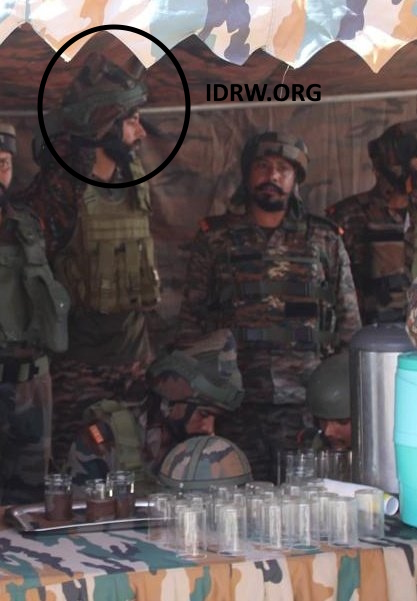

A significant development in the Indian Army’s equipment modernization has seen Sikh soldiers sporting the Kavro SCH 111 T ‘Veer’ helmet, designed specifically for Sikh soldiers. The helmet, developed by Indian firm MKU Limited, is designed to be worn over a cloth patka or turban, providing all-around ballistic protection across the head.
The Indian Army began receiving these helmets last year, and they offer NIJ Level IIIA protection, capable of resisting 9 mm bullets. MKU emphasizes the helmet’s lightweight, anti-allergic, all-weatherproof, and chemical-safe properties, along with its excellent shock absorption capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
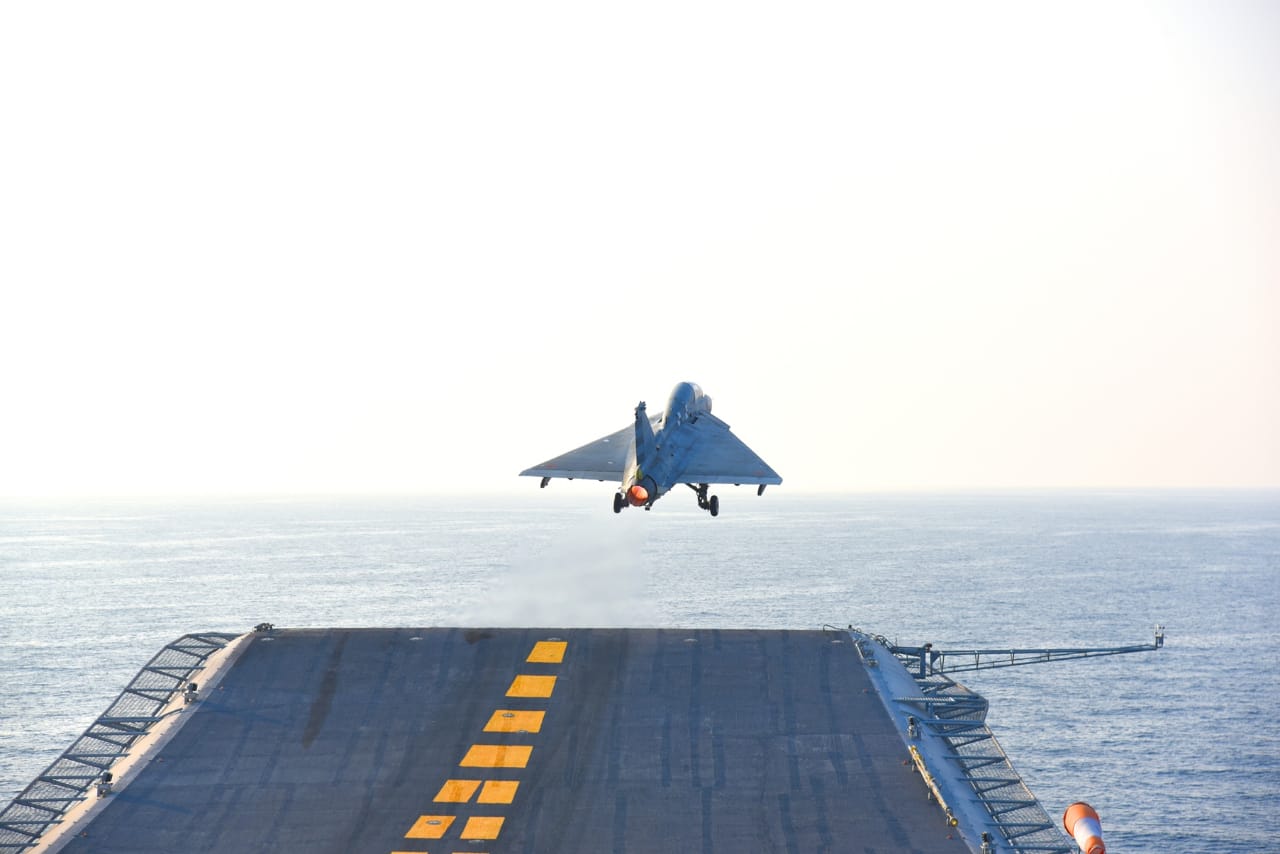

Jitendra J Jadhav, a Distinguished Scientist and the Director General of the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA), has revealed that the Indian Navy’s acquisition of a crucial squadron of LCA-Navy carrier-based fighters is currently delayed due to pending government procedures. However, he expressed optimism that the procedural hurdles would be resolved soon, leading to the induction of the squadron.
The Indian Navy has been in pursuit of enhancing its naval aviation capabilities, specifically with the acquisition of a new squadron of indigenous LCA-Navy carrier-based fighter jets. These jets are essential for strengthening India’s naval presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and beyond. The squadron is expected to be deployed on India’s latest aircraft carriers, such as the INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

A team of Indian researchers has proposed a new regional aircraft design that could revolutionize air connectivity within the country. In a collaborative effort, Prasenjit Das from IISER Mohali and Prof. Prodyut Das from IIT Kanpur have introduced the D12, a 20-seater aircraft designed specifically for UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) operators.
The D12 is notable for its versatility. It can be easily stretched to accommodate up to 40 passengers without requiring additional certification, making it a cost-effective solution for airlines.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
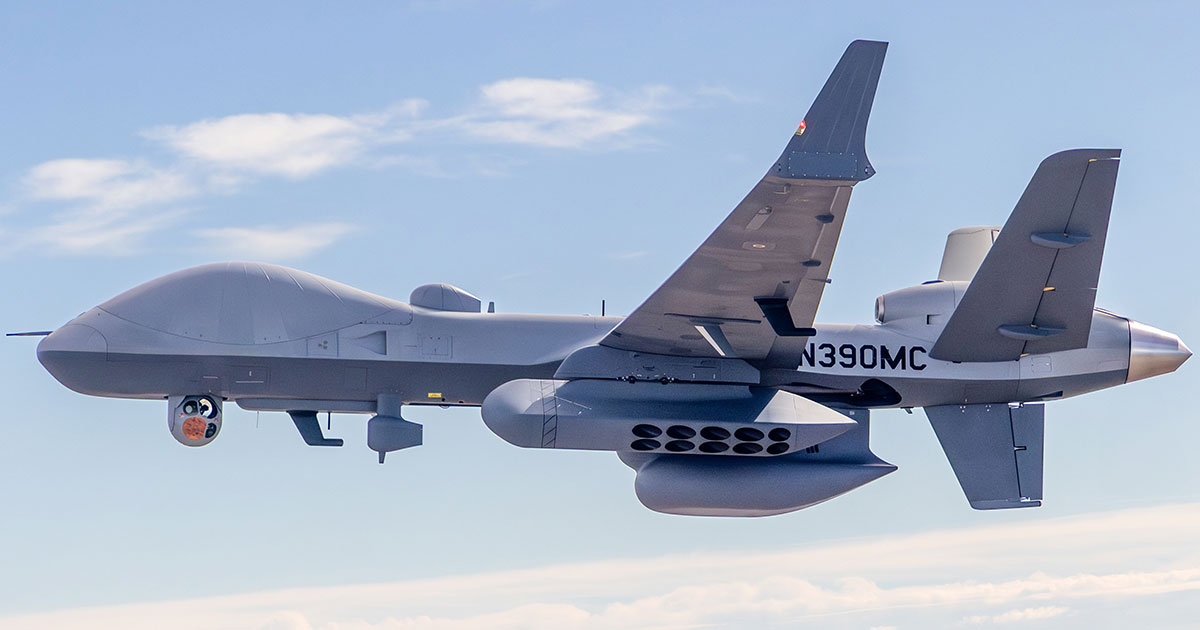

The Indian armed forces are set to receive the MQ-9B armed High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Remotely Piloted Aircraft Systems (RPAS), manufactured by General Atomics, between 2029 and 2030. This acquisition marks a major step in strengthening India’s surveillance, reconnaissance, and strike capabilities. The deal, valued at nearly $3.5 billion, was signed under the Foreign Military Sales (FMS) programme with the U.S. government. The 31 drones ordered include 15 Sea Guardians for the Indian Navy and 16 Sky Guardians for the Indian Army and Air Force (eight each).
According to defense officials, the first MQ-9B unit will be delivered in 51 months, with the final unit expected by 72 months after the contract signing and initial payment. This indicates that the delivery window will span from January 2029 to September 2030. The deliveries will be spaced out across 21 months, ensuring that India progressively receives its fleet of 31 drones.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
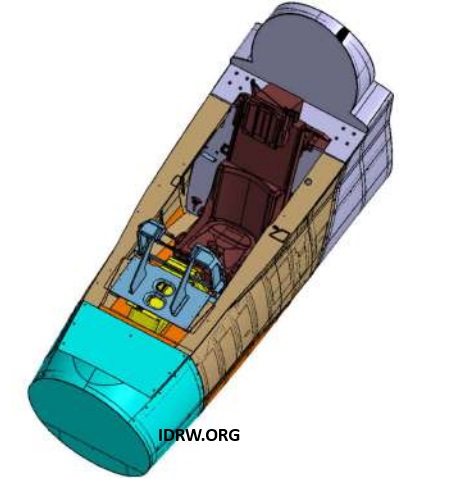
In an exciting preview of what’s to come for India’s defense aviation sector, the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) will be showcasing the Mock-front cockpit section of the Tejas MkII at the upcoming Aero India 2025. The highly anticipated event will take place from February 10th to February 14th, 2025, in Bengaluru, providing a platform for ADA to demonstrate significant advancements in the Tejas MkII program.
The image of the showcased mock-front cockpit section, recently released, highlights the impressive dimensions: 3427L X 1990H X 1390W, signaling the scope of ADA’s efforts in designing a state-of-the-art fighter cockpit. The mock section includes various structural components that are integral to the overall cockpit design and functionality of the upcoming Tejas MkII.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India’s state-owned shipyard, Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers Ltd (GRSE), has embarked on an ambitious initiative to indigenously design and develop hovercraft for military operations. As part of this effort, GRSE has sought collaboration from the private sector to build a prototype with high indigenous content, aligning with the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative to reduce dependency on foreign manufacturers and strengthen India’s defense capabilities.
Hovercraft, also known as Air Cushion Vehicles (ACVs), are highly versatile and can traverse a range of terrains, including sand, marshes, mud, ice, and water. Their unique ability to glide over various surfaces without the need for specialized infrastructure like harbors or docks makes them invaluable for military operations. However, India currently lacks expertise in hovercraft design, relying heavily on foreign technology and equipment. This reliance on foreign Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) not only creates logistical challenges but also limits the ability to tailor hovercraft to the specific operational needs of the Indian military.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Navy is taking a significant step toward enhancing its future combat capabilities by seeking the design and development of a High-Power Laser Source with an output greater than 10 kW. This initiative is aimed at fostering collaboration with private sector companies, who will receive naval funding to bring this cutting-edge technology to life. The Navy’s goal is to leverage laser-based technologies for both weapon systems and sensors, positioning itself at the forefront of next-generation naval warfare.
The Indian Navy has outlined specific requirements for the High-Power Laser Source that private sector companies must meet in order to secure development contracts. The primary requirements are as follows:
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
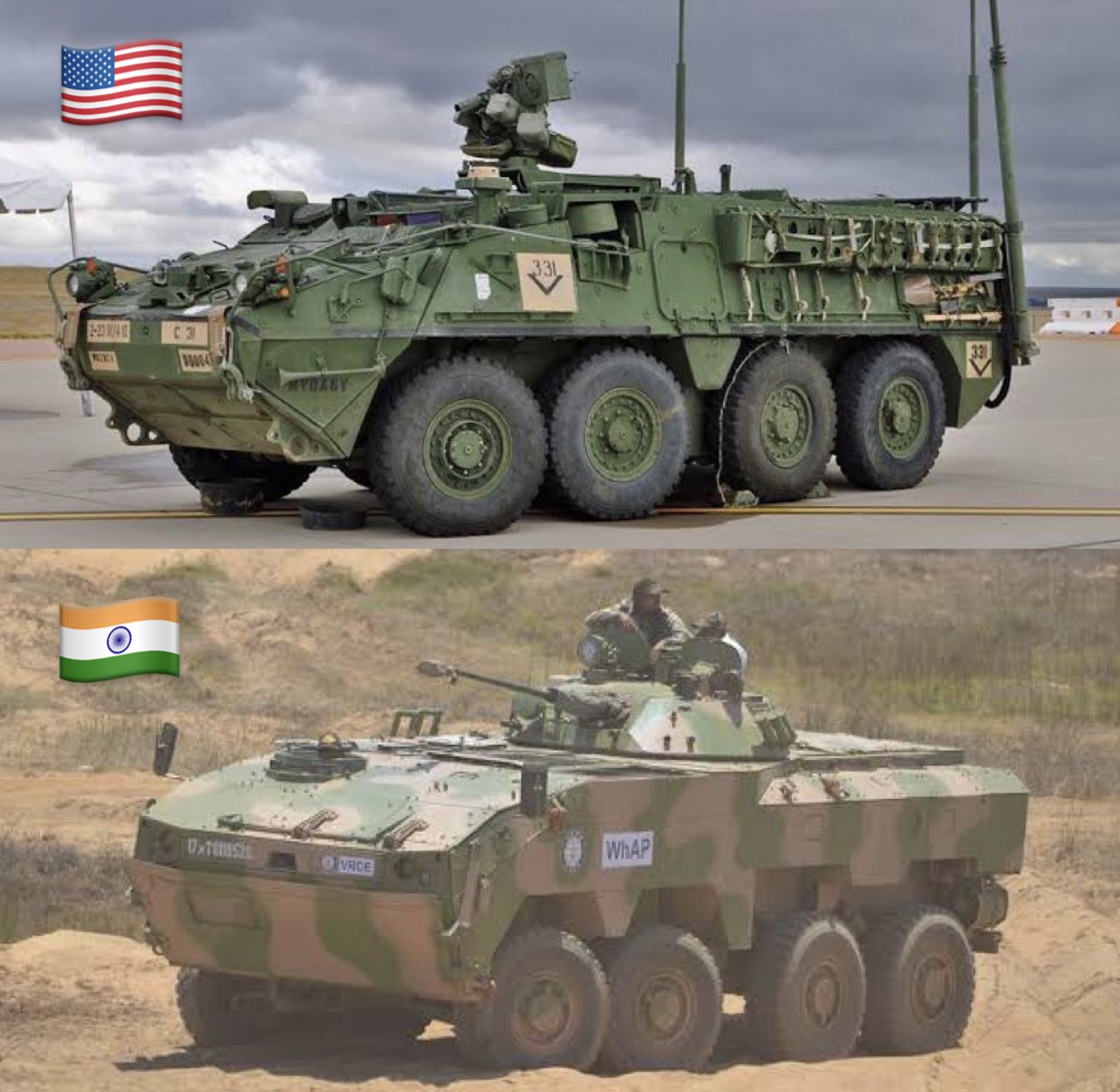

Amid deteriorating diplomatic relations between India and Canada, industrial partners involved in India’s Wheeled Armoured Platform (WhAP) program are urging the Ministry of Defence (MoD) to reconsider its plans to procure Stryker armoured vehicles from Canada. The indigenous WhAP program, a joint initiative between DRDO and Tata Advanced Systems, offers a competitive alternative and has gained international traction, including potential orders from Morocco.
WhAP’s partners like Tata, Mahindra, and Kalyani are developing their own variants of the vehicle, making it a viable and homegrown substitute. With diplomatic tensions rising, defense experts in India are also advocating for India to withdraw from talks with U.S. officials concerning Canadian defense assets.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

In a recent discussion on The Gaurav Arya Podcast, Air Marshal Anil Khosla, former Vice Chief of Air Staff (VCAS) of the Indian Air Force (IAF), emphasized the need for a phased procurement approach for Rafale fighter jets rather than purchasing them in bulk under the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender. This suggestion aligns with previous recommendations from former Chief of Defence Staff General Bipin Rawat and former Defence Minister Manohar Parrikar, both of whom highlighted the financial strain and opportunity costs that a bulk procurement could impose on other critical defense programs.
Khosla’s rationale for phased acquisition revolves around the rapid evolution of fighter jet technology. A staggered purchase of Rafales would allow the IAF to benefit from upgrades and newer systems integrated into each batch, keeping India’s fleet at the cutting edge. He noted that buying all 114 jets in one go, as proposed in the MRFA tender, could lead to outdated technology by the time the entire fleet is delivered. By splitting the procurement into phases, the IAF can integrate the latest avionics, sensors, and weaponry with each successive batch of Rafales, ensuring the fleet remains modern and relevant for longer.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

In a significant boost to India’s defense export capabilities, Samtel Avionics System Ltd, based in Uttar Pradesh, has signed a contract with the Malaysian Air Force to equip its fleet of Sukhoi-30MKM fighter jets with Multi-Function Displays (MFD) and Head-Up Displays (HUD). This contract further strengthens the long-standing defense ties between India and Malaysia, while highlighting India’s growing role as a global defense technology provider.
The Multi-Function Displays (MFDs) being supplied by Samtel Avionics will enhance the capabilities of the Sukhoi-30MKM fighter jets by providing pilots with better situational awareness and a more intuitive interface to manage flight data and combat systems. Available in sizes of 5″x5″, 6″x6″, and 5″x4″, these MFDs will provide the Malaysian Air Force with advanced avionics that will modernize and extend the operational life of its Su-30MKM aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Army’s Provisional Staff Qualitative Requirements (PSQR) for the Zorawar Light Tank has sparked interest, especially in comparison to China’s Type 15 Light Tank, which weighs around 35 tons. Both tanks are intended for high-altitude operations along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and other challenging terrains. However, the Indian Army has intentionally kept the Zorawar’s weight around 25 tons, significantly lighter than its Chinese counterpart. This decision was guided by several critical operational requirements that go beyond the conventional focus on firepower and armour.
According to a senior Indian Army officer closely involved with the project, four key factors influenced the Zorawar’s design specifications: airlifting capabilities for high altitudes, amphibious capability, power-to-weight ratio, and nominal ground pressure. These features are essential for operations in the rugged and varied terrain where the Zorawar is expected to be deployed, including the Himalayan borders near the LAC and the Rann of Kutch, a vast salt marsh area between India and Pakistan.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

During National Security Adviser Ajit Doval’s recent visit to Paris, crucial discussions took place between Doval and top French officials regarding strategic defense cooperation. Among the key topics was France’s offer to assist India in the development of two nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs) for the Indian Navy. This cooperation could mark a significant leap forward in India’s naval capabilities, as France has proposed sharing Pump jet propulsion technology and other non-nuclear technologies from its Barracuda-class SSN submarine program.
Sources familiar with the talks revealed that France’s offer goes beyond just technical assistance. Paris has expressed its willingness to cooperate on a range of submarine technologies, including the Pump jet propulsion system—a technology that enhances the stealth and efficiency of nuclear submarines. While it remains unclear if France has formally offered the complete design of its Barracuda-class submarines, all non-nuclear technologies integrated into these advanced vessels are reportedly on the table.
Continue reading