Idrw Team
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

The Indian Army is turning heads with its latest addition to its arsenal: All-Terrain Vehicles (ATVs) equipped with Konkurs anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) systems. Images surfacing from the Indian Army Southern Command reveal Arctic Cat Alterra TBX 700 ATVs sporting these powerful missiles, showcasing a potent combination of mobility and firepower.
These nimble ATVs offer several advantages over traditional armored vehicles. Their lighter weight allows them to navigate rough terrain with ease, making them ideal for mountainous and remote regions. Additionally, their relatively low cost compared to tanks and other heavy vehicles provides the Army with a cost-effective way to enhance their firepower in strategic locations.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Air Chief Marshal RKS Bhadauria, former chief of the Indian Air Force, has delivered a resounding vote of confidence in the upgraded Tejas Mk1A fighter jet, declaring it superior in several aspects even to the formidable Mirage-2000 currently in service. This statement comes as the country grapples with the question of finding a suitable replacement for the ageing MiG-21 fleet.
While acknowledging the MiG-21’s Squadrons as the first recipient of the Tejas Mk1A, Bhadauria emphasized that the new aircraft’s capabilities far surpass its predecessor it is replacing. He stated that the Mk1A is not just a MiG-21 replacement, but a leap forward in terms of technology and firepower, leaving both the MiG-21 and, surprisingly, the Mirage-2000 in its dust.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Azista Aerospace, a leading provider of satellite and Satcom application products, has announced a strategic partnership with Forge for the DISC 8 Challenge. This challenge focuses on developing a lightweight, multiband Software Defined Radio (SDR) for ships, submarines, and aircraft, significantly enhancing communication capabilities across diverse platforms.
The proposed SATCOM solution aims to revolutionize communication capabilities for maritime and airborne platforms. The multiband functionality encompassing UHF, S, C, Ku, and Ka bands ensures seamless connectivity across various frequencies, enabling robust communication in diverse environments. The lightweight and compact design promises enhanced mobility and flexibility for deployment on ships, submarines, and aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
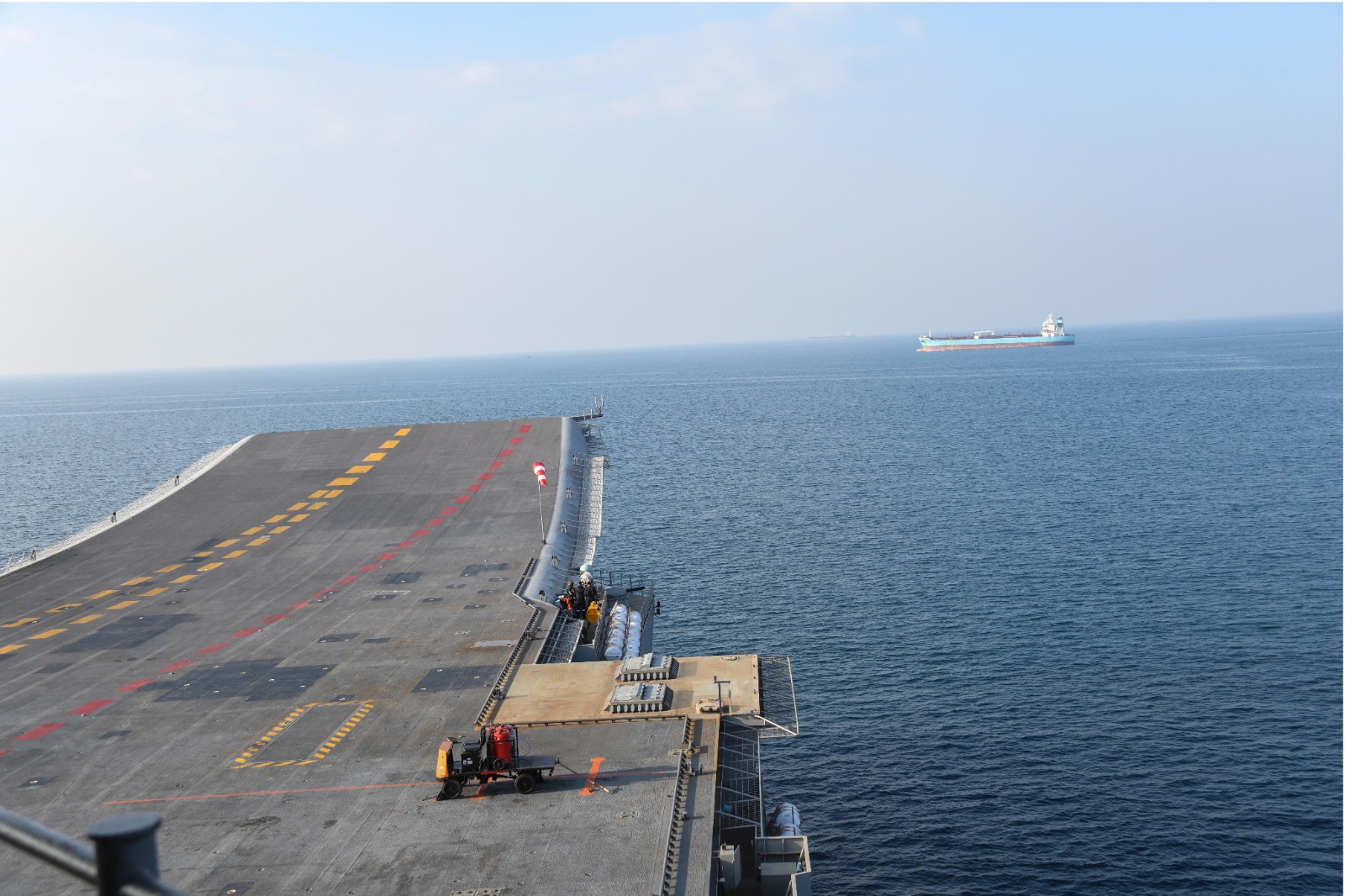

Get ready for a double dose of Indian naval power! India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier, INS Vikrant, is back in action after undergoing major upgrades. Now equipped with cutting-edge technology and weapons systems, it’s poised to join its predecessor, INS Vikramaditya, in safeguarding the nation’s maritime interests.
At the heart of Vikrant’s resurgence lies the EL/M-2248 MF-STAR, a multifunction active electronically scanned array (AESA) naval radar. This Israeli-made marvel provides unparalleled situational awareness, scanning vast stretches of the ocean for threats like enemy aircraft, missiles, helicopters, and drones.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

In a landmark move for both maritime security and India’s innovation ecosystem, Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), a leading Defence Public Sector Undertaking (DPSU), has signed the first procurement contract under the iDEX initiative with Blurgs Innovations Private Limited. This strategic partnership marks a significant step towards bolstering India’s maritime domain awareness with cutting-edge Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology.
Blurgs Innovations, an iDEX winner, has developed TRIDENT, an intelligent maritime domain awareness tool that promises to revolutionize the way we monitor and protect our vast coastlines. TRIDENT utilizes advanced AI algorithms to detect anomalies in real-time, providing crucial insights into suspicious activities and potential threats. This shift from traditional monitoring methods to anomaly-based detection offers several advantages:
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

The Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) has marked a significant milestone in its 2023 Year-End Review, confirming the successful deployment of the Medium-Range Surface-to-Air Missile (MRSAM) system. This air defense system, crucial for safeguarding India’s airspace, has been commissioned in five firing units and one training center of the Indian Air Force (IAF) throughout the year.
One of the most notable deployments of the MRSAM is near India’s northwestern borders with Pakistan. On October 9th, 2023, the IAF stationed the system at Air Force Station (AFS) Adampur in Jalandhar district, Punjab. This strategic placement strengthens India’s air defense capabilities in a sensitive region known for potential aerial threats.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

In a display of cutting-edge Indian technology, the President of India, Droupadi Murmu, witnessed the NRT Nimbus Tether Drone during the integrated Fire Power exercise conducted by the Indian Army at Pokhran on December 23rd. This tethered drone, developed by NewSpace Research and Technologies (NRT), stands as a testament to India’s growing prowess in the realm of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and its commitment to the Make In India and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives.
The NRT Nimbus Tether Drone, equipped with a best-in-class electro-optical (EO) and infrared (IR) sensor, stole the show with its ability to provide persistent surveillance in both plains and the extreme Super High Altitude Areas (SHAA) environment. This capability makes it a valuable asset for the Indian Army, enhancing its situational awareness and operational effectiveness in diverse terrains.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Recent developments in the military capabilities of Pakistan have raised eyebrows in the South Asian region, particularly with regard to its artillery rocket systems. Generous Chinese assistance has played a pivotal role in bolstering the Pakistani Army’s arsenal, leading to the successful testing of the Fatah I and Fatah 2 variants of the Chinese A100 and A300 rocket systems. These advancements have granted Pakistan a considerable edge, particularly in terms of range, when compared to India’s ongoing efforts to upgrade its artillery rocket systems.
The successful tests of the Fatah I and Fatah 2 variants mark a significant milestone for Pakistan, as these rocket systems boast ranges of 140km and 400km, respectively. The crucial element behind these advancements is the substantial support provided by China, which has enabled Pakistan to rapidly enhance its artillery rocket systems. The newfound capabilities position Pakistan ahead of India in terms of range, creating a strategic advantage for the Pakistani military.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
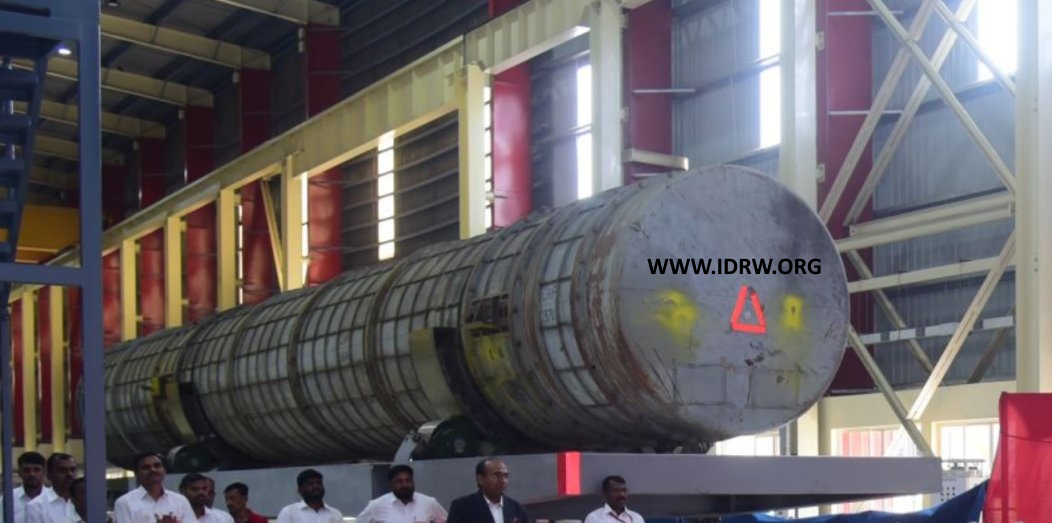

In recent days, the internet has been buzzing with discussions and claims surrounding a remarkable 70-ton Rotation Cum Resting Fixture (RCRF) canister, crafted by Electropneumatics and Hydraulics (I) Pvt. Ltd. The canister, constructed from high-strength steel and featuring an electro-mechanical high-precision leveling system, has become the subject of intense curiosity and speculation about its intended use.
While the authenticity and impressive nature of the canister are undeniable, divergent opinions have emerged within the Indian Open Source Nuclear Information Technology (OSNIT) community regarding its purpose. Some assert that the canister is specifically designed for the Agni-VI intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). In contrast, others challenge this assertion, pointing out that the Agni-V Mk2 missile, developed using composite materials, has successfully reduced its weight from 55 tons to 50 tons. This faction contends that the canister may be associated with the Agni-VI program, given its substantial size and capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Big Bang Boom Solutions (BBBS), a promising Chennai-based startup in the defense sector, has recently confirmed the successful completion of a testing campaign for its Kamikaze Drone. This accomplishment represents a significant milestone for BBBS, showcasing the company’s commitment to innovation and security. The Indian Army’s invaluable support during the testing phase has been acknowledged as instrumental in reaching this milestone.
BBBS has been on a mission to revolutionize defense technology through innovative solutions, and the successful testing of the Kamikaze Drone is a testament to the company’s dedication. The development and deployment of advanced drones align with the evolving needs of modern defense, offering new capabilities to address dynamic security challenges.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

In a testament to India’s growing prowess in the field of space technology, three innovative Indian space startups have secured a coveted spot on the list of “20 Emerging SpaceTech Startups to Watch in 2024.” The list, compiled by Austria-based StartUs Insights, an innovation intelligence company, recognizes promising ventures that are set to make significant contributions to the rapidly evolving space industry.
1. OrbitAID: Pioneering Orbital Fuel Stations
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
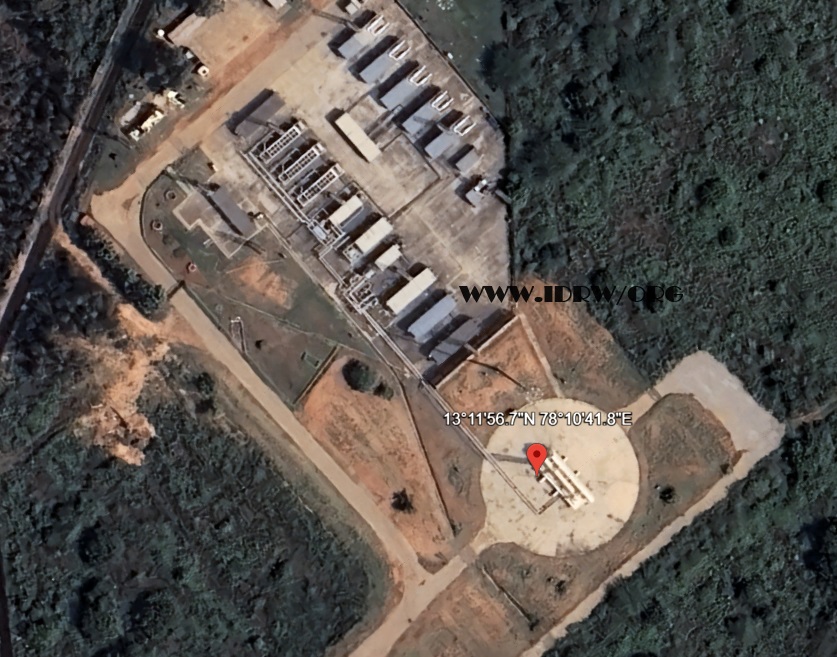
In a significant stride towards enhancing its national security, India’s Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) coverage is visibly expanding, with recent developments indicating an extension to major cities in the southern region. The expansion comes on the heels of the completion of Phase I, which saw the installation of a Long-Range Tracking Radar series in strategic locations, including Udaipur, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Rajasthan.
Satellite images have now confirmed a new site near Bangalore featuring the ELM-2090S Spectra, an Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) air defense radar. This development signifies a notable augmentation of India’s BMD coverage, originally intended for the Delhi-NCR Region and Mumbai. The extension of coverage to major cities in the south, such as Bangalore and Chennai, underscores the nation’s commitment to fortifying its defenses against potential ballistic missile threats.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Tesscorn Systems India Private Limited, a Bangalore-based innovator, is soaring into the future of Unmanned Air Vehicles (UAVs) with its biomimetic approach. By studying the highly optimized flight mechanisms of insects and birds, Tesscorn is unlocking the secrets of nature for next-generation UAV and Micro Air Vehicle (MAV) design.
At the heart of Tesscorn’s work lies Fluid-Structure Interaction (FSI) investigations. LaVision’s cutting-edge FSI system allows them to simultaneously analyze both the fluid flow around the wings and the wings’ structural deformation and strain. This powerful combination of synchronized Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) and Digital Image Correlation (DIC) measurements provides invaluable insights into the complex interplay between wing movement and airflow.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

India’s state-owned Mazagon Dockyard Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) is optimistic about securing a contract for three additional Scorpène submarines for the Indian Navy by the end of 2024. This follows their recent submission of a commercial offer on December 11th. As per information obtained by idrw.org, the first submarine delivery is anticipated from 2031 onwards.
These three follow-on Scorpènes will be advanced versions of the six submarines already in production. They will incorporate the indigenously developed Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) system by DRDO, replacing several outdated subsystems with newer technologies.’
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM
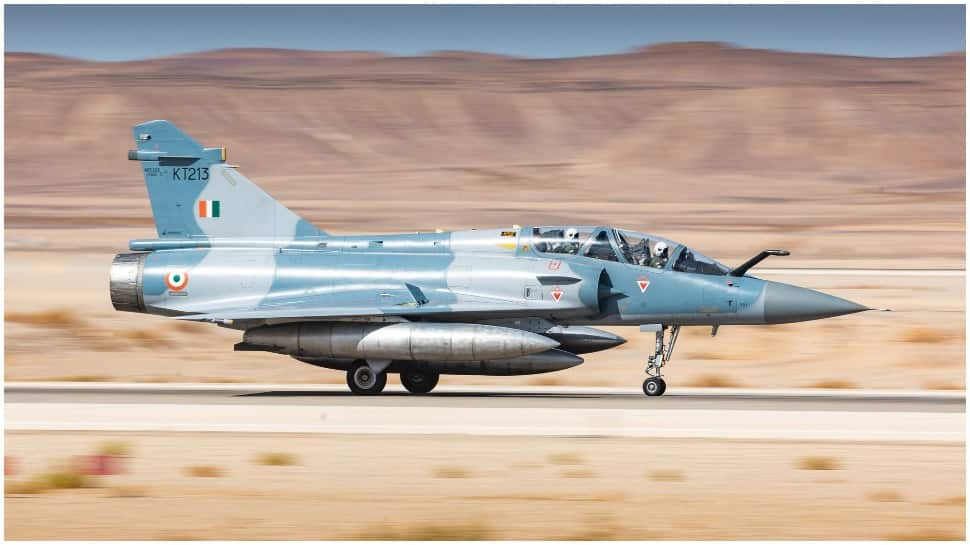

Indian Air Force (IAF) has set its sights on procuring additional Mirage 2000 aircraft, specifically the Twin-Seater variant. This decision comes in the wake of a recent accident that resulted in the loss of one Mirage 2000 aircraft, prompting the need for replacements. The IAF’s commitment to maintaining and enhancing its operational strength is evident in this pursuit of additional Mirage 2000s.
The Mirage 2000 has been a mainstay of the IAF for over three decades, forming the backbone of three squadrons stationed at the Gwalior airbase. These versatile multirole fighters have played a crucial role in various conflicts, including the Kargil War and the Balakot airstrikes. Currently, India operates around 50 Mirage 2000s, with plans to keep them operational until at least 2035.
Continue reading