SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
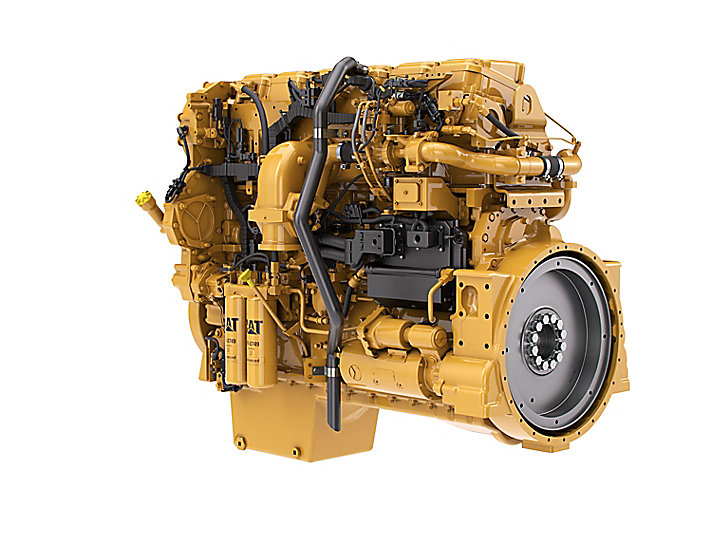
The joint development and production of the latest Stryker armoured infantry combat vehicles between India and the US face a hurdle: engine incompatibility. While both nations expressed interest in the project, India’s demanding terrain necessitates a more powerful engine than the current offering.
The Indian Army requires an engine capable of handling the harsh conditions of its borders, particularly the high altitudes of Ladakh and Sikkim. Caterpillar’s C7 engine, used in current Stryker models, falls short with its 300 horsepower output.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Oliver Burkhard, CEO of ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS), has proposed an intriguing prospect for India’s shipbuilding industry. If TKMS is chosen for the Indian Navy’s Project-75I tender, Burkhard envisions India becoming a hub for TKMS submarines in the Asia-Pacific region.
TKMS has joined forces with Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd (MDL) to submit a bid for Project-75I. This collaborative effort focuses on building six advanced submarines for the Indian Navy, with an estimated cost exceeding Rs 45,000 crore.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
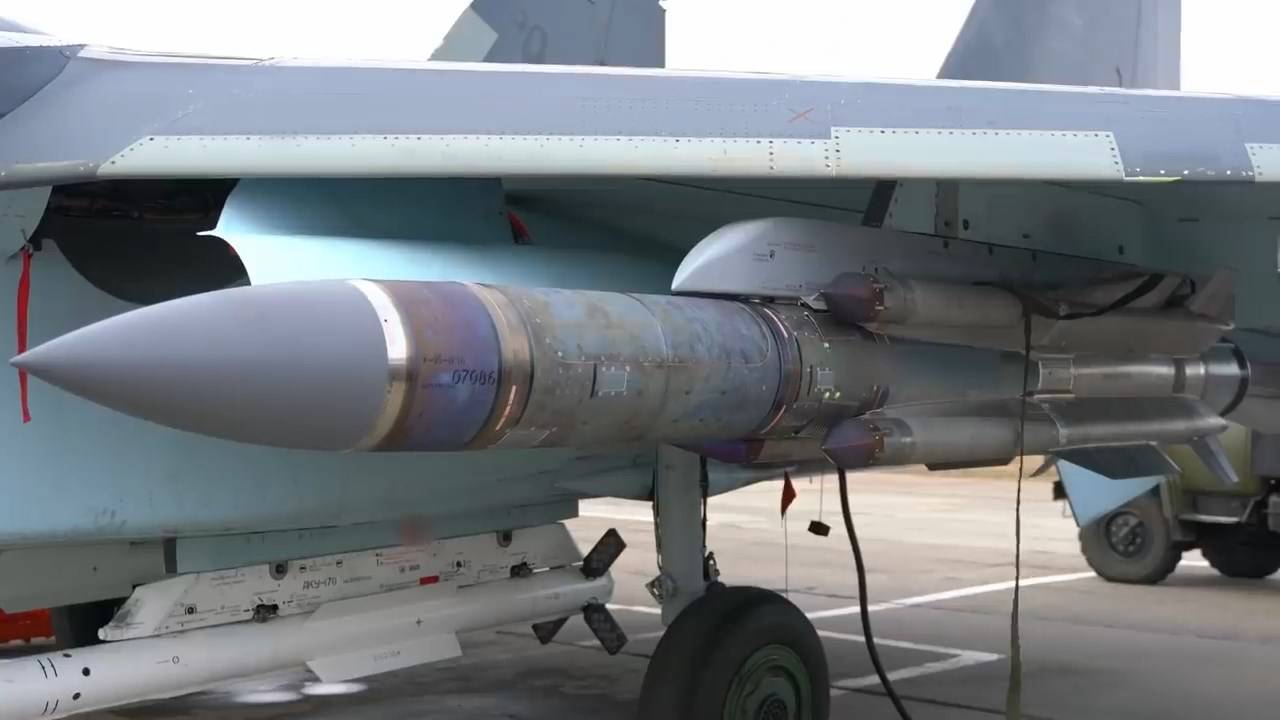

The Indian Air Force, operating under the Ministry of Defence, has issued a call for Expressions of Interest (EoI) from Indian firms for the repair, refurbishment, and life extension checks of X-31P air-launched missiles. This initiative falls under the category of ‘Missiles with Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) Support’ and aims to involve Indian firms through joint ventures (JV) or memoranda of understanding (MoU) with the OEM of the missile. The following paragraphs detail the proposal and its scope.
The primary objective of this initiative is the comprehensive repair, refurbishment, and life extension of life-expired X-31P missiles currently held in various categories. The life extension process will encompass all aspects assigned by the OEM, including but not limited to.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
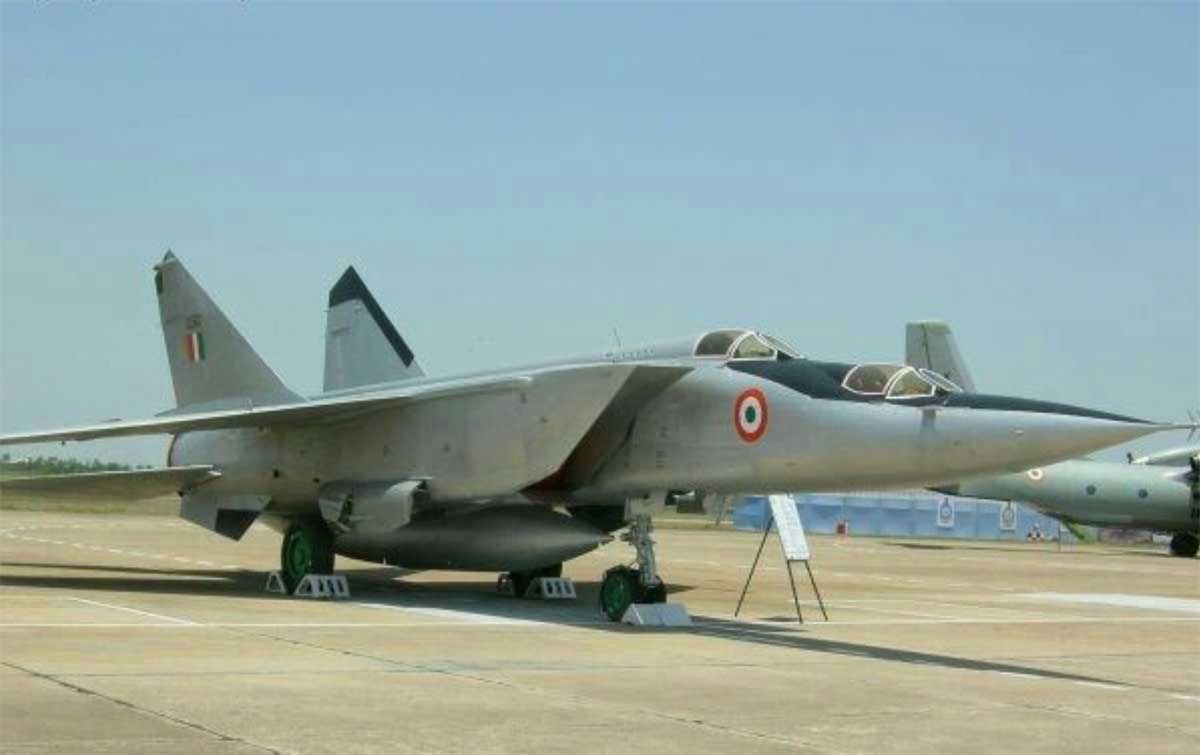

In May 1997, tensions soared in South Asia as an Indian Air Force (IAF) MiG-25 streaked across Pakistani airspace. The telltale boom of breaking the sound barrier shattered the calm, sending shockwaves through Islamabad and scrambling Pakistani defenses. But their efforts were in vain. The MiG-25, nicknamed “Foxbat” by NATO, was simply too fast and too high.
This wasn’t a random act. The MiG-25, a product of the Cold War era, was a technological marvel. Capable of reaching speeds of Mach 2.5 and soaring over 70,000 feet, it flew comfortably beyond the reach of any Pakistani interceptor at the time. This operational advantage made it the perfect platform for covert reconnaissance missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

India and China, both major Asian powers, have a long history of acquiring military equipment from Russia. However, their approaches to the Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighter jet program differed significantly. While China opted to reverse-engineer the Su-30MKK (a less advanced variant) and develop its own indigenous versions, India pursued a different path.
India’s Su-30MKI program involved a complex technology transfer agreement with Russia. This agreement allowed India to progressively manufacture the Su-30MKI domestically, with increasing levels of indigenous content over time. The goal was not just to assemble the aircraft but to gain the knowledge and expertise to potentially design and develop future generations of fighter jets.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The war in Ukraine has seen a rise in the use of small, agile drones, particularly First-Person View (FPV) drones, for reconnaissance and even attacks. While sophisticated air defense systems are ideal, recent media reports suggest a surprisingly effective countermeasure: the humble pump-action shotgun. This article explores why these shotguns are proving surprisingly useful against drones.
FPV drones, often commercially available and easily modified, pose a growing threat to soldiers on the ground. Their small size and maneuverability make them difficult to detect and shoot down with traditional weaponry.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Air Force (IAF) took a pivotal step towards bolstering its combat capabilities with the inauguration of the Weapon System School (WSS) today at Begumpet. The ceremony was officiated by Air Chief Marshal VR Chaudhari, Chief of the Air Staff (CAS).
This significant development follows the IAF’s 2022 decision to establish a dedicated Weapon System Branch (WSB). The WSS serves as a vital training ground for officers entrusted with operating ground-based and specialist weapon systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India’s defence exports have reached a historic milestone, clocking in at a record Rs 21,083 crore in the financial year 2023-24. This marks a significant achievement and highlights the growing capabilities of the Indian defence industry.
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has set a new target for the future – exporting over Rs 50,000 crore worth of defence equipment by 2028-2029. This ambitious goal reflects the government’s commitment to fostering a robust domestic defence industry and positioning India as a major player in the global arms market.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian Navy is gearing up to bolster its amphibious capabilities with a fleet of Landing Platform Docks (LPDs) built indigenously. This follows a Request for Information (RFI) issued in 2021. Two Indian shipyards, Cochin Shipyards Ltd (CSL) and Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers Ltd (GRSE), have thrown their hats in the ring with their own designs. Additionally, L&T Shipbuilding and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) have proposed designs based on collaborations with international OEMs (Original Equipment Manufacturers).
The LPDs envisioned by the Navy will boast an impressive capacity. Each vessel is expected to accommodate a crew of 540 sailors and carry up to 900 troops. These behemoths will measure approximately 200 meters in length and displace up to 8 meters of water when fully loaded. In terms of speed, a cruising speed of 14 to 16 knots is desired, with a remarkable range of 10,000 nautical miles at economical speed for extended deployments.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
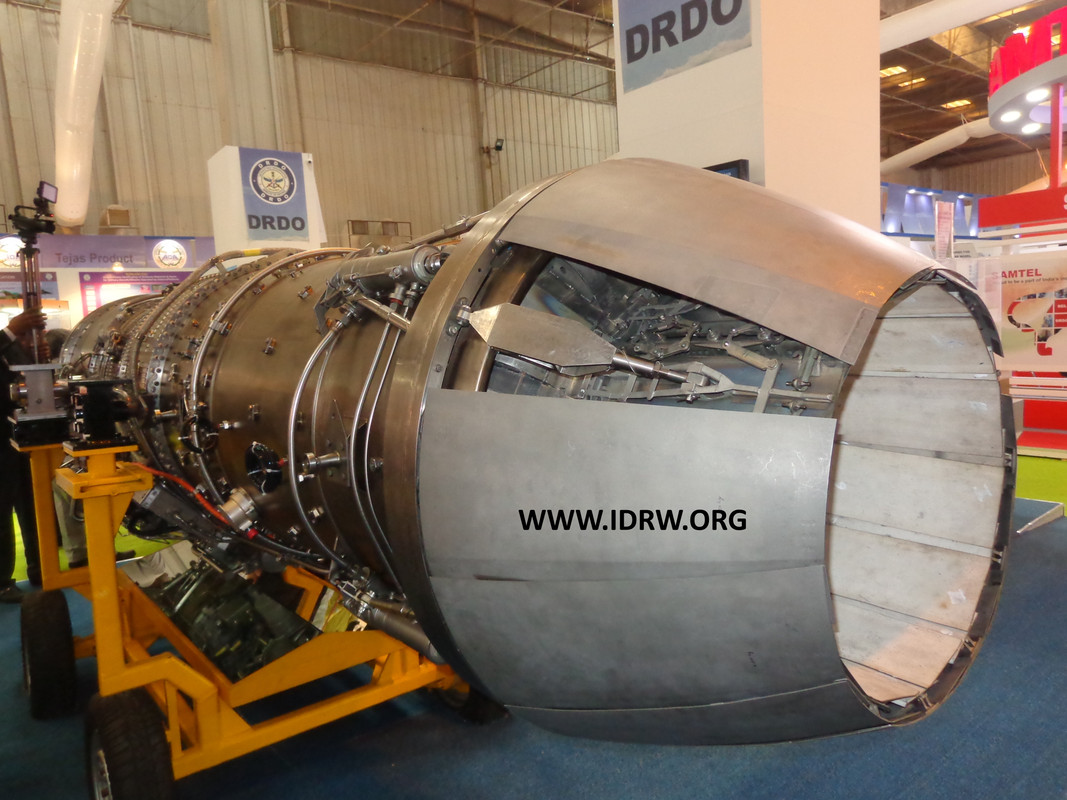

Report going around claiming the French company Safran has cleared the Kaveri engine for integration with the LCA Tejas fighter jet are misleading. This information actually dates back to 2018, not a recent development.
For clarification, DRDO in its 2017 annual report provided details of the significant progress made with the Kaveri engine that year. Five prototypes underwent a total of 145 hours of testing, including successful completion of critical tests and the first-ever transient test simulating idle to max reheat conditions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Navy has taken a giant leap towards self-reliance in munitions with the successful certification of a new, domestically developed explosive. Manufactured by Solar Industries, SEBEX-2 promises to revolutionize the Navy’s arsenal with its superior power.
SEBEX-2 boasts a blast effect exceeding any currently used solid explosive. This innovative formulation packs a punch – it’s reported to be 2.01 times more powerful than a standard TNT explosion! The destructive potential of explosives is measured in TNT equivalence, with higher numbers signifying greater impact. SEBEX-2’s impressive 2.01 rating positions it as a true force multiplier.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

A somber reminder of the inherent dangers faced by Indian soldiers emerged in Eastern Ladakh, where a T-72 tank remains stuck in the strong currents of the Shyok River near Saser Brangsa. This incident underscores the constant risks associated with river crossings undertaken by troops using tanks and BMPs (Infantry Fighting Vehicles) across numerous rivers and streams in the region.
Five Indian Army soldiers lost their lives in June 2024 when their T-72 tank met with an accident during a river-crossing exercise near the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in the Leh district. This heartbreaking incident serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of such maneuvers.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
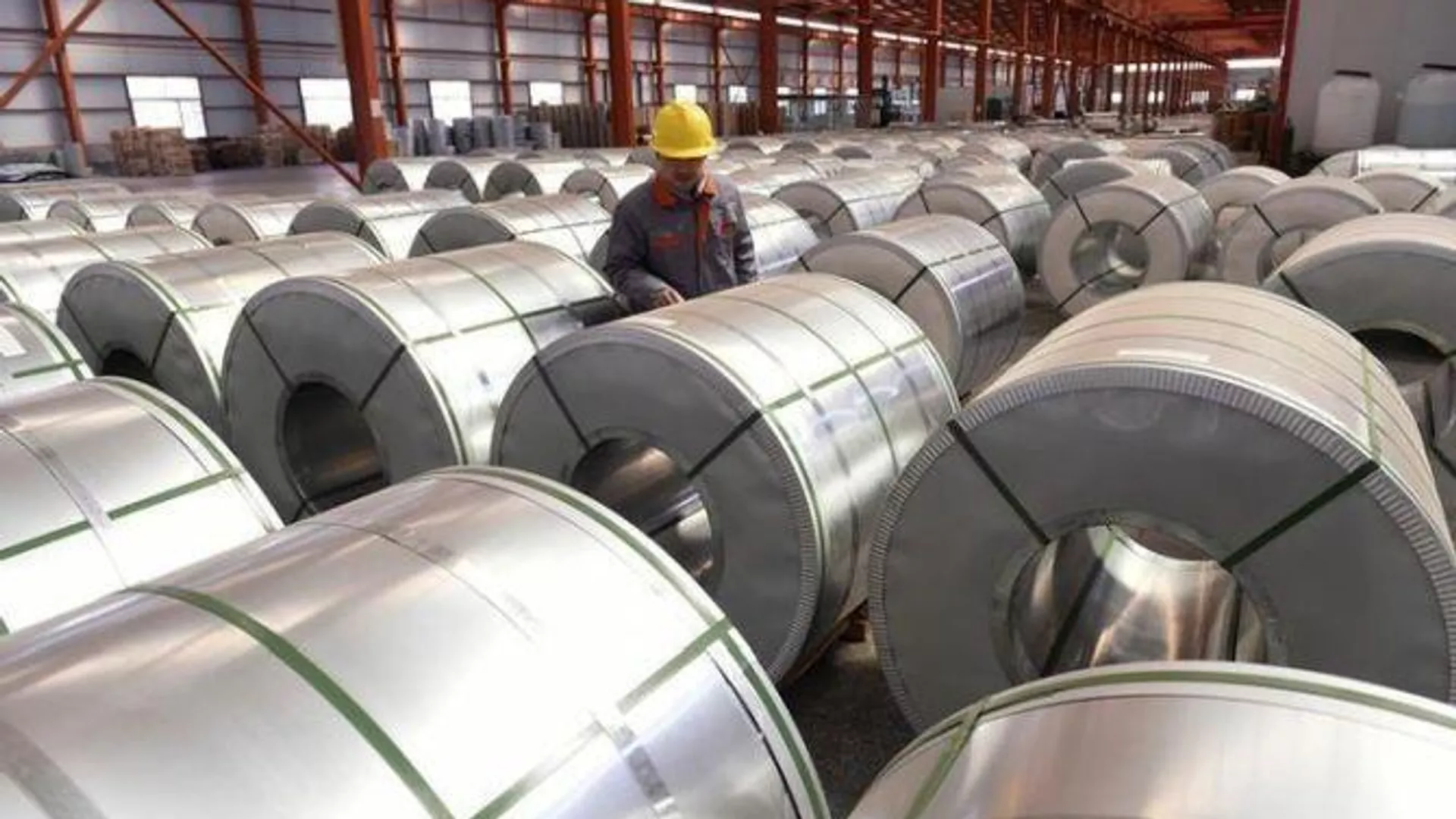

In a surprising turn of events, India has emerged as an aluminum supplier to Russia, the world’s second-largest aluminum exporter. This development, reported by Sputnik based on Indian customs data, marks a first for recent times.
According to the analysis, India exported 44,800 tons of unprocessed aluminum to Russian companies in April 2024, valued at $16.5 million. This shipment is particularly noteworthy given Russia’s well-established position as a major aluminum exporter, with exports valued at $6.5 billion in 2023.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is setting its sights on self-reliance in underwater warfare with Project-76, an ambitious initiative to design and develop a new generation of indigenous conventional submarines for the Indian Navy.
Project-76 will be a collaborative effort between DRDO and the Warship Design Bureau (WDB) of the Indian Navy. The WDB’s expertise in naval design will be crucial in shaping the submarine’s form and function.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
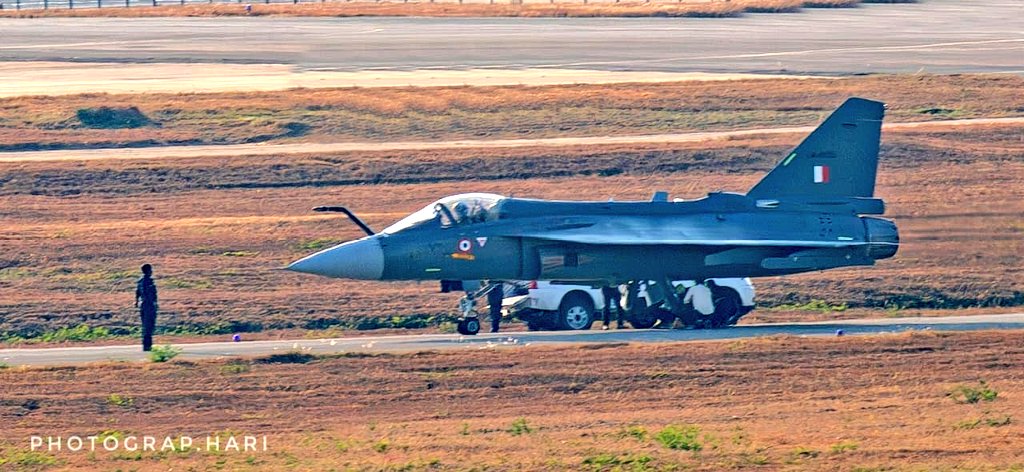

The Indian aviation industry witnessed a significant milestone on March 28th, 2024, with the successful maiden flight of the first Tejas Mk1A fighter jet. This marks a crucial step towards bolstering the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) capabilities.
Following its successful maiden flight, the Tejas Mk1A had to undergo a series of mandatory trials. These tests were crucial in ensuring the aircraft meets all operational requirements and performs flawlessly under various conditions and also validates many of the newer technologies in the jet.
Continue reading