Idrw Team
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The High Commissioner of India in Australia recently met with a delegation of key Indian shipbuilders, including Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE), Mazgon Dock Limited, Goa Shipyard Limited, and Hindustan Shipyard Limited. The focus of the discussions was on exploring collaborative opportunities by leveraging the strengths of both India and Australia’s shipbuilding industries.
This meeting highlights the growing interest in collaboration between the two countries in the maritime sector. By combining their expertise and resources, India and Australia can potentially strengthen their respective shipbuilding capabilities and compete more effectively in the global market.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
India’s ambitious collaboration with Russia to develop the Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) program, a project based on the Su-57 platform, came to an end in 2018. While the official reasons remained unclear at the time, new reports shed light on the potential factors that led to India’s withdrawal.
Disagreements on technical aspects appear to have played a significant role in the program’s demise. Sources suggest India desired a two-seater variant of the FGFA, similar to the Su-30MKI fighter jets, a request not readily met by Russia. Additionally, concerns regarding the transfer of critical technology and design specifications from Russia to India reportedly caused friction.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

NewSpace Research and Technologies has unveiled its latest innovation – the PYGMY Vision-based kinetic attack drone platform. This cutting-edge drone boasts a lightweight design and is packed with features that make it a game-changer for military operations.
The PYGMY’s lightweight construction allows for both air and ground launch, making it adaptable to various deployment scenarios. The drone can be equipped with third-party payloads, giving users the flexibility to customize it for specific missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
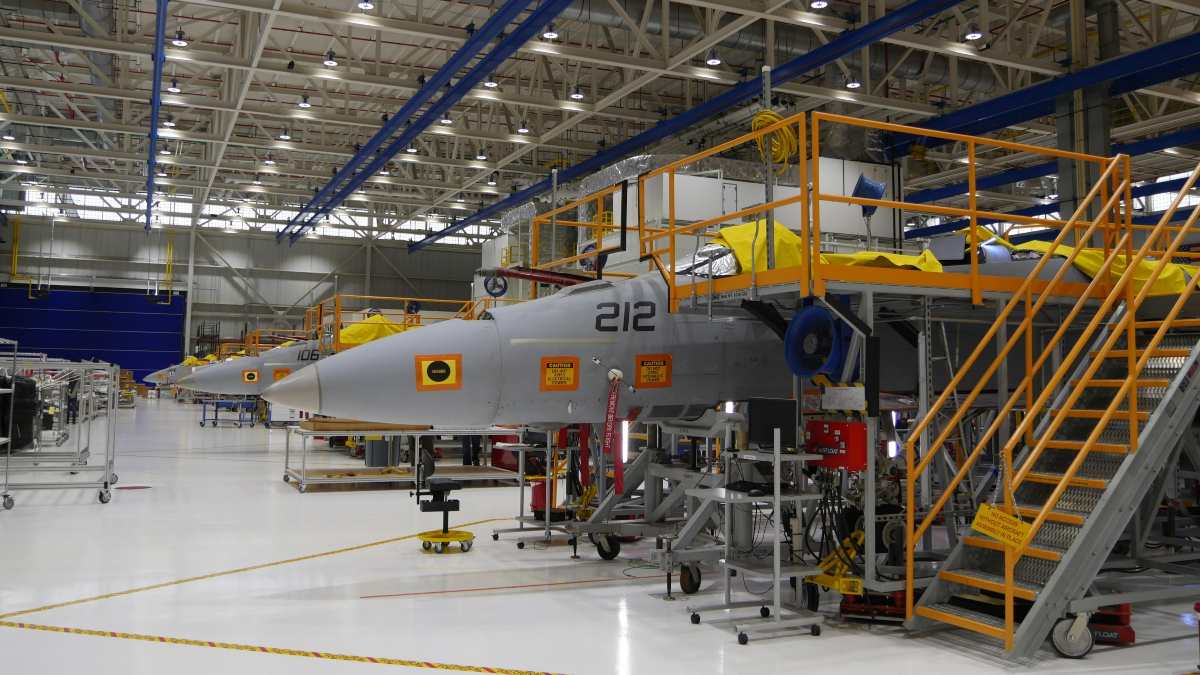

The U.S. Navy has secured a crucial contract modification with Boeing for the final 17 F/A-18E/F Super Hornets, marking a potential turning point for the iconic fighter jet’s production future.
This $1.1 billion contract, announced on March 19th, comes after stalled negotiations last year. The deal secures 10 F/A-18F Lot 46 aircraft and an additional seven from Lot 47, ensuring deliveries begin in late 2026 and conclude by spring 2027.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

China’s domestically-produced passenger aircraft, the C919, is making waves in the aviation industry. Built by the state-owned Commercial Aviation Corporation of China (COMAC), the C919 has garnered significant interest, with around 1,200 orders – primarily from domestic airlines. However, its global ambitions might face a hurdle in the form of the world’s fastest-growing aviation market: India.
According to leaked internal company documents, COMAC plans to actively promote the C919 in various Asian markets. This strategic move aims to capitalize on the region’s burgeoning aviation sector. The C919, a narrow-body jet designed to compete with the Airbus A320neo and Boeing 737 MAX families, offers airlines an alternative within the single-aisle aircraft category.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is on the lookout for a development and production partner. This collaboration aims to create mission systems for a new generation of maritime patrol aircraft based on the C295 platform.
The project envisions two variants of the patrol aircraft, Multi-Mode Maritime Aircraft (MMMA) is a variant intended for the Indian Coast Guard, enhancing their capabilities in various maritime operations. Medium Range Maritime Reconnaissance (MRMR) is Designed for the Indian Navy, the MRMR variant will bolster their long-range surveillance and reconnaissance missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The Indian Army is set to procure 550 indigenously-developed ASMI 9×19mm submachine guns (SMGs) from Lokesh Machine Ltd (LKM) at a cost of ?4.6 crore. This marks the first major order for the ASMI, a significant development for India’s defense indigenization efforts.
The ASMI is a domestic 9×19mm SMG designed to utilize the 9×19mm Parabellum cartridge, a common caliber used by the Indian Army and other security forces across the country. This rimless, tapered cartridge is known for its affordability and widespread availability, making it a popular choice for handguns and SMGs.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The Indian Army has signed a contract with Bengaluru-based Tonbo Imaging to equip Dragunov Sniper Rifles (DSRs) with advanced night vision sights. This upgrade will significantly enhance the capabilities of the Army’s snipers.
The EK-Gen2 is more than just a night sight; it’s a Smart Thermal Weapon Sight (STWS) offering advanced features for improved sniper effectiveness. The EK-Gen2’s state-of-the-art thermal imaging core provides superior detection and engagement capabilities compared to older image intensifier sights. This allows snipers to operate effectively in low-light conditions or complete darkness.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The Ministry of Defence’s Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO) has announced a new challenge under the iDEX DISC-11 initiative. This program seeks technological advancements in two crucial tank components: starter-generators and ultra capacitors.
The challenge focuses on developing replacements for the existing ??-10-1C and ??-18-1C starter-generators currently used in T-72 and T-90 tanks, respectively. These DC electric machines serve a dual purpose.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM.

@CjVarghese96
CJ Varghese, a distinguished innovator hailing from Kerala, has once again made waves in the realm of defense technology with the recent granting of a patent by the Patent Office of the Government of India. This patent marks a significant milestone in Varghese’s illustrious career, adding to his impressive portfolio of multiple patents, and heralds a breakthrough in the field of artillery defense systems.
The newly patented innovation centers around a Multiple Artillery Rocket Interceptor Kill Vehicle System, designed to counter the threat posed by swarms of artillery rockets with unparalleled precision and efficacy. At its core, Varghese’s system boasts several novel features and technological advancements that set it apart from conventional defense mechanisms.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The Pakistan Air Force (PAF) is poised for a significant shift in its combat capabilities as it grapples with the impending retirement of nearly 200 fighter jets by 2030. This large-scale retirement plan, if realized, could lead to a temporary dip in overall squadron strength.
The crux of the issue lies with the ageing Mirage-III/5 fleet, numbering over 150. These French-origin jets are rapidly approaching the end of their airframe service life. Dassault, the original manufacturer, has ceased production of spare parts for the aircraft and its engines, decades ago further plans to buy retired jets to be used as Spares have not gone ahead thus limiting operational viability of shouldering on for more years.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
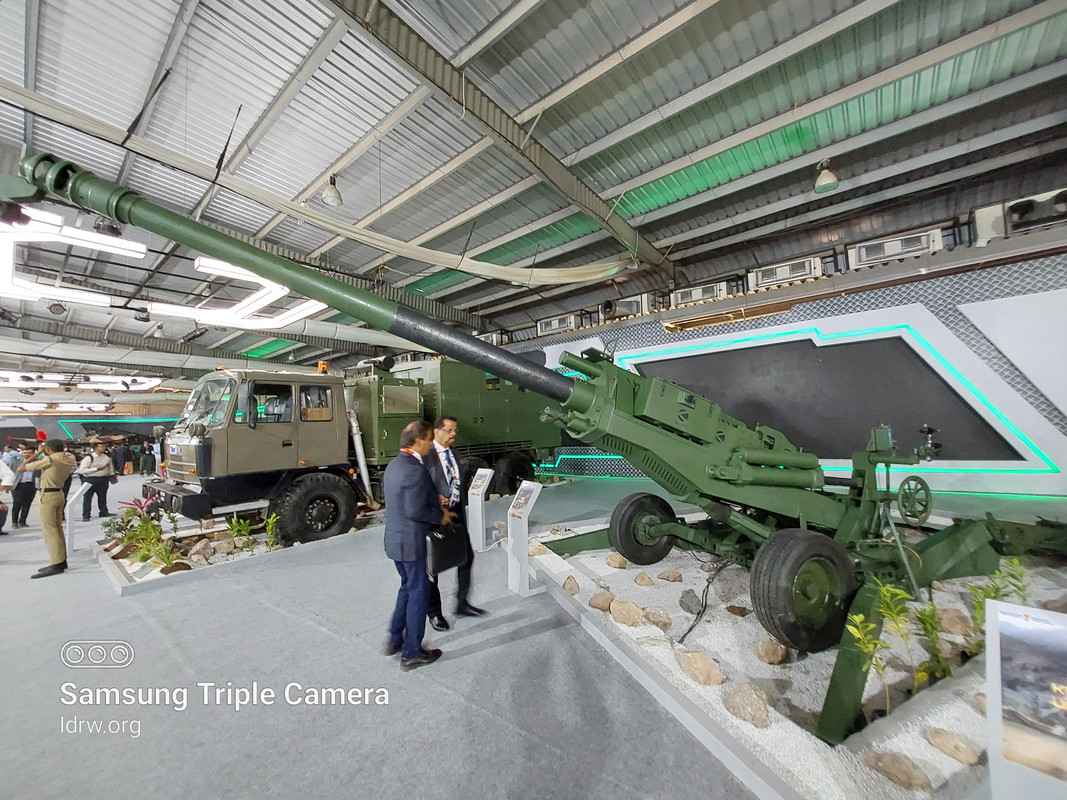

Baba Kalyani, the Managing Director of Bharat Forge, has set an ambitious goal for India’s defense sector. He aspires to make India the number one manufacturer of artillery in the world by 2030. This vision comes amidst India’s growing defense exports, encompassing artillery guns, drones, and rifles.
“It is my vision and dream to be among the top three artillery exporters in the world,” Kalyani said. “Now we are number one in the business. So we are targeting that in the artillery sector, we will be the largest manufacturer in the world with the best of technologies.”
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
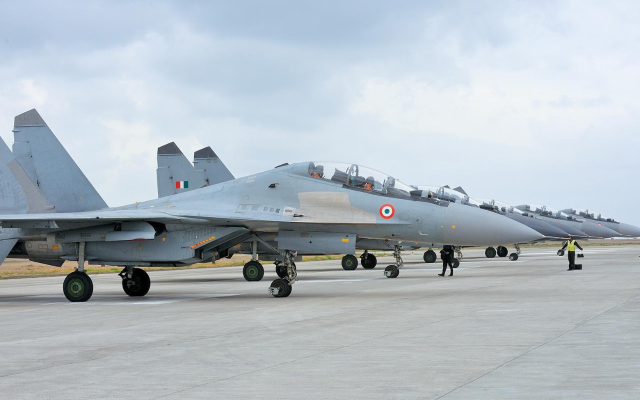

Indian Air Force (IAF) Chief Air Chief Marshal VR Chaudhari recently addressed concerns regarding the impact of the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine on the IAF’s fleet of Russian-made aircraft.
Chaudhari highlighted the IAF’s proactive approach towards “Indianization,” a strategy that involves manufacturing crucial components for its aircraft within India. This initiative has significantly reduced dependence on foreign suppliers, including Russia, for spare parts. As a result, the Ukraine conflict has had a minimal effect on the supply of spares for many Russian aircraft operated by the IAF.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
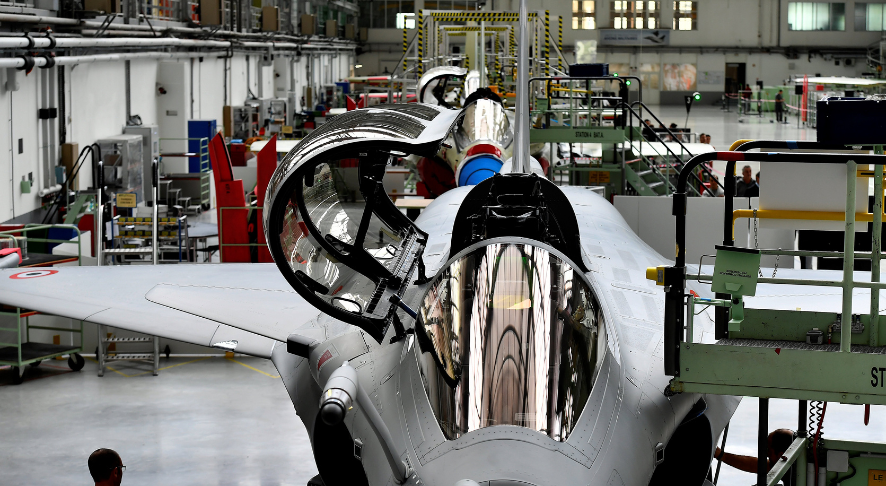

Defense Analyst Ranesh Rajan, in an interview with idrw.org, has cast doubt on the viability of acquiring 114 Rafale fighter jets under the Make in India program within the framework of the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender.
Rajan argues that the sheer cost of such a large-scale purchase, estimated at around $25 billion, could put significant strain on India’s defense budget. He suggests that prioritizing this acquisition might delay or even derail funding for crucial domestic projects like the Tejas MkII and AMCA fighter jets.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
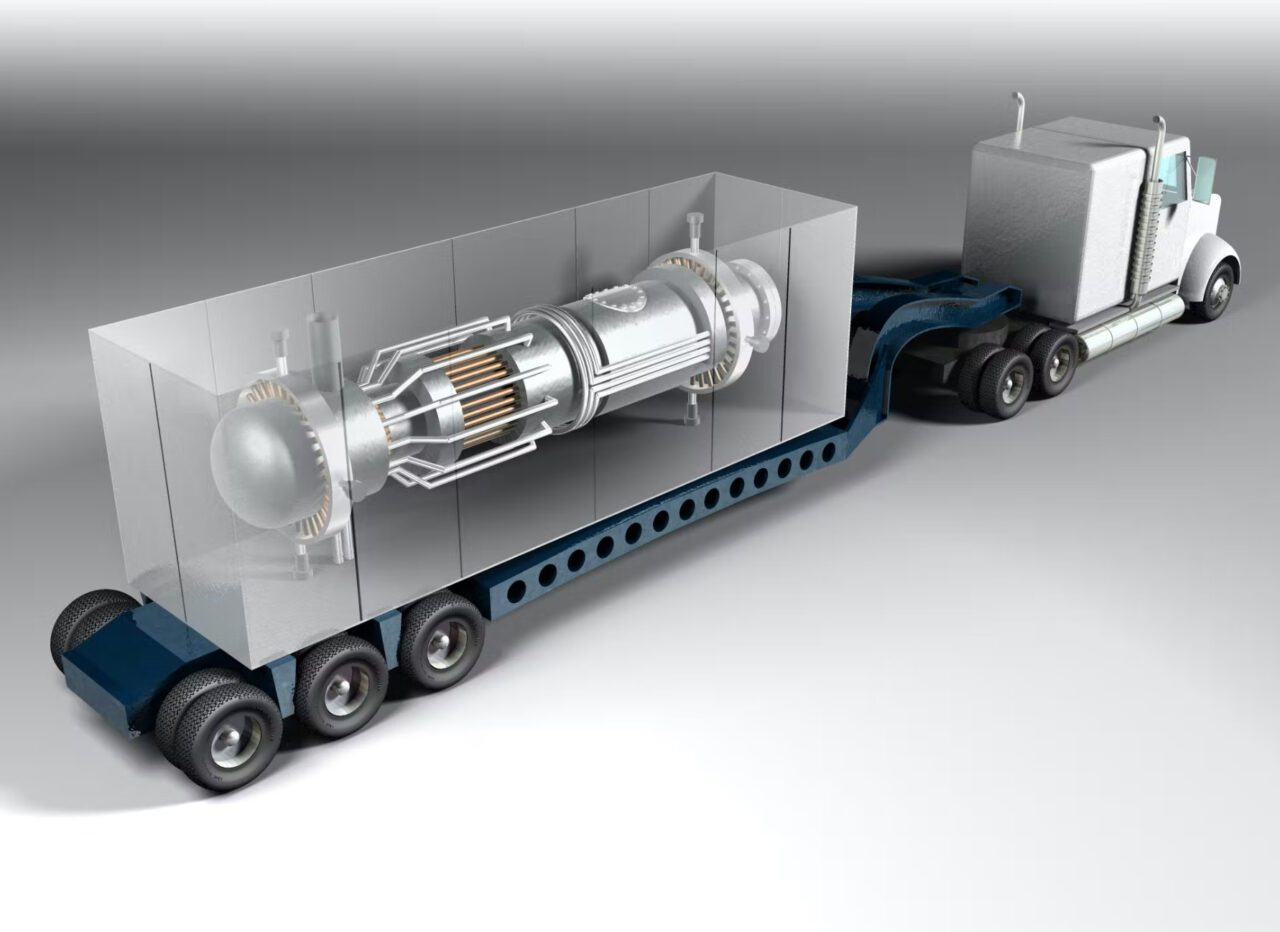
The Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) is reportedly developing a mobile reactor technology with wide-ranging applications. While details remain undisclosed by BARC, experts believe it could be a dual-use system, potentially impacting both civilian and military sectors.
The concept of a mobile reactor presents exciting possibilities. It could provide a reliable and continuous power source for remote locations currently lacking access to traditional infrastructure. This could be particularly beneficial for regions with challenging terrain or underdeveloped grids.
Continue reading