News Beat
News Beat reporting is an idrw.org initiative to let our Readers to report News Based on Actual facts but some how has not been reported in Main Stream Media .
SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
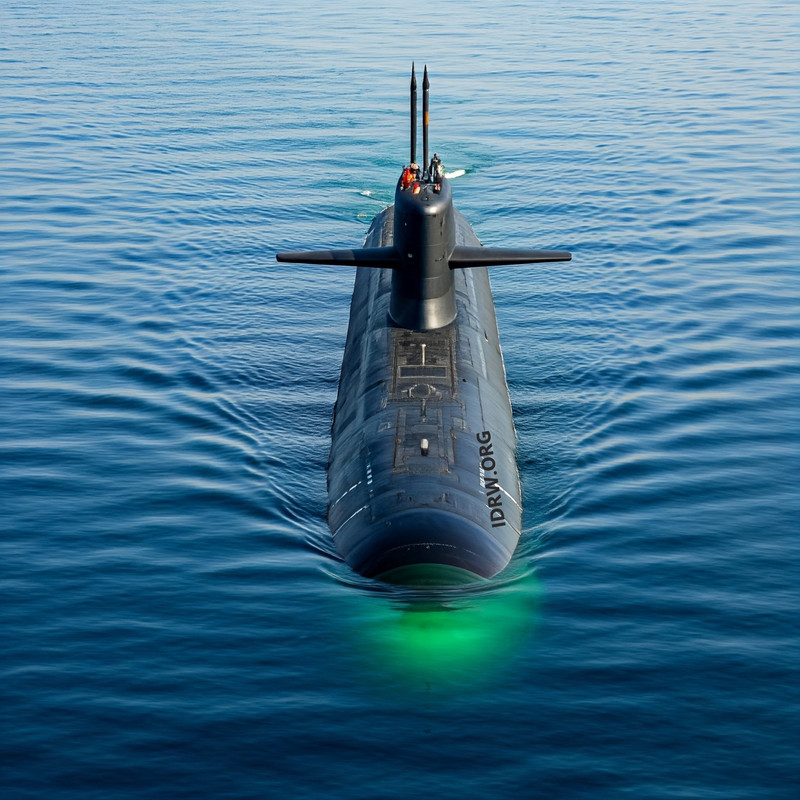

India’s nuclear attack submarine program recently received Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) approval for the construction of two nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs), a critical step forward in strengthening India’s maritime defence capabilities. New details, as reported by the Times of India (TOI), suggest that these submarines will have a displacement of nearly 10,000 tons, significantly larger than previously speculated figures of 6,000-7,000 tons.
The increased displacement of India’s nuclear attack submarines places them in the same league as the American Virginia-class submarines, specifically the SSN-774 Block V variant, which displaces around 10,200 tons. This would make India’s SSNs comparable to some of the most advanced nuclear attack submarines (SSNs) in the world in terms of size and potential capability.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
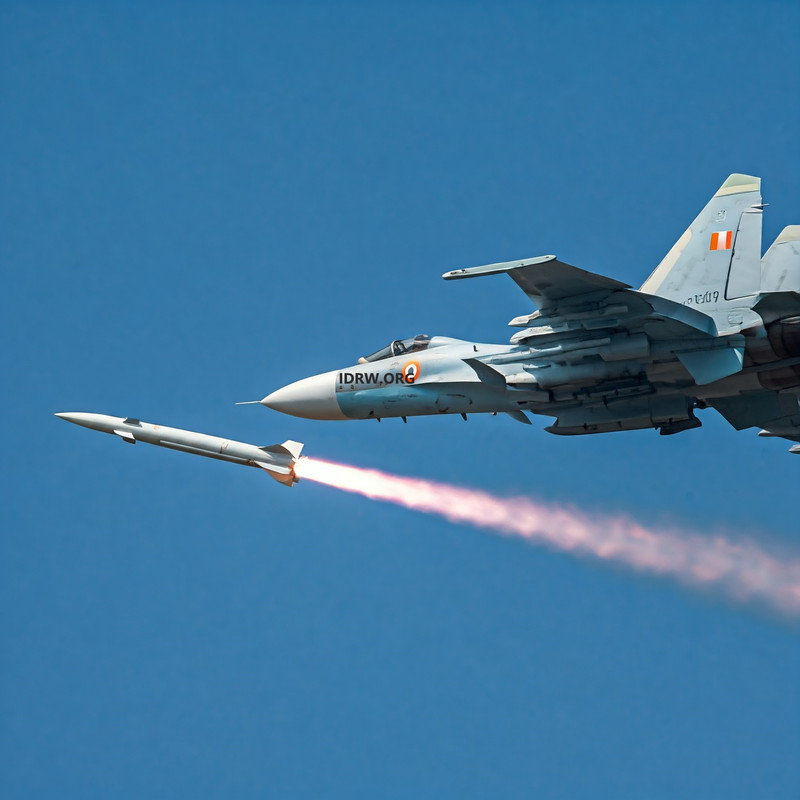

In response to the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) call for expedited development, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is set to commence initial trials of the Air-Launched Long Range Land Attack Cruise Missile (ALLCM) program from 2025 onwards.
The ALLCM, based on the subsonic cruise missile designed and developed by the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) for the Indian Army, will be launched from IAF’s Sukhoi-30MKI jets. The IAF variant will be approximately 1.3 tons lighter due to the removal of the first-stage solid rocket booster.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
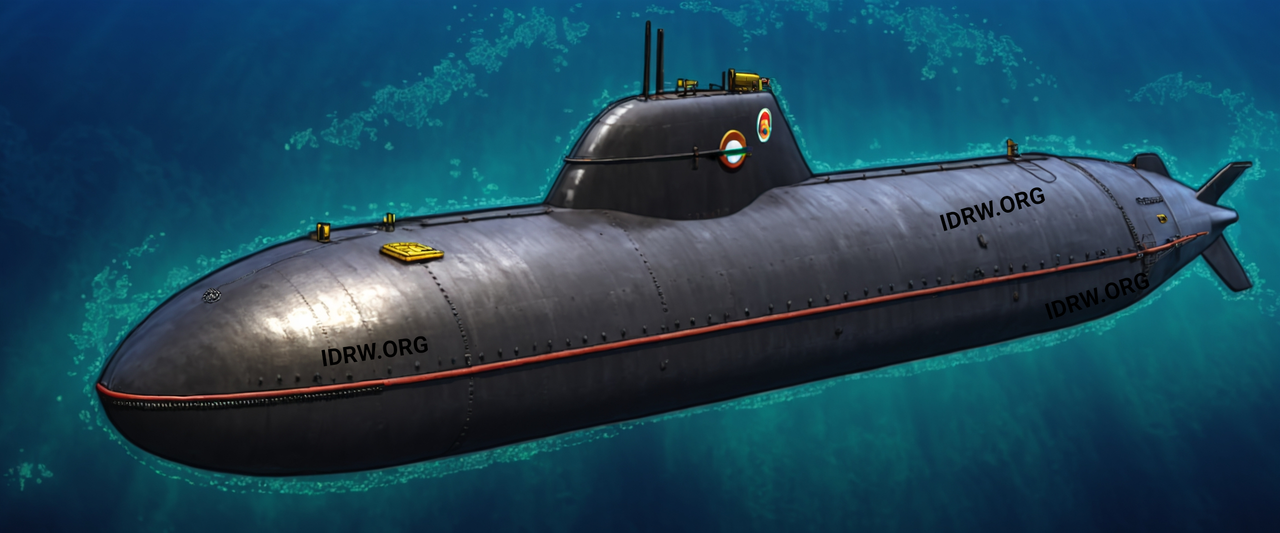

The exit of German Chancellor Angela Merkel in 2021 paved the way for ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS) to make a strong comeback in India’s prestigious P75I submarine project.
During Angela Merkel’s 16-year tenure as Chancellor, TKMS, despite being a frontrunner for India’s P75I submarine project, faced several obstacles. These challenges included stringent export controls and high demands for technology transfer (ToT) from the Indian Navy. TKMS raised concerns that some of the requirements, such as the high indigenous content percentage and almost unlimited liability for the foreign technology partner, were nearly impossible to meet.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Eurofighter Typhoon consortium has quietly intensified its campaign to secure the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) lucrative tender for 114 fighter jets under the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) program. The consortium has reportedly raised concerns with the Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) regarding Dassault Aviation’s ability to meet India’s price expectations and delivery timelines for its Rafale jets, which are also competing in the MRFA program.
According to MoD sources cited by idrw.org, Dassault has been facing difficulties scaling up its production of Rafale jets at its facility in France. The French company is expected to reach a production rate of only 24 jets annually by 2025, leading to questions about whether Dassault can meet the stringent delivery schedule outlined by India. Furthermore, Dassault’s plans to produce Rafale jets at a new facility in India face complications. The company reportedly insists on full control over its Indian production plant, a condition that may not align with India’s expectations for technology transfer and local partnership under the “Make in India” initiative.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
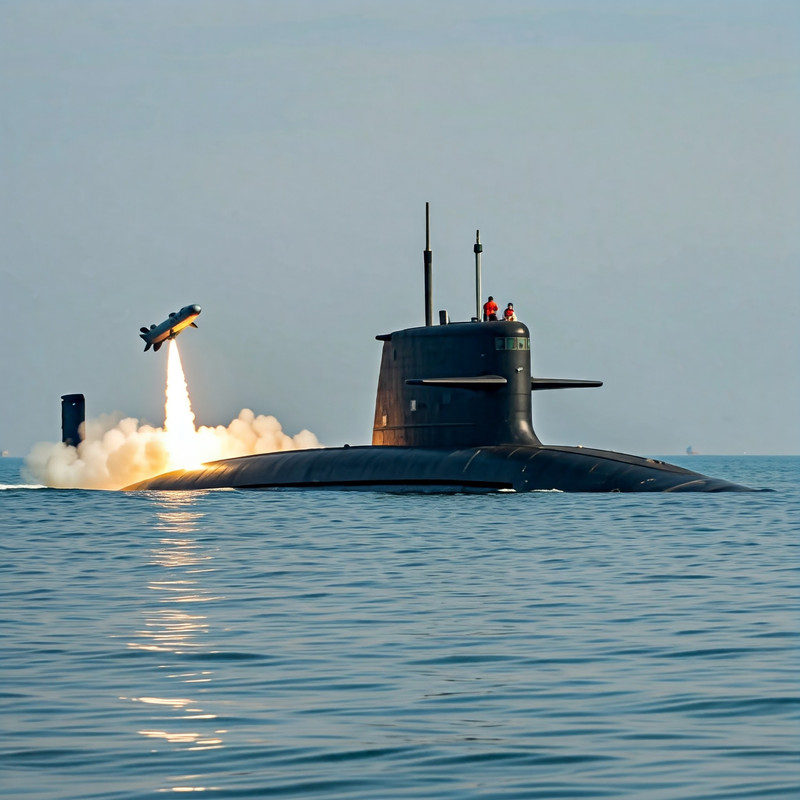

India’s quest for self-reliance in underwater warfare takes a significant leap forward with Project-76, a program aimed at developing next-generation, indigenous submarines equipped with a Vertical Launching System (VLS). This marks a major advancement in Indian naval capabilities, offering the potential to launch long-range land-attack and anti-ship cruise missiles, significantly enhancing offensive and defensive capabilities.
Project-76 submarines are being designed by the Warship Design Bureau (WDB) with a targeted displacement of 3,000 tons. This design choice offers greater submerged volume compared to previous classes, allowing for advanced features and increased operational flexibility.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

A senior Indian Air Force (IAF) official, speaking anonymously to idrw.org, has expressed a preference for private sector companies to be involved in the production of the fighter jet chosen in the upcoming MRFA (Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft) tender. This tender aims to acquire 114 fighter jets for the IAF.
The official cited Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), India’s state-owned aerospace company, as having a full workload. HAL is close to securing additional orders for 97 Tejas Mk1A fighter jets, on top of the 83 already ordered in 2021. Additionally, HAL is responsible for the Tejas MkII program, partnered with the 5.5th generation AMCA program, and will handle the production of the HTT-40 trainer aircraft. Plans also include the HLFT-42 supersonic trainer program.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian aerospace industry is witnessing a paradigm shift towards self-reliance with the Tejas Mk2 fighter jet program. According to Prabhulla Chandran VK, director of avionics and weapons systems at the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA), the Tejas Mk2 is poised to achieve a remarkable 90% indigenous content when it enters production in 2031.
The journey towards self-reliance for the Tejas Mk2 will be a staged ascent. The initial prototype, expected in 2026, will boast over 70% indigenous components. This impressive feat signifies substantial progress compared to its predecessor, the Tejas Mk1A, which is expected to reach 70% indigenous content within the next four years.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
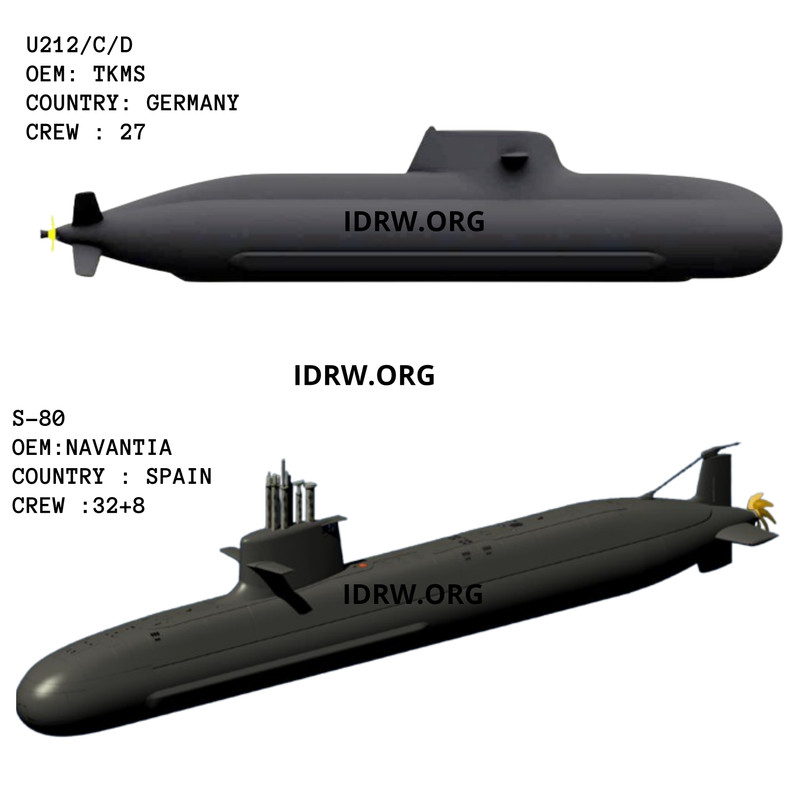

The competition for India’s prestigious P-75(I) submarine tender has taken an unexpected turn, with Spain’s Navantia challenging the leading position of ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS) of Germany. Navantia has urged the Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) to decide the winner of the contract based on a price discovery method, rather than relying on the results of the Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) system field evaluation trials (FET). This move could significantly impact the outcome of the tender for six submarines, a contract that is crucial for modernizing the Indian Navy’s underwater fleet.
Price discovery is a method where the market price of an asset is determined through the interaction of buyers and sellers. Navantia’s call for the Indian MoD to prioritize pricing in the decision-making process reflects a belief that they can offer the S-80 Plus submarines at a more competitive cost compared to TKMS. While this could be advantageous for India from a financial perspective, it diverts attention from the technical evaluations, especially the critical AIP systems that would provide submarines with enhanced endurance and stealth capabilities underwater.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Hindustan Aeronautics Limited’s (HAL) ambitious HLFT-42 program, introduced in 2023 as the “Next-Gen Supersonic Trainer,” is undergoing further design refinements. With plans for additional wind tunnel testing, HAL aims to fine-tune the platform, which captured widespread attention for its impressive capabilities and potential to meet both training and combat needs for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
The HLFT-42 is designed to be much more than a typical supersonic trainer. With a 4.5-ton weapon payload capacity and a 16.5-ton Maximum Take-Off Weight (MTOW), the aircraft promises to not only provide advanced pilot training for 4th and 5th-generation fighter jets but also serve as a light combat jet. This versatility offers the potential for multi-role missions, making the aircraft a valuable addition to the IAF’s fleet, particularly for combat teaming scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
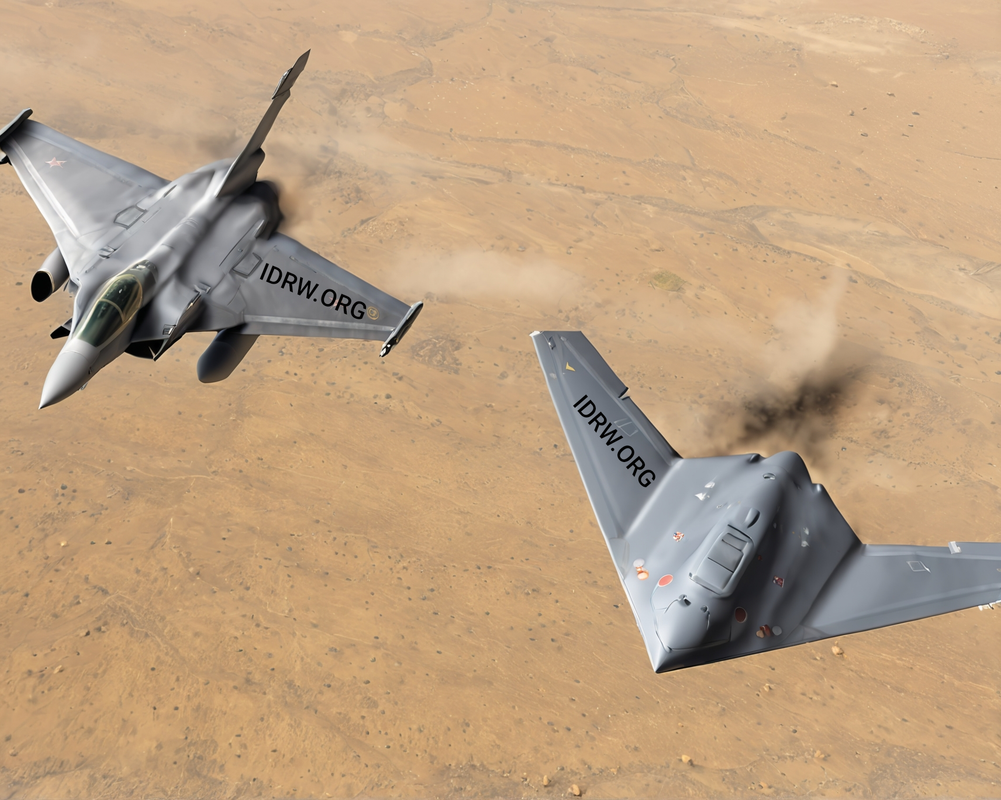

In response to emerging maritime threats and the evolving nature of warfare, the Indian Navy has called on private sector companies to collaborate in developing a Naval-Collaborative Combat Air Vehicle (N-CCAV). This initiative is aimed at addressing growing challenges posed by Anti-Access/Area Denial (A2/AD) capabilities and modern integrated air defense systems at sea. The Navy envisions the N-CCAV to complement its existing combat assets, provide cost-effective strike capabilities, and enhance operational flexibility in contested maritime environments.
In light of these challenges, the Indian Navy has expressed the urgent need to restore its counter-air and air-to-surface capabilities, particularly in the presence of high-end A2/AD threats. To address these gaps, the Navy seeks to develop Collaborative Combat Air Vehicles (CCAV), which will provide the following advantages:
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
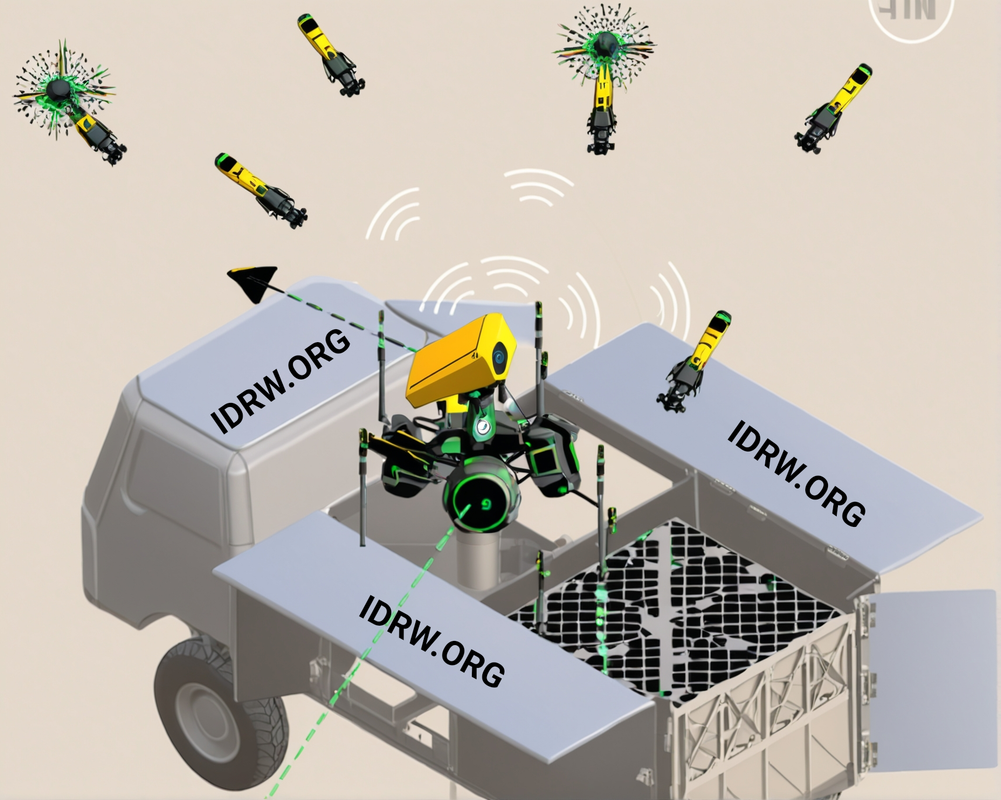
In response to the growing threat of drone swarms targeting vital installations, the Indian Air Force (IAF) has called on private sector companies to collaborate in the design and development of a multi-domain launch capable loitering aerial interceptor system. This innovative solution aims to counter swarm-drone attacks, one of the most pressing challenges in modern air defense. The system will feature autonomous, multi-drone swarms capable of neutralizing multiple airborne threats with a combination of hard and soft kill mechanisms.
The IAF recognizes that the use of drone swarms by adversaries has introduced a complex threat environment. Swarms are difficult to intercept using traditional methods due to their distributed nature, speed, and collaborative behavior. As such, the IAF’s vision is to develop an autonomous system that can intercept, engage, and neutralize multiple drones simultaneously.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is seeking innovative solutions from private sector companies to design and develop a road-mobile tethered aerostat system with integrated radar and communication capabilities. The goal is to enhance low-level radar and communication coverage over a range of 80-120 kilometers, overcoming the limitations imposed by the radio line of sight. This advanced system will play a critical role in improving aerial object detection, tracking, and communication relay, especially in remote and challenging environments.
The increasing complexity of air defense and surveillance requires systems that can provide long-range radar coverage and effective communication at low altitudes. Traditional ground-based systems face limitations due to the curvature of the Earth and obstacles in the terrain, which affect the radio line of sight. The solution the IAF envisions is a tethered aerostat system—a portable, road-mobile technology that can elevate radars and communication equipment to heights of 2,000 to 5,000 feet above ground level (AGL), thereby expanding the line of sight and providing coverage over a much larger area.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
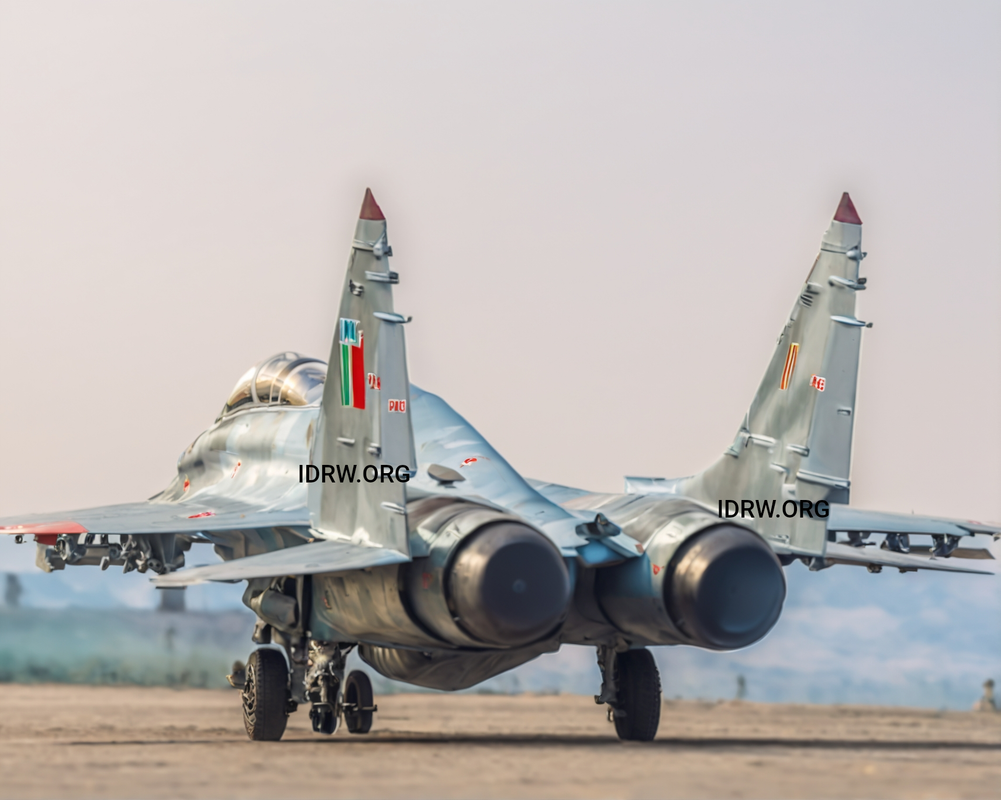

In a significant development, the Indian Air Force (IAF) and the Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) are in advanced discussions to repurpose one of the IAF’s MiG-29UPG fighter jets as a Flying Test-Bed (FTB) for the Kaveri engine program. This move comes as the IAF aims to prolong the operational life of its MiG-29UPG fleet and support indigenous jet engine development.
Originally slated for retirement in 2027, the MiG-29UPG fleet will now remain in service for an additional eight years, extending its operational role within the IAF. However, one older MiG-29UPG will be dedicated to the Kaveri engine testing program, with plans to modify it for engine trials.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF), grappling with delays in the delivery of Tejas Mk1A fighter jets due to a supply shortage of F-404 engines from GE Aerospace, is now considering extending the service life of its remaining MiG-21 Bison aircraft. The decision comes as the IAF faces the challenge of maintaining operational readiness until sufficient Tejas Mk1A jets are delivered to form a full squadron.
The MiG-21 Bison, which had been slated for complete retirement by next year, will now remain active for a little longer than initially planned. The IAF intends to slow down flying operations of the MiG-21s, ensuring that they remain in service until the Tejas Mk1A squadrons are fully operational.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s Indigenous Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&C), known as NETRA, is on the cusp of achieving Final Operational Configuration (FOC). This significant milestone marks a culmination of nearly seven years of development and testing since the program was granted Initial Operational Configuration (IOC) in 2017.
The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) plans to achieve FOC for NETRA by the end of this year. This milestone will signify that the system is fully operational and ready to meet the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) strategic requirements.
Continue reading