SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
India’s ambitious Tejas MkII program is set to advance into the developmental testing phase starting in 2025. With committed orders for 120 units and potential procurement of over 80 more units in the future, the program gained momentum following the clearance of CCS (Cabinet Committee on Security) approval last year. The Tejas MkII, an advanced variant of the indigenous Tejas fighter jet, promises to elevate India’s aerospace capabilities to new heights.
Prabhulla Chandran VK, the director of avionics and weapons systems at the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA), recently revealed that ADA is exploring the development of a Trainer variant of the Tejas MkII. Interestingly, the Indian Air Force (IAF) has not placed any such requirement for a trainer version. The move to consider a Trainer variant stems from the intention to make the Tejas MkII more appealing in the international export market.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
The AEW&CS MK-II program, aimed at developing six new Airborne Early Warning and Control (AEW&C) aircraft for the Indian Air Force (IAF), is set to embark on sensor trials on the DRDO’s A-319 “Anusandhan” Flight Test Bed (FTB) aircraft next year. The project is expected to gain further momentum in 2025, with the anticipation of the first aircraft taking to the skies by 2026. Leveraging the A-319s and A-321 variants sourced from the Air India fleet, the program marks a significant stride in enhancing India’s aerial surveillance capabilities.
The initial phase of the AEW&CS MK-II program will focus on conducting sensor trials on the DRDO’s A-319 “Anusandhan” FTB aircraft, serving as a testbed for advanced systems. Following successful trials, the DRDO will issue a Request for Proposal (RFP) to seek bids for the modification of the six-passenger aircraft acquired for the program. Airbus, the original equipment manufacturer (OEM), is currently the frontrunner to secure the contract, given its expertise in aircraft modification and integration.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
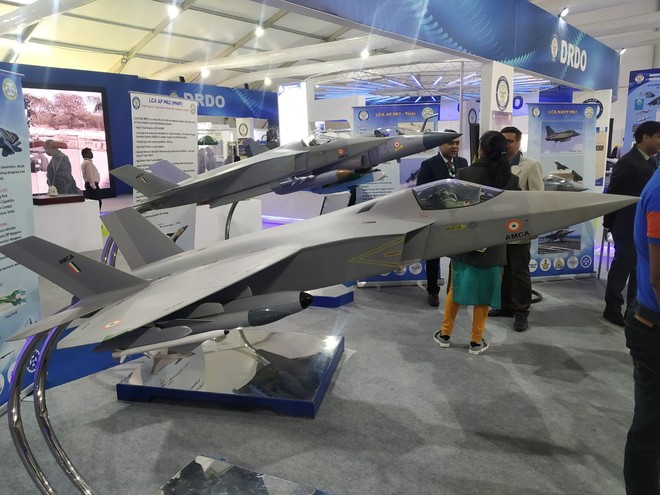

French multinational aerospace manufacturer Safran and India’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) will soon be working out formalities for the joint venture that aims to create an advanced engine that will power India’s highly anticipated 5th generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) fighter jet.
People familiar with the matter have revealed that India is poised to make a significant commitment, pledging to procure 400 engines with a thrust class of 110kN. These engines are expected to enter production in India in the mid-2030s, ensuring economies of scale are achieved, and the cost of each unit remains proportionate to approximately 30% of the AMCA aircraft’s overall value. This thoughtful approach not only empowers India to become self-reliant in engine production but also strengthens its position as a formidable player in the global aerospace industry.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
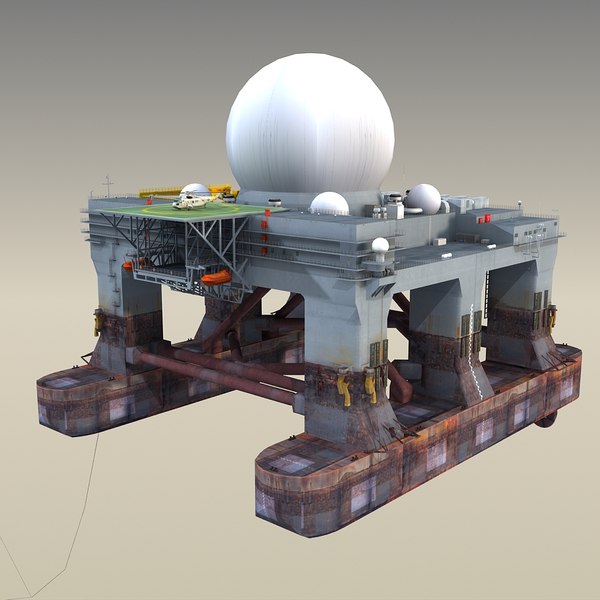

India is venturing into the development of a floating sea-based radar system as part of its Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) program. The project aims to bolster the nation’s defence capabilities by establishing an advanced radar system that can detect and track ballistic missiles, differentiate between warheads and decoys, update ground-based interceptors in real time, and evaluate the effectiveness of missile intercept attempts.
This strategic move comes as India completes Phase-I of its BMD system, with land-based installations currently providing security to key regions, including the National Capital New Delhi and India’s Commercial Capital Mumbai.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
Last month, the Indian Ambassador to Argentina, Dinesh Bhatia, along with a delegation from the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), met with Jorge Enrique Taiana and Brigadier General Xavier Isaac of the Argentine Air Force. During this meeting, India proudly demonstrated its prowess in manufacturing and showcased the Tejas fighter, garnering significant interest from the South American nation.
Argentina is keen to acquire 15-16 Tejas fighters directly from India, and it also aims to assemble an additional 30 jets locally in its own country. This proposition opens up significant avenues for collaboration, technology transfer, and joint production, further fostering a robust defence relationship between the two nations.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
In a recent media interaction, Atul Dinkar Rane, the CEO and MD of BrahMos Aerospace, made a significant statement, ruling out the possibility of equipping the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile with a nuclear warhead. The decision comes as India reaffirms its commitment to conventional warfare and clarifies its stance on the deployment of nuclear weapons.
The BrahMos missile, a joint venture between India and Russia, is renowned for its exceptional speed and precision, making it one of the most potent supersonic cruise missiles in the world. However, concerns were raised when the missile was accidentally fired from Sirsa, Haryana, in 2022 and crashed into Mian Channu, Khanewal District, Punjab, Pakistan. Pakistan swiftly claimed that the BrahMos missile could have triggered a nuclear incident, given its potential to be armed with nuclear warheads.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
In a promising development for India’s defence capabilities, the French Naval Group has joined hands with Indian private sector giant Larsen & Toubro (L&T) to work on the cutting-edge SOV-400 ‘midget submarine’ program. This collaborative effort aims to develop a versatile and highly efficient submarine optimized for Special Forces missions, catering to the needs of smaller navies. The SOV-400, with its advanced features and capabilities, has the potential to become a game-changer in the realm of naval warfare.
The SOV-400 is envisioned as a compact and agile submarine with a 400-ton displacement, designed to excel in Special Forces operations. With the ability to carry up to 10 Special Forces operators, this midget submarine offers unrivalled flexibility and adaptability for covert missions. Notably, the lower hull of the SOV-400 can accommodate two 4-person Swimmer Delivery Vehicles (SDVs), allowing for rapid insertion and extraction of Special Forces units.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
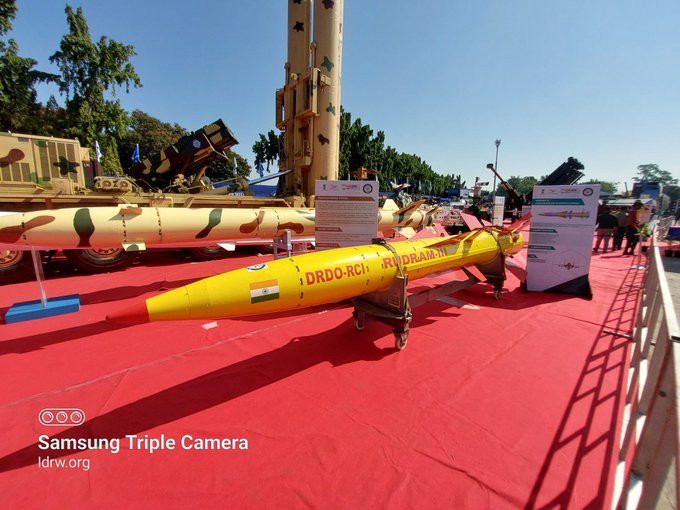

PICTURE OF RudraM-III
In a groundbreaking development, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has achieved yet another milestone, successfully conducting trials of the Rudram-II, an advanced Air-to-Surface Missile (ASM) with impressive capabilities. Dr Samir V Kamat, Chairman of DRDO, confirmed this remarkable achievement to local media, signaling a significant leap forward in India’s indigenous defence capabilities.
The Rudram-II has been designed to be launched from two of India’s most potent fighter aircraft, the Sukhoi-30 and Mirage-2000, marking a strategic enhancement to the firepower of the Indian Air Force (IAF). The missile boasts an impressive operational range of 300 kilometers, allowing it to reach distant targets with unmatched precision and effectiveness.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a significant step towards bolstering India’s indigenous defence capabilities, the country is set to receive its first Made in India C295 aircraft in 2026. This momentous achievement follows the Rs 21,000-crore deal signed with Airbus Defence and Space, Spain, in September 2021, marking a major stride in India’s journey towards self-reliance in defence production.
The first 16 C295 aircraft, under the terms of the agreement, will be delivered in ‘fly-away’ condition from Airbus’s final assembly line in Seville, Spain. The delivery process is expected to be completed by September 2025, paving the way for the induction of these advanced aircraft into the Indian Air Force (IAF) fleet.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Nuclear Thermal Rocket Engines @ NASA
In a groundbreaking collaboration, the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) are set to revolutionize space exploration by jointly developing a cutting-edge nuclear thermal rocket engine. This technology holds the key to faster and safer interplanetary missions, reducing transit times and mitigating risks for astronauts.
Interplanetary missions have always captivated the human imagination, but their realization has been hindered by the formidable challenges of vast distances and long transit times. Conventional chemical propulsion systems, while reliable, have limitations when it comes to the energy required to propel spacecraft across vast cosmic distances. Nuclear thermal rocket engines, on the other hand, offer an innovative solution that promises to propel humanity deeper into the cosmos.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
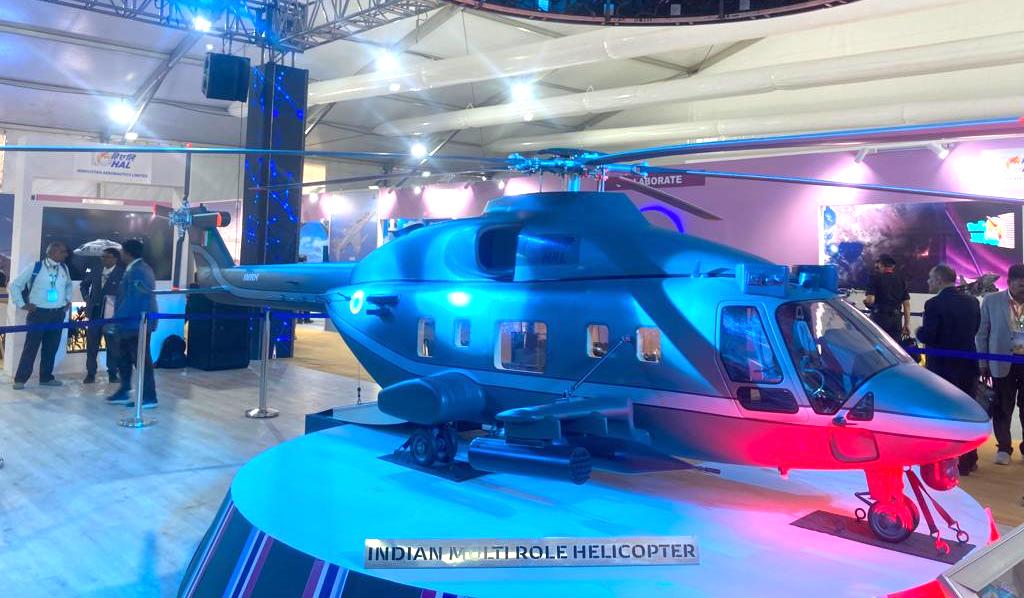

The Indian Multi-Role Helicopter (IMRH) project, proposed by the prestigious Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL), is gearing up for significant advancements in the coming months. As the Detailed Project Report (DPR) nears completion, the HAL is preparing to submit it for approval from the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) in the next month.
Anticipated to receive clearance from the CCS by the last quarter of this financial year, HAL is eagerly moving forward with its vision for the IMRH.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
India and France have agreed to further cooperation on ambitious submarine projects following the successful conclusion of the Kalvari class submarine program. This partnership hints at a closer working relationship between the two nations as they embark on India’s most ambitious submarine program yet—the development of three nuclear attack submarines for the Indian Navy.
The French Naval Group has been vocal about its interest in collaborating with India on the supply and development of “Non-Nuclear” systems for India’s nuclear attack submarine program. This collaboration opens up possibilities for joint initiatives and technology transfer between the two countries, further strengthening their defence ties.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The ambitious Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program is poised to take off following a landmark agreement between India and France to jointly co-develop a new engine for India’s fifth-generation AMCA fighter jet. The breakthrough might soon come when Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) grants clearance for a ?15,000 crore investment in the AMCA program, encompassing prototype development and flight testing.
The engine front had been a key obstacle, and the Ministry of Defense (MoD) was eager to resolve the engine deal before the AMCA program could progress further. With the engine collaboration in sight, the chances of the AMCA receiving CCS clearances are expected to align with the final agreement for engine development, potentially later this year or early next year.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
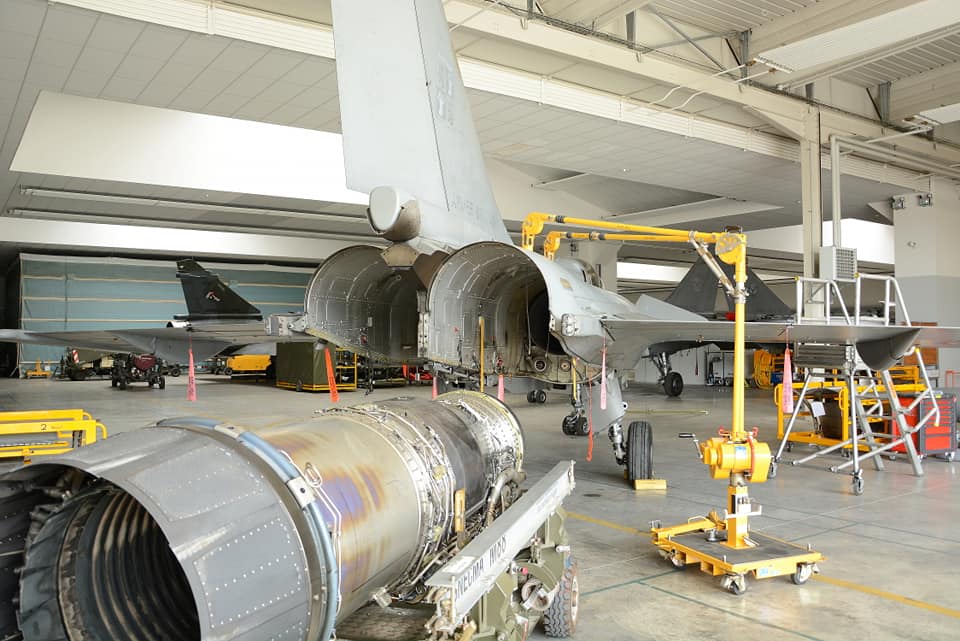

In a significant development for the future of military aviation, France’s Safran Group is working on a heavily modified M88 engine to power its sixth-generation fighter jet prototypes. The same engine is expected to serve as the base for the development of an Indo-French jet engine for India’s fifth-generation AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) fighter jet program. This collaboration marks a crucial step in advancing the capabilities of both nations’ fighter fleets and strengthening their defence ties.
The M88 engine, which currently powers the Dassault Rafale, is known for its reliability and performance, producing 75kN of wet thrust. However, India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) requires an engine capable of generating 75kN of dry thrust and wet thrust of around 110-120kN for the ambitious AMCA program. Safran Group is rising to the challenge, working on a high-thrust engine capable of delivering 125-130kN thrust for France’s sixth-generation fighter jet.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
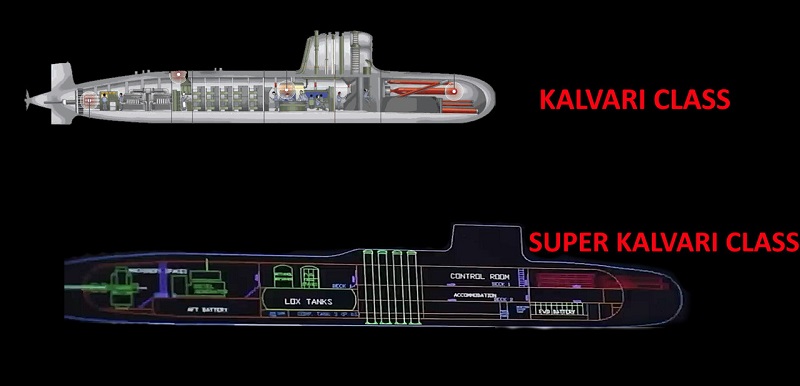
India’s state-owned Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and the Indian Navy have initiated the design work for a new class of Hunter Killer SSK (Diesel-Electric) submarines. The detailed engineering design is expected to be completed by 2028, with construction on the submarines projected to commence from 2032 onwards.
The upcoming submarine will be based on the technology obtained from the Kalvari Class submarines while incorporating approximately 70% indigenous technologies. It will undergo significant upgrades to its propulsion system, batteries, sonar systems, navigation system, communication systems, weapons systems, life support systems, and fire control systems.
Continue reading