SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter (TEDBF) program, which aims to develop a next-generation naval fighter aircraft for the Indian Navy, may face further delays as the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) clearance for the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) 5th generation program is expected to take precedence.
The CCS clearance for the AMCA program, which focuses on the development of an indigenous 5th-generation fighter jet, is likely to be granted only by the end of this year, potentially causing a ripple effect on the TEDBF program.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Indian Air Force (IAF) have agreed to revise their approach for the development of the Next-Generation Close Combat Missile (NGCCM), potentially leading to an extended timeline for its completion. The decision was made to develop the NGCCM from scratch instead of incorporating an infrared-homing seeker onto an existing airframe, which was initially planned as a temporary solution using the Astra-Mk1 Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM) airframe.
The IAF has set high expectations for the NGCCM, anticipating significant cost reductions in weapon procurement and maintenance across its fleet. By adopting a standardized Close Combat Missile (CCM) for its aircraft, the IAF aims to streamline its arsenal and enhance operational efficiency. To achieve this goal, the IAF plans to equip the MBDA-developed Advanced Short-Range Air-to-Air Missile (ASRAAM) as a common infrared (IR) missile, replacing the R-73 missiles on the Su-30MKI fleet, as well as being compatible with the Tejas Mk1A and Mk2 aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

French aerospace and defence multinational company Safran, in collaboration with Hindustan Aeronautics Ltd (HAL), a state-owned aerospace heavyweight in India, is actively seeking a partnership with a private Indian aerospace company specializing in the manufacturing of engine components, particularly combustors for the development of new high thrust engines for India’s AMCA program if India chooses to partner with them.
Safran and HAL had previously signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in the previous year to initiate the joint development of this high-thrust engine. The co-development process is expected to involve Safran, the Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE), and a private Indian aerospace company. The engine’s production will be overseen by a joint venture plant between Safran and HAL located in Bangalore.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

According to recent reports from Times Now, French aerospace engine manufacturer Safran is emerging as a potential supplier for a new engine in India’s 5th generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. Safran has expressed its intention to offer full Transfer of Technology (ToT) for the co-developed engine, with no restrictions on sensitive issues.
Sources familiar with the matter have revealed idrw that India’s negotiation position has strengthened after securing an 80% ToT agreement for the F414 engines. Indian authorities are now determined to press for Intellectual Property Rights (IPR) and ToT at a level no less than 85-90% of the engine’s value in discussions with potential engine manufacturers, including Safran and Rolls Royce, who have expressed keen interest in participating in the program.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) has renewed its efforts to secure a wet lease agreement for a refuelling tanker from France, specifically Airbus A330 MRTT, to meet the growing demand for air-to-air refuelling training. This initiative aims to cover training requirements for various Indian fighter aircraft, including the Rafale, Su-30MKI, Jaguar, and Tejas.
The IAF currently faces challenges in conducting a minimum of 100 hours of monthly training due to the limitations of the IL-78-based air tankers. These tankers have been plagued by low serviceability issues, hampering training activities. To address this issue and ensure uninterrupted training, the IAF is seeking alternative solutions.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a significant development, the United States Department of Defense and Space Force have signed their first international Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA) with Indian startup 114ai and 3rditECH. The agreement aims to collaborate with General Atomics to co-develop components using cutting-edge technologies in AI and semiconductor fields for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drones.
This groundbreaking partnership between the US defense sector and Indian startups signifies a growing global recognition of India’s technological capabilities and the potential for collaboration in advanced fields. The CRADA provides a platform for joint research, development, and innovation, fostering an exchange of ideas and expertise between the two countries.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Mazagon Dock Limited (MDL), an Indian shipyard, has announced plans to integrate the DRDO (Defence Research and Development Organisation)-developed Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) system on the first Kalvari class submarine, which is scheduled for completion and refit within the next two years.
The Kalvari class submarines are based on the renowned French Scorpène class submarines, which are widely exported and operated by countries such as Brazil, Chile, and Malaysia. However, the Kalvari class submarines currently do not possess an AIP system.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
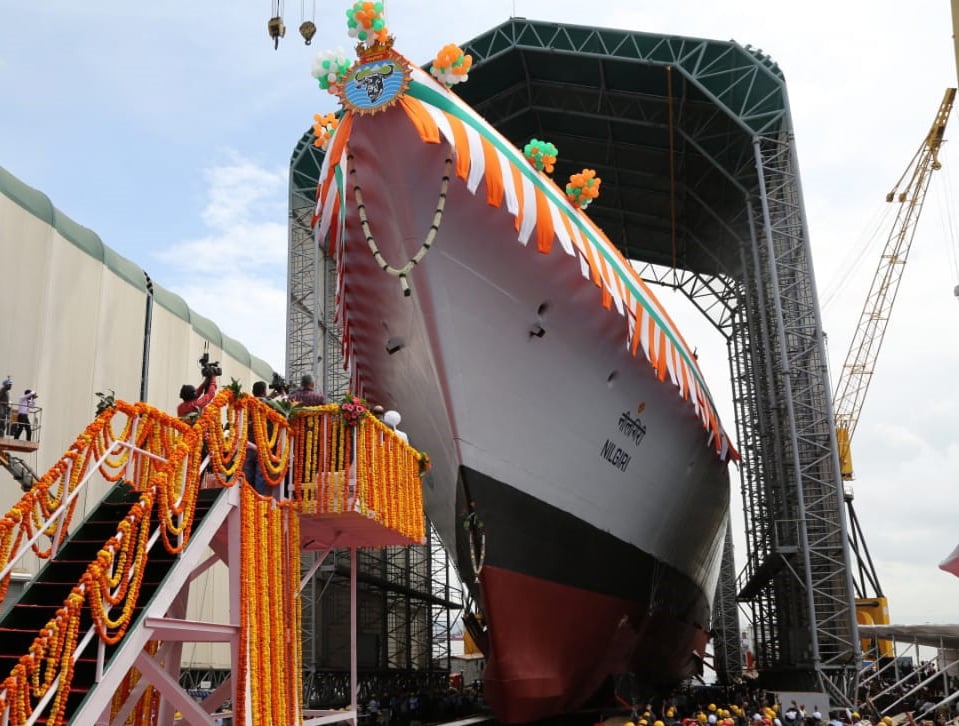

The Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) is actively working towards establishing India as a prominent weapons exporter in the global defence sector. While the country has achieved significant success in recent years, it still holds a relatively small share of the market. In a strategic shift, the MoD is now focused on exporting weapons systems that offer higher value, including domestically-developed warships for the Indian Navy.
Recognizing the challenges posed by long delivery timelines from Indian Public Sector Undertakings (PSUs), the MoD has been encouraging private-sector shipyards to enter the shipbuilding segment, which has traditionally been dominated by government-owned companies. The ministry is keen on addressing the issue of delayed deliveries and aims to enhance the competitiveness of Indian shipyards in the tender process.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Egypt, one of the leading importers of Russian weapons, is actively exploring alternatives to reduce its dependency on Russian-made weaponry. With India and China emerging as potential options, Egypt is keen to seek support from India to maintain and supplement its existing arsenal of Russian-origin weapons systems.
Currently ranked among the top three importers of Russian weapons, Egypt holds 9.3 percent of the market share, following India and China. However, the country aims to diversify its sources and explore partnerships with nations that possess significant expertise in weapons manufacturing and have developed indigenous substitutes for Russian systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
India has made a formal request to the United States of America, urging the inclusion of Lockheed Martin’s AGM-MR (Medium-Range) missiles on its fleet of MQ9B drones. The AGM-MR missile, currently in the developmental phase, offers double the range of the AGM-114 Hellfire missiles commonly equipped on MQ9B UAVs.
With increased stand-off range becoming a critical factor in operating in contested areas, the Indian Air Force (IAF) has expressed its interest in adopting the JAGM-MR missiles. This development opens up possibilities for increased capabilities not only for the Indian drone fleet but also for the IAF’s Apache helicopters.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a bid to reduce dependency on foreign equipment manufacturers, the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) of India recently issued a Request for Information (RFI) for the development of an indigenously built Air-to-Air Refueling Probe.
This move has garnered interest from two Indian private-sector firms. The ADA aims to enhance the self-reliance of India’s defence industry by relying on domestic manufacturers, thereby strengthening the country’s aerospace capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
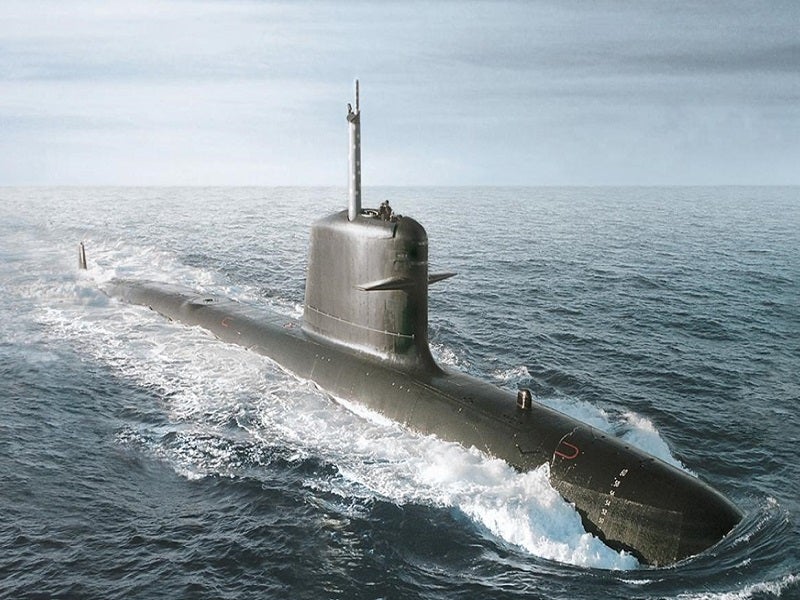

India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) has awarded a contract to Larsen & Toubro (L&T), a leading private sector company, for the manufacturing of two fuel cell-based Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) System Modules. These modules are designed to enhance the capabilities of the Kalvari Class submarines in the Indian Navy.
The AIP technology has been developed and demonstrated by the Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL) under the DRDO. In addition, the Ministry of Defence plans to undertake the indigenous development of a 500KWh Lithium-Ion Battery (LIB) System for submarines, which will replace the existing Lead-Acid Batteries (LAB) in the Kalvari fleet.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
India’s journey towards developing an indigenous unmanned air vehicle (UAV) program has encountered its fair share of challenges over the past two decades. However, recent developments indicate a turning point, as the country makes significant strides in its UAV capabilities. With the introduction of programs like MALE Tapas and Archer-Ng, and plans to develop High-Altitude, Long-Endurance (HALE) class UAVs, India is poised to make substantial progress with the support of American defence contractor General Atomics.
India’s decision to procure 31 MQ-9B SeaGuardian UAVs from General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI) marks a significant milestone in the country’s UAV program. The establishment of Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) facilities, coupled with collaborations with Indian private sector companies like Kalyani, showcases India’s commitment to local manufacturing and self-reliance in the UAV domain. This move will not only strengthen India’s defence capabilities but also foster technological advancements within the country.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s pursuit of stealth unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs) has faced obstacles in recent years, particularly concerning the acquisition of US-made Predator C “Avenger” drones. Despite India’s interest in purchasing these advanced drones, concerns from the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) and the US Congress have posed challenges to the sale.
However, recent developments, such as the procurement of MQ-9B SeaGuardian UAVs from General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, may change India’s stance on acquiring stealth UCAVs, signaling a potential shift in its capabilities and strategic priorities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
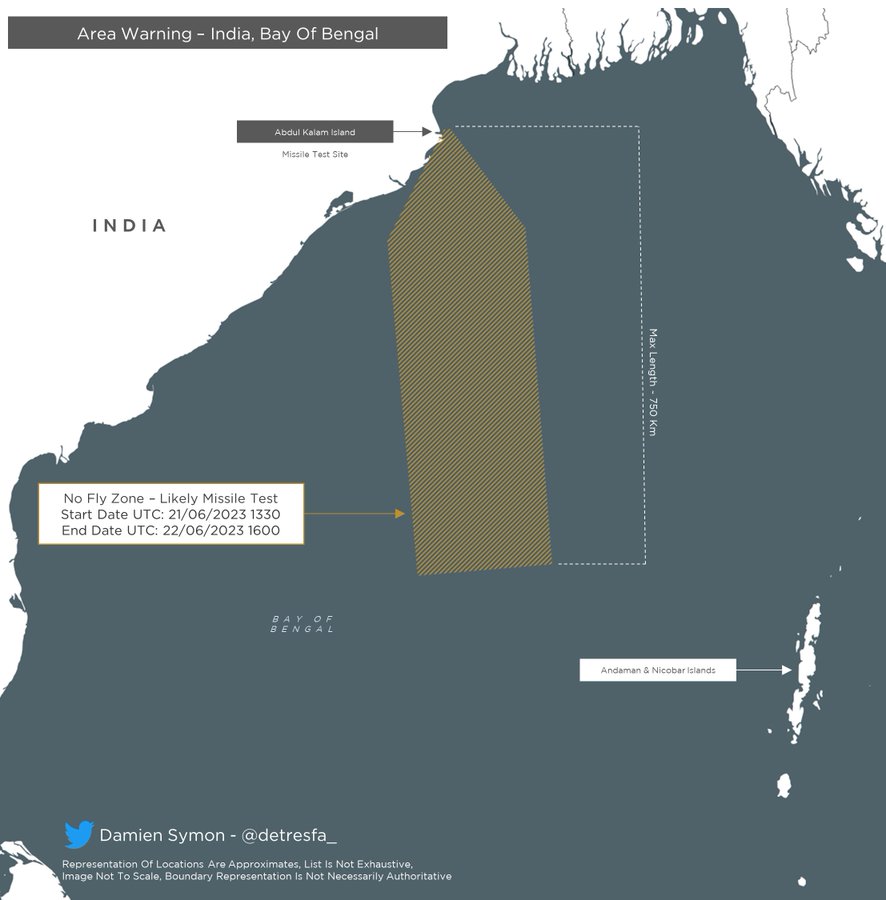
India has issued Revised Notices to Airmen (NOTAM) for a launch of a missile in the Bay of Bengal for the period from 01-02 July. Original NOTAM was issued for 21-22 June 2023 as per information provided by Twitter user Damien Symon@detresfa_.
The designated area for the NOTAM is 750km in length which indicates it might be a test of the Agni-I from Abdul Kalam Island.
Continue reading