SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
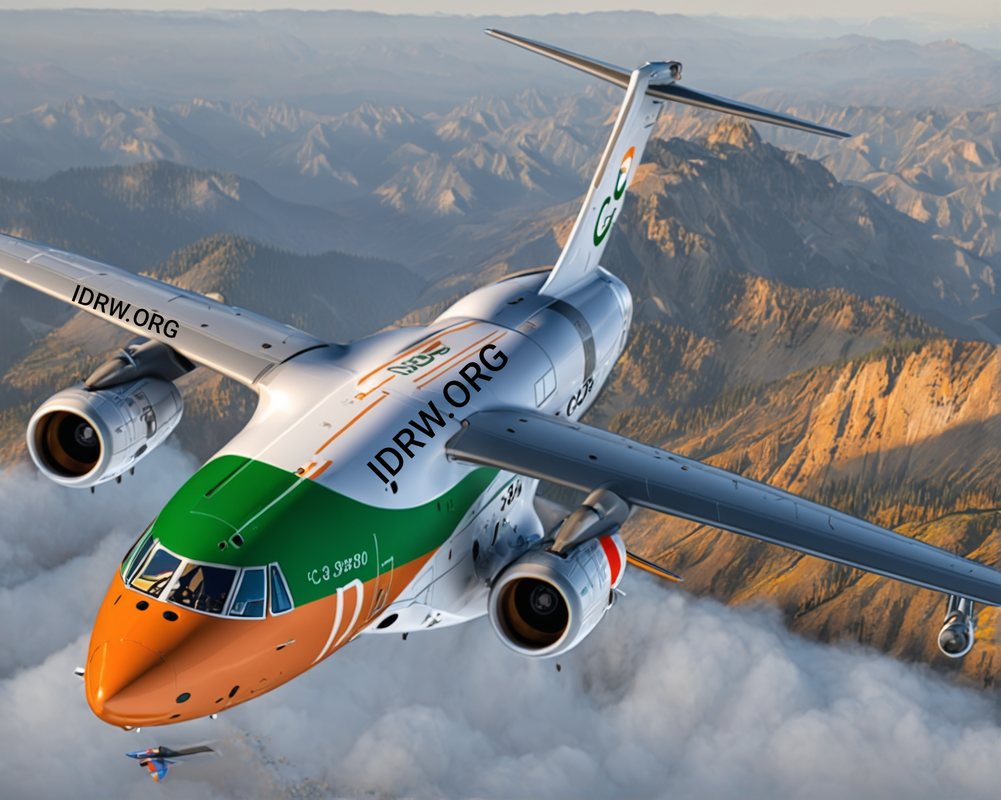

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is currently evaluating offers for its Medium Transport Aircraft (MTA) project, which aims to replace the ageing An-32 and Il-76 platforms. While the RFI has generated significant interest from various global aerospace manufacturers, a new factor has emerged that could significantly narrow down the contenders.
Both the IAF and the Indian Army have expressed a strong desire for the MTA to be capable of carrying the 25-ton Zorawar Light Tank to forward positions. This requirement has effectively eliminated Lockheed Martin’s C-130J Super Hercules from the race.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
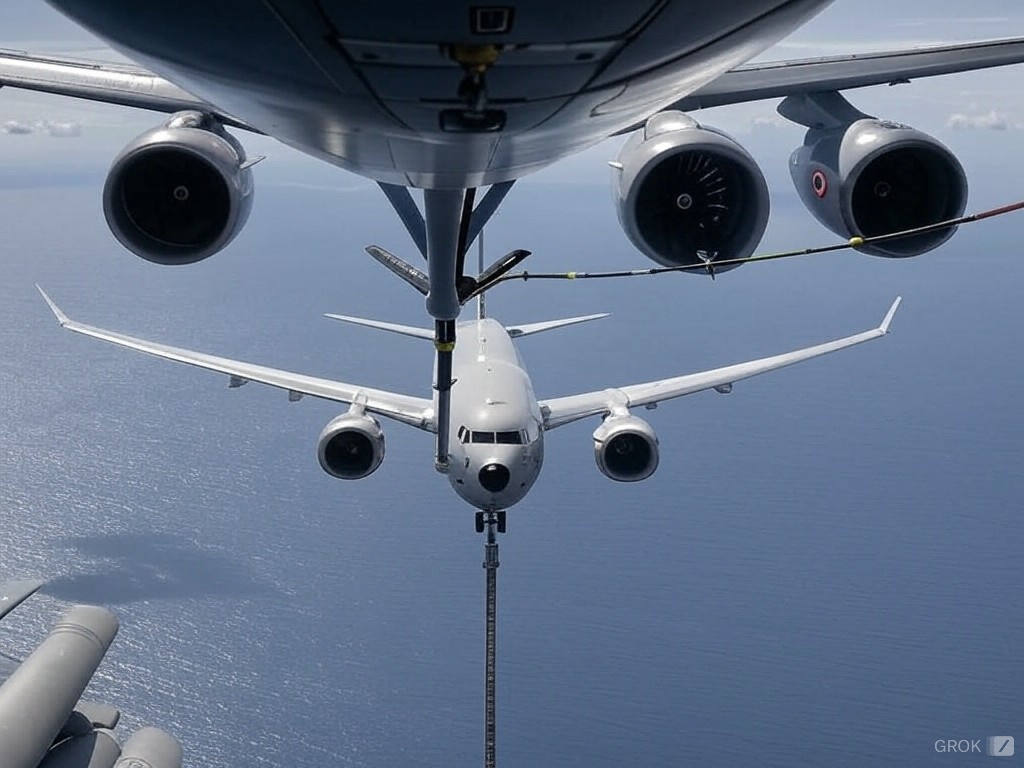

As India seeks to strengthen its maritime capabilities in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), the Indian Navy is planning to induct a fleet of air-to-air refuellers. These refuelling aircraft will play a critical role in extending the operational range of the Navy’s fighter jets and maritime patrol aircraft, ensuring sustained surveillance and dominance across the vast maritime expanse.
The strategic importance of the IOR, with its dense maritime traffic and proximity to key global trade routes, demands a robust naval presence. Mid-air refuelling is essential for maintaining prolonged missions and ensuring rapid response capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
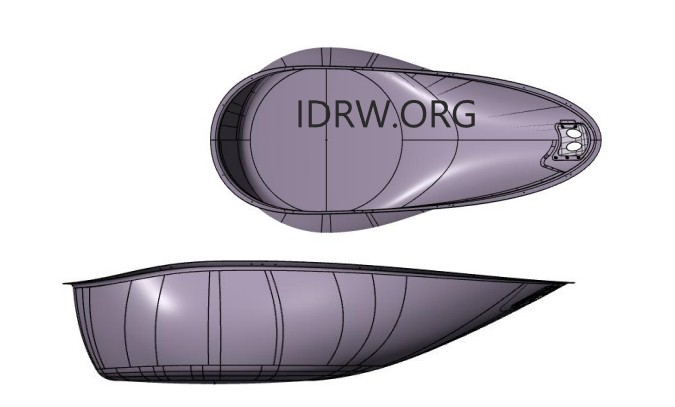

The Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE), a key research and development arm of India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), continues to make significant strides in the design and development of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). ADE has developed various UAV platforms, including tactical UAVs, surveillance UAVs, and target drones, catering to a wide range of mission profiles with versatile payload combinations and endurance capabilities.
As part of its ongoing efforts, ADE is now focusing on the development of Multi-Function Phased Array Radar (MPAR) and Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) radomes for its Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) UAV platform.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

Pune-based defense technology company Aethrone Aerospace has successfully conducted harbour trials of its aerial delivery system for 50 kg underwater autonomous targets. This milestone marks a significant advancement in integrating aerial platforms with underwater unmanned systems, showcasing the company’s ability to deliver autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) via airborne systems.
The trials demonstrated the system’s capability to accurately deliver 50 kg payloads designed for underwater operations. The next phase involves testing the technology with manned helicopters, a critical step toward operational readiness. Aethrone Aerospace also plans to extend this capability to shipborne unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), enabling the deployment of swarms of unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) in maritime environments.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
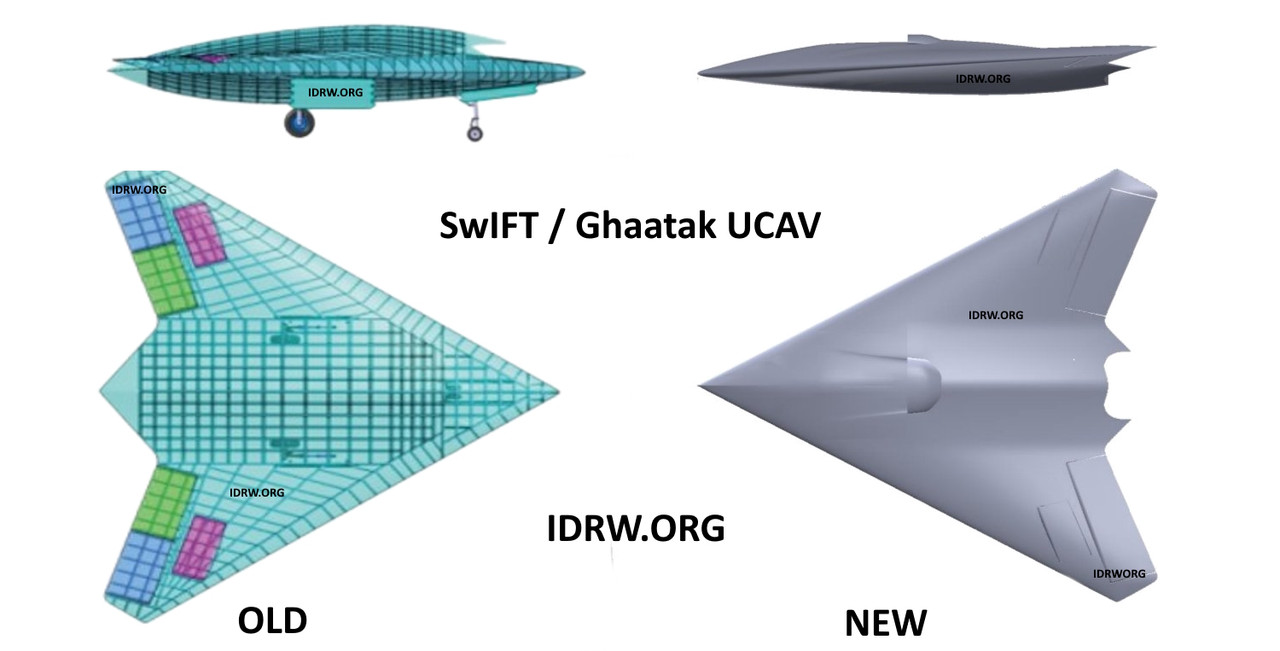
India’s ambitious Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) MkII, slated for operational debut around 2032-33, will be the first fighter jet to integrate an AI-operated unmanned bomber—a Heavy Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle (UCAV)—as part of a cutting-edge “family of systems” approach. This innovation represents a significant leap forward in both combat autonomy and aircraft-drone coordination, with the introduction of the Ghatak UCAV, a stealthy drone bomber designed for a variety of high-stakes missions.
The Ghatak UCAV, a 13-ton unmanned aircraft based on a flying-wing design, will be a key asset in the AMCA MkII’s arsenal. Designed with composite materials and stealth coatings, the Ghatak will have a reduced radar cross-section, making it difficult for enemy radars to detect. This UCAV will be able to perform multiple roles, such as Striking enemy radars, Conducting reconnaissance missions, and Acting as a mini-bomber, capable of taking out armored columns and critical enemy infrastructure.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s ambitious Netra MkII Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AWACS) program, based on the Airbus A321 platform, is facing new challenges as negotiations between Airbus and India’s Ministry of Defence (MoD) hit a roadblock over the cost of converting the ex-Air India A321 aircraft. Airbus has proposed a conversion cost that is nearly twice the initial estimate set by the Indian Air Force (IAF) and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), significantly inflating the overall program budget.
To streamline the Netra MkII program, the IAF has already acquired six Ex-Air India A321 aircraft that were initially used for commercial passenger services. These planes, now held by the Ministry of Defence, were chosen due to their availability and suitability for conversion into AWACS platforms.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) has taken a significant step forward in its Netra Mk1A Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AWACS) program by entrusting Embraer, the Brazilian aerospace giant, to source EMB-145 regional jets for the upgraded platform. The Ministry of Defence (MoD) recently approved the IAF’s plan to enhance its AWACS capabilities by procuring additional aircraft to bolster India’s aerial surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities.
The IAF already operates three Netra Mk1 AWACS, also based on Embraer’s EMB-145 regional jets. These aircraft, however, are set to receive an advanced successor, the Netra Mk1A, featuring enhanced radar systems and surveillance capabilities. Since Embraer has ceased production of the EMB-145 jets, the IAF has turned to the Brazilian company to find suitable airframes from global operators who may be interested in reselling their fleets.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
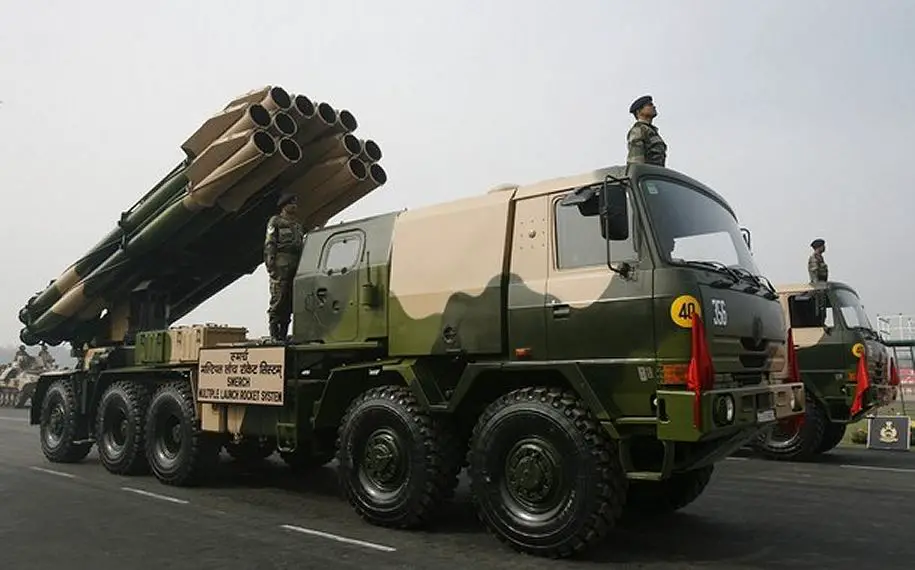

The Indian Army is moving forward with plans to extend the service life of its SMERCH ammunition system, in collaboration with private Indian vendors. This initiative is part of the Army’s broader efforts to ensure the continued operational readiness of its artillery systems while concurrently developing advanced alternatives to replace older systems.
The SMERCH, a Russian-made multiple rocket launcher system, is one of the core elements of India’s artillery capabilities, but with its ammunition nearing the end of its service life, the Indian Army has set in motion a process to extend the operational life of the ammunition.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
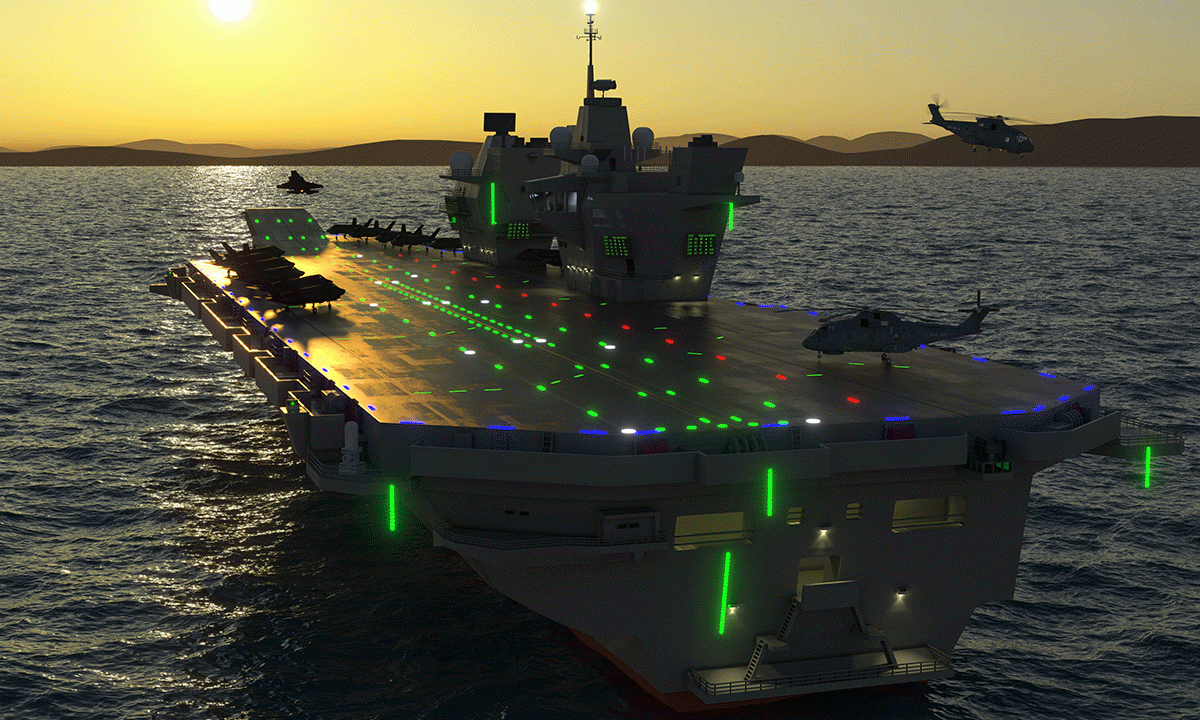
Navi Mumbai-based Elcome Integrated Systems Pvt. Ltd. has been chosen by the Indian Navy through the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) initiative to develop the Advanced Flight Control (AFC) Deck Lighting System for aircraft carriers. This project represents a significant step in modernizing and indigenizing critical systems essential for safe and efficient aircraft operations on naval platforms.
The AFC Deck Lighting System will be designed to integrate advanced technologies, offering greater efficiency, reliability, and compatibility with modern naval aviation requirements.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
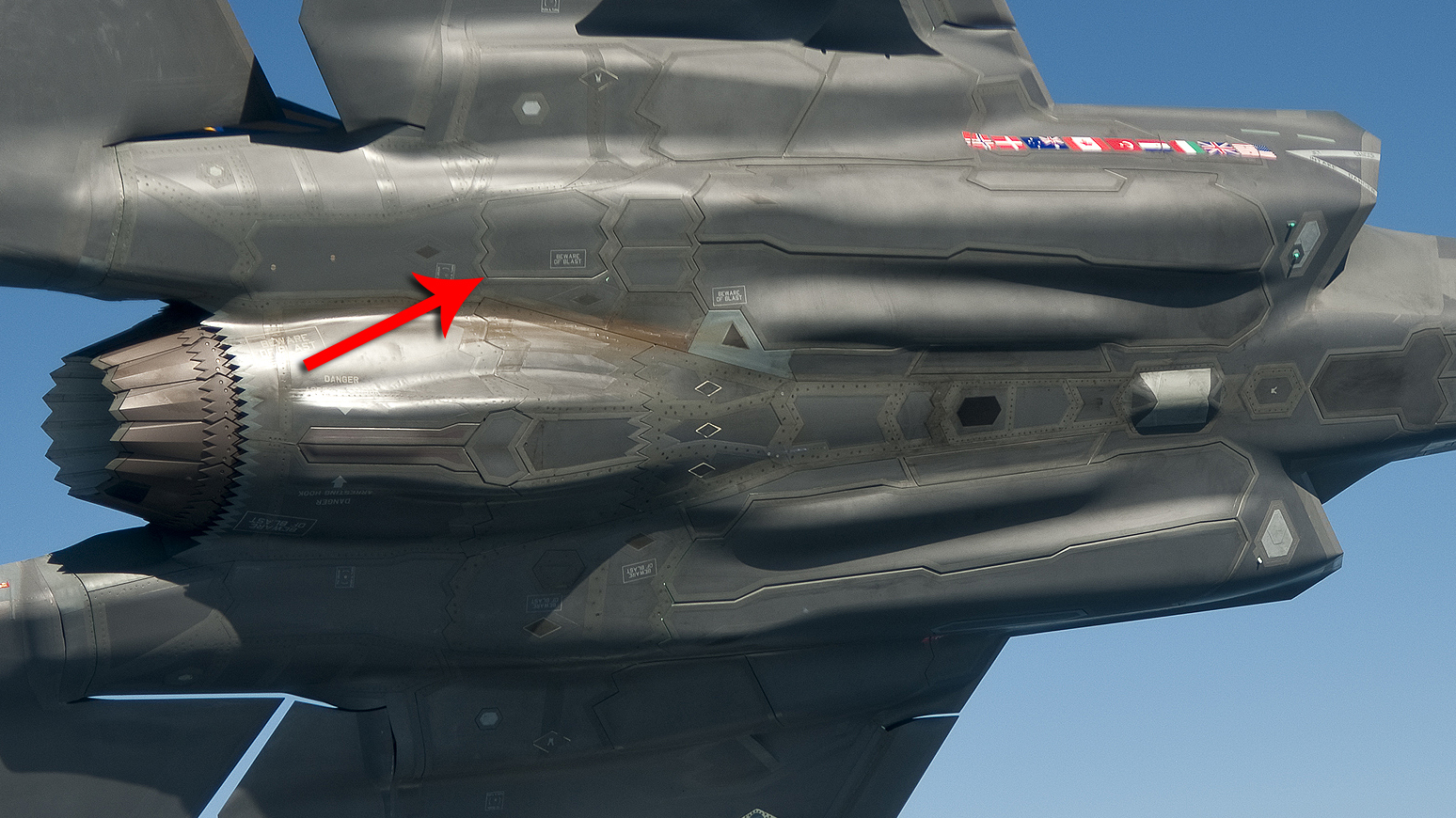

India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, the nation’s ambitious fifth-generation stealth fighter jet project, is set to incorporate sophisticated countermeasure systems to enhance its survivability in contested airspace. Among these systems are concealed chaff countermeasure flares and radio frequency countermeasures (RFCM), critical for protecting the aircraft from a wide range of missile threats.
A hallmark of fifth-generation fighter jets is their Low Observability (LO), or stealth, which reduces the aircraft’s radar signature. The AMCA will feature towed decoy doors that remain closed during normal operations to preserve its stealth characteristics. These doors will open only when deploying countermeasures, ensuring that the aircraft’s radar cross-section (RCS) remains minimal during combat.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
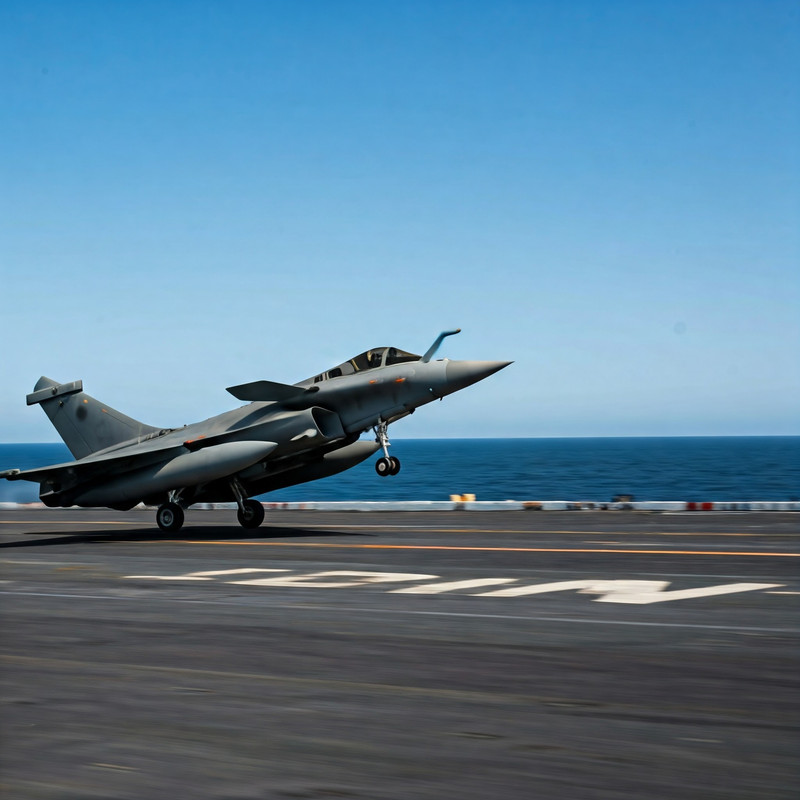

The Indian Navy’s Rafale M, a variant of the Rafale fighter jet designed for carrier operations, will come equipped with the French-built Exocet anti-ship missile. However, the Exocet’s relatively short range of just 70 kilometres has prompted the Navy to explore additional options for more potent anti-ship capabilities. This includes the integration of locally developed anti-ship missiles that offer significantly longer ranges and enhanced capabilities to counter modern naval threats.
The Exocet missile, despite its legacy as a reliable anti-ship weapon, has come under scrutiny for its limited range. With only 70 kilometres of reach, the Exocet is vulnerable to the increasing sophistication of modern warships equipped with long-range air defence systems. These systems are designed to intercept and destroy incoming threats, including fighter jets launching missiles from relatively close distances. For the Indian Navy, this raises concerns about the survivability of Rafale M jets if they rely solely on the Exocet for anti-ship missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Army is moving forward with plans to modernize its infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) by procuring air burst ammunition for the 30mm cannon guns on the BMP-2 and BMP-2K vehicles. This ammunition will provide the Army with enhanced capabilities to neutralize aerial threats like drones, which are increasingly being employed in combat and surveillance missions by adversaries.
The Indian Army operates approximately 2,900 BMP-2/2Ks, and the new ammunition will be tailored to operate across the diverse terrains and climatic conditions in which the Indian Army functions, from scorching deserts to high-altitude cold regions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The Indian Navy is taking a significant step forward in modernizing its capabilities by exploring the induction of a new class of autonomous submarine vessels in the 100-ton range. These small, highly maneuverable warships are designed to bolster coastal defense and conduct operations in shallow waters, aligning with India’s maritime security needs.
The new vessels, each weighing approximately 100 tonnes, will be equipped with advanced combat capabilities, including weapons, mine clearance systems, and surveillance equipment. Defence sources informed India Today that these unmanned vessels are expected to play a key role in monitoring and countering activities of adversarial forces across multiple fronts.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
N8SI.JPG)
India’s Guided Pinaka missile system, developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has emerged as a highly cost-effective and precision-guided artillery weapon, with a unit cost of ?70 lakh. This positions it as a competitive alternative to similar global systems like the Guided Multiple Launch Rocket System (GMLRS) Unitary round developed by Lockheed Martin, which costs approximately ?1.2 crore per unit.
When compared to Lockheed Martin’s GMLRS Unitary, the Guided Pinaka proves to be a more cost-effective solution, with the unit price being approximately 60% lower. The GMLRS Unitary round, priced at around ?1.2 crore per unit, delivers precision strike capability with a 200-pound warhead and a range exceeding 70 kilometers. The cost differential becomes even more significant considering that the Guided Pinaka, priced at ?70 lakh per unit, offers the same range and mission capabilities, making it a formidable competitor in the market.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Russia has reportedly expressed interest in supplying an advanced turbofan engine for India’s ambitious 5.5gen Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. This offer includes a Transfer of Technology (ToT), aligning with India’s goal of boosting indigenous defence capabilities. The engine in question is the successor to the Klimov RD-33, which will incorporate fifth-generation technology from Russia’s AL-41F1S engine.
The next-generation engine, being developed by Russia’s ODK Klimov, promises key advancements tailored to meet the India’s AMCA requirements.
Continue reading