Idrw Team
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG


In a significant boost to India’s Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk1A program, GE Aerospace has reaffirmed its commitment to supply 12 F404-IN20 engines to Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) by the end of 2025, following a revised delivery schedule. The announcement comes after GE delivered the first of 99 contracted engines on March 25, 2025, with plans to ship two additional engines starting in July, despite a brief agreed-upon pause in the delivery timeline. This development, reported by idrw.org that HAL can operationalize the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) first Tejas Mk1A squadron by year-end, a critical step in addressing India’s dwindling fighter squadron strength.
The F404-IN20 engine, a high-thrust variant tailored for the Tejas Mk1A, is a cornerstone of India’s indigenous fighter jet program. The initial delivery in March 2025 marked the end of a nearly two-year delay, attributed to global supply chain disruptions and the complexities of restarting the F404-IN20 production line, dormant since 2016 after GE fulfilled an earlier order of 65 engines for the Tejas Mk1. The first engine arrived at HAL on April 3, 2025, and with two more engines scheduled monthly from July, GE has committed to delivering a total of 12 engines by December 31, 2025. This includes the initial unit plus 11 additional engines, aligning with HAL’s goal to produce at least eight Tejas Mk1A jets—six fighters and two trainers—sufficient to form the IAF’s first squadron of 18 aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


India announced the development of a cutting-edge 81mm Mortar Telemetry Bomb, a non-explosive round designed to revolutionize artillery training and fire-control calibration. Equipped with advanced sensors, this innovative munition captures critical flight data such as velocity, trajectory, and environmental conditions in real time, transmitting the information wirelessly to ground systems. The development, spearheaded by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with private industry partners, marks a significant step in India’s push to enhance the precision and effectiveness of its artillery systems.
The 81mm Mortar Telemetry Bomb is fired like a conventional mortar round but serves an entirely different purpose. Instead of delivering an explosive payload, it is embedded with sensors that monitor its flight parameters throughout its trajectory. These sensors track key metrics, including muzzle velocity, angular deviation, and atmospheric effects like wind speed and temperature, which can impact a mortar’s accuracy. The data is transmitted live via a secure telemetry link to a ground-based fire-control system, allowing artillery units to analyze and adjust their firing solutions in real time. This capability is expected to significantly improve the calibration of mortar systems, ensuring greater accuracy during live combat scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is actively developing a new Gun-Launched Anti-Tank Guided Missile (GLATGM) designed specifically for the 105mm rifled cannon of the Zorawar Light Tank. This development marks a significant step in enhancing the lethality and versatility of the indigenous light tank platform, which is being co-developed by DRDO and Larsen & Toubro (L&T) for high-altitude operations.
The Zorawar Light Tank, currently undergoing developmental trials, is designed to provide mobile firepower in difficult terrain such as the Himalayan regions of Ladakh and Arunachal Pradesh. The tank will feature a new Indian-made 105mm high-pressure cannon, replacing the Belgian Cockerill 105mm cannon used in the first prototype. DRDO’s development of a compatible ATGM aims to expand the tank’s firepower beyond conventional rounds, enabling it to engage and destroy armored targets at extended ranges.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
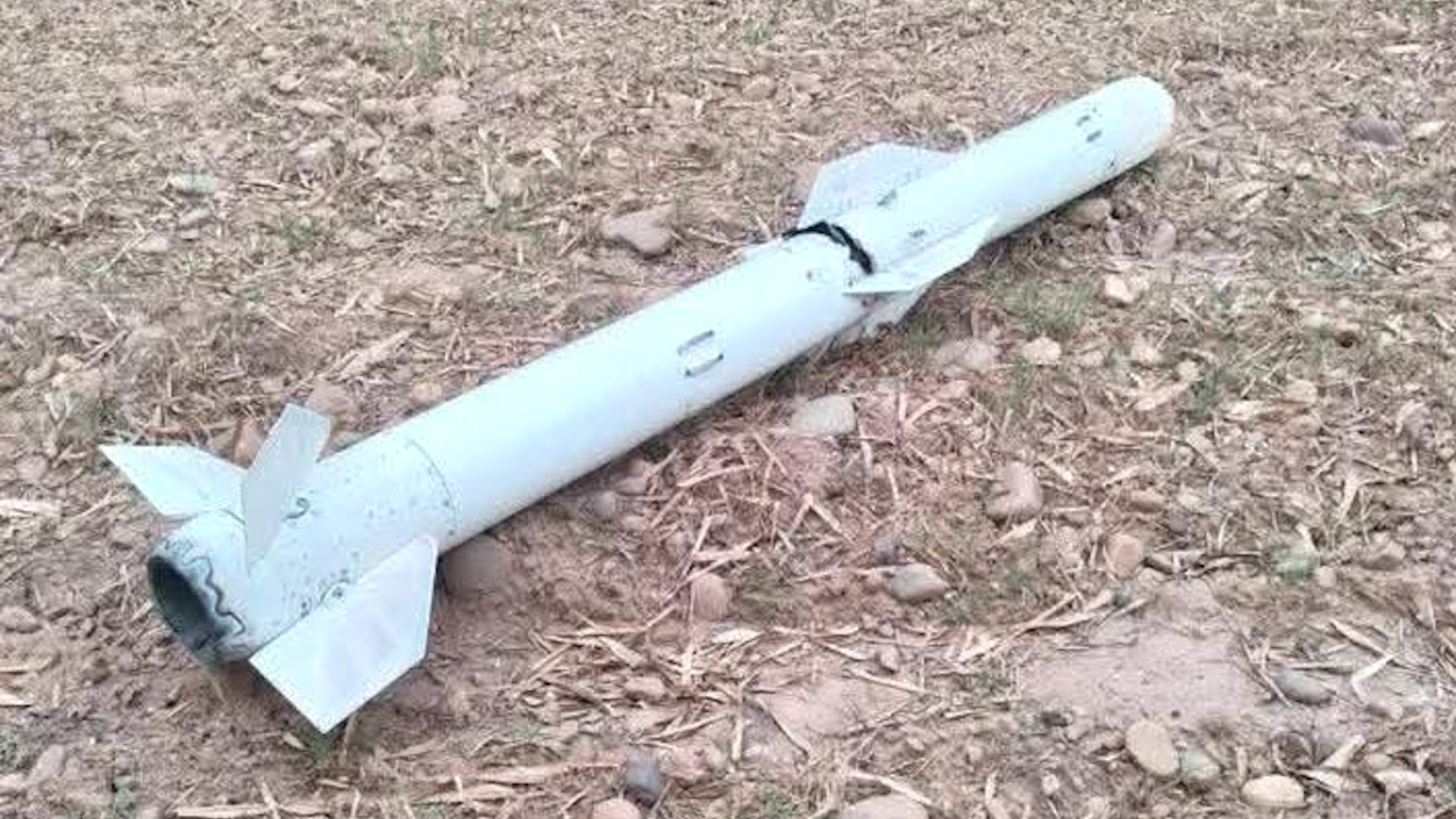


In a significant development following the recent India-Pakistan aerial clashes, Japanese radar engineers and electronic warfare (EW) experts are set to be the first foreign specialists to access detailed information on the Chinese-made PL-15E beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile (BVRAAM) recovered by India.
According to sources close to idrw.org, the missiles, fired by Pakistan Air Force (PAF) jets during Operation Sindoor, were rendered ineffective by India’s advanced EW systems, leading to the recovery of several near-intact PL-15E units, complete with their guidance systems and seekers. This breakthrough offers a rare opportunity to study one of China’s most advanced air-to-air weapons, drawing global attention as nations like Japan seek to counter the growing threat of Chinese military technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
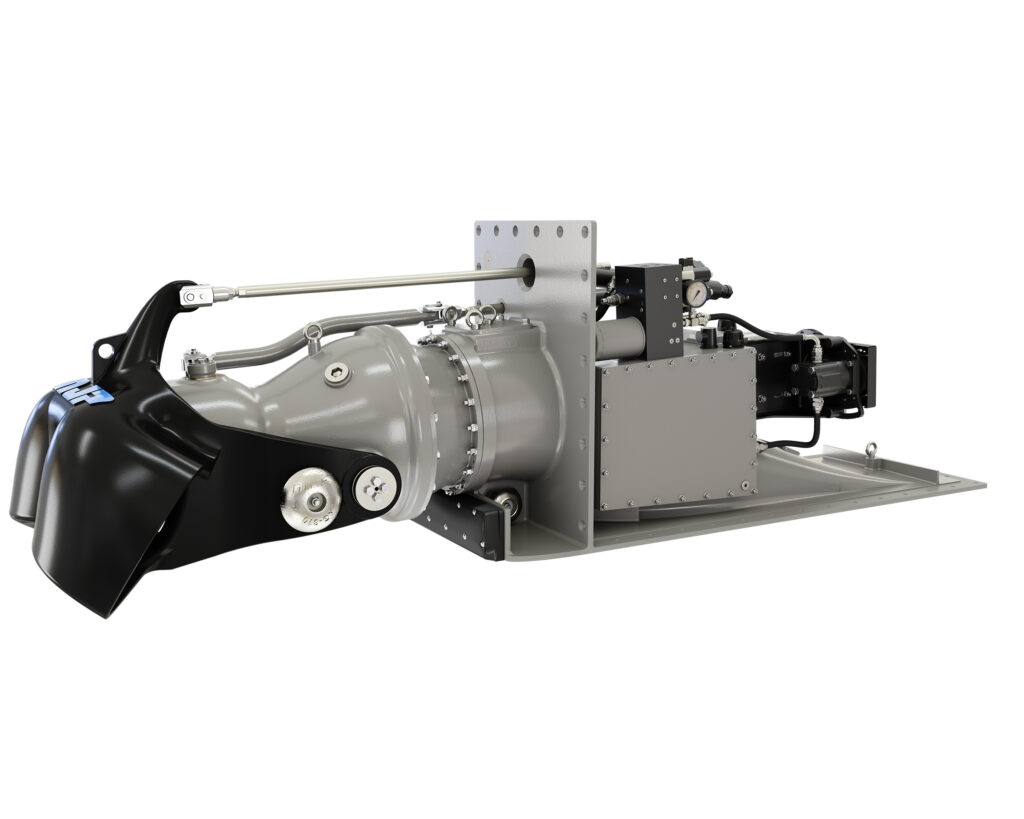

Larsen & Toubro’s Precision Engineering Systems (L&T PES) has solidified its position as a trailblazer in India’s defence innovation landscape with the successful sea trials of its indigenously developed 651 kW (885 hp) Waterjet Propulsion System in April 2025, integrated into the Indian Navy’s Fast Interceptor Craft (FIC). Building on this milestone, L&T is now setting its sights on a more powerful 3500 kW (4760 hp) waterjet propulsion system.
The 651 kW Waterjet Propulsion System, developed under the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) Technology Development Fund (TDF) scheme, boasts over 70% indigenous content and was validated for high-speed operations, maneuverability, and shallow-water performance aboard FICs. These vessels, critical for coastal defence, surveillance, and anti-smuggling missions, benefit from waterjets’ ability to generate thrust by accelerating water through a pump, offering superior control and efficiency compared to conventional propellers. The system’s success, highlighted by DRDO’s X post (@DrdoTdf), demonstrates L&T’s capability to deliver reliable, homegrown maritime solutions, setting the stage for scaling up to the 3500 kW class.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


Armoured Vehicles Nigam Limited (AVNL), a public sector defence company headquartered in Avadi, Chennai, is spearheading an ambitious initiative to develop a new generation of light tanks tailored for India’s diverse and challenging operational environments, particularly high-altitude warfare. In a strategic pivot towards advanced Western technologies, AVNL is engaging with global defence giants such as Belgium’s John Cockerill and Israel’s Elbit Systems to integrate cutting-edge command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (C4ISR) systems, lightweight firepower, and advanced survivability features into its next-generation platforms.
While earlier speculation linked AVNL to a potential collaboration with Russia’s Rosoboronexport for the 2S25 Sprut-SD light tank, the company’s recent focus on Western designs signals a shift towards modular, high-tech solutions to meet India’s future battlefield requirements.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Indian Army has taken a significant step toward bolstering its air defense capabilities with the successful completion of internal trials for the AK-630M integrated Mobile Gun System (MGS). Following the trials, the system is now progressing to the next phase of testing, with minor alterations being incorporated based on feedback from the initial evaluations. This development underscores India’s ongoing efforts to modernize its military and address emerging aerial threats with advanced, indigenous solutions.
The AK-630M, originally a naval close-in weapon system (CIWS) developed by the Soviet Union (and later Russia), has been adapted for land-based operations in this integrated MGS configuration. The system features a 30mm six-barrel rotary cannon, capable of delivering a high rate of fire—up to 5,000 rounds per minute—making it highly effective against low-flying aircraft, drones, and incoming missiles. Mounted on a mobile platform, as seen in the image of a truck-based turret system, the AK-630M MGS offers enhanced mobility and flexibility, allowing rapid deployment across diverse terrains to counter aerial threats.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The recent India-Pakistan skirmish, dubbed Operation Sindoor, marked a pivotal moment for India’s defence industry, providing a real-world proving ground for an array of indigenously developed weapons from the private sector. Conducted in May 2025, this operation saw the Indian Armed Forces deploy and test advanced platforms, including Tata Advanced Systems Limited’s (TASL) ALS-50 Loitering Munition, NewSpace Research and Technologies’ Swarm Drones, Mahindra’s Armado Armoured Vehicle, Johnnette Technologies’ JM-1 Loitering Munition, and the VajraShot Anti-Drone Gun.
The successful battlefield use of these systems against Pakistani forces, particularly in countering drone swarms and precision strikes, has earned them the coveted “combat-tested” label, significantly enhancing their appeal in the global defence market. This milestone not only validates India’s push for self-reliance under the “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative but also positions these platforms as viable export options for countries previously hesitant due to their untested status.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


Hyderabad-based Raghu Vamsi Machine Tools (RVMT), a leading aerospace and defense manufacturing firm, has announced plans to develop a cutting-edge kamikaze drone, marking a significant step in India’s push for self-reliance in unmanned aerial systems (UAS).
The new drone, showcased at a recent industry event, will leverage a hybrid propulsion system combining jet-engine and electric propulsion technologies. Central to this project is the “INDRA RV25:240N,” a fully indigenous micro turbojet engine developed by RVMT, which the company claims offers best-in-class thrust-to-weight ratios. With a projected range of 500 kilometers, the drone aims to bolster India’s defense capabilities amid rising regional tensions, particularly following recent conflicts involving drone warfare.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has announced after securing a landmark deal for the supply of 156 Light Combat Helicopters (LCH), named Prachand, along with associated training and equipment, valued at Rs. 62,700 crore (excluding taxes), earlier this year. HAL has confirmed that the first batch of LCH Prachand helicopters will be delivered to the Indian Armed Forces starting March 2028.
The contract, a significant boost to India’s indigenous defense manufacturing, is divided into two segments: 66 LCHs for the Indian Air Force (IAF) and 90 LCHs for the Indian Army.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


According to informed sources close to idrw.org, Indian-manufactured drones, including Johnnette Technologies’ JM-1, Solar Industries’ Nagastra-1, and Tata Advanced Systems’ ALS-250, have demonstrated superior performance compared to both imported drones and those developed locally through technical collaborations. These indigenous unmanned aerial systems (UAS) were deployed in a recent conflict with Pakistan, showcasing their advanced capabilities and reliability under combat conditions.
While foreign drones and those developed through technical collaborations have been integral to India’s defense capabilities, the indigenous systems stood out in several key areas. Sources highlighted that imported drones, though equipped with cutting-edge technology, often faced challenges related to maintenance, compatibility with local conditions, and high operational costs. Similarly, drones developed through collaborations, while benefiting from foreign expertise, sometimes lacked the customization required for India’s unique operational needs.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


Srinivasagopalan Rangarajan, Chairman and Managing Director of Data Patterns, a leading Indian defense electronics company, recently shared a significant milestone with Hindu BusinessLine. “Just 3-4 weeks ago, our seekers were flight-tested in BrahMos as part of missile trials by DRDO, and it was a textbook performance,” Rangarajan announced, highlighting the success of Data Patterns’ indigenous seeker technology in the prestigious BrahMos supersonic cruise missile program.
In missile systems, the seeker is a critical component responsible for detecting and tracking targets, ensuring precision strikes even in complex combat scenarios. The flawless performance of Data Patterns’ seeker during the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) recent trials underscores the growing capability of India’s private defense sector in delivering cutting-edge technologies for strategic programs.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


In a landmark step toward achieving self-reliance in defense manufacturing, the Indian Navy signed a ?270 crore project sanction order with Kirloskar Oil Engines Limited (KOEL) on April 2, 2025, for the design and development of a 6MW medium-speed marine diesel engine. This contract, executed under the Make-I category, not only aims to reduce India’s dependence on imported high-capacity diesel engines but also lays the foundation for a scalable 3-10MW engine family, with KOEL confidently asserting its capability to develop a 10MW, 20-cylinder variant based on the V12, 6MW design.
This initiative, celebrated as a pivotal moment for India’s defense industrial ecosystem, will power the propulsion and generation systems of Indian Navy and Indian Coast Guard vessels, strengthening maritime security in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Indian Army’s formidable T-90 ‘Bhishma’ tanks, a mainstay of its armored divisions, have received a game-changing upgrade that allows them to operate underwater for up to an hour. The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has developed advanced equipment to keep tank crews operational even when fully submerged, significantly enhancing the tanks’ ability to navigate rivers along India’s borders with Pakistan and China.
With over 1,100 Russian-made T-90 tanks in active service, these main battle tanks form the backbone of India’s armored forces. The country’s riverine terrain, particularly along its northern and western borders, poses a challenge for tank operations during military maneuvers. While the T-90 is designed to withstand water exposure, the primary concern has been the safety and functionality of the crew—typically four to five members—when submerged.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


In a significant stride for India’s aerospace and defense sector, Flying Wedge Defence & Aerospace has showcased a cutting-edge prototype of an Unmanned Combat Aerial Vehicle (UCAV) at a recent event. Dubbed the “Autonomous Aerial Aircraft,” this prototype bears a striking resemblance to SR-UAV (Surveillance and Reconnaissance Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) class systems, signaling a promising advancement in indigenous defense technology.
The unveiling took place at an exhibition aligned with the “Make in India” initiative, in collaboration with Suhas Tejaskanda, as indicated by the event branding. The prototype was displayed at Flying Wedge’s facility located at Bengaluru, Karnataka . The sleek, stealth-inspired design of the UCAV, with its angular lines and matte black finish, suggests a focus on low-observability and high maneuverability—key traits for modern combat drones.
Continue reading