SOURCE: PTI


The Bombay High Court on Wednesday refused to provide any relief to a Dalit PhD student suspended from the Tata Institute of Social Science (TISS) for alleged misconduct and anti-national activities.
A division bench of Justices A S Chandurkar and M M Sathaye dismissed the plea filed by the student, Ramadas K S, against the institute’s April 2024 decision of suspending him for two years. “The order suspending the petitioner (Ramadas) does not suffer from any illegality or perversity. We find that this is not a fit case to interfere. There is no merit in the petition and the same is dismissed,” the HC said.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Air Force (AF) Mk2, an advanced iteration of India’s indigenous fighter program, is being designed with cutting-edge engineering principles to optimize productivity, quality, and operational efficiency. According to an engineer from the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) speaking to idrw.org, the Mk2 incorporates Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA), Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing (GD&T), and Tolerance Stack-Up Analysis to ensure precision, interchangeability, and ease of production.
These features, combined with modular construction and Model-Based Design (MBD) concepts, promise to slash aircraft cycle times and reduce effective operating costs—positioning the Mk2 as a cost-effective yet potent addition to the Indian Air Force (IAF) by its projected induction in the early 2030s.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


In a recent interview with idrw.org, prominent defence analyst Ranesh Rajan weighed in on the evolving timeline of the Twin Engine Deck-Based Fighter (TEDBF) program for the Indian Navy, arguing that the Indian Air Force (IAF) was justified in distancing itself from the project. The TEDBF, designed to meet the Navy’s need for a carrier-capable 4.5++ generation fighter, has seen its development schedule slip significantly, with the first flight now projected for 2030 and induction delayed to 2038.
Rajan contends that these delays render the program irrelevant for the IAF, which is better served focusing on the Tejas MkII and the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) to meet its future combat needs.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of India has recently unveiled its expansive plans to bolster the nation’s defense capabilities through the development of 12 distinct hypersonic missile systems. This ambitious program encompasses a range of technologies, including Hypersonic Glide Vehicles (HGVs), anti-hypersonic missile systems, and hypersonic cruise missiles, positioning India as a formidable contender in the global race for advanced missile technology.
As nations like the United States, Russia, and China accelerate their own hypersonic programs, India’s multi-pronged approach aims to ensure strategic deterrence and operational superiority across diverse combat scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


At the India Today Conclave, Air Chief Marshal AP Singh, Chief of the Air Staff of the Indian Air Force (IAF), provided a riveting account of the performance of the IAF’s Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighters during a tense standoff with Pakistan in 2019. Reflecting on the events following the Balakot airstrike, the Air Chief Marshal revealed how two Su-30MKIs successfully defended vital Indian installations against a potential raid by Pakistani F-16s armed with advanced AIM-120 AMRAAM (Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missile) missiles. His remarks underscored the resilience and capability of the IAF’s frontline fighters in countering a sophisticated adversary, dispelling doubts about their effectiveness in modern aerial combat.
The 2019 aerial engagements between India and Pakistan occurred in the aftermath of the IAF’s airstrike on a Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM) terrorist camp in Balakot, carried out on February 26, 2019, in retaliation for the Pulwama attack that killed 40 Indian CRPF personnel. The strike deep inside Pakistani territory escalated tensions, prompting Pakistan to retaliate the following day. On February 27, the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) launched a large-scale operation, deploying multiple fighter jets, including F-16s armed with AMRAAMs, in an attempt to target Indian military installations near the Line of Control (LoC).
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
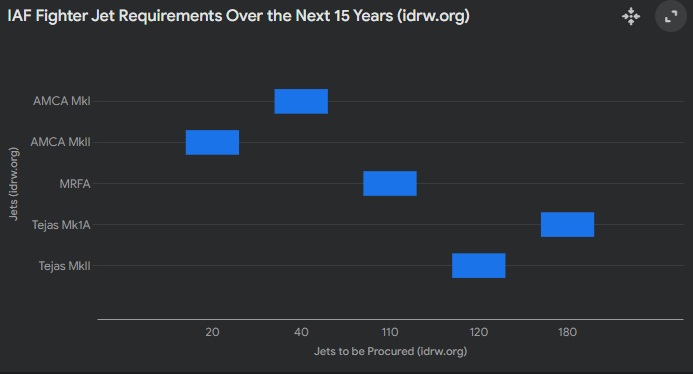

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is grappling with a critical shortfall of nearly 200 fighter jets as of March 06, 2025, a gap that threatens its operational edge in an increasingly volatile region. With an additional 250 aircraft slated for retirement by 2040—including aging MiG-21s, MiG-27s, Jaguars, and early Mirage 2000s—the IAF faces the daunting task of acquiring approximately 450 new jets over the next 15 years. This figure, equivalent to the entire current fighter fleet of the Pakistan Air Force (PAF), underscores the scale of India’s modernization challenge. To bridge this gap, the IAF is banking on a multi-pronged strategy involving the Tejas Mk1A, Tejas MkII, Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), and the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) program, though significant hurdles remain.
Currently, the IAF operates around 31 squadrons (each with 18-20 aircraft), well below its sanctioned strength of 42 squadrons needed to counter dual threats from China and Pakistan. The shortfall of 200 jets reflects delays in procurement, production bottlenecks, and the phased retirement of legacy platforms. Over the next 15 years, as 250 more aircraft retire, the IAF’s requirement balloons to 450 jets by 2040—a timeline critical to maintaining air superiority in the Indo-Pacific region.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Sikorsky S-92, an American twin-engine medium-lift helicopter designed and manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft, a subsidiary of Lockheed Martin, is emerging as a strong contender in the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) quest to fulfill its Very Very Important Person (VVIP) transportation requirements. Renowned for its versatility, safety, and reliability across civil and military helicopter markets, the S-92 is vying to secure a prestigious role in India’s defense ecosystem, catering to the high-profile travel needs of the nation’s top dignitaries.
The IAF’s VVIP requirement stems from the need to replace its aging fleet of Mi-8 helicopters, which have served as the backbone for transporting India’s President, Prime Minister, and other senior leaders since the 1970s. The quest for a modern replacement has been a long and complex journey, marked by the controversial cancellation of the AugustaWestland AW101 deal in 2014 due to bribery allegations. Since then, the IAF has sought a helicopter that meets stringent security, operational, and political criteria. The S-92, already a trusted platform for VVIP transport globally, is positioning itself as a frontrunner in this race, leveraging its proven track record and adaptability.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) released its latest report on global arms transfers for the period 2020–2024, revealing a significant 61 per cent increase in Pakistan’s arms imports compared to the 2015–2019 period. The report underscores China’s growing dominance as Pakistan’s primary arms supplier, with Beijing accounting for 81 per cent of Pakistan’s arms imports in 2020–2024, up from 74 per cent in the previous five-year period. Meanwhile, China solidified its position as the world’s fourth-largest arms exporter, holding a 5.9 per cent share of global arms exports, though its efforts to expand its market face resistance from many large importers due to political considerations.
Pakistan’s 61 per cent surge in arms imports between 2015–2019 and 2020–2024 reflects its ongoing efforts to modernize its military amid persistent regional tensions, particularly with India, and security challenges along its borders with Afghanistan and Iran. The increase aligns with Pakistan’s strategic priorities, including countering India’s growing military capabilities and addressing internal security threats. The SIPRI report notes that this growth in imports occurred despite global trends showing a marginal decline in overall arms transfers, highlighting Pakistan’s position as one of the world’s significant arms buyers.
Continue readingSOURCE: PTI


The US Director of National Intelligence Tulsi Gabbard, Canadian spy chief Daniel Rogers and Britain’s MI6 boss Richard Moore will be among top global intelligence czars converging in India this weekend to attend a security conclave, people familiar with the matter said on Tuesday.
India’s National Security Advisor Ajit Doval is set to chair the conclave on March 16 which is expected to deliberate on ways to enhance intelligence-sharing to combat terrorism and various transnational crimes. Intelligence chiefs of Australia, Germany, New Zealand and several other friendly countries of India are also expected to join the deliberations to be held in New Delhi.
Continue readingSOURCE: PTI

Opposition members, mainly from the Congress and the DMK, on Wednesday staged a protest in the Lok Sabha over clearance granted to a renewable energy project near the India-Pakistan border and staged a walk out after “not getting a satisfactory reply” from the government.
Asking a supplementary during Question Hour, Manish Tewari of the Congress said national security and energy security have to go hand in hand.
Continue readingSOURCE: PTI


US Vice President J D Vance is likely to travel to India later this month, according to a media report. “Vance will travel to India later this month alongside Second Lady Usha Vance, a report in Politico said, citing three sources familiar with the plans.
It marks Vance’s second foreign trip as vice president after making his world stage debut in France and Germany last month, the report said. Usha Vance’s parents Krish Chilukuri and Lakshmi Chilukuri emigrated from India to the US in the late 1970s.
Continue readingSOURCE: IANS


Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Mauritius PM Navinchandra Ramgoolam on Wednesday expressed satisfaction over their comprehensive discussions on the entire gamut of bilateral relations and agreed that their special and close bilateral partnership has acquired significant strategic depth after being raised to an Enhanced Strategic Partnership.
The ‘India-Mauritius Joint Vision for an Enhanced Strategic Partnership’ released on the second and final day of PM Modi’s landmark State Visit to the Indian Ocean archipelago highlights the special and unique relationship between the two countries that remains unparalleled, given the shared bonds of history, language, culture, heritage, kinship, and values.
Continue readingSOURCE: PTI


The Reliance Group’s digital services company Jio Platforms Limited has signed an agreement with SpaceX to offer Starlink’s broadband internet services to its customers in India, the company said on Wednesday.
The agreement is subject to SpaceX receiving authorisation to sell Starlink in India. The development came a day after Jio’s rival Bharti Airtel signed a similar pact with SpaceX. “Our collaboration with SpaceX to bring Starlink to India strengthens our commitment and marks a transformative step toward seamless broadband connectivity for all.
Continue readingSOURCE: IANS


A soldier was injured on Wednesday in suspected sniper fire along the Line of Control (LoC) in Jammu and Kashmir’s Rajouri district. Officials said that the soldier sustained a suspected sniper fire injury along the LoC in the Kalsian area of the district’s Nowshera sector this morning.
“The injured soldier was immediately airlifted to the Army hospital in Udhampur town. Security forces have started a search operation in the area,” officials said. Earlier, a soldier was injured in a firing incident from across the LoC in the Krishna Ghati (KG) sector of the Poonch district.
Continue readingSOURCE: PTI


Peoples Democratic Party (PDP) chief Mehbooba Mufti on Wednesday said the Centre’s ban on Awami Action Committee (AAC) and Ittihadul Muslimeen (IM) could be an arm-twisting tactic and asserted the people of Kashmir now need a healing touch rather than a “muscular policy”.
Noting that Mirwaiz Umar Farooq was being provided Z-Plus cover by the Centre, she said had he been an anti-national, he would not have been accorded such security. The Centre on Tuesday banned the AAC, headed by Kashmir’s influential cleric Mirwaiz Umar Farooq, and Shia leader Masroor Abbas Ansari-led IM for five years for their alleged anti-national activities, supporting terrorism and fuelling secessionist activities.
Continue reading