SOURCE: IDRW.ORG

In a significant stride towards self-reliance in defence technology, Dr. Samir V. Kamat, Secretary of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), announced the development of indigenous fuel for the ramjet engine of the BrahMos missile and scramjet propulsion systems. This advancement is set to play a crucial role in reducing India’s dependence on foreign sources for critical defence technologies.
The development of indigenous fuel for ramjet and scramjet engines marks a pivotal moment for India’s defence capabilities. Ramjet engines, which power the supersonic BrahMos missile, rely on air-breathing propulsion technology, making them highly efficient at high speeds. Scramjet engines, a variant of ramjets, are designed for hypersonic speeds and are key to next-generation missile systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
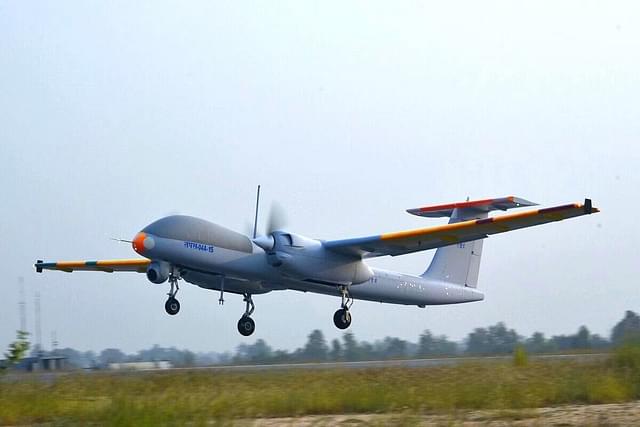

The Indian-developed Tapas drone program has reached a turning point, with the Indian Navy recently placing an order for four TAPAS-BH-201 drones. This development comes amidst a backdrop of both progress and setbacks for the project.
Drawing inspiration from the American MQ-9 Reaper, DRDO initiated the Tapas program in 2010. The drone’s maiden flight occurred in 2016. With a length of 31 feet, a wingspan of 67 feet, and a weight of 1,800 kg, the Tapas boasts a payload capacity of 350 kg and an impressive endurance exceeding 24 hours.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

A common misconception suggests China’s DF-21D missiles pose an immediate threat to Indian aircraft carriers in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). This article dismantles this myth by examining the challenges China would face in such a scenario.
Targeting a moving aircraft carrier requires real-time data. While China has satellites, their data transmission isn’t instantaneous. Even with the fastest processing times, there’s a gap between data acquisition and relaying it to launch platforms. Additionally, satellite data itself has inherent errors in tracking targets and their own positions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

A new report by the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), a leading arms control think tank, has challenged a long-held assumption about India’s nuclear arsenal. The report suggests that India may have begun a practice known as “mating” – storing nuclear warheads with their delivery systems (missiles or bombers) during peacetime.
Mating nuclear warheads with delivery systems significantly reduces the warning time before a potential nuclear launch. This can heighten tensions and increase the risk of accidental or unauthorized use of nuclear weapons. Traditionally, both India and China were believed to keep their warheads separate from launchers during peacetime, providing some buffer in case of a crisis.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
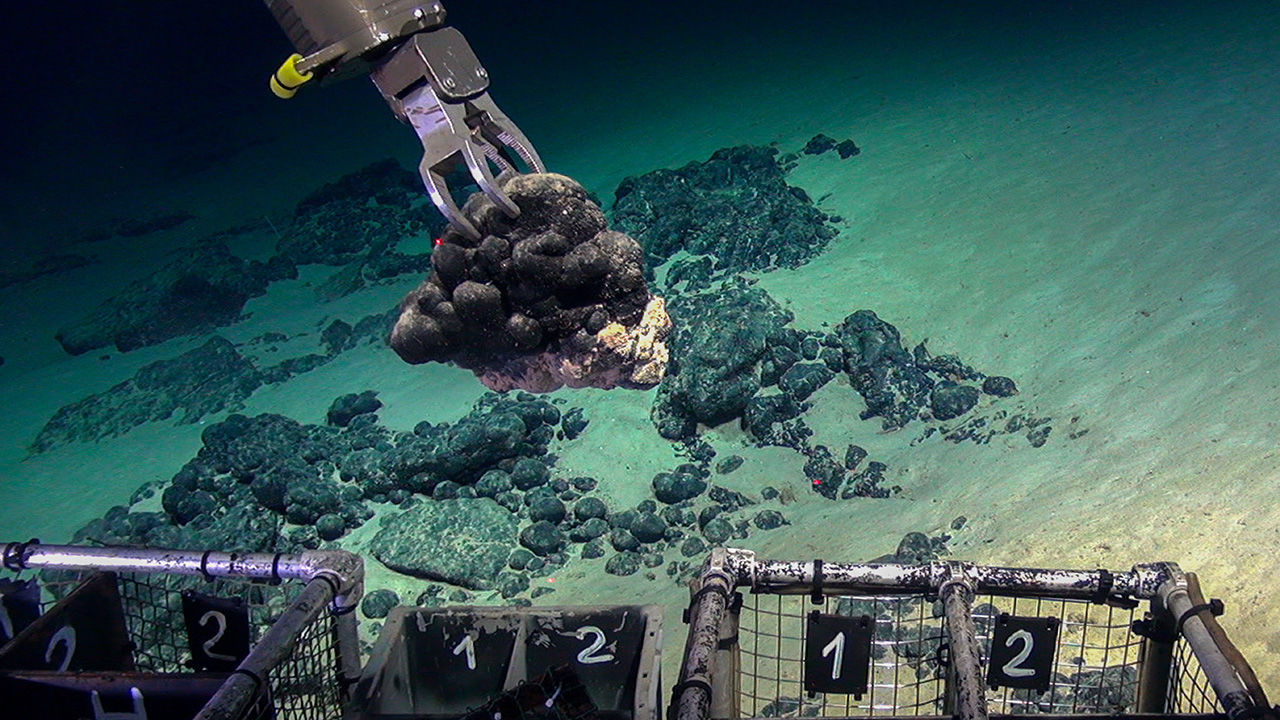

India’s quest to explore a cobalt-rich underwater mountain in the Indian Ocean has encountered a hurdle. The Afanasy Nikitin Seamount, located east of the Maldives and central to the Indian Ocean, is believed to hold significant reserves of cobalt, a vital mineral for electric vehicles and batteries.
In January, India approached the International Seabed Authority (ISA) in Jamaica, seeking approval to explore the region. Established in 1994, the ISA, under the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, regulates economic activities on the seabed beyond national jurisdictions.
SOURCE: AFI

India’s visa issuance to Chinese nationals has witnessed a dramatic drop since the 2020 Galwan border conflict. This policy shift, driven by national economic security concerns, comes amid ongoing trade imbalances.
Prior to the Galwan clash and the pandemic, India granted roughly 200,000 visas to Chinese nationals in 2019. However, a reevaluation of Chinese investments in India led to a drastic decrease, with only 2,000 visas issued in 2024. Over the past eight months, the number has slightly inched up to 1,500, primarily catering to the electronics industry’s needs.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
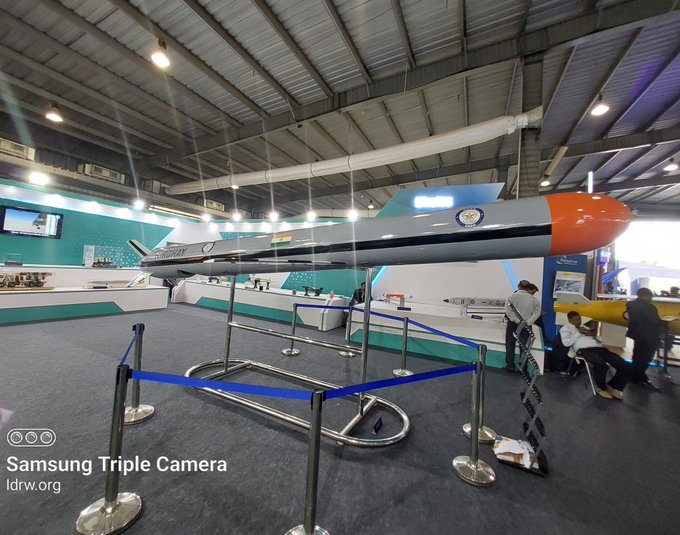

The Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) Advanced Defence Establishment (ADE) is on a roll. Following the successful development of the land-based Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missile (LRLACM) and its predecessor, the ITCM, ADE is now setting its sights on a naval variant.
The next chapter in the LRLACM story is the development of a ship-launched version. This sea-based missile will be integrated with a frontline warship to undergo further developmental trials. Fortunately, DRDO has already developed the Universal Vertical Launch Module (UVLM) cells required for the LRLACM program, paving the way for seamless integration.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
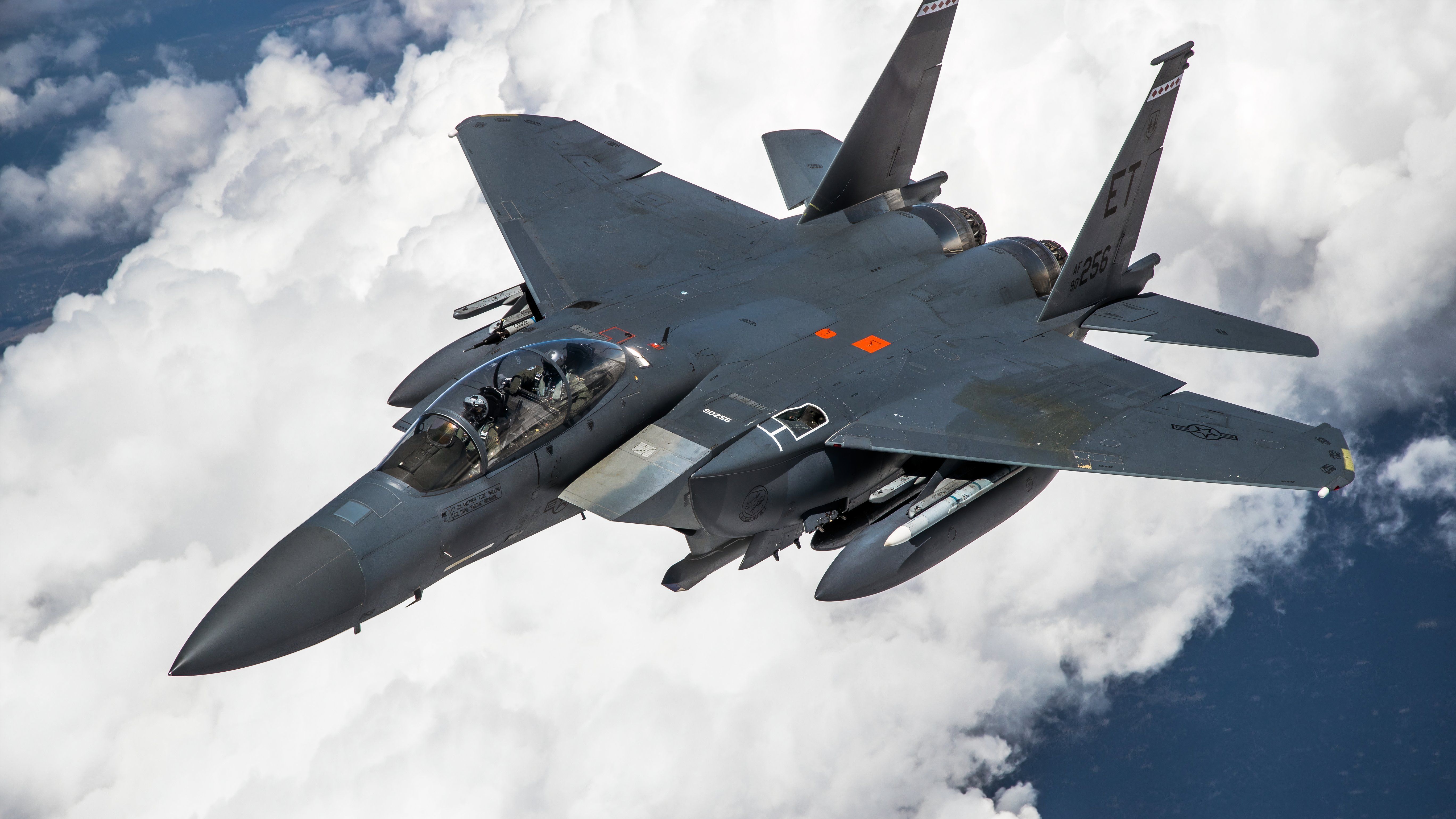

In its ambitious bid to modernize and expand its aerial combat capabilities, the Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to acquire 114 multi-role combat aircraft (MRCA) from the global market. Among the contenders, The Boeing Company’s F-15EX Eagle-II stands out as a highly capable and advanced option. This aircraft offers cutting-edge technology and exceptional performance metrics, making it a strong candidate for the IAF’s MRCA program.
Boeing’s confidence in the F-15EX making the final cut stems from significant improvements and its impressive capabilities compared to previous offerings. During the last MRCA selection process, Boeing had proposed the F-18 E/F fighter jets, which did not progress past the technical evaluation rounds. However, with the F-15EX, Boeing is optimistic about a different outcome.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

On March 27, 2019, India surprised the world with the announcement of Mission Shakti, a successful anti-satellite (ASAT) missile test. Prime Minister Narendra Modi revealed that a ballistic missile interceptor, the Prithvi Defence Vehicle Mark-II (PDV MK-II), developed by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), destroyed an Indian Microsat-R satellite in low Earth orbit.
Mission Shakti wasn’t impulsive. The targeted satellite, launched weeks prior at a deliberately low altitude, hinted at a controlled debris creation strategy. The small size of the satellite and the intercept method (hit-to-kill) further supported this intention.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
Bengaluru-based Si2 Microsystems Private Limited is facing sanctions from Japan over accusations of supplying advanced technology to Russia’s defense sector. The Japanese government alleges that Si2 Microsystems provided sensitive semiconductors and systems specifically designed for military electronics applications.
Si2 Microsystems reportedly specializes in miniaturization techniques using a three-dimensional system-in-package (SiP) approach. This technology is believed to have aided the Indian defense industry in achieving self-sufficiency in manufacturing electronic subsystems and systems critical for missiles, radars, and other weapon platforms.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

India’s space agency, ISRO, is all set for the third and final developmental flight of its Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV), designated SSLV-D3. The launch is scheduled for NET (Not Earlier Than) July 10th, 2024, marking a significant milestone towards making SSLV fully operational.
SSLV is a cost-effective launch vehicle specifically designed for mini, micro, and nano satellites. Built for industry production, it caters to the growing demand for a launch-on-demand platform for these smaller satellites. The vehicle boasts a unique three-stage configuration. The first three stages utilize solid propulsion, while the terminal stage employs a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module (VTM) for precise orbital insertion.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Russia and India are poised for closer military cooperation following Moscow’s approval of a draft agreement outlining procedures for the mutual deployment of troops, warships, and aircraft. This development signifies a significant step towards bolstering Eurasian security, according to analysts.
The agreement is expected to expedite logistical processes for joint military exercises between the two nations. This could include smoother troop movements, quicker clearances for military hardware, and simplified administrative procedures, leading to more efficient and effective joint operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

In a significant leap forward for drone defense technology, RattanIndia Enterprises’ step-down subsidiary, Throttle Aerospace Systems, has announced the commencement of trials for its indigenously developed anti-drone platform, The Defender. This state-of-the-art system leverages vision-based techniques and powerful artificial intelligence to actively track and neutralize rogue drones, marking a crucial advancement in safeguarding against aerial threats.
The Defender is specifically designed to address the increasing threats posed by unauthorized drones. Utilizing non-lethal methods, it captures rogue drones using a net, ensuring minimal collateral damage. The platform is augmented by advanced AI capabilities, which enhance its efficiency and precision in tracking and neutralizing targets.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The P17 Alpha Project, involving the construction of three advanced warships for the Indian Navy, has progressed significantly. All three vessels have been successfully launched, and construction is underway at a steady pace as per Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers Ltd (GRSE).
While all three ships have already been launched, construction continues at a steady pace. The first ship boasts an impressive 70% physical progress, while the second and third ships are at 60% and 47% completion, respectively.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
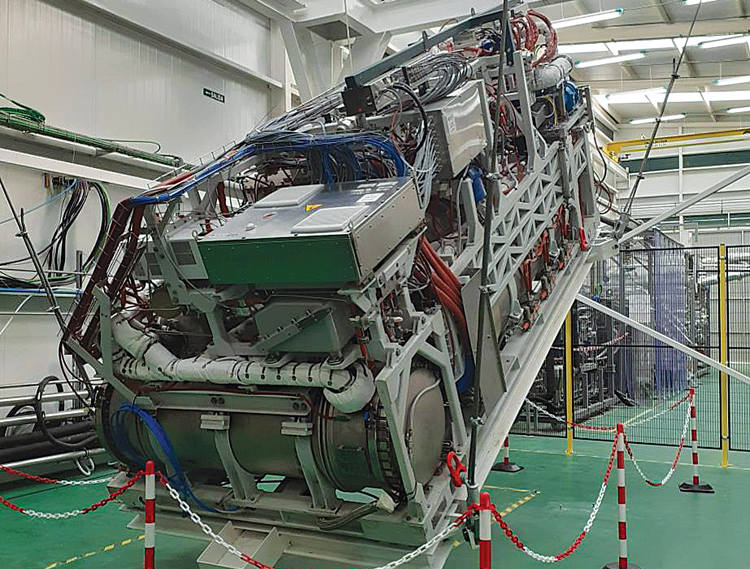

The Indian Navy is gearing up for crucial trials in Spain to evaluate critical equipment for its Project 75 India, aimed at acquiring six advanced submarines. This news comes courtesy of Spanish shipyard Navantia, a key partner in the project.
The focus of these trials lies on Navantia’s innovative Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) system, a technology that significantly enhances underwater endurance for submarines. Notably, Navantia successfully completed land-based trials of the system in 2023, simulating demanding real-world conditions.
Continue reading