Idrw Team
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG
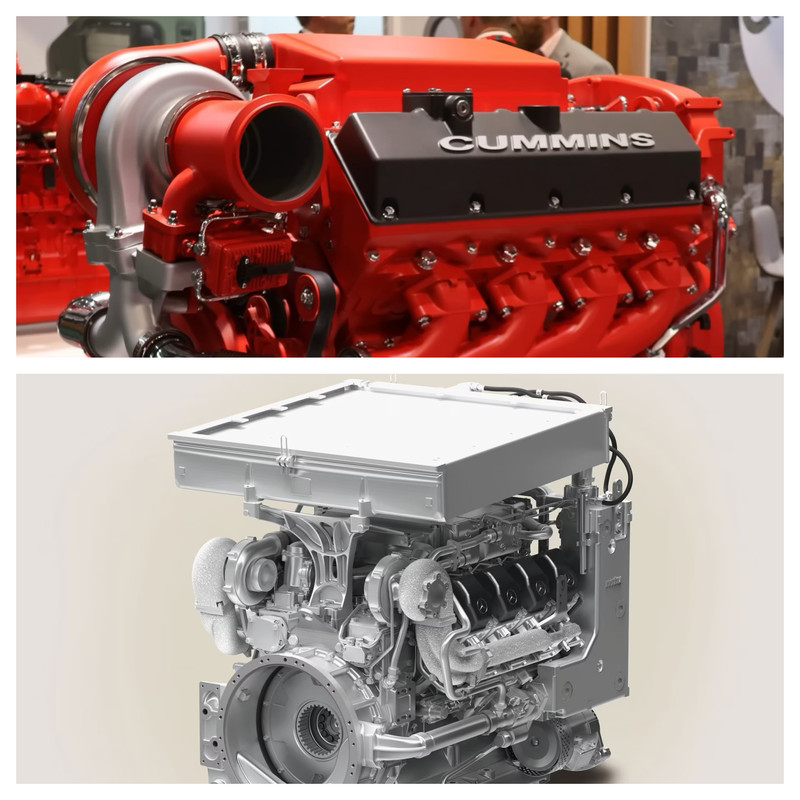
India’s Zorawar Light Tank program has taken an interesting turn with reports suggesting two potential engines in the running. While Rolls-Royce, through its MTU division, confirmed the supply of the MTU 8V199 TE21 engine as initially planned, export data reveals the presence of Cummins VTA903E-T760 engines also being shipped to India.
The MTU engine boasts a powerful 600 kW (804hp) output, while the Cummins T760, a modified version of the VTA903E-T750, delivers a close 567kW (760 HP). Both companies claim their engines have been supplied for the program.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

NewSpace Research and Technologies (NRT) has aced a significant test, showcasing its prowess in the high-altitude drone delivery domain. Their recent accomplishment not only surpasses a previous record but also bolsters India’s self-reliance in drone technology.
NRT successfully conducted flight operations for a 100 kg Maximum Take-Off Weight (MTOW) class Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) at Umling La, the world’s highest motorable pass at a staggering 19,024 feet.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian-developed Astra MkII, a Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM), is nearing its final hurdle before user trials, according to internal sources at DRDO. This indigenous missile is poised to become the mainstay of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) BVRAAM arsenal.
The Astra MkII has undergone a rigorous testing process, including captive trials, separation trials, unguided dual-pulse motor trials for various ranges, and seeker trials. These tests have validated the missile’s core functionalities, paving the way for full-scale testing against target drones.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
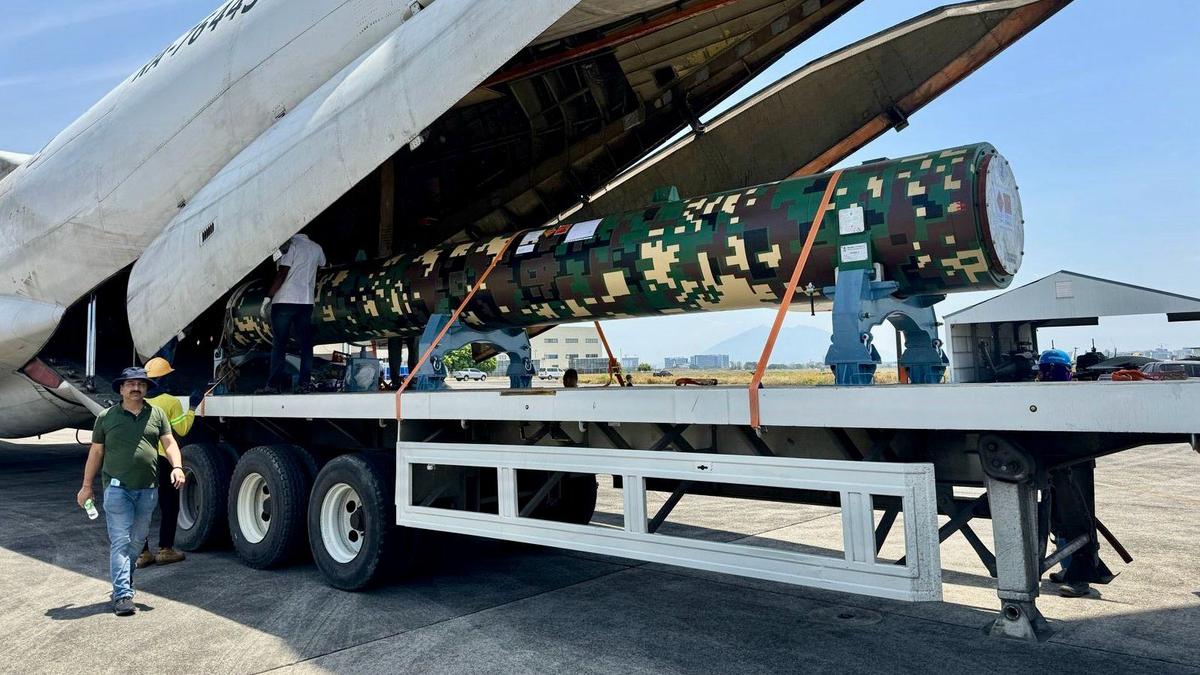

The Philippine Marine Corps (PMC) is bolstering its coastal defenses with the acquisition of BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles from India. This marks a significant development in the Philippines’ modernization efforts to address maritime security concerns.
The PMC is currently taking delivery of three batteries of the shore-based anti-ship variant of the BrahMos missile. Each battery comprises four launchers, each housing three missiles with a staggering range of 290 kilometers. This translates to a significant increase in the Philippines’ ability to deter and counter potential threats at sea.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is contemplating acquiring a fleet of pre-owned Mirage 2000 fighter jets from Qatar, along with spare M53 engines, to fortify its ageing fighter squadrons. This potential deal comes amidst concerns about the longevity of the IAF’s existing Mirage 2000 fleet, many of which are nearing the end of their service life due to engine limitations.
Qatar has proposed selling its fleet of 12 Mirage 2000-5 fighters, including nine single-seat 2000-5EDAs and three dual-seat 2000-5DDAs. These jets are particularly attractive because they come with 14 Snecma M53-P2 afterburning turbofan engines – vital components for extending the operational life of the IAF’s current Mirage 2000 fleet.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Navy’s much-anticipated INS Vagsheer, the sixth and final Kalvari-class submarine, is set to see a delay in its induction. Launched in April 2022 from the Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) in Mumbai, in collaboration with the Naval Group of France, the submarine was initially expected to join the Indian Navy in early 2024.
The INS Vagsheer began its sea trials in May 2023, a crucial step before its official commissioning. However, recent reports suggest the induction has been pushed back to November or December of this year. While the official reasons for the delay haven’t been disclosed by MDL, sources speculate it might be due to the integration and testing of indigenous equipment.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Navy’s underwater arsenal is set for a potential boost with renewed talks on acquiring additional Kalvari-class (Scorpène) submarines. State-owned Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) is reportedly in advanced discussions for a deal estimated at a whopping ?35,000 crore (US$4.19 billion).
While the final price might see some reduction after negotiations later this year, each upgraded Kalvari-class submarine is expected to cost between $1.2 billion and $1.3 billion. This marks a significant jump of over 62% compared to the six Kalvari-class submarines previously acquired by India at a cost of ?23,652 crore (US$4.1 billion in 2023). This translates to a cost per unit of ?3,942 crore (US$680 million in 2023).
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Bengaluru-based Tardid Technologies Pvt Ltd made a splash at Eurosatory 2024, showcasing its innovative AI-based solution for naval vessels: PRESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF HULL & MACHINERY (PAH&M). Tardid’s motto for PAH&M, “Sweat in peacetime so you can relax in difficult times,” aptly summarizes its philosophy. This system aims to prevent potential problems at sea by proactively monitoring a ship’s hull and machinery.
Naval vessels endure a unique set of challenges compared to commercial ships. They operate in harsh conditions, experience extreme maneuvers, and are constantly exposed to corrosive environments. This results in significantly higher fatigue on a naval vessel’s hull compared to its commercial counterparts. Furthermore, fatigue cracks typically begin on the surface in the short term but move deeper within the metal over extended periods.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

State-owned Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVNL) is set to license produce the Russian KAMAZ-53949 Typhoon-K vehicle in India. Having successfully completed internal trials of the locally manufactured Typhoon-K, AVNL is now poised to offer this advanced military vehicle to the Indian Army.
The Typhoon-K motor vehicles are designed to provide integrated logistics support to combined arms and special units, including peacekeeping formations, in various environments. These vehicles are versatile, capable of carrying personnel and military cargo, and serve as a basic chassis for mounting various technical systems and weapons.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India has issued a Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) restricting airspace usage between July 17 and 26, 2024, sparking speculation about a possible missile test. The designated area encompasses both the ‘AD Launch Site’ in West Bengal and the APJ Abdul Kalam Island launch pad off the coast of Odisha.
This has led analysts to believe that the test might involve the AD-1 Interceptor missile, a crucial component of India’s Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) Phase-II program. The inclusion of both launch sites in the NOTAM suggests the possibility of interceptor and target missile launches from separate locations.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
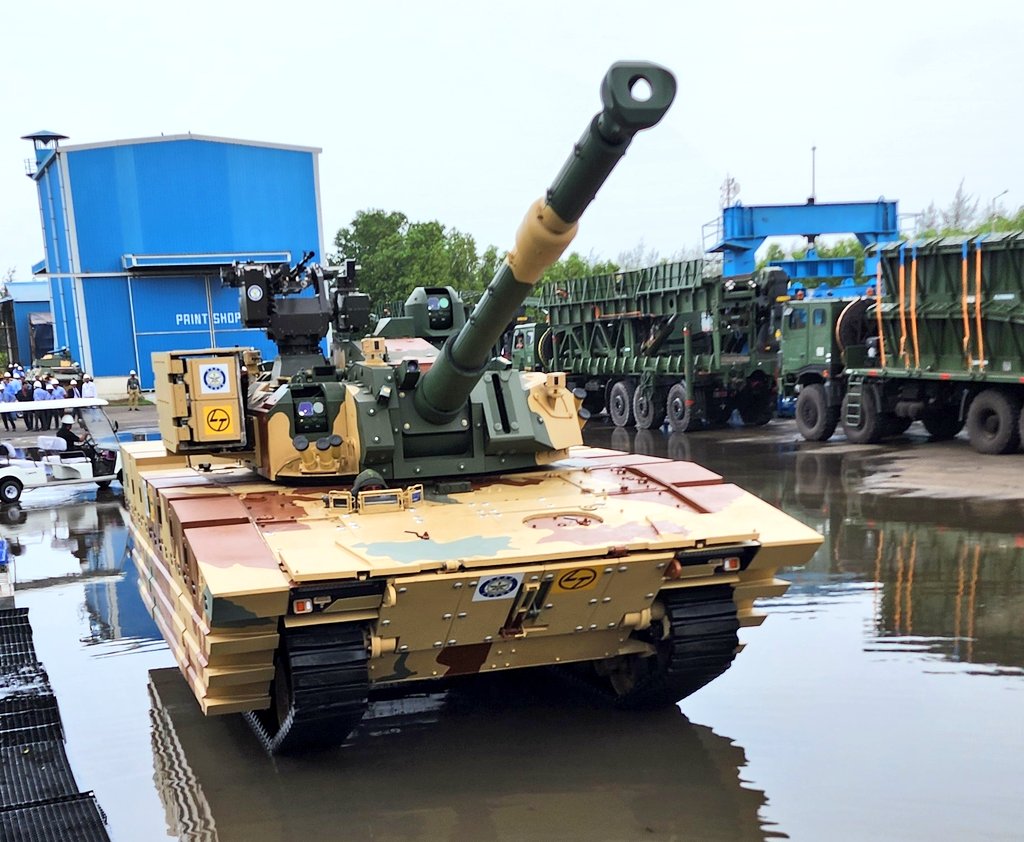

India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has unveiled the first images of its highly anticipated Zorawar Light Battle Tank. Developed in collaboration with private sector giant Larsen & Toubro (L&T), the Zorawar is poised to undergo army trials following the successful completion of internal testing.
Designed for swift maneuverability in high-altitude regions, the Zorawar is a compact powerhouse weighing in at 25 tons. It packs a punch with a 105mm gun, ideal for engaging enemy targets. The tank boasts advanced optics from French company Safran Paseo, enhancing situational awareness for the crew.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Army is mulling a significant increase in its initial requirements for the Stryker combat vehicle. Talks are currently underway with the potential manufacturer to develop an army-specific variant of this 8-wheeled armored personnel carrier, with a Technology Transfer (ToT) agreement for indigenous production in India.
Initial discussions centered around procuring 350 Stryker vehicles. However, the Indian Army is now considering doubling this number to 530 units. This substantial increase reflects the army’s growing interest in the Stryker’s capabilities and its potential to equip 10 battalions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
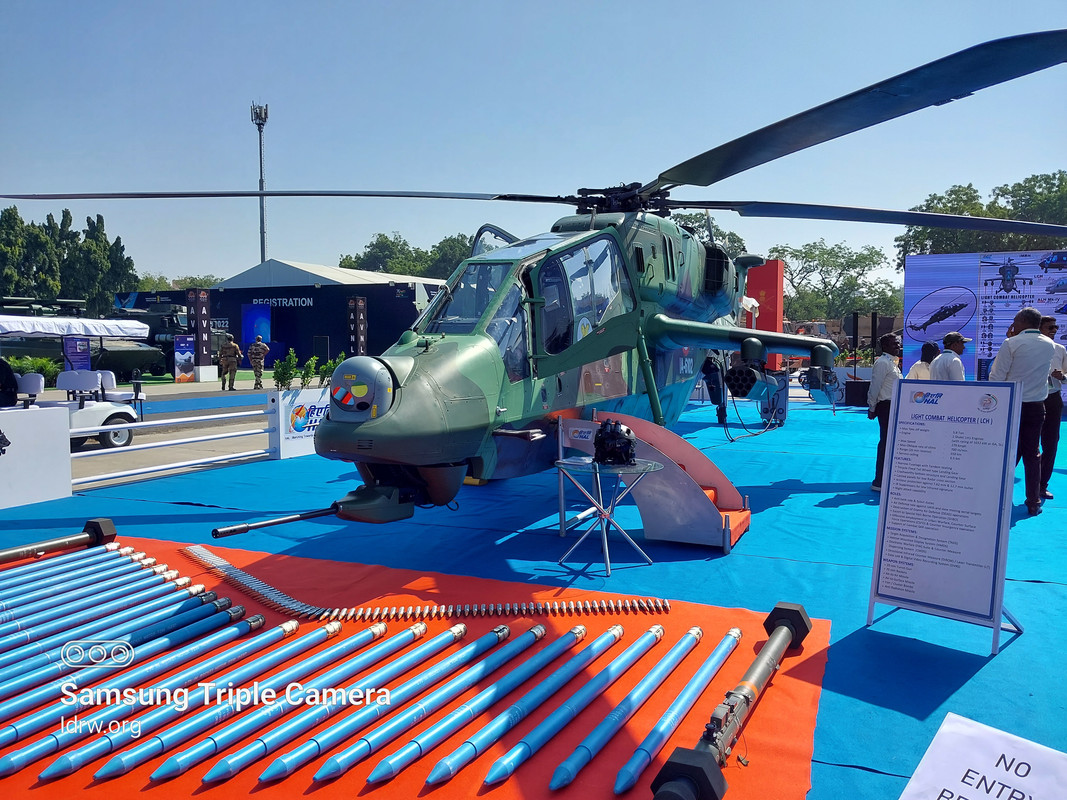

Former Air Chief Marshal Fali H. Major (Retd.), the only helicopter pilot to ever lead the Indian Air Force, has expressed his strong support for the government’s decision to procure a large number of attack helicopters. This historic deal, valued at approximately ?50,000 crore, marks the biggest single helicopter order ever placed by an Indian company and represents a significant boost to the country’s defense sector.
In a media interaction, Air Chief Marshal Major welcomed the news but emphasized the importance of gradually increasing indigenous content in the helicopters. He highlighted that while the current 45% domestic content is a positive step, it should be progressively raised to “respectable levels.” This, according to Major, would ensure an “80% availability rate” for the helicopters, maximizing their operational efficiency for the armed forces.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
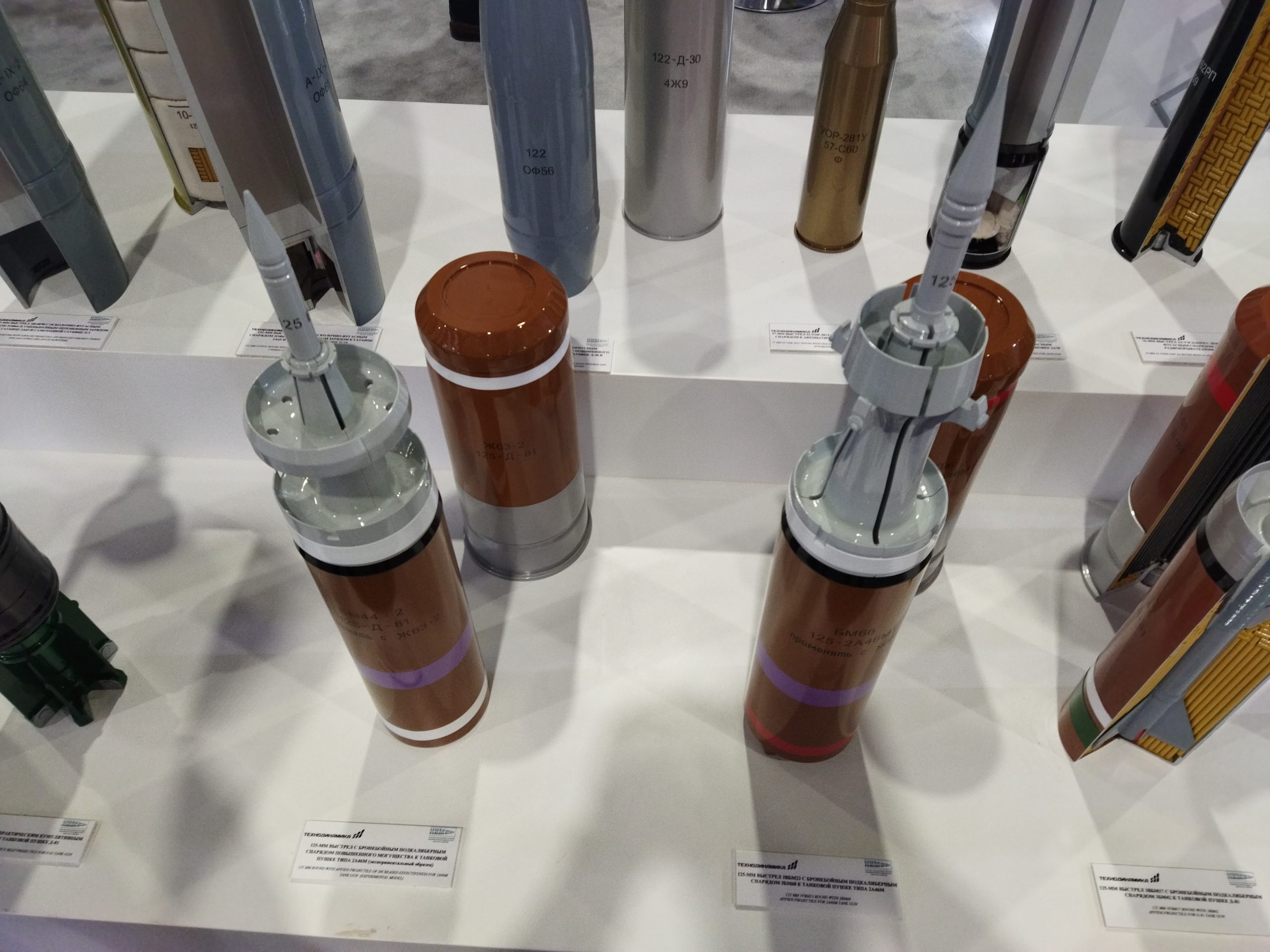

Rosoboronexport/Rostec, a prominent Russian defense exporter, has collaborated with an Indian company to establish the manufacturing of the 3VBM17 Mango Armor-Piercing Fin-Stabilized Discarding Sabot (APFSDS) rounds within India. This initiative aligns perfectly with India’s “Make in India” program, promoting self-reliance in critical defense equipment.
The 3VBM17 Mango APFSDS rounds are designed to penetrate and defeat armored vehicles equipped with composite armor. These advanced rounds are crucial for modern armored warfare, providing superior performance against heavily protected targets. The locally manufactured Mango rounds will equip Indian tanks with enhanced firepower, ensuring they can effectively engage and neutralize contemporary armored threats.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Navy’s Kolkata-class destroyers are renowned for their formidable firepower. However, a closer look reveals a lighter-than-expected surface-to-air missile (SAM) count compared to some global counterparts of similar size. While the Navy has remained tight-lipped on the official reasoning behind this, discussions with Navy officials shed some light on the issue. Balancing cost and physical limitations appears to be the key factor.
Offensive systems like the BrahMos missiles, while incredibly powerful, are also large and expensive. This translates to a trade-off – fewer missiles for a higher upfront cost.
Continue reading