SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
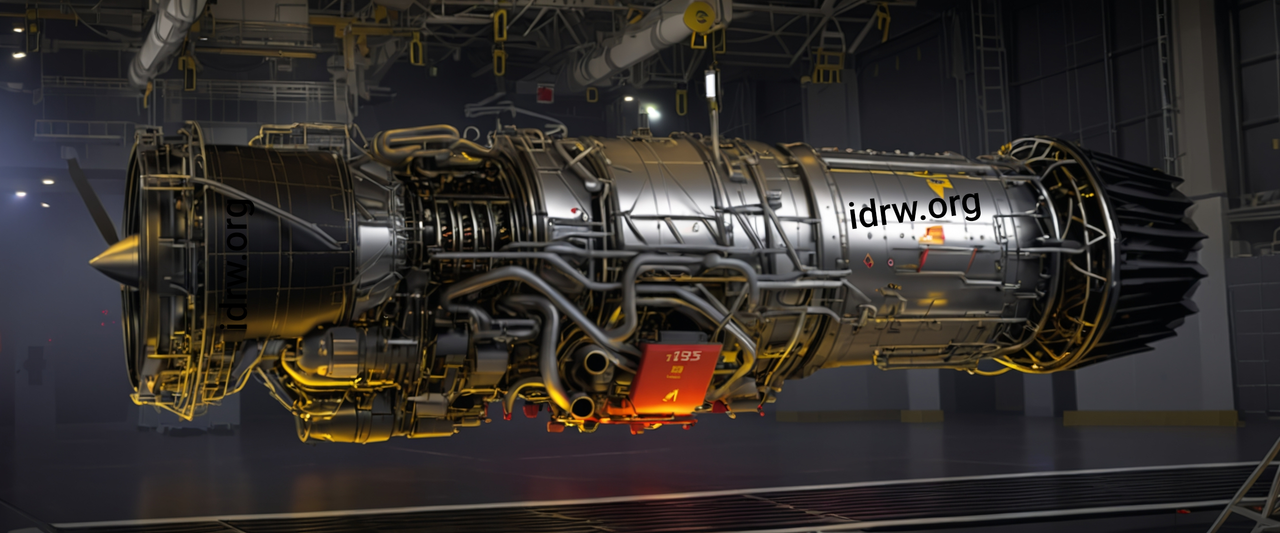
In an exclusive conversation with idrw.org, a senior official from Safran, the French aerospace giant, confirmed that the forthcoming 110kN thrust engine, to be developed in collaboration with India’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) for the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, will feature a completely new core design, distinct from the M-88 engines currently used in the Rafale jets.
The Safran official emphasized, “The 110kN engine will not share any core components or technology from the M-88. It’s designed from the ground up to meet the specific requirements of the AMCA.” This revelation underscores a significant commitment to innovation, ensuring that the engine will be tailored to the unique challenges and specifications of India’s 5th-generation fighter jet program.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a bid to rekindle a long-stalled joint venture, Russia has approached India to reconsider the development of the Multirole Transport Aircraft (MTA) project. This proposal comes after the Indian aerospace giant, Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), had previously withdrawn from the project due to disagreements over engine specifications.
The MTA was intended to be a collaborative effort between Russia’s United Aircraft Corporation and India’s HAL, aimed at replacing India’s ageing fleet of Antonov An-32 transport aircraft. The project, initially envisioned in 2007, saw India planning to procure 45 aircraft, with Russia looking to acquire around 100. However, the venture hit a snag in 2016 when HAL decided to pull out, primarily due to differences over the selection of engines and management of the project.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

After a service span from 2002 to 2024, the Indian Navy has officially de-inducted its fleet of Searcher MK II Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). This decision marks the end of an era for these short-range UAVs within the naval service, as confirmed by a high-ranking official to idrw.org.
The Searcher MK II, with a weight of 500 kg and a payload capacity of just 68 kg, was initially inducted into the Indian Navy at a time when Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) and High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) UAVs were not widely available or considered for naval applications. Despite their de-induction, these UAVs will not be immediately disposed of. Instead, they will be kept in storage, as stated by the official, to be potentially reactivated if future needs arise.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Bengaluru-based NewSpace Research and Technologies (NRT) has set its sights on the development of the Abhimanyu, a Collaborative Combat Aircraft (CCA) that promises to redefine tactical aerial capabilities. This innovative unmanned platform is designed to operate as part of a Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUMT) system, providing a cost-effective, expendable solution tailored for multiple mission profiles including Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR), kinetic attacks, decoy operations, and Electronic Warfare (EW).
The Abhimanyu stands out due to its Tactical Interdiction and Attack Air Vehicle (TIA-AV) design philosophy, focusing on being low-cost, intelligent, and expendable. This approach aims to deliver a platform that can be deployed in large numbers for various combat scenarios, enhancing operational flexibility and reducing the risk to human pilots. The modular design of the Abhimanyu allows it to adapt swiftly to different mission requirements, from gathering intelligence to engaging in direct combat or electronic warfare, making it a versatile asset on the battlefield.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

According to reports from MaxDefense Philippines, the Philippine Army is engaging in advanced negotiations with India’s BrahMos Aerospace to procure additional coastal batteries of the BrahMos anti-ship missile. This move is part of the broader Integrated Shore-Based Anti-Ship Missile System (ISBASMS) Acquisition Project, which involves both the Philippine Army and the Marine Corps.
The ISBASMS project is an evolution from the earlier Land-Based Anti-Ship Missile System (LBASMS) Acquisition Project, which had initially planned for the acquisition of two missile batteries. The new initiative significantly scales up this ambition, with discussions now focused on securing nine missile batteries.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In an exclusive interview, Abdul Basit, who previously served as Pakistan’s High Commissioner to India, made bold claims regarding the comparative strengths of the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) and the Indian Air Force (IAF). Basit, now known for his diplomatic insights and commentary on Indo-Pak relations, stated that the PAF currently holds a superiority over the IAF, a position he predicts will only strengthen with the induction of the J-35A and TAI TF Kaan fighter jets into Pakistan’s fleet.
Basit began the interview by discussing the current capabilities of both air forces. He highlighted that despite India’s numerical advantage in terms of aircraft numbers, Pakistan has managed to maintain a qualitative edge through strategic acquisitions and upgrades. “The Pakistan Air Force has been proactive in modernizing its fleet, ensuring that we are not only matching but in some respects surpassing the capabilities of our neighbors,” Basit remarked.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Indian Army Chief General Upendra Dwivedi has taken a significant step towards rekindling the traditional recruitment of Gorkha soldiers from Nepal into the Indian Army. In a recent appeal, General Dwivedi personally requested his Nepali counterpart to reconsider the recruitment process which has been on hold since the onset of the Covid-19 pandemic and further complicated by the introduction of India’s Agnipath military recruitment scheme.
“I have personally requested the Nepal Army chief to revive the recruitment of the ethnic Gorkha community in the Indian Army. I am very hopeful that it will resume sooner than later,” General Upendra Dwivedi told The Telegraph. This statement reflects the urgency and importance India places on the recruitment of Gorkhas, known for their valor and loyalty, which have been integral to the Indian Army since the 1947 tripartite agreement involving India, Nepal, and the UK.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

In a significant move to counterbalance regional security threats posed by China and Pakistan, India Plans to commission the Russian-manufactured Voronezh radar at the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) campus in Challakere, Karnataka. This over-the-horizon radar system, known for its impressive 6,000 km range, marks a pivotal upgrade in India’s strategic defense capabilities.
Once known predominantly as India’s ‘Edible Oil City’, Challakere has now transformed into a burgeoning hub for science and technology. Located approximately three hours from Bengaluru, this area hosts key establishments like the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), DRDO, the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), and the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC). This concentration of scientific talent and infrastructure has turned Challakere into a focal point for advanced research and development in defense and space technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
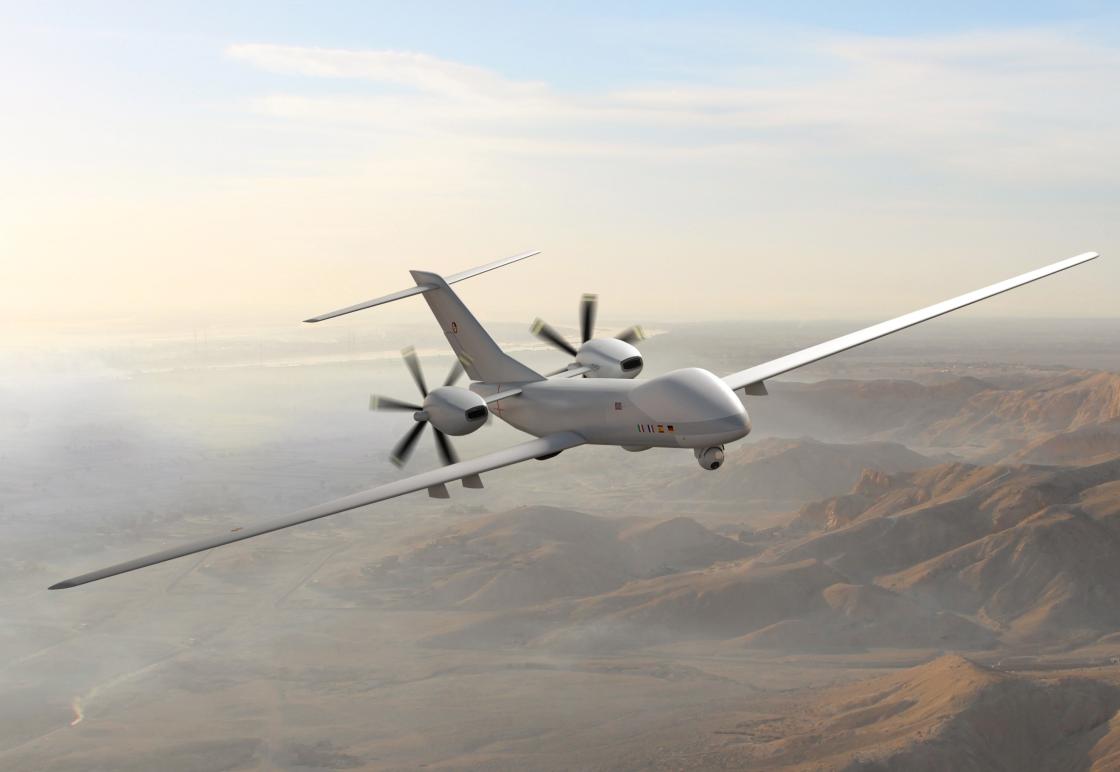

In a significant move towards enhancing global defense cooperation, Italy is actively seeking to involve India in its part of the Eurodrone project, a collaborative European initiative also involving Germany, France, and Spain. This project aims to develop a medium-altitude, long-endurance remotely piloted airborne system known as Eurodrone, tailored for intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, and reconnaissance (ISTAR) missions, as well as for civil purposes.
The Eurodrone, a result of a joint venture by industry giants Airbus, Leonardo, and Dassault Aviation, is not just another unmanned aerial system; it’s a cornerstone for Europe’s strategic autonomy. By developing this cutting-edge technology, European countries aim to reduce their reliance on non-European UAS, thereby enhancing their independent operational capabilities. The program underscores a commitment to equipping the Armed Forces of the participating nations with systems that are at the forefront of technological advancement, meeting the sophisticated needs of modern warfare and peacekeeping operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is facing one of its most significant challenges in recent times, with a noticeable decline in its combat strength, which has sparked discussions and criticisms about the government’s, particularly Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s, approach to defense strategy. Defense Minister Rajnath Singh’s recent comments and the broader narrative around the IAF’s capabilities have put the spotlight on this issue.
The IAF has been grappling with a reduction in its fighter squadrons, currently hovering around 30 when the sanctioned strength is 42. This shortfall is attributed to several factors Many of the IAF’s aircraft are at the end of their service life, with delays in acquiring new jets or upgrading existing ones. Projects like the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) and delays in the Tejas program have contributed to the gap in combat strength.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
In a significant departure from tradition, the indigenously developed Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Dhruv and the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas will not participate in this year’s Republic Day flypast, according to official statements from the Indian Air Force.
Wing Commander Jaideep Singh, the Indian Air Force Public Relations Officer, announced that the ALH Dhruv has been excluded from the aerial display due to a recent grounding of its entire fleet. “The ALH Dhruv will not be part of the flypast as the entire fleet of 330 helicopters across the armed forces has been grounded,” he stated. This decision follows a precautionary measure after an Indian Coast Guard ALH crashed in Porbandar, Gujarat, on January 5. Under the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP), all helicopters of this type are undergoing thorough inspections.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a strategic move aimed at bolstering the capabilities of India’s defense sector, Lotus Advance Technologies Pvt Ltd, based in India, has entered into a groundbreaking partnership with Steadicopter Pvt Ltd from Israel. This collaboration is set to revolutionize the Rotary Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (RUAV) landscape in India, focusing on delivering cutting-edge technology tailored for the Indian Armed Forces and Paramilitary Forces.
Lotus Advance Technologies Pvt Ltd, known for its prowess in advanced manufacturing and strategic partnerships in defense technology, brings to the table a significant capability in mechanical manufacturing and electronic testing and assembly. Their state-of-the-art facility in Uttar Pradesh, certified by notable institutions like HAL and DGAQA, is geared up to manufacture and supply innovative solutions to the Indian defense sector.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Amid the spiritual fervor of the Maha Kumbh 2025 in Prayagraj, an unexpected attraction has captured the imagination of millions of devotees and visitors – the ‘Tejas Pandal’. Inspired by India’s indigenous Light Combat Aircraft, HAL Tejas, this pandal was meant to symbolize national pride and technological achievement. However, upon closer inspection, the design has sparked discussions for reasons beyond the anticipated.
The ‘Tejas Pandal’, while initially conceived to honor the HAL Tejas, has instead taken on a hybrid appearance, reminiscent of both the Chinese-Pakistani JF-17 Thunder and the American F-16 Fighting Falcon, aircraft not part of the Indian Air Force’s current inventory. This unexpected design convergence has not only made the pandal a talking point but also a subject of curiosity and critique among aviation enthusiasts and the general public alike.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) has been given the green light by the Ministry of Defence (MoD) to complete the Critical Design Review (CDR) for the Twin Engine Deck-Based Fighter (TEDBF) program, specifically tailored for the Indian Navy’s aircraft carrier needs. In an exclusive interview with idrw.org, ADA officials expressed optimism about the potential for a modified version of the TEDBF to serve the Indian Air Force (IAF), should there be interest.
The TEDBF, a 26-ton aircraft designed for naval operations, could be adapted for Air Force use by removing features like the folding wings and the heavy-duty undercarriage and landing gear, which are essential for carrier operations. This adaptation process, according to ADA officials, could be accomplished in less than two years, presenting a significant opportunity for the IAF to leverage indigenous technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
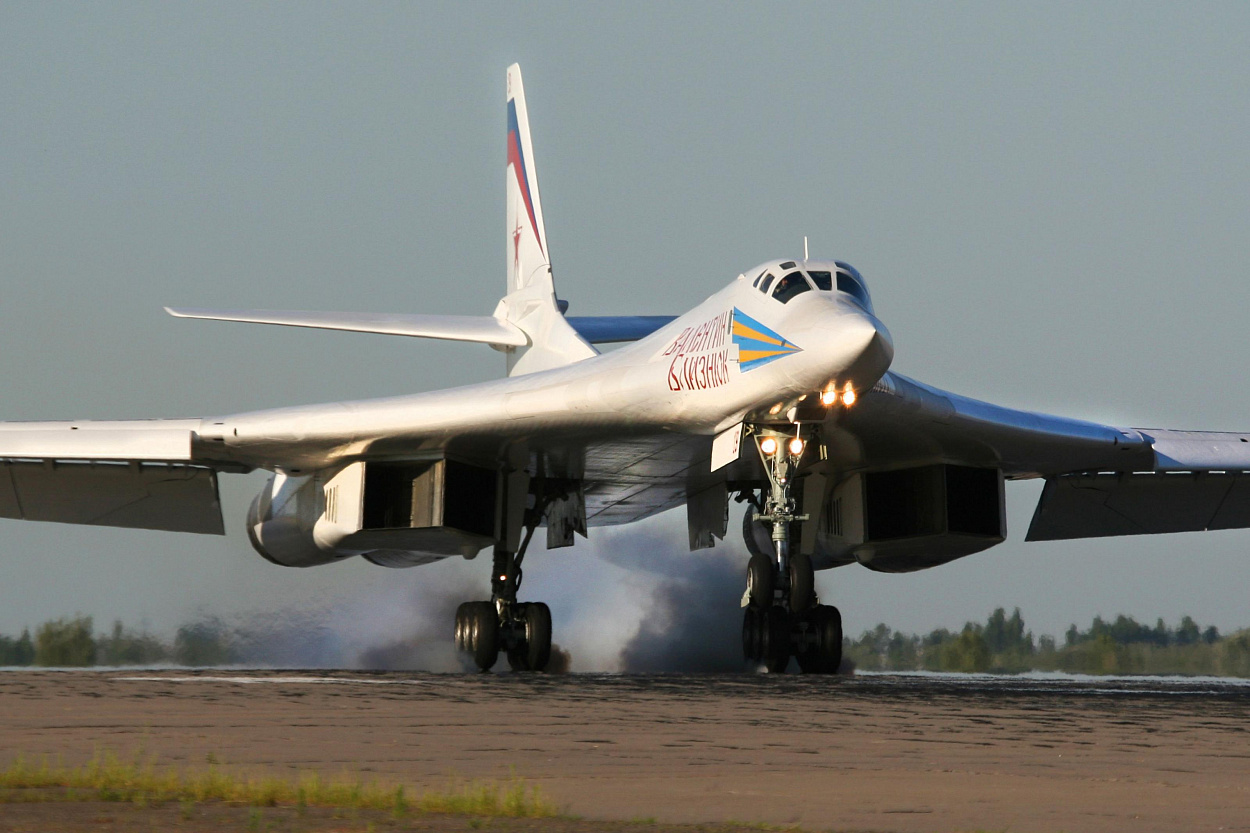

In a significant revelation, a high-ranking official from the Indian Air Force (IAF) has indicated to idrw.org that there is little interest in procuring the Russian Tu-160 strategic bombers. Despite the aircraft being indirectly offered, the IAF seems deterred by the presumed high operational costs and the lack of suitable infrastructure to support such a fleet in India.
The Tu-160, also known as the “White Swan” or “Blackjack” by NATO, is one of the largest and most powerful strategic bombers in the world. Its advanced capabilities, including carrying a range of nuclear and conventional munitions over long distances, come at a steep price. The maintenance, operation, and lifecycle management of these sophisticated aircraft would require a significant investment, which, according to the IAF official, might not be justifiable given the current budgetary constraints and strategic priorities.
Continue reading