AFI
SOURCE: AFI


Pakistan’s Defense Minister Khawaja Asif claimed that Pakistan Air Force (PAF) J-10CE fighter jets, possibly equipped with the KG600 jamming pod, successfully disrupted the radar and communication systems of four Indian Air Force (IAF) Rafale jets patrolling near the Line of Control (LoC) in Kashmir. The assertion, which suggested that the Chinese-made J-10CE overwhelmed the Rafale’s advanced Thales RBE2 Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar, sparked widespread skepticism and ridicule on social media and among defense analysts.
Critics pointed to the technological superiority of the Rafale’s SPECTRA electronic warfare (EW) suite and dismissed Pakistan’s claims as exaggerated propaganda, highlighting the limitations of the KG600 jammer and Chinese EW technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Amid escalating tensions with India following the April 22, 2025, Pahalgam terrorist attack that killed 26 civilians, the Pakistan Navy has reportedly requested the deployment of 12 Pakistan Air Force (PAF) F-16 Block 52 fighter jets to defend its ports and warships against potential attacks from the Indian Navy’s MiG-29K carrier-based fighters.
This request, reported by defense sources close to AFI, comes as India deploys its aircraft carriers, INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya, in the Arabian Sea, signaling robust maritime power projection. However, the F-16 Block 52, primarily a land-based multirole fighter, lacks configuration and expertise for anti-ship missions over open waters, raising questions about the Pakistan Navy’s strategy. This article analyzes the rationale, feasibility, and implications of this deployment, situating it within the broader context of India-Pakistan naval and air dynamics.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


India’s pursuit of self-reliance in aerospace through the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program—a 5.5-generation stealth fighter—has reached a critical juncture. With global powers like the United States, China, and Europe advancing sixth-generation fighter technologies, India faces the challenge of keeping pace while addressing regional threats from China’s J-20 and emerging platforms.
A potential collaboration with the UK-led Tempest program, part of the Global Combat Air Programme (GCAP) involving Japan and Italy, could provide a transformative boost to India’s AMCA program. By securing access to Tempest’s advanced engine technologies with local production rights, India could not only enhance the AMCA but also lay the foundation for sixth- and seventh-generation fighter jets through 2060.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
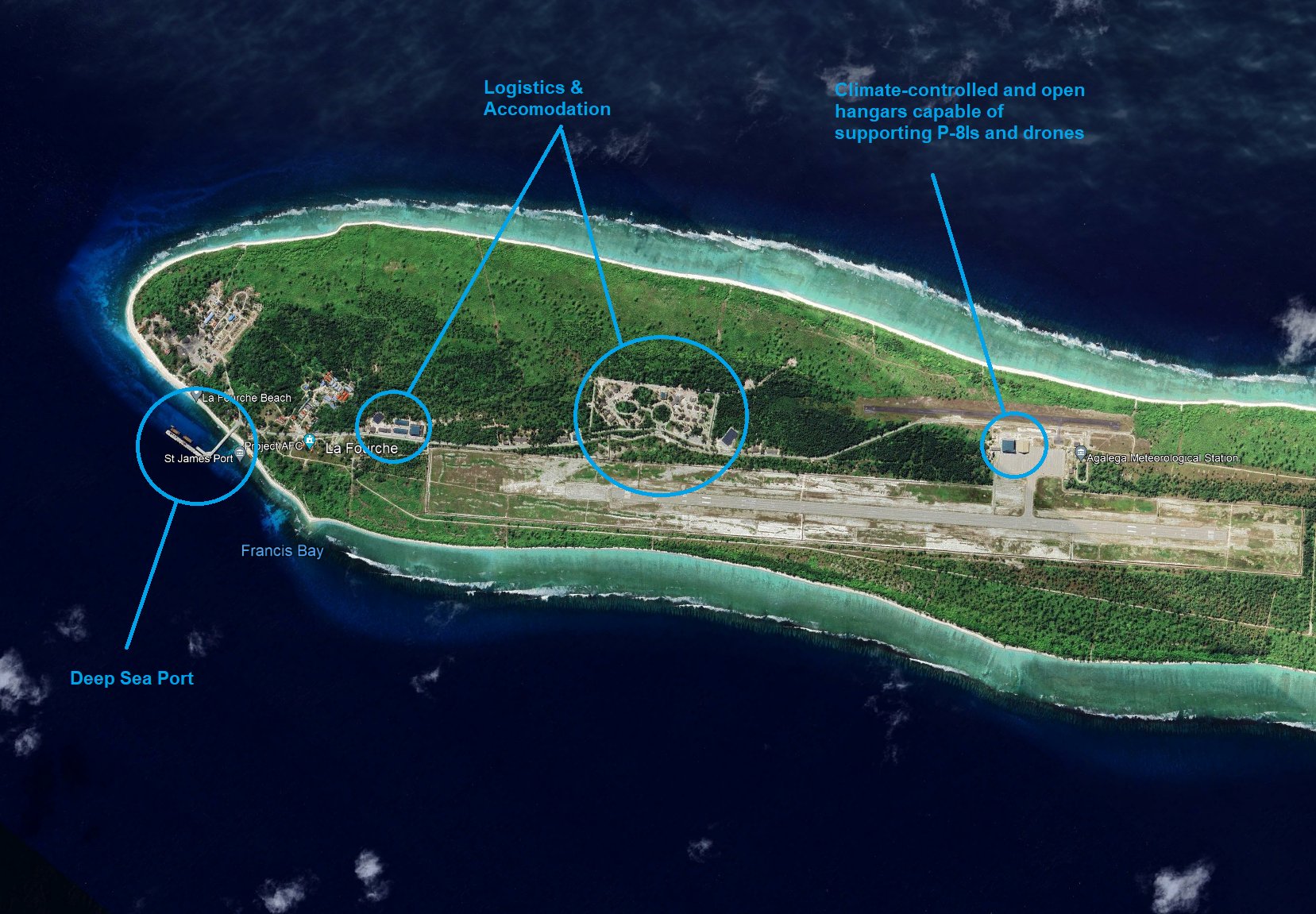

In a bold move to assert its dominance in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), India has established a pivotal military base on the remote Agalega Island, part of Mauritius, located near one of the world’s busiest maritime waterways—the Mozambique Channel. Inaugurated in February 2024, this base, equipped with a 3,000-meter airstrip and a deep-water jetty, is designed to host large military aircraft like the Boeing P-8I Poseidon and naval warships, transforming Agalega into a launchpad for operations across the farthest reaches of the Indian Ocean.
This strategic outpost, often overlooked due to its isolation, holds immense geopolitical significance as India counters China’s expanding influence through its “String of Pearls” strategy with its own “Necklace of Diamonds” approach. As U.S. Navy Admiral Alfred Thayer Mahan prophesized over a century ago, “Whoever controls the Indian Ocean will dominate Asia. The destiny of the world will be decided on its waters.” Today, this prophecy resonates more than ever.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


A leaked document from the China National Aero-Technology Import & Export Corporation (CATIC), a Chinese state-owned defense company, has shed light on a recent arms deal with the Pakistan Air Force (PAF). According to the document, Pakistan has acquired 240 PL-15E beyond-visual-range air-to-air missiles (BVR-AAMs) as part of a larger defense procurement package. However, the document clarifies that the PL-15E variant supplied to Pakistan has a capped range of 145 kilometers, contrary to claims in Pakistani media that the PAF had procured the PL-15 variant used by the Chinese People’s Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF), which boasts a range exceeding 200 kilometers.
The leaked document details a loan of CNY 10,136,650,000.00 (approximately USD 1.4 billion) from CATIC to the PAF for the procurement of 20 J-10CE fighter jets, the 240 PL-15E missiles, 10 KWS-10B spare power plants, and one flight management system (FMS), along with associated stores and services. The deal, executed on a seller’s credit basis, highlights China’s continued role as a key defense supplier to Pakistan.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On May 2, 2025, the Indian Air Force (IAF) conducted historic day-and-night landing and takeoff drills on a 3.5-kilometer airstrip along the Ganga Expressway in Shahjahanpur, Uttar Pradesh. This marked India’s first expressway airstrip equipped for 24/7 fighter jet operations, featuring advanced lighting, CAT II Instrument Landing System (ILS), and reinforced pavement.
The exercise, involving Rafale, Sukhoi-30 MKI, Mirage-2000, MiG-29, Jaguar, C-130J Super Hercules, AN-32, and MI-17 V5 helicopters, comes amid heightened tensions with Pakistan following the April 22, 2025, Pahalgam terror attack that killed 26 civilians. This article explores the strategic purpose of these night landing exercises, particularly whether they enable India to maintain counterstrike capabilities against Pakistan even if its airfields are preemptively targeted.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a disturbing escalation of espionage activities, Pakistani intelligence agents, impersonating Indian Navy officers, have been reported making phone calls to officials at the INS Kadamba naval base in Karwar, Karnataka, and the Eastern Naval Command in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh, to extract sensitive information about India’s aircraft carriers, INS Vikrant and INS Vikramaditya, as well as other warships, including INS Subhadra.
These incidents, reported in early May 2025 by Public TV English and Organiser, follow closely on the heels of the National Investigation Agency (NIA) arresting three individuals in February 2025 for leaking classified details about INS Kadamba and INS Vikramaditya. The Pakistani operatives have also allegedly attempted to honeytrap Indian Navy personnel, prompting the Indian Navy to issue strict directives against sharing sensitive information. This article examines the nature of these espionage attempts, their strategic implications amid India-Pakistan tensions, and India’s response to safeguard its naval assets.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a surprising move, the Indian government has terminated the tenure of Dr. Krishnamurthy Subramanian as Executive Director (India) at the International Monetary Fund (IMF) with immediate effect, six months before the completion of his three-year term. The decision, announced on April 30, 2025, by the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC), comes days before a critical IMF board meeting scheduled for May 9, 2025, to review a proposed $1.3 billion climate resilience loan to Pakistan—a move India strongly opposes.
The abrupt recall, detailed in a Times of India report, has sparked speculation about underlying tensions, including disagreements over IMF datasets and allegations of impropriety related to Subramanian’s book promotion.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Saif Automations Services LLP, a pioneering robotics and automation startup based in Visakhapatnam, has made significant strides in maritime safety by supplying over 200 remote-controlled life buoys to the Indian Navy. These innovative, battery-powered, self-propelled devices, co-engineered with India’s Ministry of Defence, have already been credited with saving 10 lives in real-world rescue operations, marking a transformative step in water rescue technology.
The remote-controlled life buoy, developed under the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) challenge for Unmanned Surface Vehicles, is designed to perform swift and safe rescues in challenging aquatic environments, including seas, lakes, and rivers. Weighing just 12 kilograms, the buoy is lightweight, portable, and equipped with a high-powered battery that supports up to 90 minutes of operation at moderate load and eight hours of GPS tracking. With a top speed of 7 knots (approximately 14 meters per second), it outpaces human swimmers, reaching distressed individuals faster than traditional rescue methods. Its robust 3-kilometer radio communication range, independent of internet or tower signals, ensures reliability even during adverse conditions like cyclones or network disruptions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In the wake of the April 22, 2025, terror attack in Pahalgam, Jammu and Kashmir, which claimed 26 lives, Bharat Karnad, Senior Fellow in National Security Studies at the Centre for Policy Research, New Delhi, has proposed bold and decisive military objectives for India’s retaliation against Pakistan. In a blog post published on April 30, 2025, Karnad argues that capturing the Haji Pir Salient and Skardu, both strategically critical locations in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK), is “eminently doable” and should be the Indian military’s primary goals to deliver a lasting blow to Pakistan’s asymmetric warfare tactics.
Karnad’s proposal comes amid heightened India-Pakistan tensions following the Pahalgam attack, attributed to The Resistance Front (TRF), a proxy of Pakistan-based Lashkar-e-Taiba (LeT). India has already suspended the Indus Waters Treaty, closed its airspace to Pakistani aircraft, and revoked visas for Pakistani nationals, signaling a shift from strategic restraint. However, Karnad criticizes the Indian government’s initial response, including Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s efforts to seek international support, which failed to secure even a mention of “Pahalgam” in a UN Security Council resolution. He urges India to act unilaterally, emphasizing that “India does not need anybody’s permission or support to retaliate harshly against Pakistan for its asymmetric terrorist warfare undermining national security.”
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In the wake of the April 2025 Pahalgam terror attack, which killed 26 civilians in Jammu and Kashmir, some Pakistani commentators, including veteran journalist Najam Sethi, have revived claims labeling India’s past terror incidents, such as the 2016 Pathankot airbase attack, as “false flag” operations orchestrated by India to malign Pakistan. Sethi’s assertions, echoed in a recent interview flagged by X user @DrAyeshaRay on April 28, 2025, align with a broader Pakistani narrative dismissing cross-border terrorism links.
However, these claims are directly contradicted by credible evidence, including investigative reporting by Pakistani journalist Ahmad Noorani, who confirmed in January 2016 that the Pathankot attackers infiltrated from Pakistan, a fact acknowledged by Pakistan’s civilian intelligence and even the Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI). This article debunks Sethi’s false flag narrative, leveraging Noorani’s reporting, official investigations, and strategic context to affirm the Pathankot attack’s Pakistani origins.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Abhijit Iyer-Mitra, a noted defense analyst, has sparked a critical discussion on India’s strategic approach to potential military strikes against Pakistan. In a recent post on X (@Iyervval ), Iyer-Mitra outlined India’s historical weaknesses in escalation management, the need for public humiliation to deter Pakistan, and the risks of inter-service rivalry complicating operations. With speculation of imminent Indian strikes, his analysis highlights the delicate balance India must strike to achieve its objectives while minimizing the risk of spiraling conflict. This article delves into Iyer-Mitra’s arguments, their implications, and the broader strategic context of India-Pakistan tensions as of April 26, 2025.
Iyer-Mitra identifies India’s primary strategic weakness as its inability to accurately predict escalation dynamics and define clear de-escalation pathways. “India’s great weakness, historically, has been escalation prognostications (how will they respond) & de-escalation pathways (essentially what war termination would entail),” he writes. This refers to India’s challenges in anticipating Pakistan’s response to military actions and planning how to end a conflict without uncontrolled escalation.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


As tensions simmer along the India-Pakistan border, India is placing significant trust in its indigenous Akash Air Defence System to counter a range of aerial threats, including Pakistani military jets, Turkish-made Bayraktar TB2 drones, and Chinese Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicles (UCAVs) like the CH-4 and Wing Loong II. With Pakistan bolstering its arsenal through acquisitions from Turkey and China, the Akash system’s versatility and proven capabilities make it a cornerstone of India’s air defence strategy.
As of 2016, Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) was producing 50–60 Akash missiles per month, a rate that has likely scaled up to meet growing domestic and export demands. Here’s a deep dive into how the Akash system is poised to neutralize Pakistan’s aerial threats and why it remains a game-changer in the region.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Pakistan Air Force (PAF) may be compelled to phase out its stockpile of 500 AIM-120C-5 Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missiles (AMRAAMs) by the end of 2028, as the missiles approach the end of their operational service life. Acquired in 2010 under a $650 million F-16 ammunition contract signed in early 2006, these missiles, with an estimated unit cost of $1.3 million, have been a cornerstone of the PAF’s air-to-air combat capabilities. However, the aging propulsion systems and stringent maintenance requirements may force their retirement unless extended through costly service life extension programs (SLEPs).
The AIM-120C-5, manufactured by Raytheon (now RTX), is an all-weather, beyond-visual-range missile powered by a solid-fuel rocket motor enhanced under the AMRAAM Propulsion Enhancement Program (PEP). This upgraded motor, housed in the WPU-16/B propulsion unit, offers improved range and performance over earlier variants, with an operational range of approximately 105-120 kilometers. The PEP motor is designed to withstand operating and storage temperatures ranging from -65°F to +145°F, but its baseline service life is rated at 10 years from manufacture, which for the PAF’s missiles would have expired around 2020, given their production in the late 2000s.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Several major European airlines, including Lufthansa, Air France, British Airways, and SWISS, have begun voluntarily avoiding Pakistani airspace due to escalating tensions between India and Pakistan, following Pakistan’s closure of its airspace to Indian carriers. This development, reported by The Times of India, is causing significant disruptions to international flight routes, increasing operational costs, and extending travel times for passengers.
The decision by European carriers comes in the wake of Pakistan’s airspace restrictions, effective from April 24, 2025, which barred Indian-registered aircraft, charter operators, and private jets from overflying its territory. The move was part of Pakistan’s retaliatory measures after India accused Pakistani nationals of involvement in the April 22 Pahalgam terror attack, which killed 26 Hindu tourists in Jammu and Kashmir. India responded by closing its airspace to all Pakistani-registered aircraft, including military planes, from April 30 to May 23, 2025, further intensifying the aviation standoff.
Continue reading