AFI
SOURCE: AFI


In a remarkable testament to India’s growing prowess in defense manufacturing and exports, the fiscal year 2023-24 has seen the United States, France, and Armenia emerge as the top three destinations for Indian military hardware. This development marks a significant milestone in India’s journey towards self-reliance in defense and showcases the country’s expanding influence in the global defense market.
India’s defense exports hit an all-time high, reaching ?21,083 crore ($2.6 billion) for the fiscal year 2023-24. This figure represents a substantial increase from previous years, underlining the success of initiatives like “Make in India” and “Aatmanirbharta” (self-reliance), which have been pivotal in boosting domestic production and export capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


India’s potential procurement of the Lockheed Martin F-35A Lightning II has been a subject of considerable debate among defense analysts. Recently, defense analyst Ranesh Rajan told AFI that India should only consider acquiring the F-35A if it receives full access to the fighter’s mission computer source code and AESA (Active Electronically Scanned Array) radar system, similar to what Israel has negotiated for its F-35I Adir variant. This access would allow India to integrate indigenous weaponry and communication systems, ensuring interoperability with Indian and Russian-made fighter jets like the Su-30MKI.
The F-35A, while one of the most advanced stealth fighters in the world, comes with strict operational restrictions imposed by the United States. These restrictions prevent foreign operators from fully customizing the aircraft’s systems to their own operational needs. If India were to acquire the F-35A under standard Foreign Military Sales (FMS) terms, it would face significant limitations in integrating Indian weaponry, upgrading subsystems, and ensuring seamless connectivity with its existing combat aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Harnessing the expertise and knowledge accrued from the construction of the MILGEM Class Ships, the Pakistan Navy is now setting its sights on a new horizon with the development of the JINNAH Class Frigates (JCF). This initiative marks a significant milestone as it will be the first instance of Pakistan designing and building a frigate-sized warship entirely on its own soil.
The MILGEM project, a collaborative effort with Turkey, has been instrumental in providing Pakistan with hands-on experience in shipbuilding, from design to commissioning. This partnership not only delivered four advanced corvettes to the Pakistan Navy but also facilitated a comprehensive transfer of technology (ToT), enabling Pakistani engineers and technicians to grasp the nuances of naval ship construction. The MILGEM ships, known in Pakistan as the Babur-class corvettes, have been a stepping stone, giving the Pakistan Navy the confidence and capability to embark on the more ambitious JCF project.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
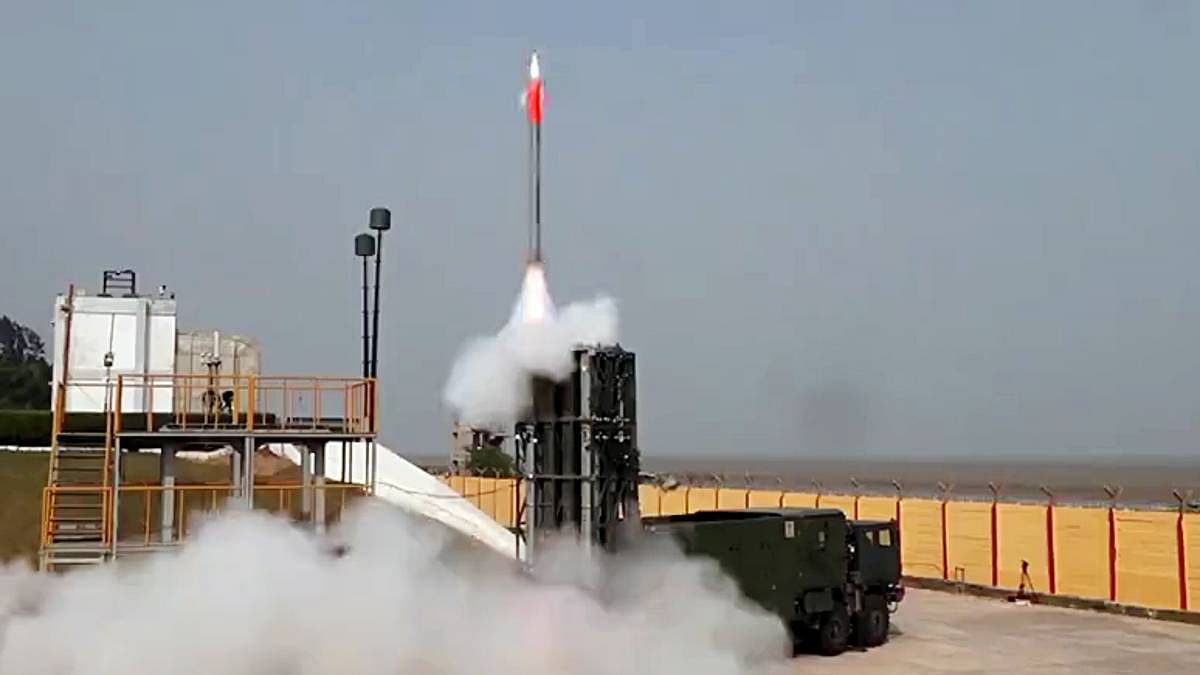


In a strategic move to fortify its defenses along the Eastern border with China, India has significantly ramped up the deployment of the Medium Range Surface-to-Air Missile (MR-SAM) system, in collaboration with Israel. This escalation in defense capabilities comes at a time when tensions remain high along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), particularly in the sensitive regions of Ladakh, Sikkim, and Arunachal Pradesh.
Ladakh, having been a focal point of recent border skirmishes, is already under the protective umbrella of both the MR-SAM and the indigenously developed Akash missile systems. The MR-SAM, known as “Abhra” in India, has been instrumental in providing air defence against a variety of aerial threats, including fighter jets, drones, and cruise missiles. The presence of these systems in Ladakh sends a clear message of India’s preparedness to safeguard its territorial integrity from air-based threats.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Founded in 2022 by Hitendra Singh and Kajal Rajbhar, T-Hub-incubated aerospace startup SpanTrik was born from a vision to transform humanity’s approach to space exploration. “Traditional rockets are magnificent feats of engineering but incredibly wasteful. After a mission, most of the rocket is lost, falling into the ocean. That’s why we are building ‘Raven,’ a fully reusable rocket designed to change the game,” explains co-founder Kajal Rajbhar.
Set to launch in 2028, Raven is SpanTrik’s flagship project designed to support a variety of missions, from deploying mega constellations of satellites and carrying payloads to the Moon to aiding humanity’s steps toward Mars. “Raven can carry 8 to 22 tonnes to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) and 5 tonnes to Mars. What sets it apart is its green propulsion system, which uses LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) and LOX (Liquid Oxygen). These fuels are environmentally friendly, aligning with our commitment to sustainability,” Kajal shares.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Mumbai’s innovative startup scene has just gotten a boost with Air Recon unveiling its game-changing ‘Quick-release Systems’ designed for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and Ground Control Systems (GCS). This breakthrough technology, tailored to integrate with standard-issue plate carriers, promises to enhance rapid deployment and maneuverability for tactical operations.
Air Recon’s Quick-release Systems represent a significant leap in the integration of drone technology with personal equipment.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


A newly unveiled scale model of the Tejas MkII highlights an advanced strike and air mission configuration, showcasing India’s growing indigenous combat capabilities. The model demonstrates an impressive combination of weaponry, reinforcing Tejas MkII’s role as a versatile multirole fighter.
The showcased loadout includes a diverse mix of air-to-air and air-to-surface weaponry, emphasizing its capability for deep strike and defensive operations. The configuration consists of.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In an insightful dialogue with Sputnik India, Igor Korotchenko, a noted military analyst and editor-in-chief of Russia’s ‘National Defense’ magazine, emphasized the strategic importance of an advanced aerospace defense system for India. Amidst an escalating Indo-Pacific arms race, Russia’s offer to aid India in building such a defense is seen not just as a military upgrade but as a monumental legacy for Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
India’s geopolitical landscape is fraught with challenges, primarily from its two neighboring rivals, China and Pakistan, both of whom boast sophisticated air forces and ballistic missile capabilities. Korotchenko articulates that in the realm of national defense, “A capable aerospace defense system is a mark of a global power and a top military state.” He draws parallels with even non-state actors like the Houthis, who have managed to develop capabilities in drones and ballistic missiles, underlining the necessity for India to fortify its defenses.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Hyderabad-based startup, Redon Systems, has made significant strides in defense technology with the development of an indigenous 6×3 wheeled, tube-launched loitering munitions system. The introduction of their Multi-Barrel UAV Launcher (MBUL) offers a new paradigm in the rapid deployment of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), providing a strategic advantage in military operations.
The MBUL system is engineered to launch up to 16 UAVs either simultaneously or in a rapid succession, which is critical in time-sensitive combat scenarios. The launcher uses a pneumatic barrel system, where launch angles can be customized to meet specific mission requirements. This innovation ensures minimal turnaround time for continuous UAV operations, with a reload time that supports uninterrupted engagements.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


A comparative analysis of the front sections of four modern frigates—the Chinese PLAN Type 054A (545), the French-Italian FREMM (F-597), the Indian Navy’s P17A (F33), and the Russian VMF Project 22350 (417)—reveals significant differences in armament, highlighting how the Indian P17A frigate might be underarmed in comparison.
Here, we delve into the weapon systems of each vessel to understand these disparities:
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The recently finalized Project-75I submarine program, under which Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) will construct all six German ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS)-designed submarines, highlights India’s commitment to bolstering its underwater fleet. However, this winner-takes-it-all approach has sparked a debate about missed opportunities for fostering competitive and parallel submarine construction capabilities in the country.
Larsen & Toubro (L&T), an Indian private sector defense and engineering giant, has demonstrated its expertise in complex defense projects, including nuclear submarines and other naval platforms. Allowing L&T to manufacture at least two of the six submarines under Project-75I could have delivered several strategic and economic benefits.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
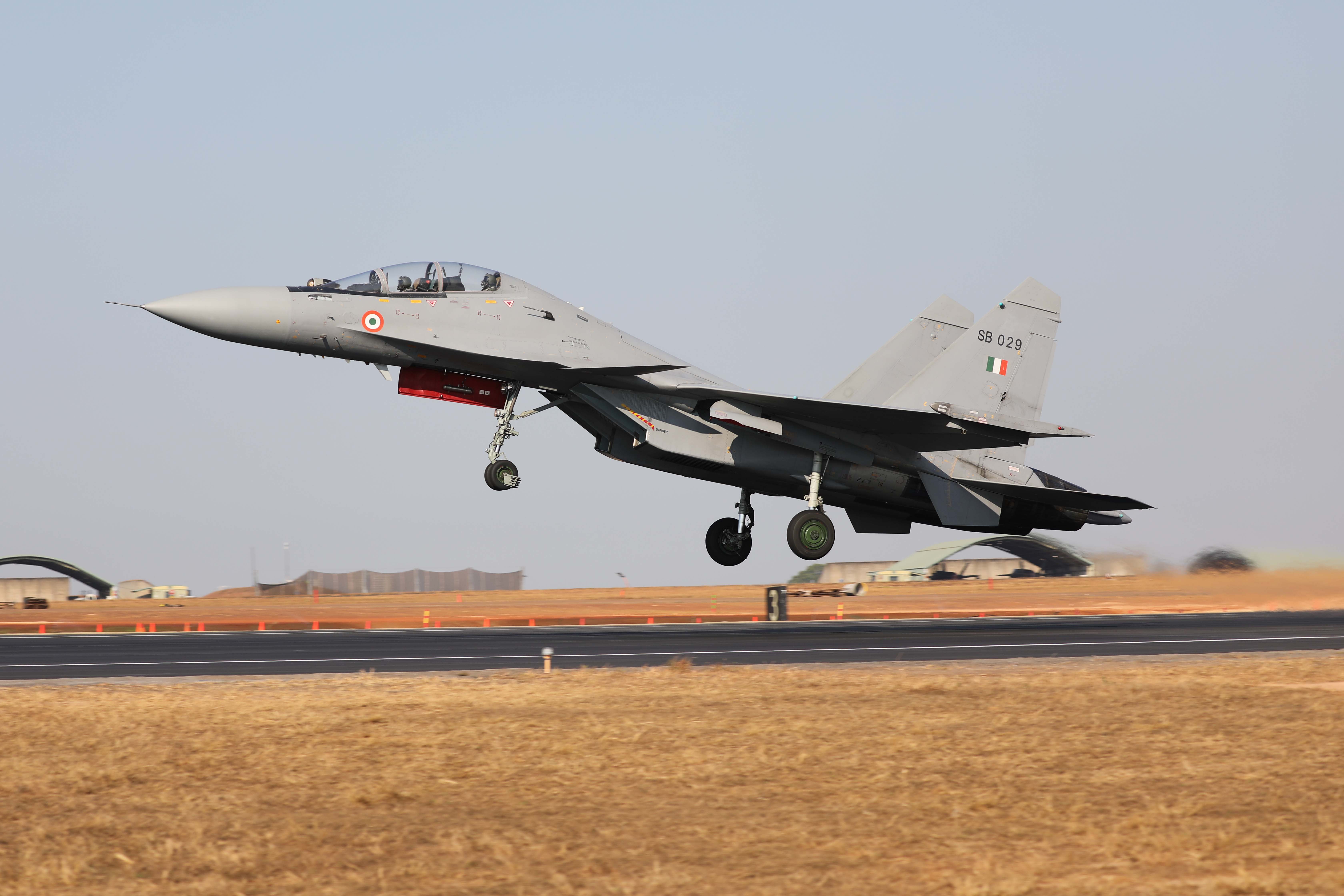


The saga of India’s Su-30MKI fighter jets, one of the largest fleets of its kind outside Russia, has highlighted a stark contrast in military technology independence between India and China. While India grapples with stringent Russian oversight for even minor modifications, China has progressed to reverse-engineering and enhancing the aircraft with domestically developed technology.
India, a long-standing ally of Russia in defense procurement, has faced significant constraints in modifying its Su-30MKI fleet. According to various reports, even changing a simple screw on these aircraft requires Russian approval to maintain warranty and technical support agreements. This dependency stems from the original technology transfer agreements where Russia provided the blueprints and technology for India to manufacture these jets under license, with stringent clauses on alterations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
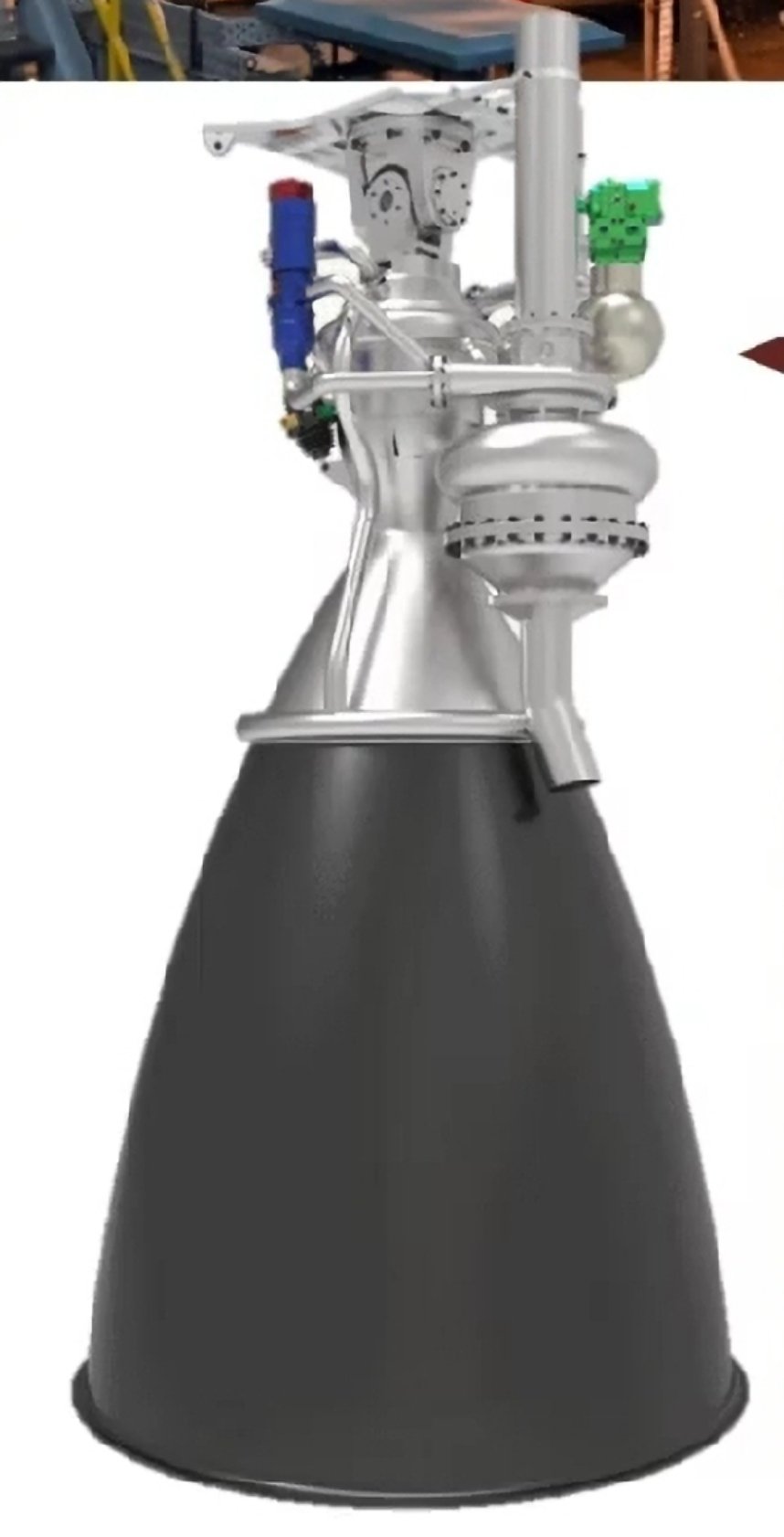


In a recent statement, Dr. M. Mohan, Director of the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC) at the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), shed light on the ongoing development of the LME-1100 methalox engine, which is pivotal for the new Next Generation Launch Vehicle (NGLV).
Dr. Mohan confirmed that the preliminary design of the LME-1100 has been completed, with detailed engineering currently in progress. He further outlined that ISRO is gearing up to prepare the engine for its hot test, a crucial step towards completing the engine’s qualification. The development and testing activities are slated to commence this year, marking a significant milestone in India’s space capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

A recent analysis comparing the construction timelines of naval ships in various countries has spotlighted a significant lag in India’s warship building pace. According to the data, Indian shipyards take an average of 85 months from the block erection phase to the commissioning of a warship, a stark contrast to other nations in the region.
For instance, Japan, known for its efficiency in shipbuilding, completes the same process in just 27 months. This remarkable speed is attributed to advanced shipbuilding techniques, stringent project management, and a well-integrated supply chain. Meanwhile, France, another major player in naval construction, takes around 46 months to commission its warships, offering a middle ground but still far quicker than India.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
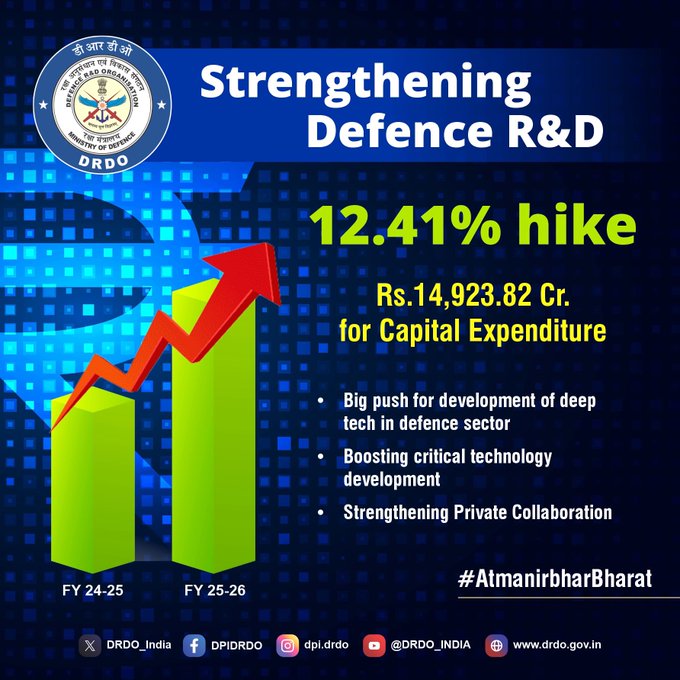

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has received a significant boost in its budget allocation for the financial year 2025-26. The Government of India has allocated ?26,816.82 crore to DRDO, reflecting a 12.41% increase from the previous fiscal year’s allocation of ?23,855.61 crore. This increase underscores the government’s commitment to strengthening indigenous defense research and development.
A substantial portion of the allocated budget, amounting to ?14,923.82 crore, has been earmarked for capital expenditure and research & development (R&D). This increase is expected to drive the development of cutting-edge defense technologies and enhance collaboration with the private sector, fostering a self-reliant defense ecosystem.
Continue reading