SOURCE: AFI

The JF-17 Thunder, a lightweight fighter jet co-developed by China and Pakistan, has sparked debate about its design lineage. While its visual similarities to certain aircraft are undeniable, the true story behind its origins is more nuanced.
Initially, the belief was that the JF-17 stemmed from the MiG-33, a single-engine variant of the MiG-29 Fulcrum. The Soviet Union reportedly offered the MiG-33 design to China after the Cold War’s collapse. This theory gained traction due to the JF-17’s use of the RD-93 engine, a derivative of the RD-33 used in the MiG-29 family.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

India’s current military technology research and development (R&D) expenditure, hovering around 0.65% of GDP, stands in stark contrast to major powers like China (2.14%), the US (2.83%), and even South Korea (4.8%). This disparity presents a compelling argument for India to significantly increase its investment in this critical area.
With a low R&D budget, India remains reliant on foreign technology for critical defense equipment. This dependence can create vulnerabilities in times of geopolitical strain and limit India’s strategic autonomy. Rapid advancements in military technology can quickly render existing equipment obsolete. Without robust domestic R&D, India risks falling behind in the technological race, jeopardizing its military capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
India’s ambitious collaboration with Russia to develop the Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft (FGFA) program, a project based on the Su-57 platform, came to an end in 2018. While the official reasons remained unclear at the time, new reports shed light on the potential factors that led to India’s withdrawal.
Disagreements on technical aspects appear to have played a significant role in the program’s demise. Sources suggest India desired a two-seater variant of the FGFA, similar to the Su-30MKI fighter jets, a request not readily met by Russia. Additionally, concerns regarding the transfer of critical technology and design specifications from Russia to India reportedly caused friction.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

NewSpace Research and Technologies has unveiled its latest innovation – the PYGMY Vision-based kinetic attack drone platform. This cutting-edge drone boasts a lightweight design and is packed with features that make it a game-changer for military operations.
The PYGMY’s lightweight construction allows for both air and ground launch, making it adaptable to various deployment scenarios. The drone can be equipped with third-party payloads, giving users the flexibility to customize it for specific missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
:quality(70)/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/archetype/EPW5A7GX3ZEZZGPEYO53VKU34Y.jpg)
Nigeria’s Air Force is set to receive a significant boost in its capabilities with the upcoming delivery of the first six M-346 Master light fighter-trainer aircraft from Italy. This marks the initial phase of a larger procurement deal involving a total of 24 M-346s.
The contract stipulates the delivery of the aircraft in four batches, each comprising six planes. This phased approach allows for pilot training and infrastructure development alongside the arrival of the new jets. Importantly, the deal also includes 25 years of logistical support from Leonardo, the Italian manufacturer.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI) is nearing completion of the second prototype for its TAI Kaan fighter jet, a significant step forward in the development of this next-generation aircraft. The final assembly and engine integration processes are on track to be finished by June or July of this year, paving the way for a series of comprehensive flight tests.
This news comes after the successful maiden flight of the first Kaan prototype in February 2024. The second prototype will undergo a rigorous testing program to assess its performance capabilities and refine its design before mass production begins.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Reports from the Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) community suggest Iran’s S-300PMU2 air defense system in Isfahan may have been damaged in a recent Israeli attack. While Iran operates the S-300PMU2 system, the specific radar targeted is believed to be a 30N6E2, also known as the Tomb Stone radar.
The New York Times, citing its analysis of satellite imagery, reported that a precision strike on the Eighth Shekari Air Base in Isfahan damaged or destroyed a “flap-lid” radar, a crucial component of the S-300 system used for tracking incoming targets.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
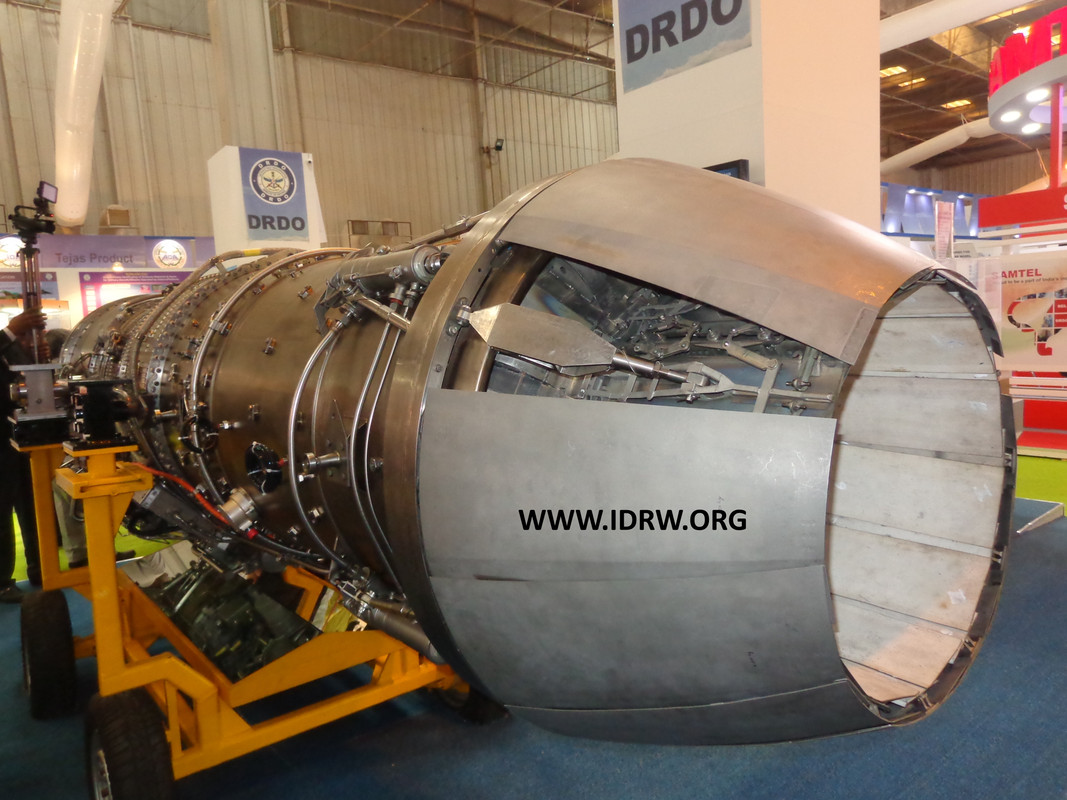

The Gas Turbine Research Establishment’s (GTRE) plan to develop the Kaveri 2.0 engine for the Tejas Mk1A fighter jet raises questions about its strategic rationale. With a targeted thrust output of 90kN, the Kaveri 2.0 seems like a logical upgrade for the Tejas Mk1A, which currently uses American F404 engines. However, the bigger picture paints a more complex story.
Looming large is the upcoming Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. This 5th generation fighter requires a much more powerful engine, with estimates suggesting a thrust requirement of around 110kN. Furthermore, reports indicate that GTRE might collaborate with an international partner for the AMCA engine, potentially leading to a core capable of generating a mighty 130kN thrust. This future-proof engine could even be adapted for India’s potential 6th generation fighter program.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
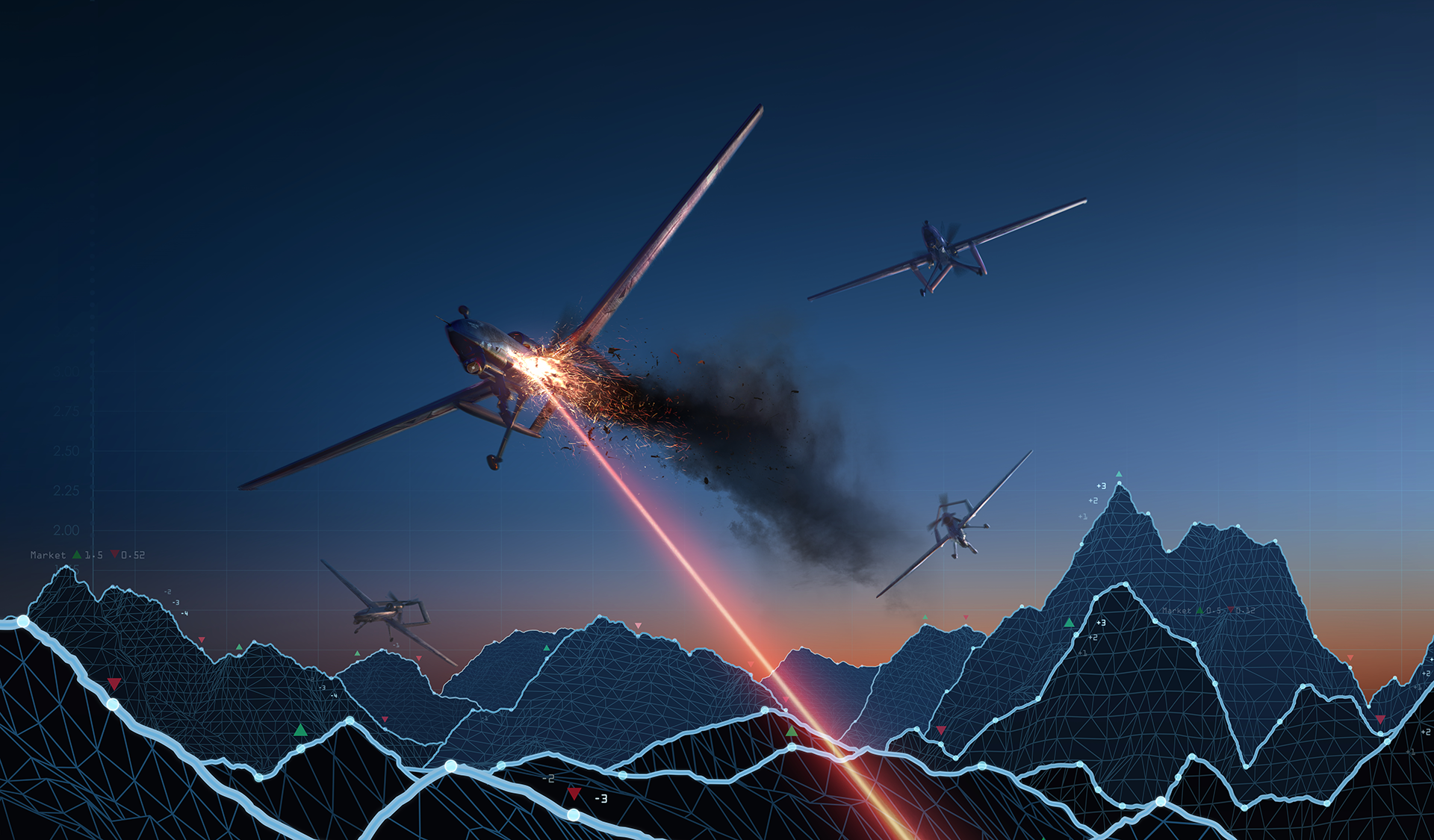

India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) is on the cutting edge of counter-drone technology with the development of high-power microwave (HPM) weapons. This Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) system boasts the potential to neutralize a range of aerial threats.
Internal documents confirm that Directed Energy Weapons (DEW) will be able to effectively take out and disable hobbyist drones and commercially available quadcopters used for malicious purposes. DEW also will be powerful enough to disable Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE)drones, often used for surveillance.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
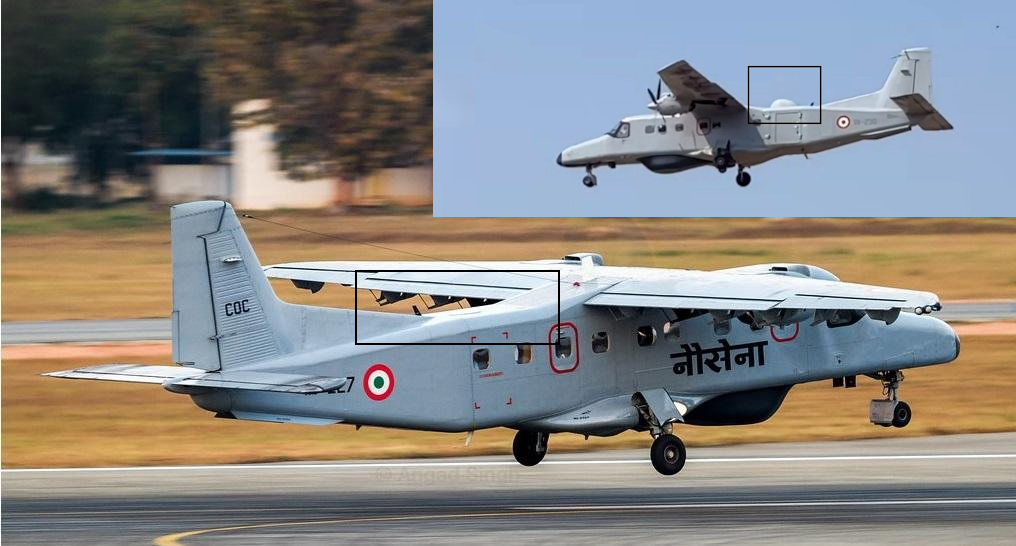

A plane spotting enthusiast (vabb_spotter IG) has captured an image of a Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) developed Dornier Do 228 aircraft sporting an unusual feature of a hump on the upper fuselage, aft of the main body.
The presence of the standard under-fuselage 360-degree maritime surveillance radar confirms the aircraft belongs to the Indian Navy. Speculation is rife about the purpose of the hump, with some suggesting it houses a satellite uplink system. This would be particularly useful given the aircraft’s frequent flights over vast stretches of ocean, enabling real-time transfer of observation data collected by its robust sensors.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

South Korea and India, both regional powers with growing military ambitions, are currently engaged in developing their own indigenous 5th generation fighter jets: the KF-21 (Korea Fighter-21) and the AMCA (Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft) respectively. While each program has its own unique goals and challenges, several key similarities exist between the two endeavors.
A core similarity lies in the strategic intent behind both programs. Both India and South Korea aim to reduce dependence on foreign suppliers for their most advanced fighter jets. Developing a domestic 5th generation aircraft fosters self-reliance in critical aerospace technologies and strengthens their respective military capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
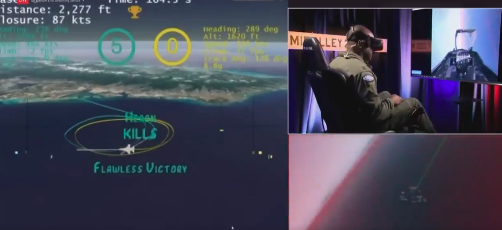
The veil has been lifted on a historic experiment by the U.S. Department of Defense’s Office of Advanced Research Projects (DARPA). For the first time ever, an AI-controlled fighter jet engaged in a simulated air battle against a human pilot.
The robotic aircraft involved in this groundbreaking exercise was the X-62A, a modified version of the F-16 fighter jet. Equipped with sophisticated artificial intelligence algorithms, the X-62A aimed to demonstrate the potential for autonomous aerial combat. Its opponent? A seasoned human pilot flying a standard F-16.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
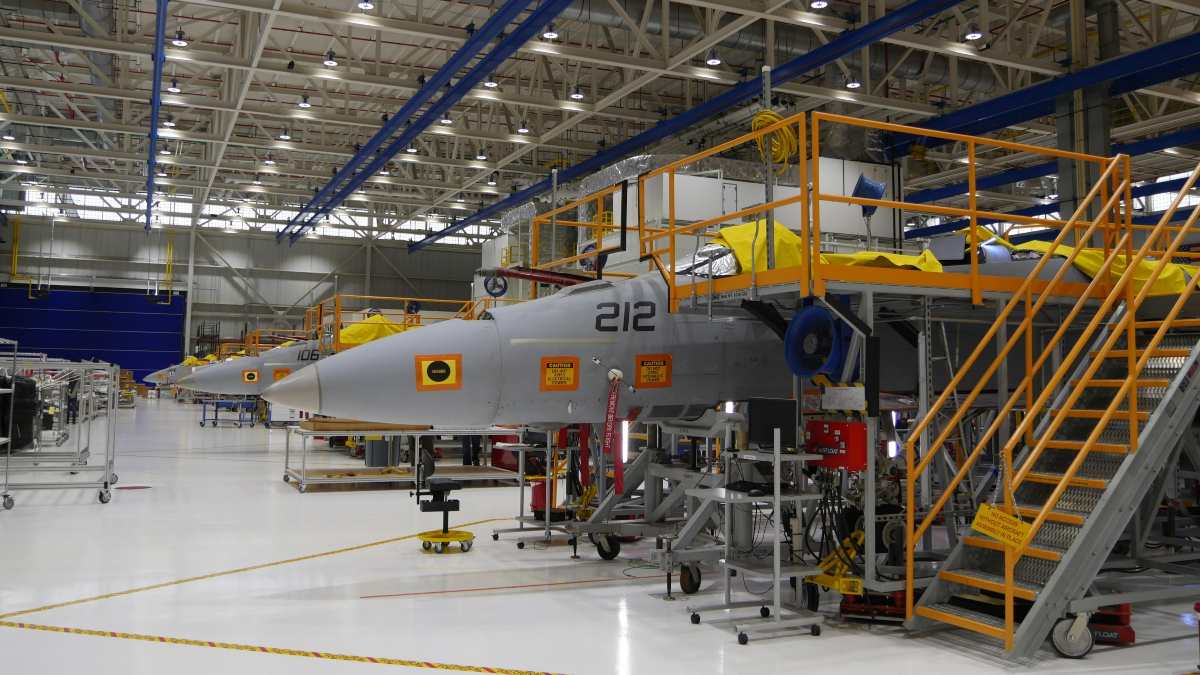

The U.S. Navy has secured a crucial contract modification with Boeing for the final 17 F/A-18E/F Super Hornets, marking a potential turning point for the iconic fighter jet’s production future.
This $1.1 billion contract, announced on March 19th, comes after stalled negotiations last year. The deal secures 10 F/A-18F Lot 46 aircraft and an additional seven from Lot 47, ensuring deliveries begin in late 2026 and conclude by spring 2027.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

China’s domestically-produced passenger aircraft, the C919, is making waves in the aviation industry. Built by the state-owned Commercial Aviation Corporation of China (COMAC), the C919 has garnered significant interest, with around 1,200 orders – primarily from domestic airlines. However, its global ambitions might face a hurdle in the form of the world’s fastest-growing aviation market: India.
According to leaked internal company documents, COMAC plans to actively promote the C919 in various Asian markets. This strategic move aims to capitalize on the region’s burgeoning aviation sector. The C919, a narrow-body jet designed to compete with the Airbus A320neo and Boeing 737 MAX families, offers airlines an alternative within the single-aisle aircraft category.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Last weekend’s massive Iranian missile and drone attack on Israel served as a real-world test of air defense capabilities. While Israel claims it successfully intercepted 99% of the incoming projectiles with its Iron Dome system, the event sparked discussions within India’s military about its own air defense readiness.
Indian military experts acknowledge the effectiveness of Israel’s Iron Dome, which has a range of approximately 70 kilometers. However, India is heavily invested in developing its own robust and indigenous air defense network.
Continue reading