Idrw Team
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
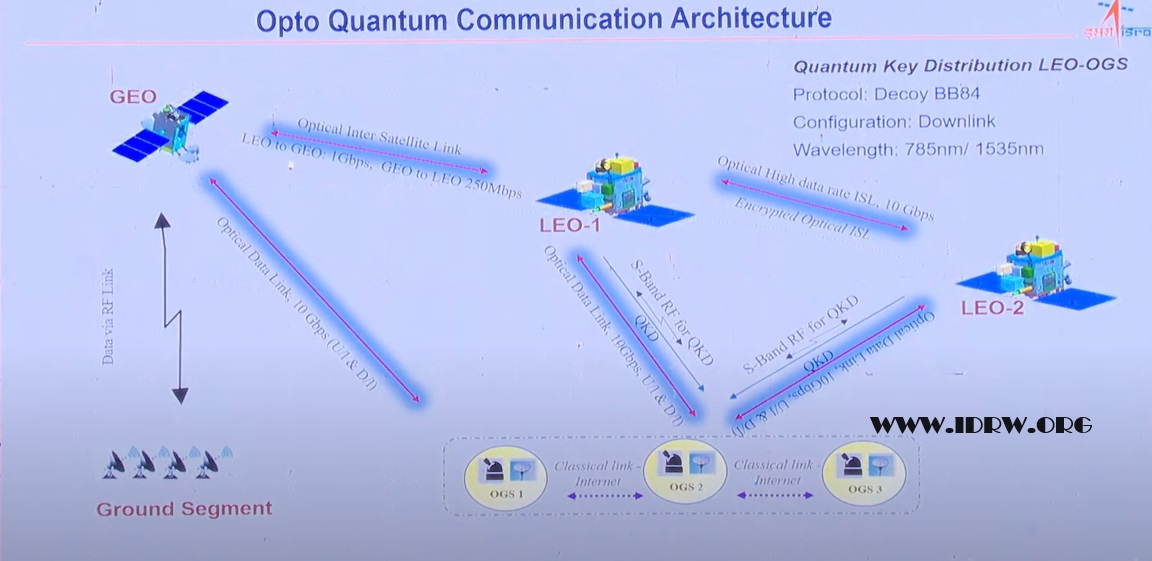
In a groundbreaking announcement at IIT Bombay’s Techfest, ISRO Chairman Dr. S. Somanath unveiled India’s ambitious journey into the realm of quantum communication. He revealed ISRO’s work on Opto Quantum Communication Architecture, specifically focusing on the development of Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) using a protocol known as Decoy BB84. This marks a significant step towards building secure and unbreakable communication networks for satellites and beyond.
QKD leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to establish unhackable communication channels. Unlike traditional encryption methods that rely on complex mathematical algorithms, QKD uses the inherent randomness of quantum particles – photons in this case – to generate a secret key shared only between the sender and receiver. Any attempt to intercept the key would inevitably disturb the quantum state of the photons, alerting the parties involved to a potential eavesdropping attempt.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
The recent claim by Tanzeela Khalil, a Research Fellow at the Islamabad Policy Research Institute, regarding India’s development of Agni-VI with a potential range of 10,000-12,000 km has sparked discussions on the strategic motivations behind such a move. Khalil argues that the development of Agni-VI is challenging to justify solely in terms of enhancing deterrence against China and Pakistan. Instead, she posits that India’s endeavors might be driven by a desire to elevate its global status or to position itself in potential deterrent relationships beyond its immediate neighbors.
The Agni-VI, if developed with a range of 10,000-12,000 km, would mark a significant advancement in India’s missile capabilities. This potential range extends far beyond the immediate threats posed by neighboring nations, raising questions about the strategic rationale behind such an ambitious development. Understanding the geopolitical landscape and India’s regional concerns is crucial in deciphering the possible motives behind the creation of Agni-VI.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has unveiled its highly anticipated Navachakshu Electronic Warfare (EW) System, marking a significant leap forward in India’s indigenous defense technology. This cutting-edge system promises to bolster the electronic warfare capabilities of two key frontline fighter aircraft: the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk1A and the Sukhoi Su-30MKI.
Navachakshu, meaning “third eye” in Sanskrit, equips these fighters with advanced Electronic Support Measures (ESM) and Radar Warning Receiver (RWR) capabilities. These crucial systems work in tandem to detect, analyze, and identify enemy radar emissions, providing pilots with real-time situational awareness of the electronic battlefield. This enhanced awareness allows them to:
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

After anxious months of waiting, India is finally set to receive its long-awaited delivery of F404-GE-IN20 engines for its indigenous Tejas fighter jets later this year. While initial projections placed the arrival date in August 2023, General Electric (GE) Aerospace CEO Amy Gowder recently confirmed a slight delay due to supply chain challenges faced during production restart after an 18-month hiatus.
Despite the setback, the news signals a critical step forward for India’s ambitious fighter program. The F404 engines are the heart of the Tejas Mk1A variant, and their arrival means production can resume full steam ahead. GE, committed to meeting India’s needs, has outlined a ramp-up plan targeting 20 engines per year, a significant increase from current production levels.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
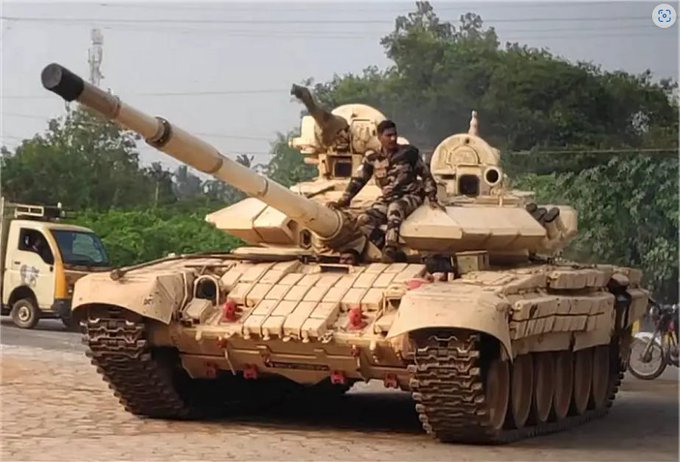

In a significant stride towards enhancing its armored warfare capabilities, the Indian Army has unveiled ATHARVA, a unique hybrid tank that seamlessly combines the main body of the T-72 tank with the advanced turret of the T-90 Bhishma. This hybrid marvel, which underwent trials in India last year, represents a strategic integration of two formidable tank models, offering a promising blend of power, agility, and cutting-edge technology.
ATHARVA’s distinctive feature lies in its innovative fusion of the T-72 tank hull with the T-90 tank turret. This integration aims to leverage the strengths of both tanks, combining the battle-tested reliability of the T-72 with the advanced features of the T-90 Bhishma turret. The result is a formidable hybrid tank that promises enhanced performance across various parameters.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

In a significant stride in India’s aerospace capabilities, the first of the newly constructed LCA-Tejas Mk1A fighter jets is poised to enter the crucial phase of its assembly process. Anticipated to initiate its first taxi trials by the middle of the upcoming month, the aircraft is set to undergo a series of flights by late February, marking a pivotal milestone in its journey towards operational readiness.
Following the taxi trials, the aircraft will embark on a series of flights in late February. By the end of March, it’s expected to have completed all necessary pre-delivery trials, paving the way for customer-mandated sorties to begin.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
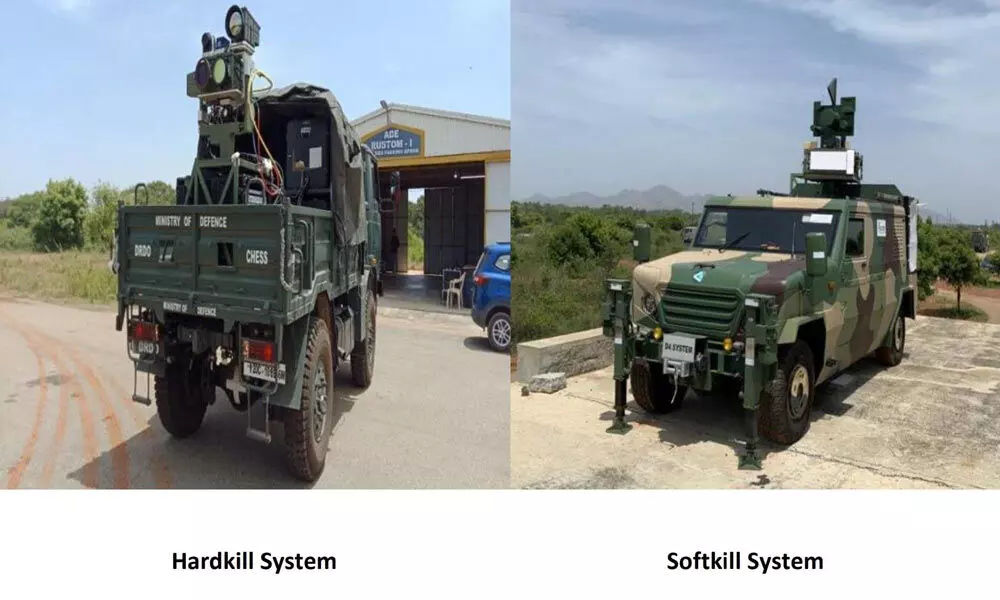

In a significant leap towards bolstering national security, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully developed indigenous counter-drone technology. This cutting-edge system, capable of detecting, soft kill, and hard kill responses against various types of drones, has already undergone successful demonstrations for armed services and internal security agencies.
The technology’s transfer to Bharat Electronics Limited, Bengaluru, for production marks a pivotal moment in India’s quest for self-reliance in defense capabilities. Additionally, four more Indian firms have been granted the Transfer of Technology for the production of anti-drone systems, amplifying the reach and impact of this groundbreaking innovation.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

The fate of DRDO’s Tapas Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) program has taken an interesting turn. While funding for its production has been diverted to the newer Archer-NG program, the Tapas story is far from over. DRDO’s Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) will continue to refine the airframe, utilizing its potential for both engine testing and future platform development.
Tapas, originally known as Rustom-II, has been a significant player in India’s UAV journey. It has achieved several milestones, including successful flights at 28,000 ft and 18 hours endurance, demonstrating its capability for surveillance and intelligence gathering missions. While not without its challenges, Tapas has paved the way for advancements in indigenous UAV design and technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

As India’s quest for a fifth-generation fighter jet gathers momentum, Rolls-Royce has thrown down a gauntlet with an audacious offer. The British engine giant has proposed co-developing a “Clean-Slate” new engine for India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, promising complete intellectual property (IP) transfer and operationalization within a flat decade.
This offer comes at a pivotal moment, coinciding with Indian Defence Minister Rajnath Singh’s upcoming two-day visit to the UK, aimed at strengthening strategic and security ties. With India’s indigenous Kaveri engine project facing delays, Rolls-Royce’s proposal presents a potentially attractive alternative.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Marking a historic milestone, the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Naval trainer prototype NP5 has successfully completed a series of landings and take-offs from India’s first domestically built aircraft carrier, INS Vikrant. This achievement, showcased in the recent DRDO Year-End Review 2023, signifies a major leap forward in India’s quest for self-reliance in naval aviation.
NP5, which made its maiden flight last August, was initially planned to undergo trials on both INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant. Its successful operation on Vikrant demonstrates the aircraft’s adaptability and robustness, paving the way for its seamless integration into the Indian Navy’s carrier operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
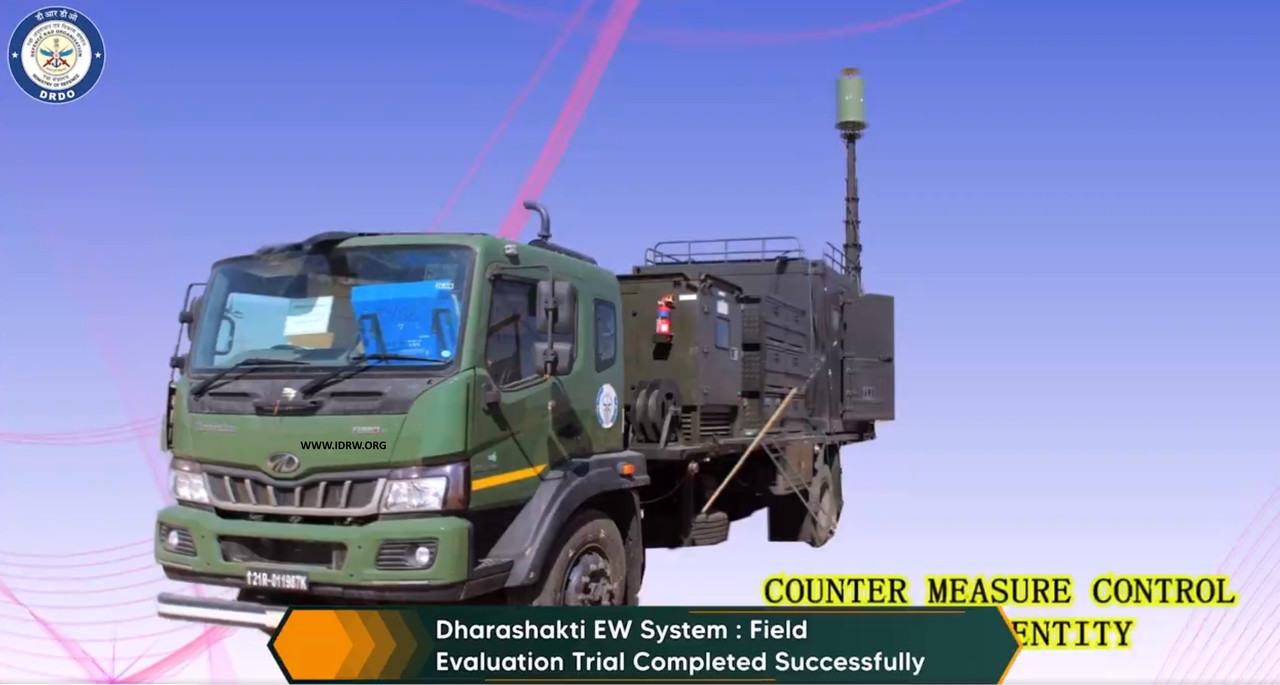

In a significant leap forward, the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) concluded 2023 on a high note, confirming the successful completion of Field Evaluation Trials for the Dharashakti Electronic Warfare (EW) System. This state-of-the-art system encompasses a comprehensive array of entities designed to address Control, Counter Measures, Jamming, Reconnaissance, and Direction Finding in diverse terrains such as deserts and plains.
The Dharashakti EW System boasts an intricate configuration comprising multiple entities, each serving a specific purpose in enhancing the electronic warfare capabilities. The key components include the Control Center Entity, Counter Measure Control Entity, Jammer UAV Entity, Reconnaissance and Direction Finding Station Radar, Jammer and High Band Entity, Jammer Interceptor Mobile Entity, and Jammer Station Very Ultra High Frequency Entity.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is gearing up for additional testing of its Naval Anti-Ship Missile – Short Range (NASM-SR) in 2024. The upcoming tests are intended to validate all technical parameters of the missile, with a particular focus on achieving its maximum range of 55 kilometers. This initiative comes following the successful flight test conducted by DRDO in November, during which the missile demonstrated a range of 35 kilometers.
The NASM-SR is a formidable naval anti-ship missile designed to enhance the capabilities of the Indian Navy. It is propelled by two two-stage solid propulsion systems, featuring an in-line ejectable booster and a long-burn sustainer. These advanced propulsion systems contribute to the missile’s agility and effectiveness in engaging maritime targets.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
Dg Propulsion Private Limited (DPPL) is celebrating a major milestone today! Their team successfully completed demo test runs for the powerful and precise DG J40 Jet engine, showcasing its capabilities for valued customers. This marks a significant leap forward for the Indian company, further solidifying their position as a leader in cutting-edge jet engine technology for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and defense applications.
Building upon the success of their DG J20 engine, DG Propulsion has raised the bar with the DG J40. This turbojet boasts a thrust capacity of up to 40 kgf, making it a true powerhouse in the world of UAV propulsion. This increased power output translates to greater range, payload capacity, and maneuverability for UAVs, opening up exciting new possibilities for military and civilian applications.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
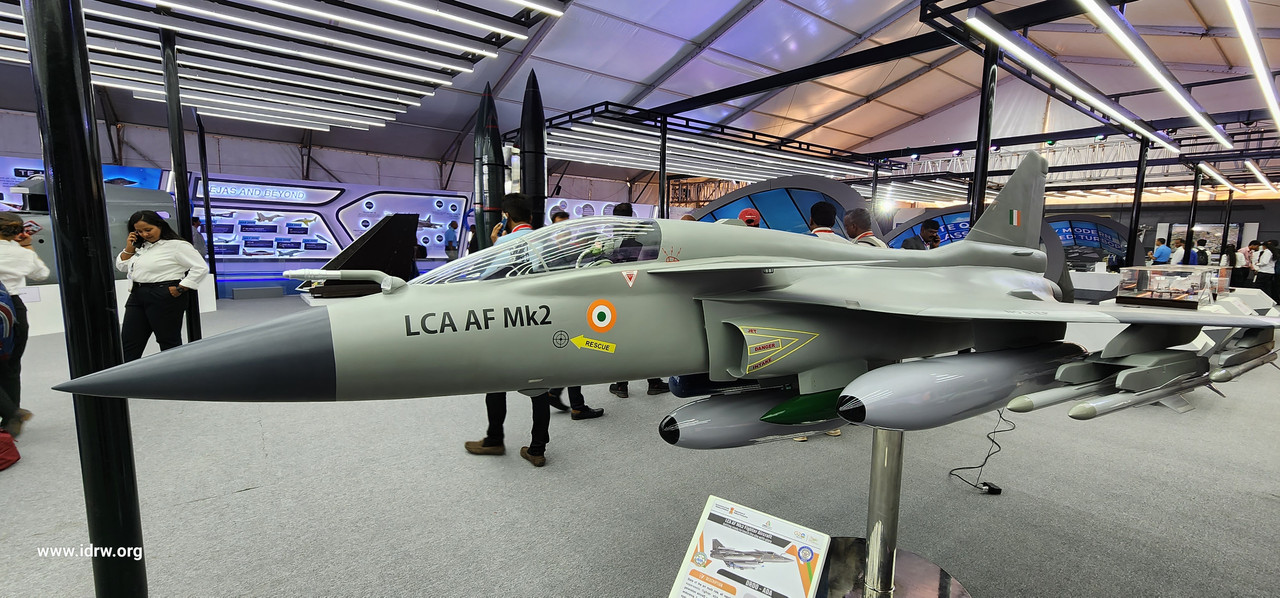

India’s Tejas MkII fighter jet, set to be powered by the American F-414 engine, will boast a modular engine bay designed to accommodate even more powerful engines in the future. This forward-thinking approach paves the way for seamless integration of a new 110kN engine currently under development for the fifth-generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program.
The F-414 engine, a proven powerhouse generating around 98kN of thrust, will provide ample muscle for the Tejas MkII fleet. However, anticipating future needs for increased power, especially in the AMCA program, the engine bay has been designed with adaptability in mind.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
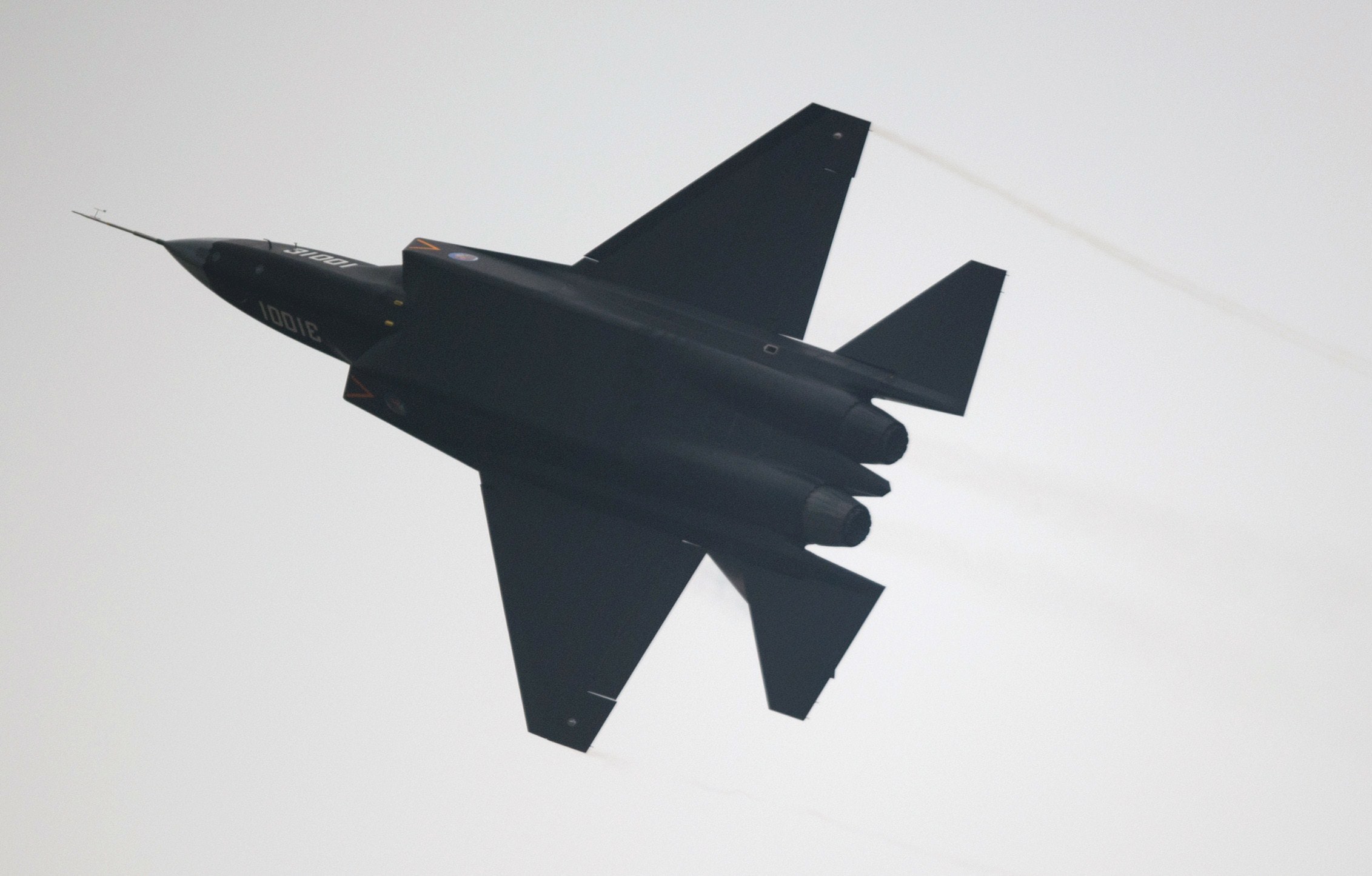

The veil has been lifted on Pakistan’s airpower ambitions, with the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) officially announcing plans to acquire China’s J-31 stealth fighter jets. This move marks a significant shift in the regional arms race, raising questions about its impact on the delicate power dynamics between Pakistan and India.
The J-31 boasts advanced stealth capabilities, designed to evade radar detection and penetrate deep into enemy airspace. Its twin-engine configuration offers enhanced power and payload capacity, making it a formidable contender in modern aerial combat. However, the J-31’s price tag and operational costs pose challenges for Pakistan. The exact number of jets to be procured remains unclear, with estimates suggesting a modest squadron due to budgetary constraints.
Continue reading