Monthly Archives: January 2025
SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
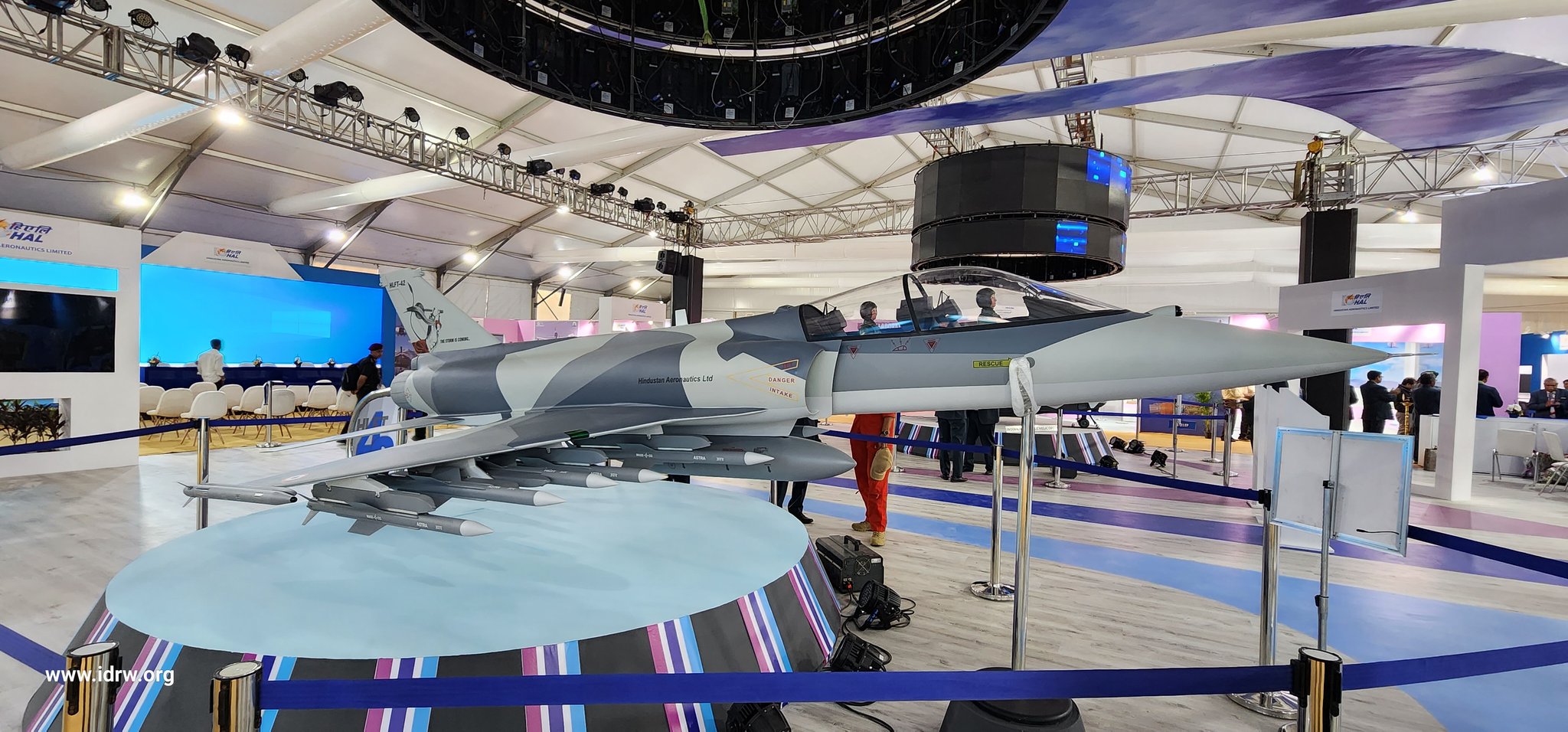


India’s defence aviation landscape is on the cusp of a technological leap as plans for the proposed Hindustan Aeronautics Limited Fighter Trainer-42 (HLFT-42) likely will incorporate cutting-edge artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. Designed to enhance pilot cadets’ learning and boost operational combat capabilities, the HLFT-42 could redefine how fighter pilots are trained in the country.
AI integration in the HLFT-42 is expected to transform training methodologies through the inclusion of virtual tactical training systems. These systems would enable cadets to simulate and practice various combat scenarios, ranging from short-range dogfights to mid- and long-range engagements. By exposing pilots to realistic combat situations in a controlled environment, this technology promises to sharpen skills and improve decision-making under pressure.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


India has reportedly received offers from Germany and Spain to join their 6th Generation Future Combat Air System (FCAS) program, as well as an invitation from the UK-Japan-Italy consortium to participate in their Global Combat Air Program (GCAP). While these proposals signal the growing recognition of India as a strategic defence partner, New Delhi remains committed to its indigenous Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, a 5.5-generation fighter jet project designed to bridge the gap between 5th and 6th-generation technologies.
While official discussions between the UK and India regarding GCAP have been confirmed, India has yet to publicly acknowledge the proposals from Germany and Spain.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
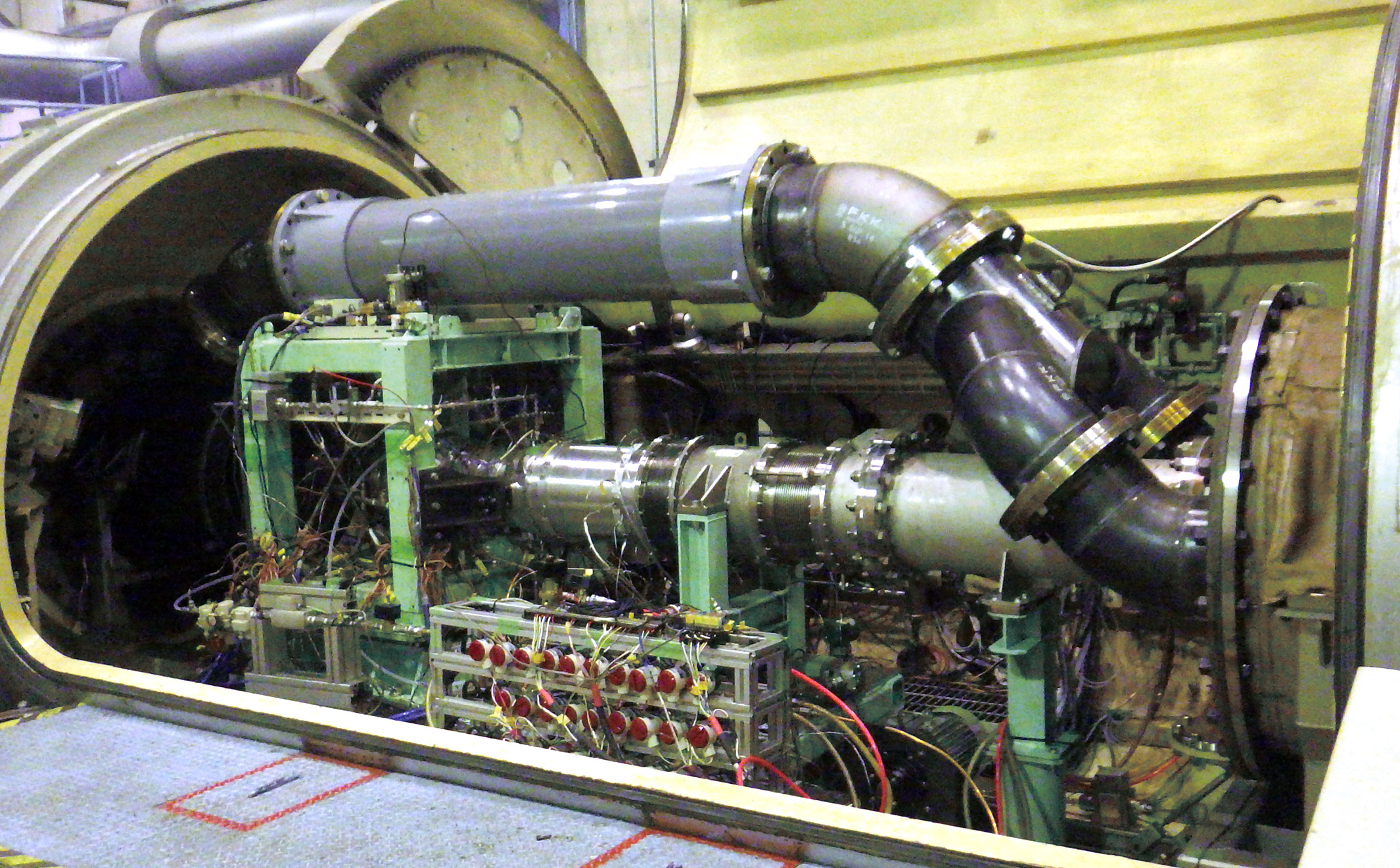

The Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE), a premier lab under India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has put forward a proposal to establish a state-of-the-art high-altitude test facility. This facility aims to simulate conditions at altitudes above 40,000 feet, providing a critical platform for the thorough testing and analysis of jet engine performance under conditions that closely mimic operational environments.
The proposed investment of ?1600 crores would enable GTRE to domestically conduct tests that are currently outsourced, particularly to facilities like the Central Institute of Aviation Motors (CIAM) in Russia. The absence of such a facility in India has been a significant bottleneck in the development of indigenous jet engines, including the much-discussed Kaveri engine and its derivatives, which are pivotal for the success of projects like the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA).
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
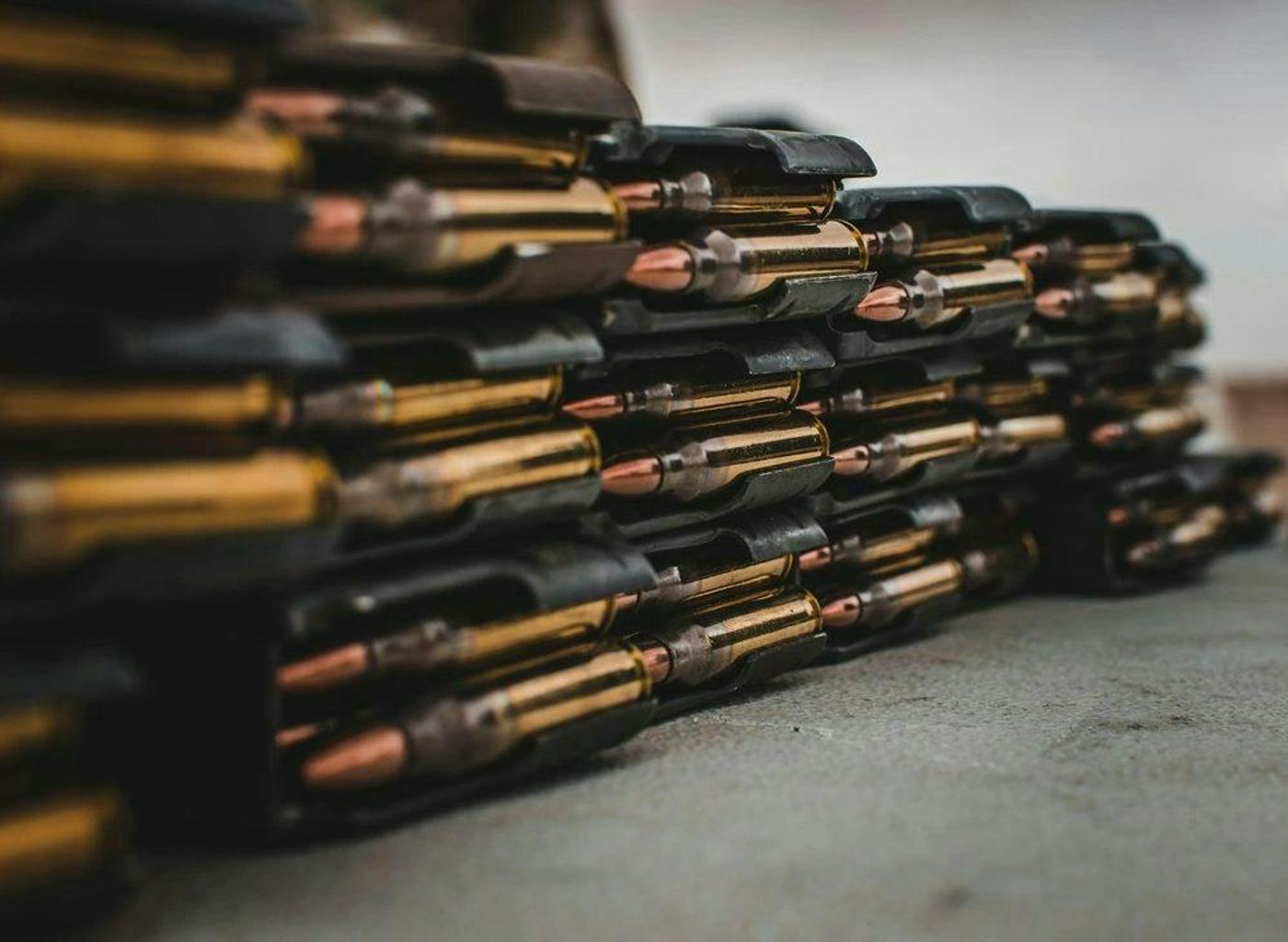


The Ministry of Defence (MoD) of India has marked a significant milestone in its journey towards self-reliance in military capabilities by indigenising the production of 154 out of 175 ammunition variants required by the Indian Army. This achievement represents an impressive 88% indigenisation rate, as part of a strategic 10-year plan to achieve complete self-sufficiency in firepower, crucial for enduring prolonged warfare scenarios.
This drive towards indigenisation is part of a broader initiative to reduce India’s dependence on foreign arms imports, aligning with the government’s ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ (Self-Reliant India) campaigns. The MoD’s focus has been on ensuring that the Indian Army can maintain operational readiness without the vulnerabilities associated with supply chain disruptions from foreign suppliers.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In recent developments from the Chinese aerospace industry, a sixth-generation fighter jet, believed to have made its maiden flight on December 26, 2024, has captured the attention of military analysts worldwide. Japanese defense experts have commented on this new aircraft, with some reactions encapsulated in the phrase, “China is amazing,” hinting at a possibly orchestrated narrative of Chinese technological superiority. However, beneath this surface praise, there lies a more critical and skeptical analysis.
The jet’s design has been a focal point for Japanese analysts, particularly its unique three-engine configuration. One expert noted, “The first thing worth pointing at and laughing at is that it’s a three-engine aircraft.” Historically, adding an extra engine to aircraft, often seen during wartime conversions of transport planes into bombers, was more out of necessity due to insufficient power than a choice for advanced design. The placement of the engine intakes is another point of contention. With one intake positioned at the rear of the cockpit, it’s described as “just ridiculous” by some, drawing comparisons to more experimental or fictional aircraft designs like the Focke-Wulf or those from anime series like “Yukikaze” and video games like “Ace Combat.”
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant boost to India’s defense capabilities, Bengaluru-based Tonbo Imaging has confirmed the dispatch of the second lot of Arjun Thermal Imaging (TI) Sights under a capital procurement contract for Medium Machine Guns (MMGs) for the Indian Army. This development marks Tonbo Imaging’s steadfast commitment to providing cutting-edge night vision and imaging solutions to the nation’s military forces.
The announcement was made with a sense of national pride, emphasizing the indigenous design and manufacturing of the Arjun TI Sights. “Proudly #madeinindia, for #India!” was the celebratory message from Tonbo Imaging, highlighting their role in supporting India’s defense autonomy and innovation as the country moves into 2025.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


In an era where aerial warfare is increasingly defined by stealth, range, and payload capacity, defense analyst Ranesh Rajan advocates for the Indian Air Force (IAF) to explore the possibilities of scaling up the design of the Ghatak Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle (UCAV) into a manned, 50-ton stealth bomber. Rajan’s proposal comes at a time when India seeks to assert its technological dominance in the region and beyond.
The Ghatak, initially a project for developing an autonomous unmanned combat aerial vehicle, has shown promise with its stealth capabilities and flying wing design. Rajan suggests that by upscaling this design into a manned configuration, India could leapfrog into the domain of strategic bombers, akin to the U.S. B-2 Spirit or the forthcoming B-21 Raider but tailored to India’s specific strategic needs.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a significant stride towards enhancing naval capabilities, Hyderabad-based Navstar Integrated Systems Pvt. Ltd has announced the successful development of a series of multifunction antenna systems specifically designed for submarines. This innovation aims to consolidate various communication and navigation functions into a single, streamlined system, thereby reducing the complexity and footprint on submarine platforms.
Navstar’s new antenna suite includes:
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant stride towards self-reliance in aerospace technology, the Delhi-based startup, DG Propulsion, has successfully conducted a test-run of its indigenous 100kg (1 kN) engine. This achievement marks a pivotal moment in India’s quest to bolster its capabilities in defense and unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology.
DG Propulsion, known for its innovative approach to jet engine development, has been at the forefront of creating homegrown solutions for high-speed UAVs and defense applications. The successful test of the 100kg engine not only showcases the company’s technical prowess but also aligns with India’s broader initiative to reduce dependency on foreign technology in critical sectors.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In an exclusive analysis, an experienced U.S. fighter pilot with over 2,000 hours in the F-16 and F-4, known here as “Bod,” shares his insights on China’s latest military aircraft, the JH-XX, which has recently been showcased in various online platforms. The discussion focuses on the capabilities, design, and potential strategic roles of this new stealth fighter bomber.
Bod’s initial reaction to the JH-XX was one of surprise at its size, noting, “The first thing that comes to mind is it’s big. I mean, that is a big fighter.” The aircraft’s large delta wing configuration immediately raises questions about its maneuverability, particularly in dogfighting scenarios due to the high wing loading which can bleed off energy quickly during maneuvers.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
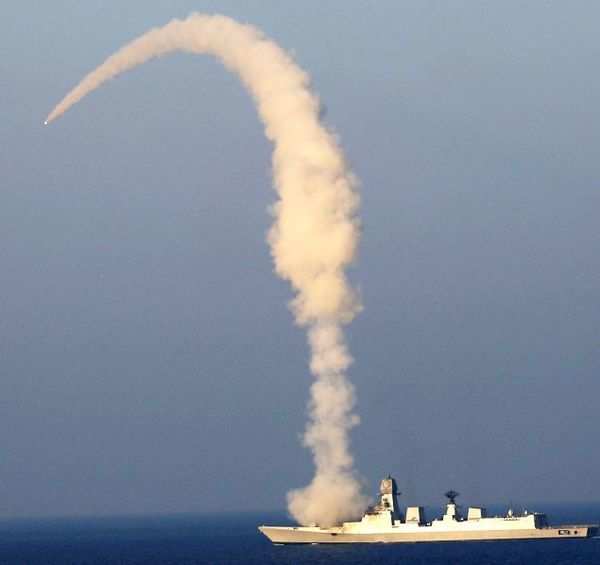


In an insightful discussion with TaiwanPlus, Don McLain Gill, a lecturer at De La Salle University in Manila, shed light on Vietnam’s strategic intentions behind potentially acquiring the BrahMos missile system from India. Gill highlighted the increasing tensions in the Gulf of Tonkin, where Chinese maritime forces have reportedly attacked Vietnamese fishermen with iron clubs and detained others, underscoring the urgency for Vietnam to bolster its defense capabilities.
“China, for instance, has been pushing the envelope in its claim over the Gulf of Tonkin. In the past few weeks, we’ve seen Chinese maritime forces beat Vietnamese fisherfolk with iron clubs, and of course, there’s the imprisonment or detainment of Vietnamese fishermen,” Gill stated. These incidents form part of Vietnam’s strategic calculations in seeking deterrents like the BrahMos missile, which could serve as a significant counterbalance to China’s aggressive maritime posturing.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Marking a significant day in India’s maritime history, January 15, 2025, is set to witness the simultaneous commissioning of three formidable combatants at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai, showcasing the Indian Navy’s growing prowess and the nation’s strides towards self-reliance in defense manufacturing.
This event will not only enhance the operational capabilities of the Indian Navy but also affirm India’s standing as a leading force in indigenous shipbuilding. The ceremony at the Naval Dockyard, Mumbai, will likely be attended by defense dignitaries, government officials, and representatives from the shipbuilding industry, underscoring the national importance of this event. It will serve as a proud moment for all involved, from the naval personnel who will operate these platforms to the engineers and workers who built them.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a recent statement to SAMAA TV, Foreign Office spokesperson Mumtaz Zahra Baloch asserted that Pakistan possesses “concrete evidence” of India conducting targeted killings within its borders. These operations, according to Baloch, are primarily aimed at individuals believed to be associated with Kashmiri terrorism on the Indian side of Kashmir.
“Pakistan has concrete evidence of India carrying out targeted killings inside Pakistan, mostly targeting people who are associated with Kashmiri’s terrorism inside the Indian side of Kashmir,” Baloch stated. This claim adds fuel to the already tense relations between the two neighboring countries, which have long been at odds over issues including territorial disputes, cross-border terrorism, and the situation in Kashmir.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a strategic move to address the ongoing delays in the supply of the high-thrust F404-IN20 engines for the Tejas Mk1A light combat aircraft, General Electric (GE) has proposed an interim solution to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). GE suggests using the lower thrust F404-GE-102 engines, which are currently manufactured by Samsung Techwin for the Korean KAI/LMTAS T-50 advanced trainer/light fighter.
The F404-GE-102 engines offer a maximum thrust of 78.7 kN with afterburner, which is slightly less than the 84 kN provided by the F404-IN20 engines specifically designed for the Tejas Mk1A. These engines are suggested as a stopgap measure until the production of the F404-IN20 engines can be ramped up to meet HAL’s requirements. Once the new engines are available, the lower thrust versions could be swapped out.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Indian Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) has announced that the Kaveri derivative engine is gearing up for another significant phase of testing. This round involves 70 hours of crucial flight trials on a Russian Ilyushin Il-76 testbed, a process expected to span nearly a month.
The technology demonstrator engines have already logged over 140 hours of testing. This includes 70 hours of ground testing at GTRE’s facility in Bangalore and an additional 75 hours of altitude testing at the Central Institute of Aviation Motors (CIAM) in Russia.
Continue reading