SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Dr Samir V Kamat, the chairman of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has announced that the Air-independent propulsion (AIP) system will be integrated into the Indian Navy’s Scorpène submarine by 2026. This significant upgrade will substantially enhance the submerged endurance of the diesel-electric submarine, bolstering its capabilities.
The AIP system will be inserted into the Scorpène submarine through a process involving cutting and welding. This innovative approach will enable the submarine to remain submerged for extended periods, significantly improving its operational effectiveness. As Dr Kamat emphasized, the success of a submarine lies in its ability to remain undetected. By staying submerged for longer durations, the AIP-equipped Scorpène will gain a tactical advantage, enhancing the Indian Navy’s capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
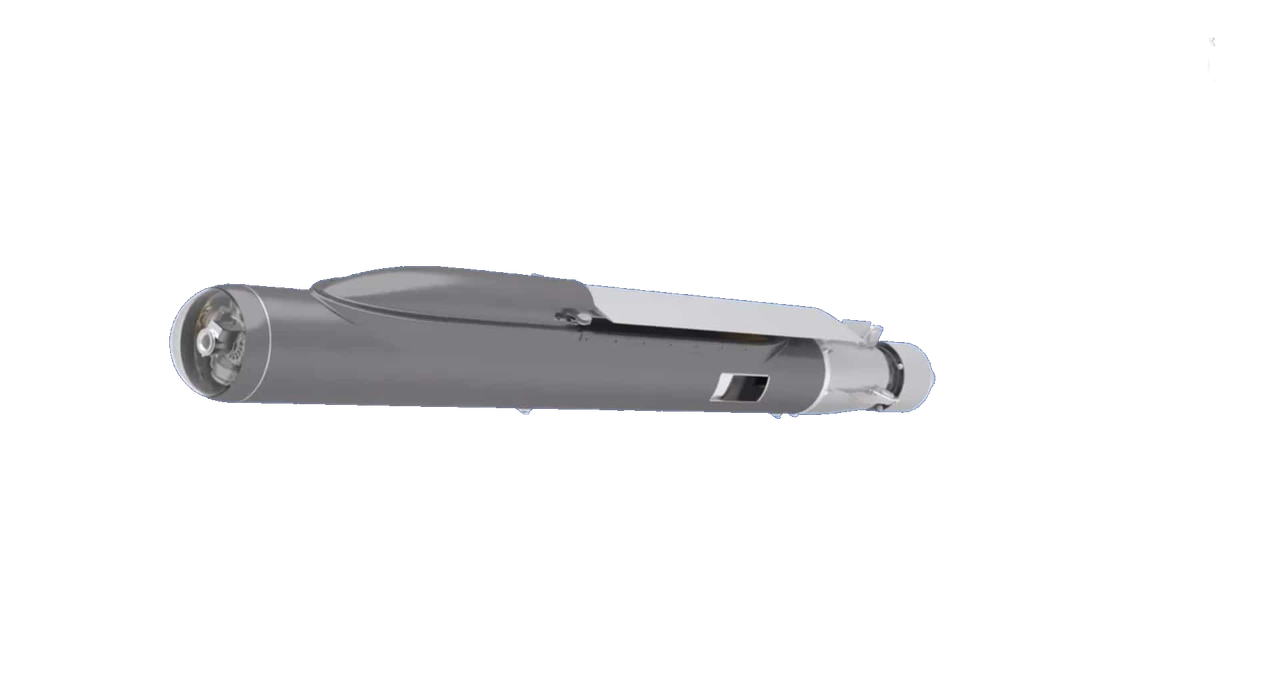

In a significant development for India’s defence capabilities, a private sector firm is now pioneering the development of turbojet-powered loitering munitions designed for the Indian Army and Navy.
These advanced munitions are set to revolutionize long-range target neutralization with their ability to strike from distances ranging from 25 km to 100 km. These loitering munitions can be launched from unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), providing flexibility and adaptability in various combat scenarios, With a range of 25km to 100km, these munitions can engage targets deep within enemy territory.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
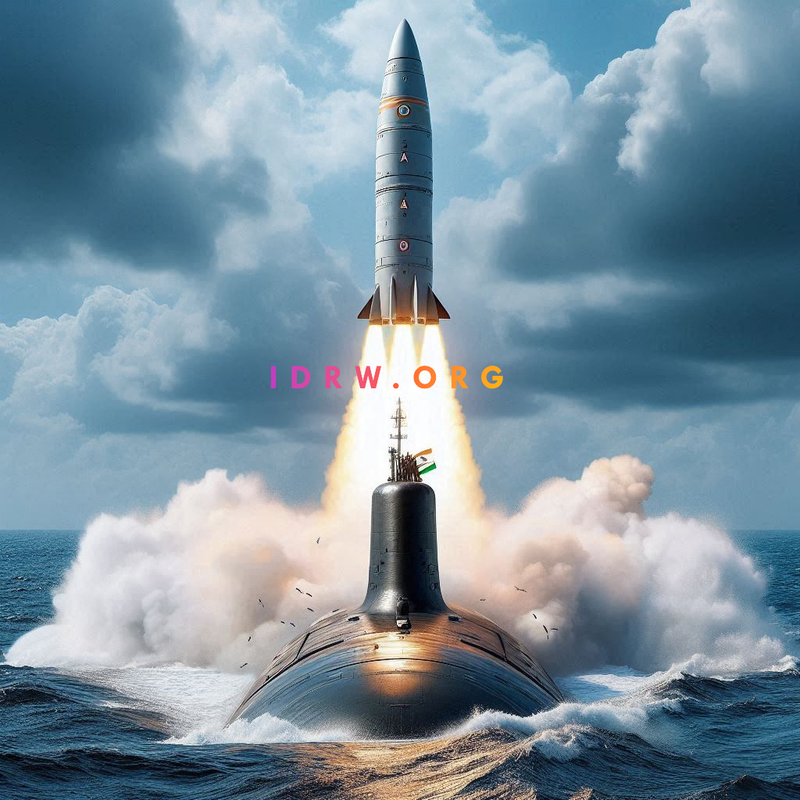

India’s nuclear deterrent has taken a significant step forward with the induction of the K-4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) onto the INS Arighat, the nation’s second nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN). While the K-4 boasts a range of 3,500 kilometers, all eyes are now on the upcoming K-5, touted as the “Big Daddy” of Indian SLBMs.
Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the K-5 is a three-stage solid-propellant SLBM with an estimated range of 5,000-6,000 kilometers. This extended range, combined with a payload capacity of two tonnes, would theoretically enable the K-5 to strike targets as far as 8,000-9,000 kilometers with lesser payload. This capability would bring major cities like Beijing within reach, even while operating in the Indian Ocean region.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
An Indian Air Force (IAF) helicopter, which made a precautionary landing in Ladakh in April 2024, is being retrieved after a months-long operation. The Boeing Apache helicopter, which landed north of the Khardung La pass, has been dismantled and is being transported by road to Leh.
The rescue mission posed significant challenges due to the high altitude of the landing site, which is around 12,000 feet. Airlifting the helicopter was not feasible due to the altitude and weight constraints of the IAF’s Chinook helicopters.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Air Force (IAF) has been a cornerstone of India’s defense strategy, but the absence of dedicated strategic bombers in its fleet has been a notable limitation. This deficiency has restricted the IAF’s ability to strike deep into enemy territory and conduct sustained long-range operations. However, there is a compelling opportunity to address this gap by utilizing existing assets: the C-17 Globemaster III transport aircraft and the indigenously developed Nirbhay Air-Launched Cruise Missile (ALCM).
The C-17 is a versatile aircraft capable of transporting troops, equipment, and vehicles over long distances. Its large cargo bay and long range make it an ideal platform for carrying and launching cruise missiles. By integrating Nirbhay into the C-17’s capabilities, the IAF could effectively transform its transport fleet into a strategic strike force.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Nibe Space Private Limited, a subsidiary of Nibe Limited, has announced a strategic partnership with leading infrastructure, defense companies, and startups in India. The collaboration aims to establish a private Earth observation constellation and a corresponding ground segment to offer a comprehensive range of space-based services.
Through this consortium, Nibe Space will leverage the expertise and resources of its partners to supply equipment, services, skills, systems, and support services necessary for building and operating the constellation. The company plans to lease the constellation to various customers and provide images and analytics as a service.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

India’s naval deterrence is set for a significant upgrade with the upcoming S5 class of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs). These underwater behemoths, boasting a submerged displacement of a staggering 13,000 tons, will be powered by a revolutionary new reactor – the 190 MW Pressurized Light Water Nuclear Reactor (PWR) – developed indigenously by the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC).
This marks a substantial leap from the 83 MW reactors currently powering the Arihant-class SSBNs. The new design, according to sources at idrw.org, is complete and awaits funding clearance before construction of a land-based prototype can begin.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG TEAM

Dassault Aviation, the renowned French aerospace company, has announced a resumption of new contract signings following a reorganization of its production and supply chain. One of the major orders expected to materialize soon is from India, which plans to ink a deal for 26 Rafale M carrier-based fighters worth approximately Rs 50,000 crore.
The Indian Navy will become the second operator of the Rafale M, joining the French Navy as the proud owner of this advanced fighter aircraft. Given the limited number of aircraft carriers in the world, India is likely to remain the second-largest operator of the Rafale M.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The India-U.S. bilateral Army exercise Yudh Abhyas has commenced at the Mahajan field firing ranges in Rajasthan on September 9, 2024. This year’s exercise is set to feature a wide range of military activities, including live-fire drills and training exercises.
The U.S. Army is participating in the exercise with a contingent that includes Stryker infantry vehicles and the M142 HIMARS (High Mobility Artillery Rocket System). The deployment of HIMARS in India marks a significant development, as the U.S. is keen to sell this advanced weapon system to the Indian Army.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Pakistan Air Force (PAF) has been tasked with developing software for the TFX Kaan, a joint venture fifth-generation fighter jet program between Pakistan and Turkey. This development was reported by the Pakistani media outlet BOL News.
Last year, Turkish Deputy Defense Minister Celal Sami Tüfekçi announced that discussions were underway to involve Pakistan in Turkey’s next-generation fighter aircraft (NGFA) program. Tüfekçi revealed that nearly 200 Pakistani engineers were already working on the TFX Kaan project.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The India-U.S. bilateral Army exercise Yudh Abhyas, currently underway at the Mahajan field firing ranges in Rajasthan, has witnessed the participation of the A-10C Thunderbolt II, an aircraft from the 25th Fighter Squadron. This marks the first time that an A-10C has joined the Yudh Abhyas exercise, showcasing the growing collaboration between the Indian and U.S. militaries.
The A-10C Thunderbolt II is a specialized aircraft designed for close air support of ground forces. Its unique capabilities, including its slow speed, maneuverability, and powerful weaponry, make it an invaluable asset in providing direct support to troops on the ground.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Samir V Kamat, the chairman of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has emphasized the critical role of space in modern warfare. In a recent statement, he highlighted the shift from traditional land, air, and sea domains to a more complex battlefield that includes cyber, information, and space.
Kamat asserted that nations with superiority in these three domains will have a significant advantage in future conflicts. He particularly underscored the importance of space, stating that India must build its expertise and capabilities in this sector to secure a strategic edge.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) today witnessed a historic moment as two new Anti-Submarine Warfare (ASW) Shallow Watercraft were launched for the Indian Navy. The vessels, named INS MULKI and INS MALPE, were launched by Smt Vijaya Srinivas, wife of Vice Admiral V Srinivas, Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief of the Southern Naval Command.
These vessels are designed to conduct anti-submarine operations in coastal waters, low-intensity maritime operations, mine-laying, sub-surface surveillance, and search and rescue missions. They are equipped with a range of weapons, including lightweight torpedoes, anti-submarine warfare rockets, a close-in weapon system, and remote-controlled guns.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

A leaked image of a wind tunnel model of an upcoming air-launched glide munition (ALGM) under development by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has revealed key details about its design and capabilities.
The model showcased above shows a deployable wing on the mid-section and four actuated rear fins in an X configuration. Notably, the munition does not appear to have its own propulsion system, suggesting that it relies on the initial boost provided by the launch aircraft to achieve its desired trajectory and range.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
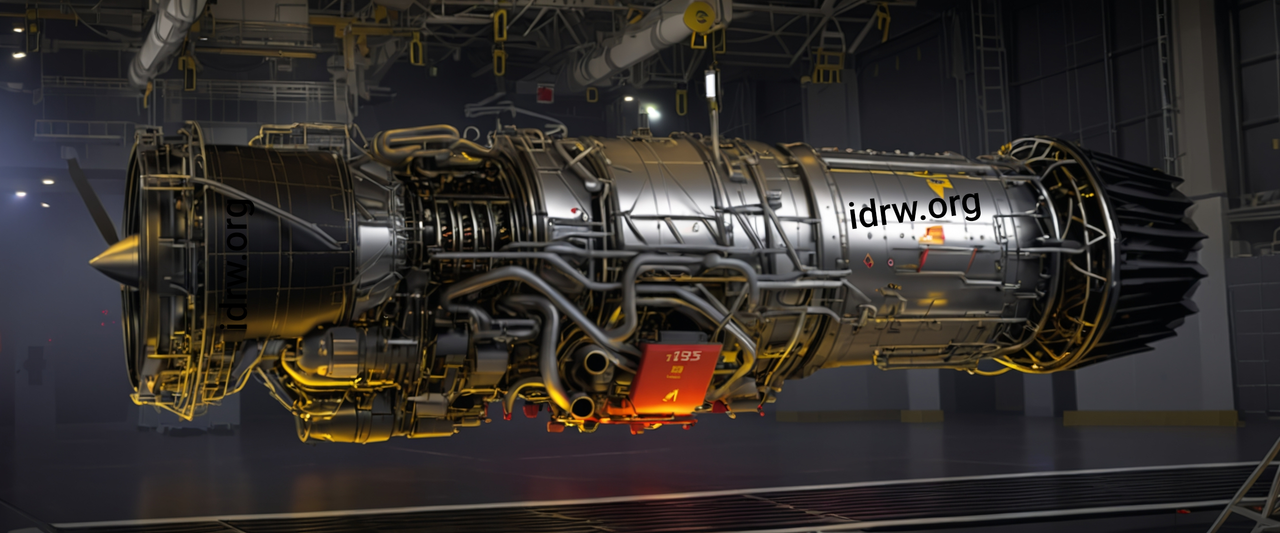
India is set to develop a new high-thrust engine for its Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, the country’s ambitious 5th-generation fighter jet project. According to sources within the Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE), which is the lead agency responsible for this development, the new engine will require a minimum accumulated 1,600 hours of running time over nearly eight years before it can be cleared for production.
The development of the new 110 kN thrust class engine, in collaboration with a foreign Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM), is projected to take nearly eight years, with extensive testing protocols set to validate its performance. GTRE sources indicate idrw.org that the initial 3-4 years of this timeline will be dedicated to ground-based testing. During this phase, the engine’s various parameters, such as fuel efficiency, reliability, and thrust output, will be meticulously evaluated.
Continue reading