AFI
SOURCE: AFI
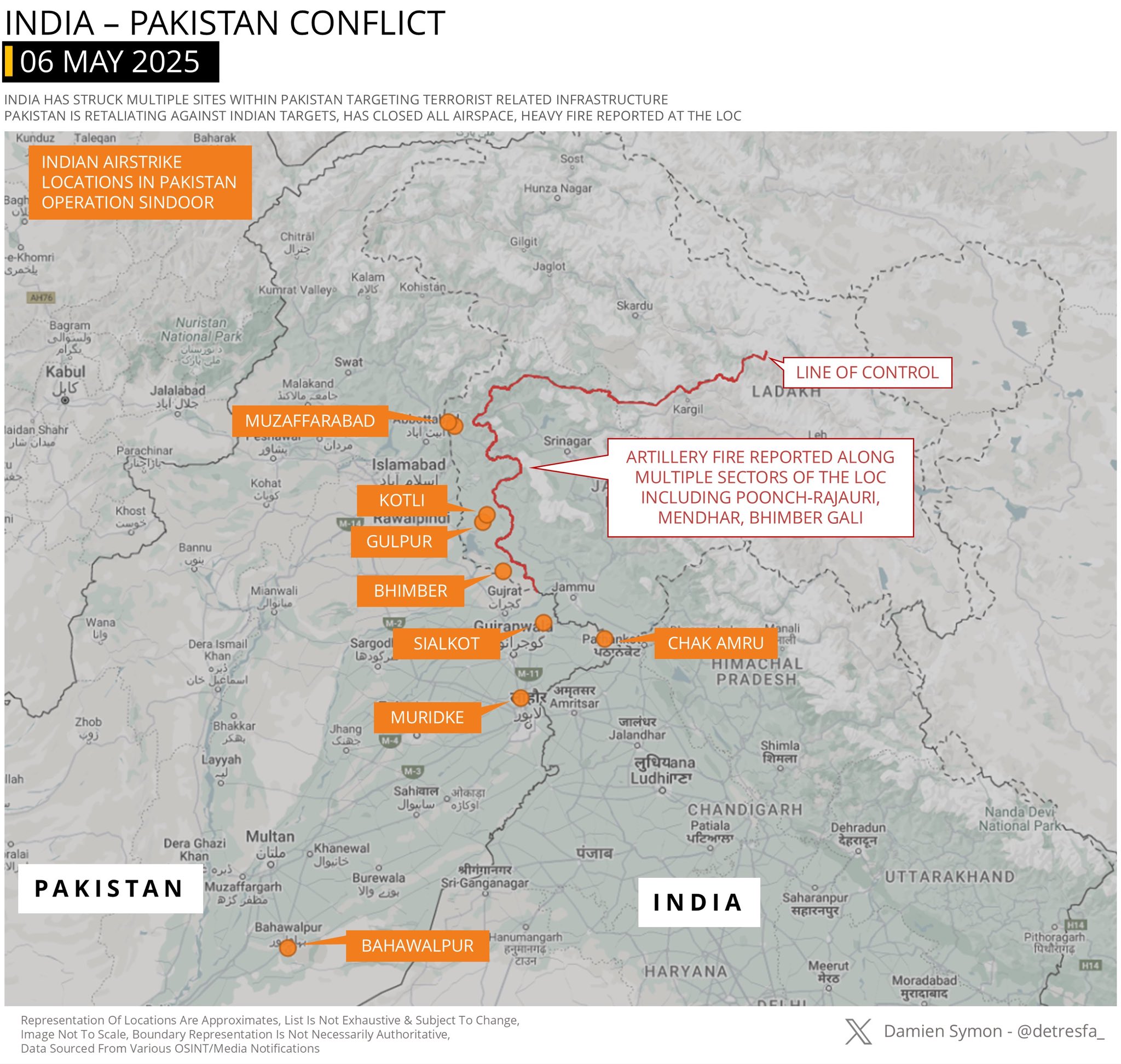

On the morning of May 6, 2025, India launched a series of precision airstrikes under Operation Sindoor, targeting terrorist-related infrastructure within Pakistan. The operation has escalated tensions between the two nuclear-armed neighbors, with Pakistan retaliating against Indian targets, closing its airspace, and heavy artillery fire reported along multiple sectors of the Line of Control (LoC).
Below is a detailed breakdown of the locations struck by Indian missiles, as mapped out in the latest reports.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On May 7, 2025, Pakistan’s Defence Minister Khawaja Muhammad Asif (@KhawajaMAsif ) retracted an earlier statement claiming that Pakistani forces had captured Indian soldiers as prisoners of war (PoWs) during the ongoing military escalation with India. Speaking live on ARY News, Asif also claimed that while Indian posts along the Line of Control (LoC) were abandoned, no Indian soldiers were taken as prisoners, directly contradicting earlier reports attributed to him. This development comes amidst heightened tensions following India’s Operation Sindoor airstrikes on May 6, which targeted terrorist infrastructure in Pakistan and Pakistan-administered Kashmir.
The current flare-up stems from India’s Operation Sindoor, launched on May 6, 2025, in response to the April 22 Pahalgam terror attack that killed 26 civilians, mostly Hindu tourists, in Indian-administered Kashmir. India blamed Pakistan for supporting the attack and conducted precision airstrikes on nine sites, including Muzaffarabad, Kotli, Bhimber, Sialkot, and Bahawalpur, using Rafale jets likely armed with SCALP cruise missiles and Hammer standoff weapons. Pakistan reported eight civilian deaths and 35 injuries, calling the strikes a “blatant act of war” and vowing retaliation. Heavy artillery fire has since been reported along the LoC, with both sides accusing each other of aggression.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On May 5, 2025, an Indian Navy Boeing P-8I maritime patrol aircraft (MPA) conducted operations over the Arabian Sea, drawing significant attention on social media. Flight tracking data revealed the aircraft’s position at 05:30 UTC, approximately 130-150 km from Pakistan Navy ships engaged in firing drills near Karachi, scheduled from 05:00 UTC on May 5 to 15:00 UTC on May 6. The P-8I’s estimated 350-km surface vessel detection range, as depicted in operational maps, covered a vast swathe of the ocean, extending deep inland towards Karachi and beyond.
This operation underscores the Indian Navy’s robust surveillance capabilities. Equipped with advanced sensors, the P-8I likely mapped not only Pakistan’s naval assets but also activities well into its coastal territory. This comes as a stark reality check for Pakistani observers who, on the previous night, shared videos claiming to have “tracked” the Indian aircraft. Far from being on the defensive, the P-8I’s vantage point suggests it held the upper hand, monitoring Pakistan’s drills comprehensively.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


As geopolitical tensions between India and Pakistan reach a boiling point in 2025, the specter of missile attacks on major Indian cities looms larger than ever before. The recent escalation, triggered by the April 22, 2025, terror attack in Pahalgam, Jammu and Kashmir, which killed 26 people, has pushed the two nuclear-armed neighbors into a dangerous standoff.
With both nations now possessing advanced missile capabilities capable of striking each other’s urban centers, Indian civilians and authorities must brace for a potential conflict unlike any seen in the four wars fought between the two countries since 1947. For the first time, the threat of civilian casualties from missile strikes on major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, or Bengaluru is a grim possibility, necessitating mental and logistical preparedness for a protracted and unprecedented conflict.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Over the years, India’s military strategy towards Pakistan has often revolved around the concept of swift, punitive responses to provocations — exemplified by surgical strikes and air raids such as the Balakot operation in 2019. While short, sharp conflicts may satisfy immediate political and military objectives, they do little to permanently shift the strategic calculus in India’s favor. In fact, a short war, no matter how successful, risks international intervention, escalatory miscalculations, and only temporary deterrence.
Instead, India must pivot towards preparing for a long war — a sustained, multidimensional campaign that would exploit Pakistan’s deep economic vulnerabilities, stretch its military logistics, and force a reckoning within its national security establishment. Such a conflict, while demanding for India, could be disastrous for Pakistan, leading to long-term strategic degradation and possibly a collapse of its coercive leverage.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


India’s defense capabilities received a major boost with the recent procurement of 26 Rafale-Marine (Rafale-M) aircraft for the Indian Navy, a deal signed on April 28, 2025, as reported by Republic World. This acquisition complements the 36 Rafale jets already in service with the Indian Air Force (IAF), but while the two variants share core technologies, the Rafale-M is uniquely tailored for naval operations. Here’s a closer look at how the Navy’s Rafale-M differs from the IAF’s Rafale fleet and what this means for India’s military strategy.
The Rafale-M is designed specifically for carrier-based operations, a stark contrast to the IAF’s Rafale C, which operates from land-based airfields. The Rafale-M features reinforced landing gear and a tail hook, enabling it to handle the stresses of landing on the short runways of aircraft carriers like INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant. Its airframe is also strengthened to endure the rigors of catapult launches and arrested landings, a necessity for naval aviation but irrelevant for the IAF’s land-based operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The escalating tensions between India and Pakistan, particularly following the April 22, 2025, Pahalgam terrorist attack that killed 26 tourists, have underscored the need for India to leverage non-military tools to counter Pakistan’s sponsorship of cross-border terrorism. One potent strategy is to fund the construction of dams on Afghan rivers, such as the Kabul and Kunar, which flow into Pakistan’s Indus River system.
By supporting Afghanistan’s hydropower and irrigation projects, India can reduce water flows to Pakistan, exerting economic pressure on its agriculture-dependent economy while strengthening ties with Kabul. This approach, exemplified by India’s funding of the Shahtoot Dam, aligns with New Delhi’s broader geopolitical strategy to isolate Pakistan and promote regional stability, serving as a precursor to any kinetic actions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On the night of May 4-5, 2025, Commodore Ahmed Hussain SI(M), Director General Public Relations (Navy) and spokesperson for the Pakistan Navy, announced on the official @PakistanNavy
X account that an Indian Navy P-8I aircraft was under the “vigilant watch” of Pakistan’s naval forces. The statement, intended to showcase the Pakistan Navy’s surveillance capabilities, quickly backfired, drawing widespread ridicule from Indian commentators and netizens.
The Indian Navy’s P-8I, a maritime patrol aircraft derived from the Boeing 737, is equipped with advanced sensors for reconnaissance and anti-submarine warfare. However, it is not a stealth aircraft, and its presence is easily detectable, especially when operating in international airspace. On this occasion, the aircraft was openly broadcasting its location on FlightRadar24, a public flight-tracking platform, making its movements visible to anyone with internet access.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


A comprehensive digital investigation conducted by Digital Lab Voyager Infosec and ISPRMonitor has debunked Pakistan’s claims of Indian involvement in terrorist attacks, revealing a web of fabricated evidence presented by Pakistan’s Inter-Services Public Relations (ISPR). Published on May 4, 2025, by The Economic Times, the investigation exposes doctored screenshots, timeline inconsistencies, and manipulated financial trails, indicating a deliberate effort by Pakistan to engineer a false narrative blaming India for attacks, including the April 22, 2025, Pahalgam terror attack in Jammu & Kashmir.
This revelation, amid escalating tensions between the two nations, underscores Pakistan’s disinformation tactics and strengthens India’s position as a victim of cross-border terrorism.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
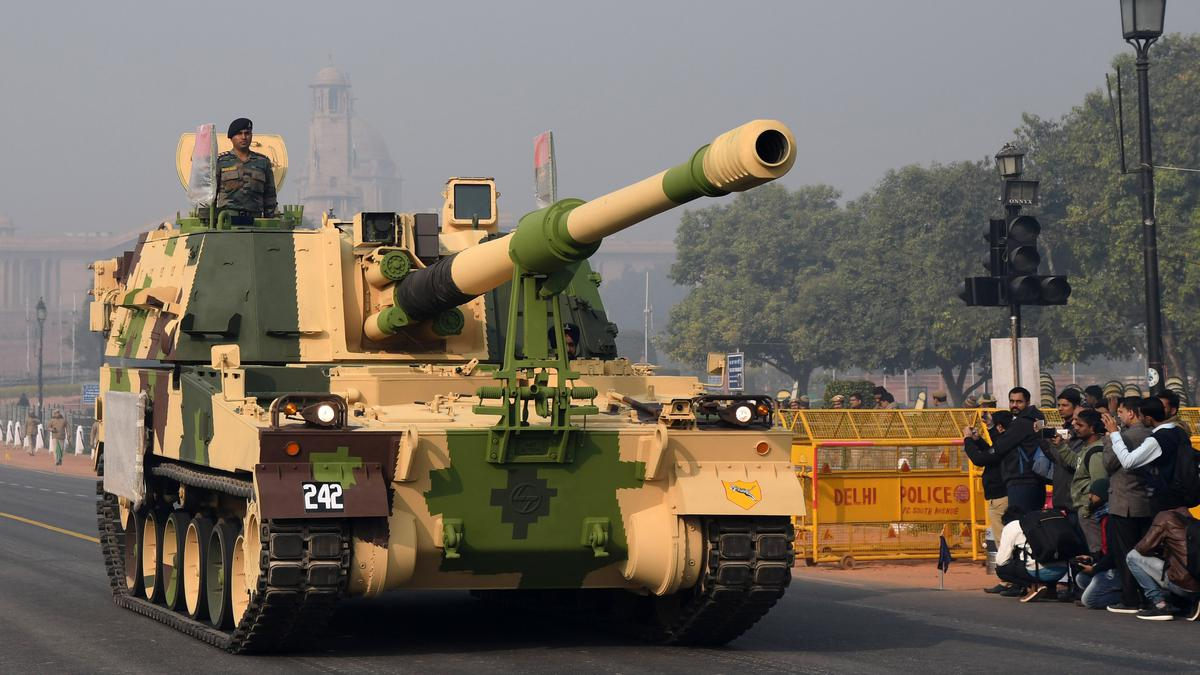


As tensions escalate along the Line of Control (LoC) following the April 22, 2025, terror attack in Pahalgam, Kashmir, which claimed 26 lives, Pakistan has intensified its military buildup, deploying advanced Chinese-made SH-15 155mm truck-mounted howitzers. This move, part of a broader defense enhancement involving air defense units, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and military exercises like Fiza-e-Badr, Lalkar-e-Momin, and Zarb-e-Haideri, aims to counter India’s formidable artillery capabilities, particularly the K-9 Vajra self-propelled howitzer.
The SH-15, acquired by Pakistan under a 2019 agreement with China’s NORINCO, is a 155mm/52-caliber wheeled howitzer mounted on a 6×6 Shaanxi truck chassis, designed for mobility and rapid deployment. With a range of 20 kilometers using conventional shells and up to 53 kilometers with rocket-assisted projectiles, the SH-15 boasts a fire rate of 4-6 rounds per minute and is operated by a crew of five. Its bulletproof cabin and computerized fire control system enhance survivability and targeting accuracy, while its lightweight 22-ton design suits diverse terrains, including hilly regions along the LoC. Pakistan’s deployment of approximately 52-200 SH-15 units, intended to replace older U.S.-made M109A5 howitzers, reflects its strategic reliance on Chinese technology to bolster firepower.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant escalation of economic fallout from the ongoing India-Pakistan tensions, major global airlines, including Lufthansa, Air France, British Airways, Swiss International Air Lines, Emirates, ITA Airways, and LOT Polish Airlines, have voluntarily ceased using Pakistani airspace, opting for longer routes to avoid the region. This development, spurred by heightened geopolitical risks following the April 22, 2025, terror attack in Pahalgam, Jammu and Kashmir, is dealing a severe blow to Pakistan’s economy, already strained by a precarious financial situation. The move, described by some as Pakistan’s “reckless airspace games,” is costing the country millions in lost overflight fees while amplifying regional instability.
The decision by these carriers comes in the wake of Pakistan’s closure of its airspace to Indian airlines on April 24, 2025, a retaliatory measure following India’s accusation of Pakistani involvement in the Pahalgam attack, which claimed 26 lives. India reciprocated by barring Pakistani carriers from its airspace until May 23, 2025, further intensifying the diplomatic standoff. While Pakistan initially allowed international airlines to continue using its airspace, the voluntary avoidance by major European and Middle Eastern carriers has compounded the economic damage, as these airlines reroute flights over the Arabian Sea, Iran, or Central Asia to reach destinations like Delhi, Bangkok, and Ho Chi Minh.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The 2019 Balakot air strike, conducted by the Indian Air Force in response to a terror attack in Pulwama, marked a significant escalation in tensions between India and Pakistan. The subsequent air skirmish highlighted vulnerabilities in both nations’ air defense systems, prompting a rapid push to acquire advanced Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) systems to bolster their aerial defense capabilities.
Since then, both countries have taken delivery of several major SAM systems to enhance their strategic deterrence and protect their airspace. This article explores the key SAM acquisitions by India and Pakistan post-2019, their capabilities, and the implications for regional security.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a recent Medium article titled The Rise of the PAF: Asia’s Third Air Power, published on May 4, 2025, Amir Husain claims that the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) is poised to become Asia’s third most powerful air force, trailing only Russia and China, based on nine analytical pillars. Husain cites the PAF’s modernization, including fifth-generation fighters like the J-35, Turkish KAAN, and indigenous PFX, alongside a robust drone fleet, cyber capabilities, and infrastructure redundancy.
However, a critical examination reveals that these claims are overstated, rooted in speculative projections rather than current realities. In 2025, the PAF ranks fourth in Asia, behind China, India, and South Korea, with significant gaps in fleet size, technological sophistication, and operational readiness that undermine Husain’s assertions. This article counters Husain’s narrative, highlighting the PAF’s limitations and why the Indian Air Force (IAF) and others maintain a clear edge.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On May 3, 2025, Pakistan conducted a test-firing of its Abdali (Hatf-II) tactical ballistic missile, a land-based, road-mobile system designed to target enemy installations and assets. The test, part of Exercise INDUS, aimed to validate operational readiness and technical parameters, including advanced navigation and maneuverability, amid heightened tensions with India following the April 22, 2025, Pahalgam terrorist attack.
Official Pakistani statements claim the Abdali has a range of 450 km, though open sources, including Wikipedia, cite a range of 180–200 km. With a Circular Error Probable (CEP) of 100–150 meters and conventional warheads—High Explosive (HE) or Improved Conventional Munitions (ICM)—the Abdali poses a limited but notable threat to India’s forward military bases and infrastructure. This article evaluates the Abdali’s capabilities, the strategic threat it presents, and how India’s layered air and missile defense systems, including MR-SAM, Akash-NG, and Ashwin (AAD), can effectively counter it.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a remarkable display of technological prowess, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully conducted a sophisticated mock “dogfight” in space, utilizing its Space Docking Experiment (SpaDeX) satellites, SDX01 (Chaser) and SDX02 (Target). This high-stakes maneuver, reported on May 4, 2025, by Deccan Herald, involved precise, close-quarters orbital maneuvers at speeds of 28,800 km/h, approximately 28 times faster than a commercial jet, in a low Earth orbit 475–500 km above Earth. T
he operation, metaphorically termed a “dogfight” due to its resemblance to aerial combat maneuvers, showcases India’s growing capabilities in autonomous satellite operations and positions it as a formidable player in space technology, following in the footsteps of China, which conducted similar exercises in 2024. This article explores the significance of ISRO’s achievement, the technical details of the SpaDeX mission, and its implications for India’s space ambitions, amidst regional tensions with China and Pakistan.
Continue reading