SOURCE: AFI

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is taking a bold step forward in space exploration, considering a proposal to deliver a cargo mission to the International Space Station (ISS) by the end of the decade. This ambitious initiative, currently under discussion with ISS partner countries, signifies India’s growing capabilities and aspirations in the realm of human spaceflight.
While the specific details of the cargo mission are yet to be finalized, it is likely to be a precursor to India’s even more ambitious Gaganyaan program, which aims to send a crewed mission to space. By participating in ISS cargo missions, ISRO can gain valuable experience in spacecraft design, docking procedures, and the critical logistics required for long-duration space missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a significant affirmation of the growing strategic partnership between the United States and India, U.S. Ambassador to India Eric Garcetti recently highlighted the robust commitment of both nations towards co-production and co-development in the defense sector. Garcetti’s remarks underscore a mutual “betting big on each other” for the next two to three decades, reflecting the deepening ties and shared strategic interests that have been steadily evolving over recent years.
The defense relationship between the United States and India has witnessed remarkable growth, marked by several landmark agreements and collaborative initiatives. The focus on co-production and co-development signals a transformative shift from mere defense trade to a more integrated and synergistic partnership. This collaboration aims to leverage the technological prowess of the United States and the manufacturing capabilities of India, fostering innovation and self-reliance in defense production.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Navy is investing in the future of its marine expertise with the commencement of the 74th Marine Propulsion Technology Course (MPCTC) at the Military Institute of Technology (MILIT) in Pune. This prestigious program brings together 19 Indian Navy officers, 4 Indian Coast Guard officers, and 12 officers from friendly foreign countries including Namibia, Philippines, and Sri Lanka.
In his inaugural address, Rear Admiral Nelson D’Souza, Commandant of MILIT, emphasized the growing importance of niche technologies in the maritime domain. He urged the student officers to actively absorb this knowledge and leverage it during their future assignments.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

The Indian-developed Astra MkII, a Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM), is nearing its final hurdle before user trials, according to internal sources at DRDO. This indigenous missile is poised to become the mainstay of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) BVRAAM arsenal.
The Astra MkII has undergone a rigorous testing process, including captive trials, separation trials, unguided dual-pulse motor trials for various ranges, and seeker trials. These tests have validated the missile’s core functionalities, paving the way for full-scale testing against target drones.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
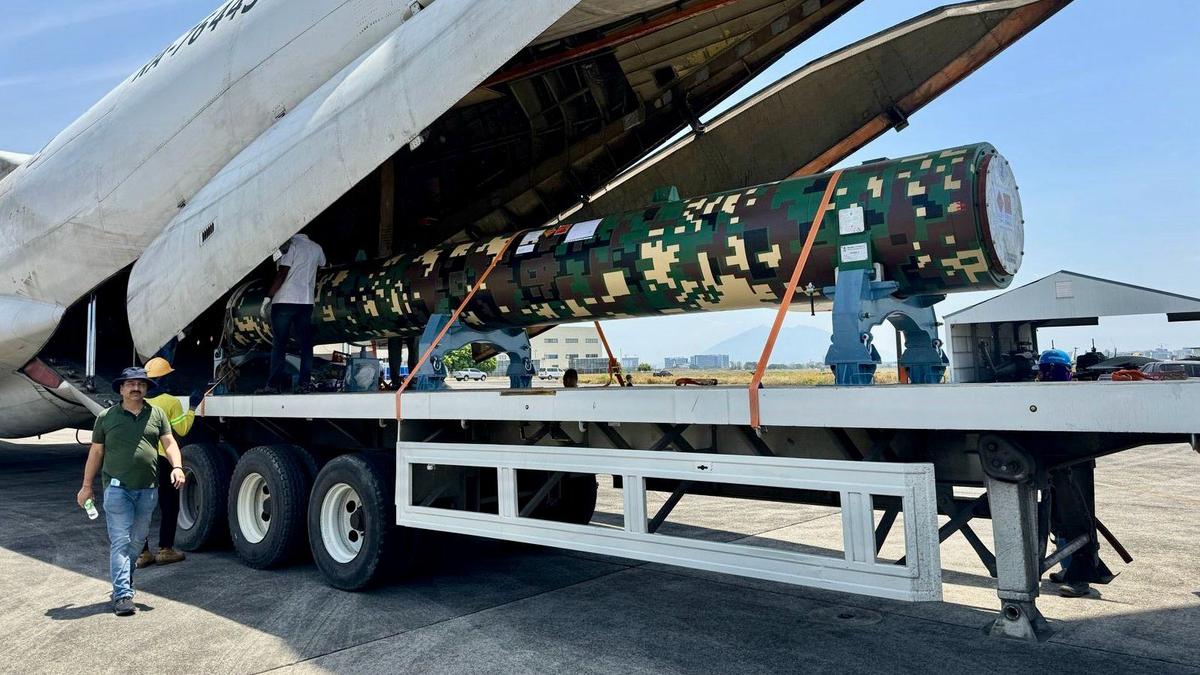

The Philippine Marine Corps (PMC) is bolstering its coastal defenses with the acquisition of BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles from India. This marks a significant development in the Philippines’ modernization efforts to address maritime security concerns.
The PMC is currently taking delivery of three batteries of the shore-based anti-ship variant of the BrahMos missile. Each battery comprises four launchers, each housing three missiles with a staggering range of 290 kilometers. This translates to a significant increase in the Philippines’ ability to deter and counter potential threats at sea.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Bangladesh Army has recently taken delivery of 11 TATA Mine-Resistant Ambush Protected (MRAP) vehicles, bolstering its capabilities in counter-insurgency operations and troop protection. These robust vehicles, manufactured by Tata Motors Defence Solutions (TMDS) in India, are specifically designed for safeguarding personnel in hostile environments.
The TATA MRAP, also known as the MPV (Mine Protected Vehicle), is a 4×4 wheeled platform designed for military, paramilitary, and police forces. The TATA MPV boasts a successful track record within India. Several Indian police forces, including those in Maharashtra and Jharkhand, utilize the MPV for operations in Naxal-affected regions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

India’s Sukhoi Su-30 MKI fighter jets are gearing up for a long-distance deployment to participate in Exercise Pitch Black 2024 in Australia. This international aerial combat exercise, held every two years, will take place from July 12 to August 2, 2024, at airbases in Darwin and Tindal, Australia.
The Indian Air Force (IAF) contingent is eager to showcase its skills on the global stage. This year’s Exercise Pitch Black is set to be the largest in its 43-year history, with participation from 20 countries and over 140 aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

A high-level delegation from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) visited Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) in Bengaluru on [Date of Visit]. The delegation was led by His Excellency Major General Lukwikila Metikwiza Marcel, Permanent Secretary, Ministry of Defence (MoD), DRC.
During the visit, Mr. Manoj Jain, Chairman and Managing Director (CMD) of BEL, received the delegation and held discussions on potential areas of collaboration in the defence sector. Mr. Jain briefed the delegation on BEL’s capabilities and its wide range of defence products and systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Air Force’s (IAF) hunt for a replacement for its aging AN-32 fleet has reignited Russian offer on it IL-276, a medium-lift transport aircraft offered by United Aircraft Corporation (UAC). This comes despite India’s previous withdrawal from the joint development program due to disagreements on engine selection. Last year at Aero India 2023 Russian delegation from Rostec held talks with Indian officials on the possibility of the joint development of the Il-276. Rostec proposed to renew the offer to co-develop the aircraft, and to allow the sale and the assembly of the Il-276 within India.
However, the IL-276 will now face stiff competition from the C-390 Millennium, a Brazilian-made aircraft by Embraer, which fits the bill for IAF. Let’s delve into the key similarities between these two contenders. Both the IL-276 and C-390M fall within the IAF’s specified range of 18 to 30 tonnes carrying capacity. This makes them ideal for transporting troops, cargo, and equipment over medium distances, fulfilling a critical role in military logistics and deployment.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
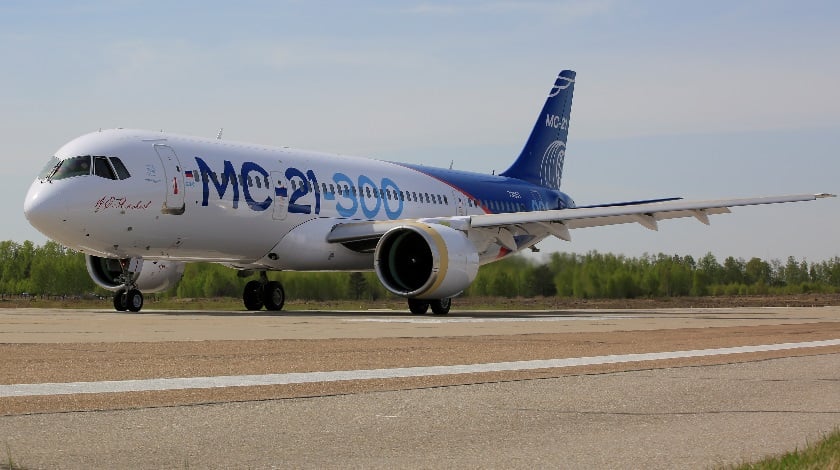

Faced with the continued refusal of Airbus and Boeing to establish final assembly lines in India, Russia has reignited its efforts to promote local production of its new commercial aircraft, the MC-21 and Il-114-300. This move comes despite India’s national carrier, Indian Airlines, being the biggest single customer for these jets, reflecting the country’s booming aviation market.
While Indian Operators has emerged as the largest single buyer for both aircraft, Airbus and Boeing have yet to commit to final assembly lines in India. Russia, sensing an opportunity, has proposed various options for industrial cooperation:
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
Several Indian companies, Including Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL), have set their sights on participating in PT PAL Indonesia’s upcoming Scorpène submarine production. This interest stems from India’s own experience with the Naval Group’s technology transfer program, which successfully enabled the domestic construction of six Kalvari-class (Scorpène) submarines.
As per information provided to idrw.org, Many Indian MSMEs that have participated in the Kalvari-class (Scorpène) submarine program have told Naval Group that they can supply much of the equipment that will be required for local manufacturing of the latest variant of the Scorpène submarines that Indonesia will acquire.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
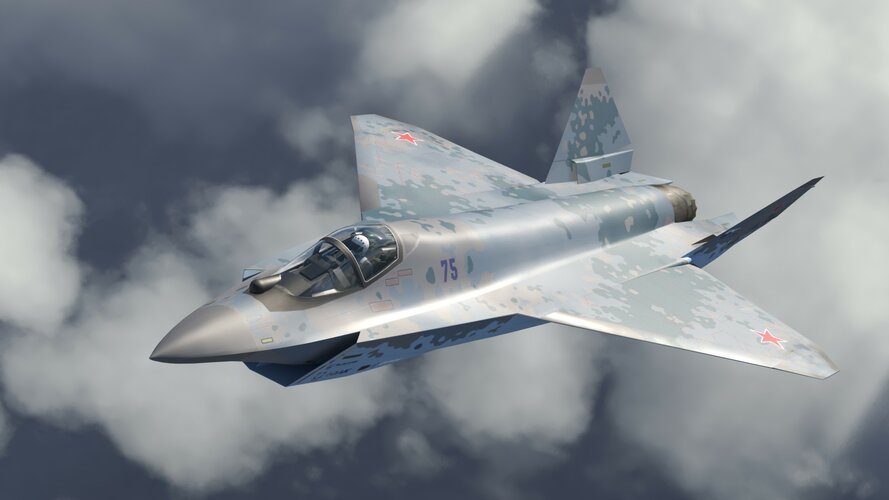

Russia is making renewed attempt to woo India with its Su-75 Checkmate light fighter jet, positioning it as the ideal successor to the aging MiG-29 fleet. This comes as India, along with several other nations, grapples with the need to replace their MiG-29s. The Su-75 Checkmate, unveiled in 2021, is a single-engine, lightweight stealth fighter that Russia touts as the ideal replacement for the MiG-29. Last year, design patents revealed a potential redesign, hinting at ongoing development efforts.
Russia has its sights set firmly on India, a long-standing partner and a nation actively seeking a replacement for its MiG-29 fleet. A 2021 Checkmate advertisement featuring pilots from potential buyer countries, including India, underscored Russia’s strategic marketing approach.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is gearing up to host its first-ever multinational air exercise, Tarang Shakti-2024, this August. The event, featuring participation from ten countries including the US, Germany, and France, is set to be a stage for a fierce competition between Boeing and Airbus for a lucrative aerial refueling contract.
The IAF is actively seeking to bolster its aerial refueling capabilities, aiming to acquire six new tanker aircraft to complement its existing fleet of Il-78MKIs. This push comes as India seeks to project its airpower further and maintain operational flexibility in its vast region.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
India’s efforts towards self-reliance in defense technology take a leap forward with the Uttam AESA radar. This indigenously developed active electronically scanned array radar is set to be integrated not just on the Tejas Mk1A fighter jets but also on a significant portion of the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) and Indian Navy’s fighter jet fleet.
The Uttam AESA radar was initially designed for the Tejas Mk1A variant, a crucial upgrade for India’s Light Combat Aircraft program. However, its capabilities have garnered wider interest. The radar will now be integrated on Naval MiG-29K Fighters, These carrier-borne fighters will benefit from the Uttam’s superior detection range and wider scanning angles compared to their current Russian Zhuk-ME radars. This will significantly enhance their situational awareness and combat effectiveness.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
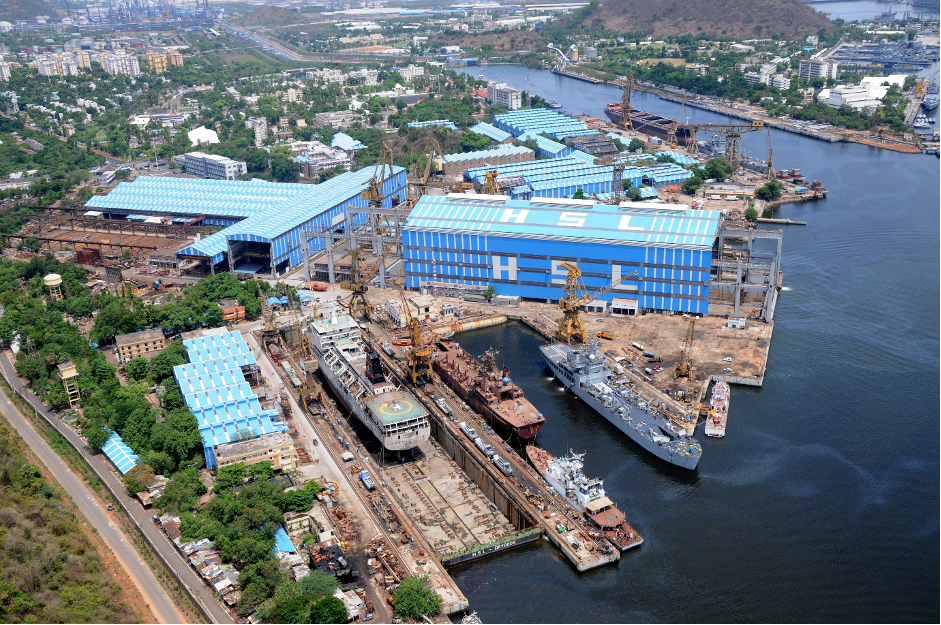

Fueled by rising global demand and government support, the Indian shipbuilding industry is setting its sights on a larger share of the global market, with a particular focus on attracting European shipowners.
Leading the charge is Garden Reach Shipbuilders (GRSE), a state-owned shipyard under the Ministry of Defense. Last week, GRSE inked a significant deal with German firm Carsten Rehder for the construction of four multi-purpose vessels, each with a capacity of 7,500 metric tons. This agreement marks a strategic pivot for GRSE, traditionally known for building warships.
Continue reading