SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
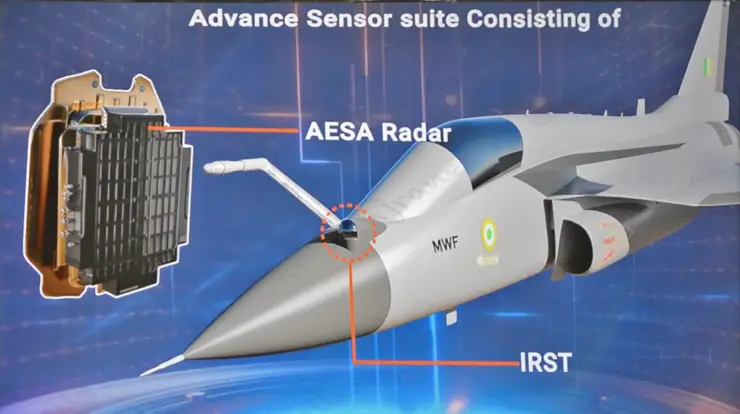

National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has released its annual report, shedding light on its innovative work in the development of Target Tracking Algorithms for Infrared Search & Track (IRST) applications. These advancements are part of a project sponsored by the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO), further reinforcing India’s capabilities in defence technology.
The report highlights the substantial progress made in the development of multi-target tracking algorithms for the IRST System and Missile Approach Warning System (MAWS) to be employed in advanced multi-role combat aircraft, including the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Mk-II and Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA).
Key highlights from the annual report include:
- Simulation Environments: NAL has successfully created simulation environments to replicate realistic scenarios involving one’s aircraft and various target situations. These simulations are crucial for evaluating the performance of multi-target tracking algorithms.
- Angle-Only Target Tracking Algorithms: The team has developed innovative tracking algorithms based on global nearest neighbourhood (GNN) and joint probabilistic data association (JPDA) techniques. These algorithms enhance the accuracy of tracking targets, a critical aspect in combat scenarios.
- Passive Ranging Algorithm: A passive ranging algorithm employing an Extended Kalman filter (EKF) in modified spherical coordinates has been developed for IRST applications. This algorithm aids in determining the range of detected objects without active radar emissions, ensuring a stealthy approach.
- Multi-Sensor Fusion: The NAL has carried out extensive work in multi-sensor fusion algorithm development. This involves the integration and fusion of data from various sensors, including radar, IRST, MAWS, and Radar Warning Receivers (RWR). Such fusion enhances the overall situational awareness and decision-making capabilities of the combat aircraft.
- Store Trajectory Computation: In collaboration with DRDO, NAL has developed algorithms for computing store trajectories for different configurations on the LCA. This is critical for understanding the separation characteristics of stores, inter-store separations, impact point computation, and stick distance achieved.
The development of these algorithms is a significant stride towards bolstering India’s defence technology capabilities, especially in the domain of airborne combat systems. It enables Indian combat aircraft to detect, track, and engage multiple targets effectively, enhancing their operational efficiency and battlefield readiness.
NOTE : Article cannot be reproduced without written permission of idrw.org in any form even for YouTube Videos to avoid Copy right strikes. Websites doing illegal reproductions will get DCMA and Legal Notices.