SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

In an article published by “The Times of India,” it has been revealed that the Indian Navy is preparing to conduct tests of Long-Range Land-Attack Cruise Missiles (LR-LACMs) from a Russian Kilo-class Electric-Diesel Conventional submarine. These LR-LACMs will be an advanced version derived from the sub-sonic Nirbhay Cruise missile program.
The LR-LACMs, which will be launched from torpedo tubes, are anticipated to have a range of 1500km. Once they enter production, they will be installed on all electric-diesel submarines within the Indian Navy’s fleet. While the exact date of the missile’s testing remains uncertain, it is expected to take place within the next 2-3 years.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

The Indian Armed Forces are set to establish the Integrated Rocket Force (IRF), which will serve as the fourth main division of the military. Functioning as a separate entity but under the authority of the Ministry of Defence, the IRF will play a crucial role as the primary defence wall of India. Equipped with a range of advanced weaponry, including surface-to-surface Pralay tactical missiles, subsonic LR-LACMs (Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missiles), BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles, Pinaka multi-barrel rocket systems, and other stand-off weapons, the IRF will enhance India’s defensive capabilities.
The creation of the IRF reflects India’s commitment to strengthening its defence infrastructure and readiness. By incorporating advanced missile systems into the IRF’s arsenal, the Indian Armed Forces aim to enhance their ability to counter potential threats and safeguard the nation’s security. These sophisticated weapons will provide the IRF with the capability to strike targets accurately and swiftly, thereby deterring any potential aggressors.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.
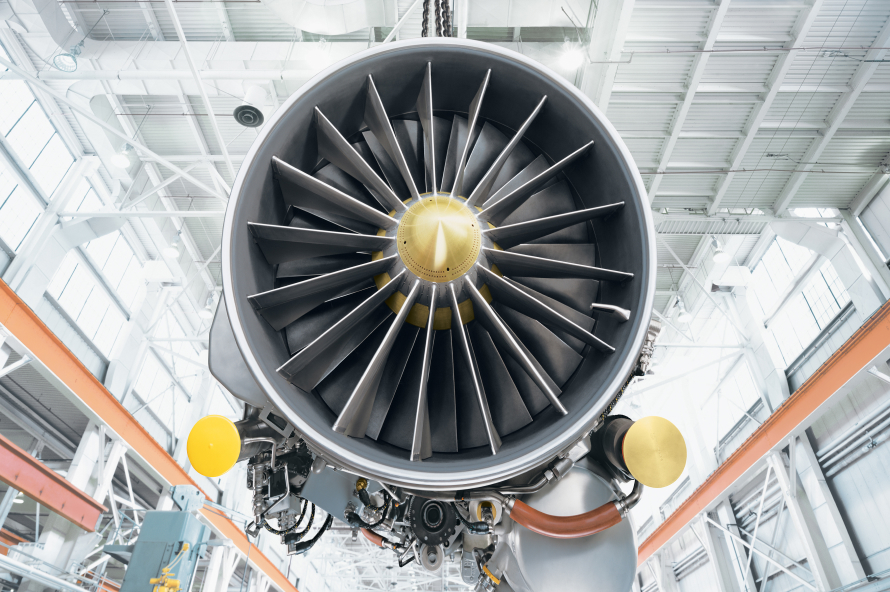

The Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) insisted on interest in establishing local assembly facilities for engines and manufacturing key parts within the country. This move aims to stabilize the production systems and ensure a steady supply of frequently replaced components, ultimately reducing operating costs while enhancing the combat readiness of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
Officials familiar with the matter told idrw that, the local manufacturing facilities and infrastructure will play a vital role in bolstering the Tejas mk2 fleet once it enters production. The initiative is seen as a significant step towards achieving self-reliance in the defence sector and reducing dependence on foreign suppliers.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

The Defence Acquisition Council, led by the Union defence minister, recently approved the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) to procure 307 Advanced Towed Artillery Gun Systems (ATAGS). Pune-based Bharat Forge has also confirmed that the contract may be finalized later this year, pending the opening and evaluation of commercial bids to determine the manufacturer for 60% of the guns, while the remaining 40% will be allocated to another manufacturer.
Bharat Forge and Tata Advanced Systems, both private sector companies, are the production partners for the ATAGS, which has been developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). Once the contract is concluded, the Indian Army will receive 75 guns per year, resulting in the formation of four ATAGS gun regiments annually.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

Safran and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) are set to commence the development of a new engine for the Indian Multi-Role Helicopter (IMRH) program later this year. The joint venture, established after signing an MoU in 2022 in the presence of Safran Global CEO Olivier Andriès and senior HAL officials, marks a significant step towards enhancing indigenous capabilities in helicopter engine technology.
Safran Helicopter Engines and HAL have already finalized a workshare agreement for the engine development of the 13-tonne IMRH and its naval variant, the Deck-Based Multi-Role Helicopter (DBMRH). Both parties have reached an understanding of the distribution of responsibilities, with HAL’s active participation in the design, development, and production of core engine components.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

During Aero India earlier this year, it was announced that the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) are collaborating on the development of a High-Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Class UAV. This UAV will be powered by a turboprop engine with a thrust of 940hp and will feature a pusher configuration. The anticipated specifications include an all-up weight of 5 tons and an impressive endurance of over 25 hours.
According to information obtained by idrw, the design configuration for the HALE UAV is expected to be finalized later this year. Once the program receives clearance, detailed work will commence, and the engineering tendering process for the prototype is likely to begin next year. The project aims to achieve a possible rollout of the UAV in late 2025.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

Earlier this year, the Indian Navy Chief confirmed plans for the development of a second indigenous aircraft carrier based on the 45,000-ton IAC-I design. However, significant modifications will be made to this carrier to enable it to operate Unmanned Combat Vehicles (UCAVs) for deck-based operations starting in 2030.
The Indian Navy has been closely monitoring the proposed UCAV platform by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO). The UCAV is expected to be powered by a Dry Kaveri engine, generating 46kn of thrust, which can be adapted for deck-based operations. The UCAV will serve as a crucial component of the strike element, capable of stealthily approaching land-based targets or engaging a flotilla of warships in the open sea.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

The Directorate General of Artillery is currently in the process of procuring Runway Independent Remotely Piloted Aircraft System (RPAS) for its Surveillance and Target Acquisition (SATA) units. To fulfil this requirement, tenders were issued under the Make-II category (no government funding is provided.). The objective is to obtain a system that can provide data on static and dynamic targets to enhance the effectiveness of firepower resources such as Guns and Rockets.
The need for this aerial surveillance platform arises from the limitations of ground-based sensors, which have restricted surveillance depth. Therefore, there is an urgent requirement for an RWI RPAS with a range of 80-100 km, capable of tactical surveillance, target acquisition, Direction of Own Artillery Fire (DOOAF), and Post Strike Damage Assessment (PSDA).
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.
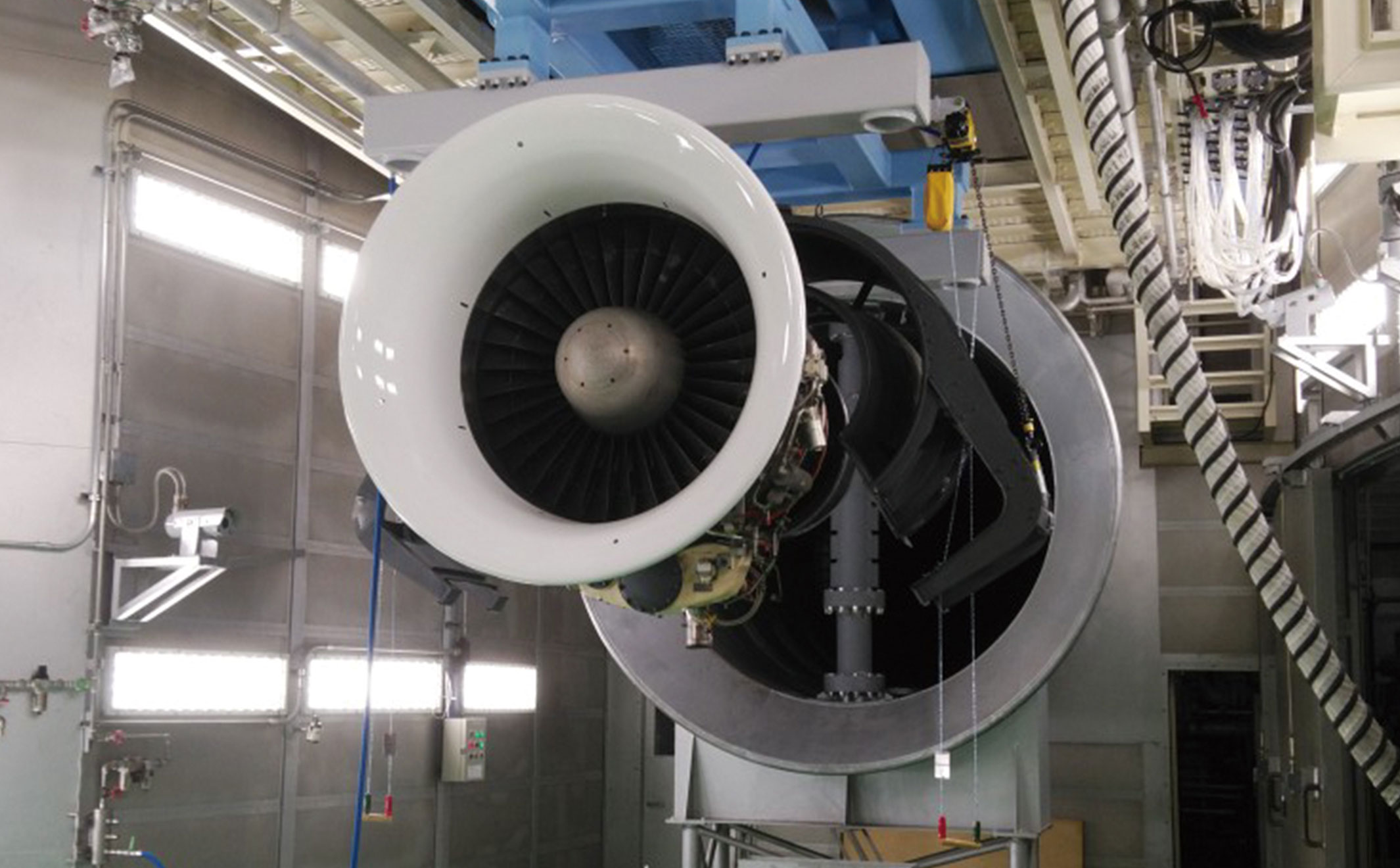

India is currently engaged in discussions with major aerospace engine manufacturers to collaborate on the development of a 110-120kN class of engine for the country’s fifth-generation fighter jet AMCA program. People familiar with the matter have told idrw that In addition to the engine itself, the deal is also said to include provisions for the establishment of a High Altitude Engine Test Facility (HAETF) and Flying Testbed Aircraft (FTB) in India, both of which will be provided or supported by the chosen aerospace engine OEMs.
idrw has learned that the aerospace engine OEMs may directly provide or assist in setting up the High Altitude Engine Test Facility (HAETF) and Flying Testbed Aircraft (FTB) in India, as these facilities are critical for developing the engine locally and conducting all levels of testing during the development process. India’s goal is to avoid relying on OEM support repeatedly.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.
In 2010, India’s Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) chose 99 F414 GE fighter jet engines to power the Mk II variant of the Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) for the Indian Air Force. The initial batch of F414-GE-INS6 engines was to be supplied by GE Aviation under the terms of the original agreement, with the remainder being produced in India through a technology transfer agreement.
At the time, the Indian Air Force was only interested in around 80 Mk II versions, which were to be built by re-engining the Tejas Mk1 airframe that was ready in 2014, with an All up weight (AUW) of 15 tons and an extended 500mm longer fuselage plug in its spine.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG.

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is planning to retire 80 Mig-21Bis jets that were procured in the mid-80s, along with an additional 40 airframes kept in reserves by 2025. The state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) that has been exploring the concept of the Optionally-manned combat aircraft (OMCA), which involves converting retired jets into suicide drones for various purposes, such as carrying out attacks or baiting air defence positions within enemy airspace has been proposing making retired Mig-21s into OMCA.
The OMCA project aims to develop platforms that can carry out auto take-off and landing without any remote pilot inputs and can be armed to carry out the first wave of airstrikes in heavily saturated airspace. However, the IAF is not fully on board with this project yet.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The No.3 Base Repair Depot of the Indian Air Force (IAF) in Chandigarh has taken up an important project to develop Kevlar safety screens for the protection of machine gun operators during operations on board transport helicopters.
Machine guns are mounted in the doorframes of these helicopters to provide fire support during special heli-borne operations such as airborne assault, troop insertion, or search and rescue missions in hostile territories. Such situations make the gunner vulnerable to enemy ground fire, and the Kevlar safety screens will offer much-needed protection.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Astra MkI Beyond Visual Range (BVR) Air-to-Air Missile (AAM), indigenously designed and developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is set to be cleared for operational roles later this year for the Mig-29K fleet, Once it clears the mandated flight trial from the aircraft.
The Indian Navy, in association with State-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), has already begun equipping the Mig-29K fleet with an upgraded Indian-designed Mission Computer (MC) on the aircraft to enable integration of Indian-made weapons like Astra MkI.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
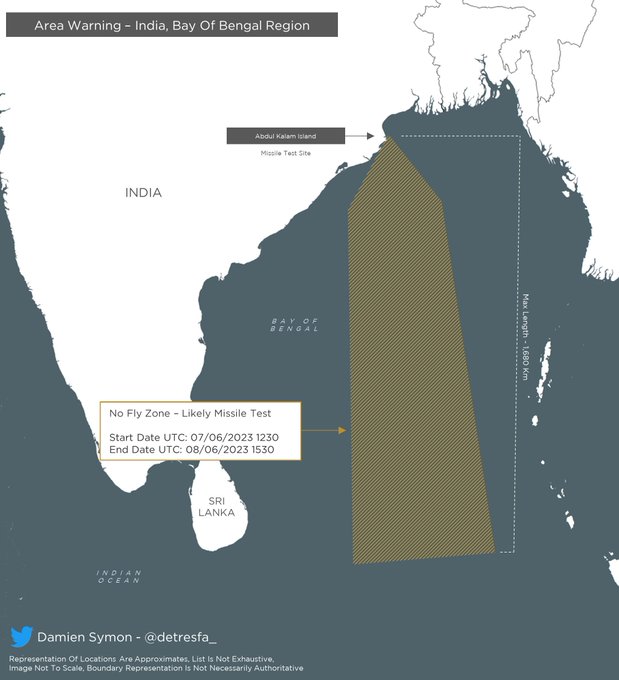
India has Rescheduled Notices to Airmen (NOTAM) for a launch of a missile in the Bay of Bengal that was issued for the period from 18-19 May 2023 to now 07-08 June 2023 as per information provided by Twitter user Damien Symon@detresfa_.
The designated area for the NOTAM is 1680 km in length which indicates it might be a test of the Agni-P from Abdul Kalam Island. Agni P is a two-stage Canisterised solid propellant ballistic missile with dual redundant navigation and guidance system.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
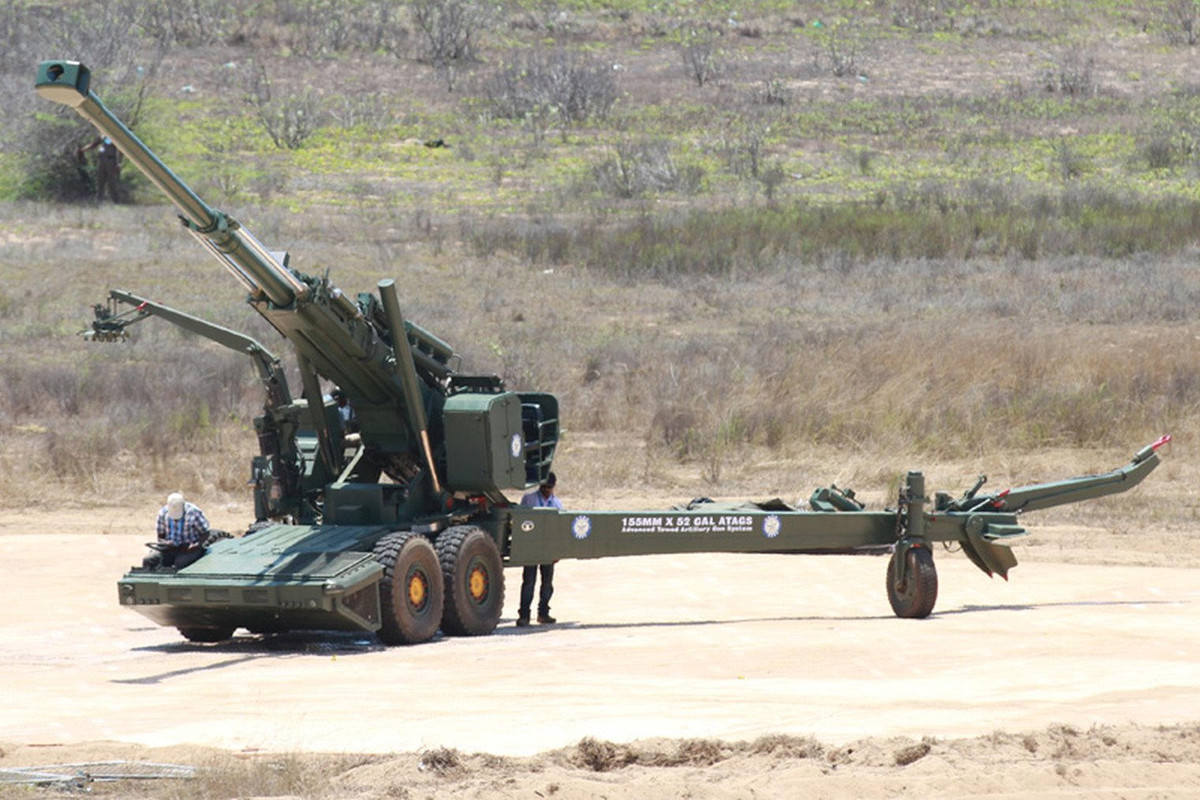

Bharat Forge, a Pune-based company, has received approval from the Ministry of Defence (MOD) for the procurement of 300 Advanced Towed Artillery Gun Systems (ATAGS), which it developed in collaboration with Tata Defence and Aerospace and state-owned DRDO. The contract for the guns is expected to be signed later this year, after the opening of commercial bids submitted by Bharat Forge and Tata Defence and Aerospace.
Under the agreement, Bharat Forge and Tata Defence and Aerospace will jointly manufacture the ATAGS at a 60-40% ratio, with the lowest bidder getting the opportunity to manufacture 60% of the guns. The second lowest bidder will have to supply the ATAGS at the same price as the lowest bidder to secure their share of the order.
Continue reading