SOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM.

Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), a leading Indian defense and aerospace company, has unveiled a groundbreaking innovation: a zero-emission Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) designed for hydrographic surveying and coastal surveillance. This versatile USV boasts eco-friendly operations and the potential for various applications, making it a valuable asset for both civilian and defense purposes.
The USV stands out for its commitment to sustainability. It leverages solar energy harvesting to power its operations, eliminating harmful emissions and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. This makes it an ideal solution for environmentally sensitive tasks like surveying and monitoring marine ecosystems.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
Australia and India are forging a closer partnership in the crucial area of Underwater Surveillance driven by concerns about China’s growing underwater military presence. This collaboration holds significant potential for enhancing maritime security in the Indo-Pacific region.
Underwater Surveillance refers to the ability to track and understand activities happening underwater, including submarine movements, underwater mines, and other potential threats. Effective UDA is essential for safeguarding vital sea lines of communication, protecting critical infrastructure, and deterring underwater aggression.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Navy successfully completed the maiden landing gear replacement of a P8I aircraft in a mere six days, showcasing the collective expertise and collaborative spirit of the team involved. The complex operation, undertaken between April 1st and 6th, 2024, at INS Rajali, involved a composite team comprising personnel from M/s AIESL, Mumbai and Indian Navy representatives.
The swift and flawless execution of this critical maintenance feat underscores the Indian Navy’s commitment to maintaining mission-readiness of its P8I fleet. The P8I is a long-range maritime patrol aircraft that forms a vital part of India’s maritime surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities. A functional landing gear system is critical for the safe operation of the aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
General Christopher G. Cavoli, head of US European Command and NATO’s Supreme Allied Commander, presented a measured assessment of Russia’s military capabilities during a Congressional hearing on April 10th. While acknowledging Ukrainian successes, he highlighted the relative strength of the Russian Air Force.
General Cavoli stated that Russia’s Air Force has only lost around 10% of its fleet despite over two years of war in Ukraine. Russia’s strategic forces, long-range aviation, cyber capabilities, and space capabilities reportedly remain largely intact.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
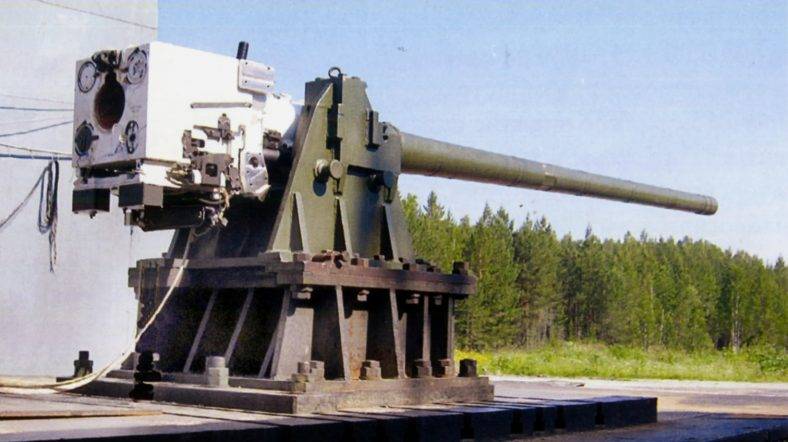

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is gearing up for the development of the Indian Army’s Futuristic Main Battle Tank (FMBT), the successor to the T-72 MBTs. In anticipation of the army’s requirements, DRDO is planning to initiate research and development (R&D) on a new 125mm smoothbore auto-loading main gun for the FMBT.
Unlike the 120mm rifled gun equipping the Arjun MBTs, the FMBT is expected to incorporate a new 125mm smoothbore auto-loading main gun. This shift in calibre aligns with the global trend towards smoothbore guns.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Recent tenders issued by DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation) hint at significant progress in the development of the STAR (Supersonic Target) missile program. The tenders for procuring lining materials for the rocket motor casing, nozzle, and other crucial components suggest that missile fabrication is well underway, paving the way for potential developmental trials later in 2024.
STAR is a revolutionary target missile designed to travel at supersonic speeds exceeding Mach 2.5. This capability will allow surface warship crews to train for effectively detecting and engaging incoming supersonic anti-ship missiles, a critical skill in modern warfare.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
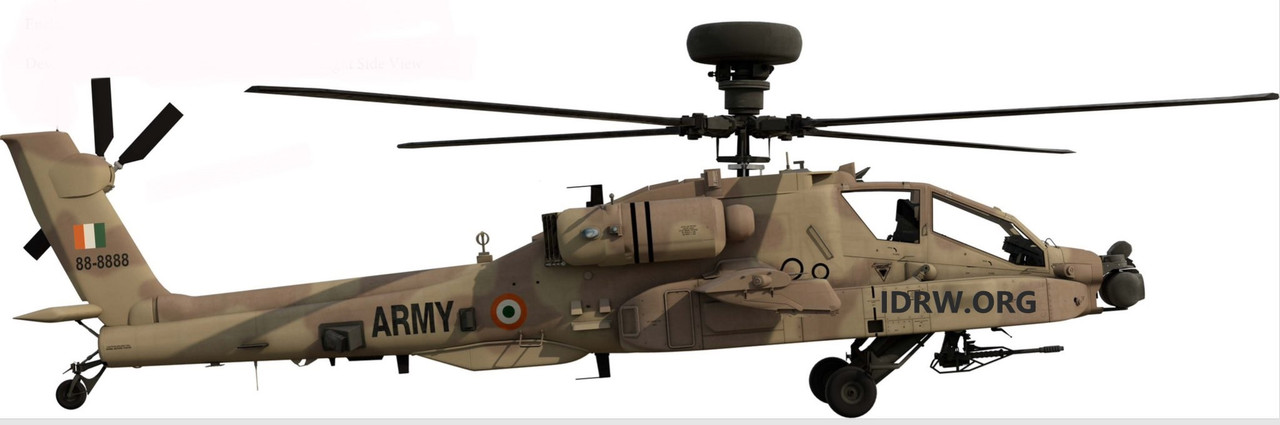

The Indian military is bolstering its attack helicopter capabilities on two fronts: American-made Apaches and domestically produced Light Combat Helicopters (LCHs).
Deliveries of the much-anticipated AH-64E Apache attack helicopters to the Indian Army are set to begin next month. The initial batch of six helicopters from the US is expected to arrive in May. This procurement comes as a separate deal from the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) existing fleet of 22 Apaches.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Previous conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan had highlighted the crucial role of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), particularly the Turkish Bayraktar TB2, in modern warfare. Armenia’s struggle against these drones has reignited interest in air defense systems capable of effectively countering such threats. Here’s how India’s Akash Air Defense System could potentially be a game changer for Armenia.
The TB2 drone has proven to be a potent weapon, particularly in the hands of Azerbaijan during the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh War. Its ability to deliver targeted strikes and conduct reconnaissance presented a significant challenge for Armenian defenses.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a significant strategic maneuver, India has embarked on a proactive initiative to bolster its military ties with key nations worldwide while simultaneously fostering opportunities for arms exports. This move comes amidst a backdrop of evolving geopolitical dynamics and increasing competition, particularly in regions where rival powers are seeking to expand their influence.
Government sources disclosed on Wednesday that India is deploying 15-16 new military and defence attaches from the Army, Navy, and Air Force to several countries, marking a notable shift in its diplomatic outreach. These countries include Poland, Armenia, Tanzania, Mozambique, Djibouti, Ethiopia, Ivory Coast, and the Philippines. This decision follows a rationalization process, wherein the number of military officials stationed at larger missions in traditional allies like Russia, the UK, and France has been streamlined.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is gearing up for a leadership change as its current chairman, Dr. Samir V. Kamath, prepares to retire on May 31st after a nearly three-year tenure. This leadership transition coincides with a period of significant transformation within the DRDO.
A high-powered committee led by former government advisor Prof. K. VijayRaghavan recently submitted a report outlining the need for the DRDO to develop cutting-edge technologies for future war scenarios. This vision necessitates a leader who can steer the organization towards these ambitious goals.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
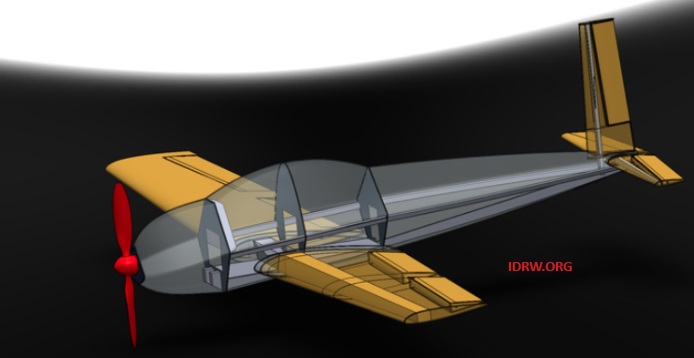
Coimbatore-based MANO AIRCRAFT is soaring into the future with their innovative Mano-I aircraft. This sleek, 2-seater carbon fiber plane is designed not just for thrills, but also for aspiring aircraft builders.
The Mano-I boasts a tandem seating arrangement, offering pilots a “top-gun” experience with independent control. But MANO AIRCRAFT isn’t just targeting seasoned aviators. The aircraft is specifically designed for ease of assembly, breaking down into five distinct kits – perfect for home-builders looking to embark on an aviation adventure.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM.

Ethiopia, a nation in the Horn of Africa, is inching closer to becoming the first African country to procure arms from India, according to sources familiar with the program told idrw.org. This potential deal, expected to be finalized by mid-2024, marks a possible turning point in Ethiopia’s military procurement strategy.
While specifics of the agreement remain under wraps, speculations point towards Ethiopia’s interest in acquiring anti-drone systems, small arms, and potentially a more significant weapons system. Traditionally, Ethiopia has relied heavily on Russia and China to fulfill its military needs. This upcoming deal with India signifies a potential diversification of its arms suppliers.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

China’s long-awaited strategic bomber, the H-20, is poised to be unveiled, marking a significant leap forward for the People’s Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) and potentially altering the balance of power in the region. Here’s why India should be wary of this development and invest in long-range anti-stealth technology.
The H-20 is believed to be a next-generation, subsonic stealth bomber similar to the American B-2 Spirit. Its stealth capabilities present a major challenge for Indian air defenses. Traditional radar systems struggle to detect stealth aircraft designed to absorb or deflect radar waves. This allows the H-20 to potentially penetrate Indian airspace undetected and deliver long-range precision strikes on critical infrastructure or military installations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
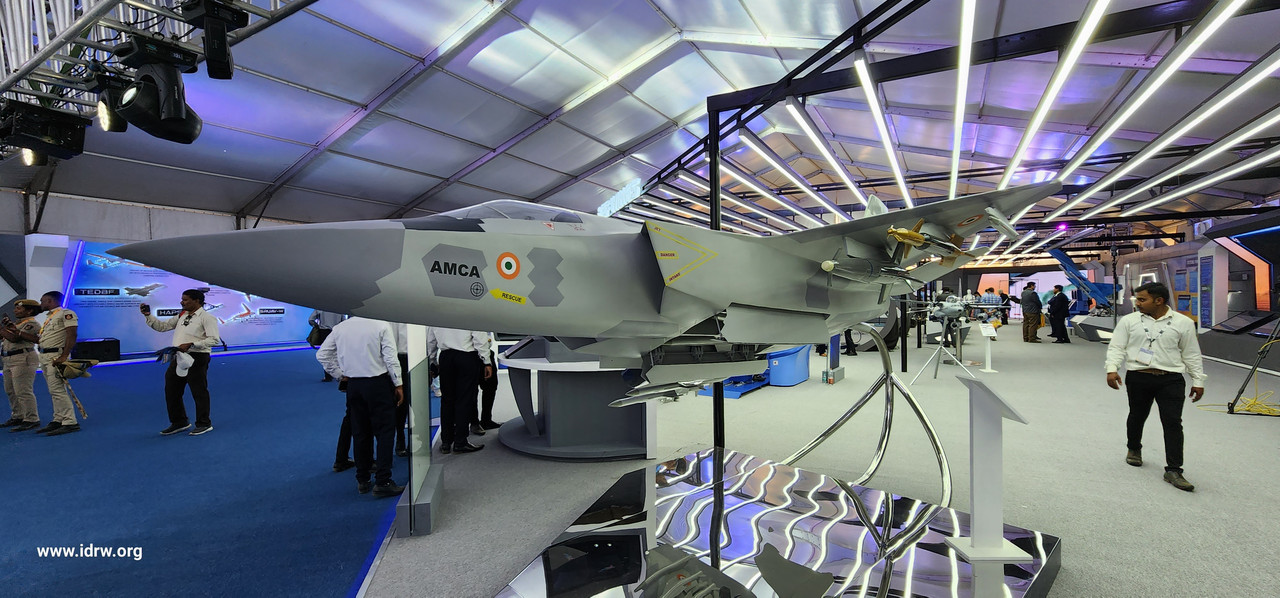

India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) is poised to take a leap forward with the integration of a Distributed Aperture System (DAS). This cutting-edge technology promises to revolutionize the AMCA’s capabilities, making it a true game changer in aerial warfare.
Imagine a fighter jet with eyes all around its body. That’s essentially what DAS offers. It’s a network of high-resolution infrared (IR) sensors strategically placed around the aircraft. These sensors continuously scan the surrounding environment, providing the pilot with a complete 360-degree spherical view.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Canada has recently made a significant acknowledgment regarding allegations of Indian interference in past elections won by Prime Minister Justin Trudeau. Following an official probe into foreign meddling in elections, unsubstantiated claims of Indian involvement have been refuted. The investigation, however, highlighted instances of Chinese influence in both the 2017 and 2021 elections.
A polling official involved in the investigation panel stated, “I do not believe that during the 2021 election, we saw evidence of the Government of India using those tools in the campaign.” This statement contradicts previous accusations made by Ottawa, which had initiated an inquiry into alleged Indian meddling amidst strained relations between the two nations. The tensions escalated following Trudeau’s accusations against the Indian government regarding the involvement in the killing of Khalistani terrorist Hardeep Singh Nijjar.
Continue reading