AFI
SOURCE: AFI


Stealth fighter jets represent the pinnacle of modern military aviation, combining advanced aerodynamics, radar-evading technology, and cutting-edge materials to dominate the skies. The Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor, Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II, and Chengdu J-20 Mighty Dragon are three of the most prominent fifth-generation fighters in service today.
While their stealth capabilities, avionics, and performance often take center stage in discussions, the design elements like surface area and the use of rivets play a critical role in their stealth profiles and overall functionality. In this article, we’ll compare these three jets in terms of their surface area and rivet usage, exploring how these factors influence their design and stealth characteristics.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
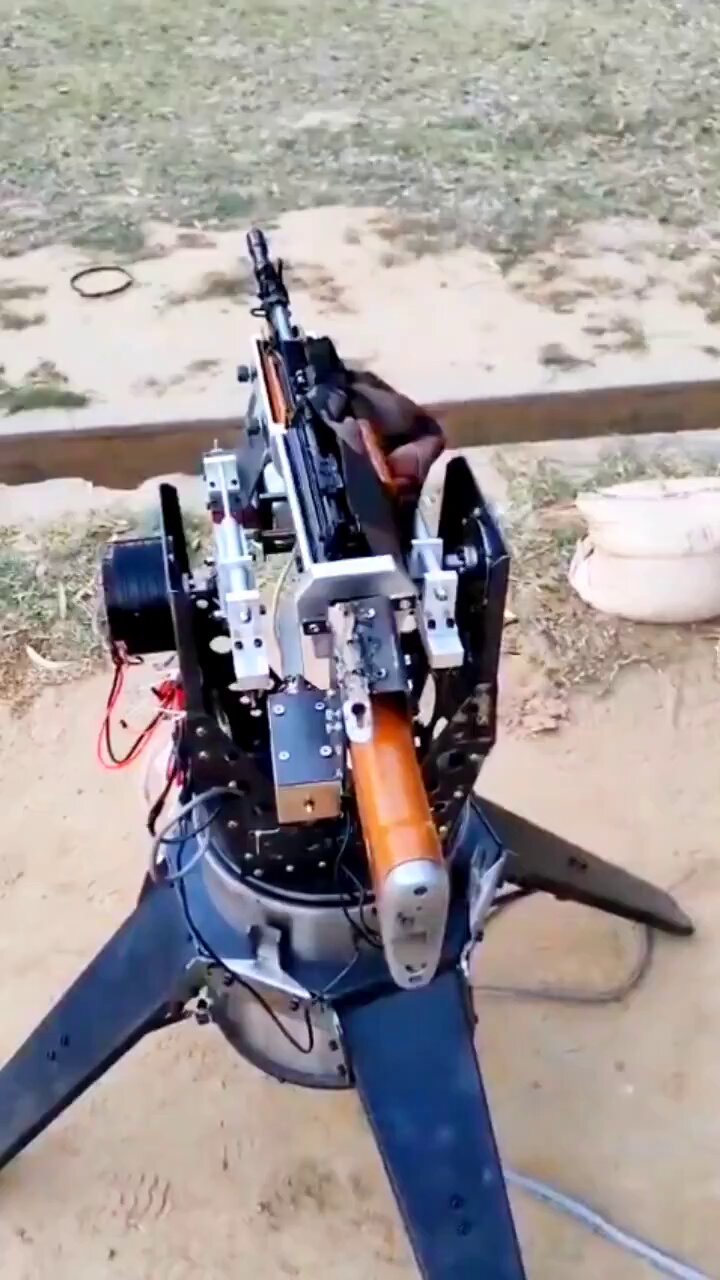


In a significant step toward integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into military technology, Dehradun-based BSS Materiel has conducted internal trials of its AI-driven autonomous weapon system designed for small arms. The trials, which took place recently, involved a prototype system for a 12.7mm caliber weapon, showcasing India’s growing focus on leveraging cutting-edge technology to enhance its defense capabilities.
BSS Materiel, a company based in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, has been working on integrating AI into small arms to create autonomous weapon systems capable of independent target identification and engagement. The prototype tested in the internal trials is designed for a 12.7mm caliber weapon, a heavy machine gun typically used for anti-materiel and anti-personnel roles. The system employs AI to enable autonomous operation, potentially allowing the weapon to detect, track, and engage targets without direct human intervention.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a strategic move to counter China’s expanding naval presence in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR), India is set to commission a new naval base for nuclear submarines and warships in coastal Andhra Pradesh by 2026. The base, located near the small village of Rambilli, approximately 50 km south of the Eastern Naval Command headquarters in Visakhapatnam, is part of India’s broader effort to strengthen its maritime capabilities.
This development, reported by The Times of India on April 7, 2025, coincides with ongoing upgrades to the Karwar naval base in Karnataka, signaling India’s intent to enhance both its eastern and western seaboards amid growing regional security challenges.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
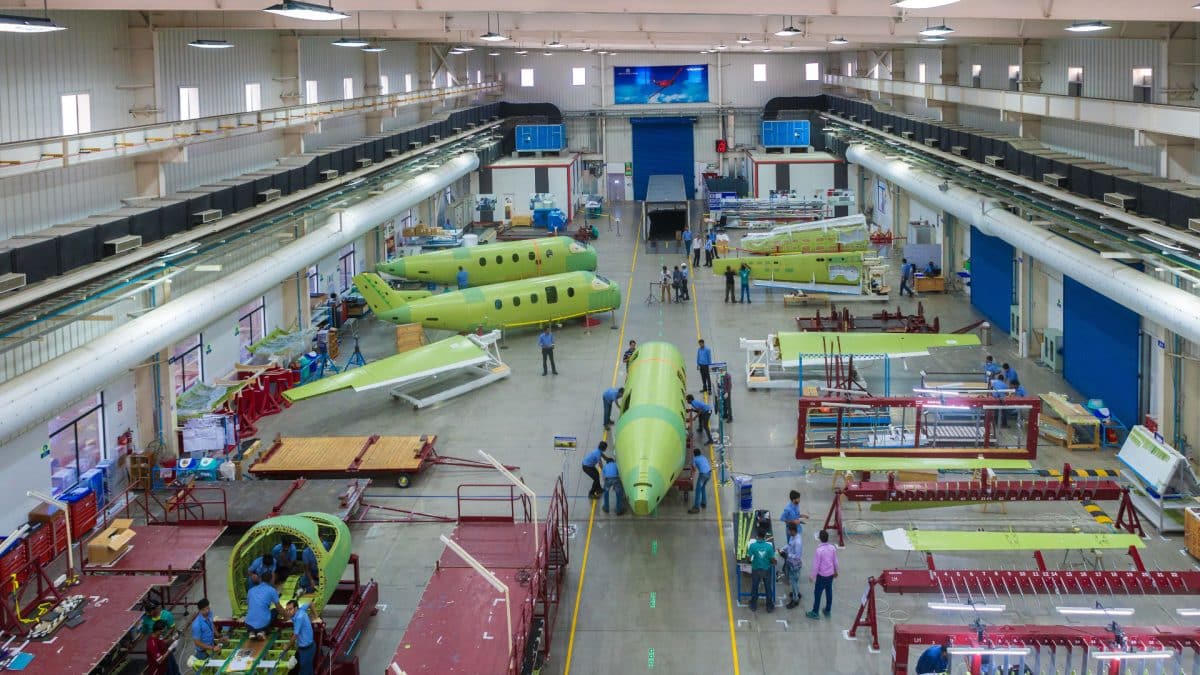


In a significant boost to India’s aerospace and defense sector, Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) has acquired a 7.4 lakh square foot plot in Karnataka’s Vemgal Industrial Area to establish a state-of-the-art aircraft manufacturing facility. The deal, valued at ?29.34 crore, was finalized with the Karnataka Industrial Areas Development Board (KIADB) under a lease-cum-sale agreement registered on February 24, 2025. The facility, which will include a final assembly line as well as Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) capabilities, marks a pivotal step toward enhancing India’s self-reliance in defense manufacturing while aligning with the government’s “Make in India” and “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiatives.
The Vemgal Industrial Area, located along the Kolar-Chikkaballapur Road (SH-96) in Karnataka’s Kolar district, is approximately 10 km from the Narasapura and Jakkasandra industrial zones and about 38 km from Bengaluru. Spanning 666 acres, this industrial hub has become a preferred destination for high-value manufacturing, particularly in the aerospace and defense sectors. Bengaluru, often dubbed India’s aerospace capital, already hosts a thriving ecosystem of aviation and defense technology firms, making it an ideal location for TASL’s new venture.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Odisha is steadily cementing its reputation as an industrially rich state, with a transformative project set to elevate its economic landscape. The Odisha government has greenlit the establishment of a titanium complex in Ganjam district, backed by an impressive investment of Rs 8000 crore. This ambitious initiative promises not only to generate significant employment opportunities but also to inject fresh momentum into the local economy, marking a pivotal step toward the state’s industrial and technological advancement.
The titanium complex is a flagship project under the Indo-Kazakh joint venture company (JVC), IREUK Titanium Limited, a collaboration between the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE), Government of India, and Kazakhstan’s Ust-Kamenogorsk Titanium and Magnesium Plant JSC (UKTMP JSC). This partnership, formalized in November 2024, leverages the strengths of both nations to create a robust titanium value chain within India. IREL (India) Limited, a central public sector undertaking under the DAE, will supply surplus ilmenite from its Odisha operations, while UKTMP JSC brings its globally recognized expertise in titanium production, including technology for manufacturing titanium slag.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a provocative statement published on April 7, 2025, in The Express Tribune, Air Commodore (Retd) Zahid Ul Hassan of the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) has claimed that the PAF is set to maintain a qualitative edge over the Indian Air Force (IAF) for the next 10 to 15 years. Hassan’s analysis hinges on the PAF’s ongoing efforts to fully operationalize its 5th generation platforms, while the IAF grapples with a strategic dilemma between pursuing self-reliance and opting for direct acquisitions.
This development, coupled with Pakistan’s focus on co-producing and acquiring 5th generation aircraft equipped with long-range stand-off weapons and first-shot capabilities, is likely to create significant challenges for the IAF, especially as China advances toward 6th generation aircraft for its air force.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Taiwan marked a significant milestone in its defense strategy as its first domestically built submarine, the Hai Kun (SS-711), commenced sea trials, a development reported by Army Recognition. The submarine, constructed by the state-backed CSBC Corporation, is a cornerstone of Taiwan’s Indigenous Defense Submarine (IDS) program, aimed at strengthening its naval capabilities amid escalating tensions with China.
The Hai Kun’s trials, which began as scheduled despite earlier funding challenges, underscore Taiwan’s determination to counter the growing threat of a Chinese invasion, particularly as the People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLAN) intensifies its activities in the region.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant advancement for India’s defense technology landscape, Bangalore-based Prime Toolings has showcased its innovative Rotating Detonation Engine (RDE), a cutting-edge propulsion system designed for short-range missiles. This development, unveiled in early 2025, positions the company at the forefront of next-generation aerospace engineering, promising to enhance India’s missile capabilities with a technology that offers superior efficiency, compactness, and performance. Prime Toolings claims that their RDE could revolutionize short-range missile systems, aligning with India’s growing emphasis on indigenous defense solutions and self-reliance under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
A Rotating Detonation Engine represents a paradigm shift in propulsion technology. Unlike traditional jet or rocket engines that rely on deflagration (subsonic combustion), an RDE harnesses continuous detonation waves—supersonic combustion events that travel around an annular chamber. This process generates thrust more efficiently by maintaining constant volume combustion, potentially offering up to 25% greater fuel efficiency compared to conventional engines. The result is a lighter, more compact powerplant capable of delivering higher speeds and longer ranges without the complexity of moving parts like compressors or turbines.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Indian Air Force (IAF), tasked with securing one of the world’s most contested airspaces, operates a dizzying array of fighter jets—MiG-21s, MiG-29s, Su-30MKIs, Jaguars, Mirage 2000s, Rafales, and soon Tejas Mk1A and MkII—spanning seven distinct types from Russian, French, British, and Indian origins. This multi-vendor patchwork, while historically driven by geopolitical and technological needs, has become a logistical and operational albatross.
With a sanctioned strength of 42 squadrons but only 31 operational as of April 2025, and a spate of crashes exposing maintenance woes, the IAF must pivot toward commonality: a streamlined fleet of three to four jet types, sharing engine linkage and covering low, mid, and high-end roles. This shift would enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and bolster combat readiness without the burden of managing 7-8 aircraft types for overlapping missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
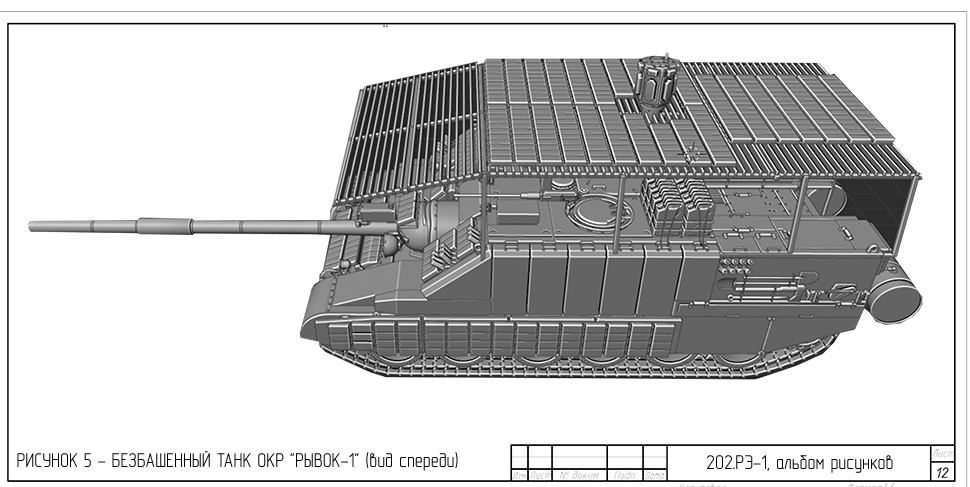

Uralvagonzavod (UVZ), Russia’s premier tank manufacturer and part of the Rostec state corporation, has unveiled a new modification of the T-90 tank, incorporating combat experience from the Special Military Operation (SMO). This latest iteration marks a significant departure from traditional tank design by eliminating the rotating turret—a feature long associated with Soviet and Russian main battle tanks since the introduction of the T-64.
According to UVZ’s press service, future tanks must retain powerful cannon armament, but the concept of a rotating turret is being abandoned due to its limitations on battlefield effectiveness and survivability. The company highlighted that modern combat scenarios have demonstrated that shifting fire between multiple targets, especially while on the move, is no longer a critical requirement for tank operations. Instead, the focus is shifting towards improving protection and firepower in a more static and controlled manner.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Hyderabad-based Dvipa Defence, a rising name in India’s small arms manufacturing sector, is set to deliver 10 units of its indigenously developed Ugram assault rifles (7.62x51mm) to the Border Security Force (BSF) for trials, as reported in posts on X dated April 4, 2025. This development marks a significant milestone for the company and the Ugram rifle, which has been positioned as a fully homegrown solution to meet the operational needs of India’s armed forces and paramilitary units. The trials with the BSF are a crucial step toward potential induction, reflecting India’s broader push for self-reliance in defense production.
The Ugram, meaning “ferocious” in Sanskrit, was first unveiled in January 2024 by the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) in Pune, in collaboration with Dvipa Defence (then known as Dvipa Armour India Pvt Ltd). Developed in a record-breaking 100 days, the rifle was designed to meet the Indian Army’s General Staff Qualitative Requirements (GSQRs), offering a 7.62x51mm caliber platform with an effective range of 500 meters and a weight of under 4 kg. Its 20-round magazine, rivet-free design, and ability to fire in both single and full-auto modes make it a versatile contender, comparable to modern AK- and AR-type rifles globally.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant strategic move, India has deployed its advanced S-400 air defense missile system near the Siliguri Corridor, colloquially known as the “Chicken’s Neck,” a narrow strip of land that connects mainland India to its northeastern states. This deployment comes as a direct response to heightened air activities by both Bangladesh and China in the region, raising concerns over security and territorial integrity in this geopolitically sensitive area.
The deployment follows reports of increased military activity by Bangladesh under the interim government led by Muhammad Yunus, which India considers an “illegal regime” following the ousting of former Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina in August 2024. Relations between New Delhi and Dhaka, once robust under Hasina’s leadership, have deteriorated sharply since her departure. Adding to the strain, Bangladesh has recently operationalized Turkish-procured Bayraktar TB2 unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) near the West Bengal border and Meghalaya, areas perilously close to the Chicken’s Neck.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


China’s Lhunze airbase, located just 100 kilometers from Tawang in India’s Arunachal Pradesh, is undergoing a rapid and significant transformation. Recent developments—new shelters, hangars, and expanded aprons—signal an ambitious military upgrade by the People’s Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF). This escalation, positioned perilously close to the Line of Actual Control (LAC) in the eastern sector, is poised to recalibrate the airpower balance in a region already fraught with tension. As India watches closely, the implications of this buildup extend far beyond mere infrastructure, hinting at China’s broader strategic intent along its disputed border.
Lhunze airbase, situated in Shannan Prefecture of the Tibet Autonomous Region, lies at an elevation of approximately 3,700 meters. Its proximity to Tawang—a culturally and strategically significant town in Arunachal Pradesh—places it within striking distance of India’s eastern frontier. Tawang, roughly 30 miles south of the McMahon Line, has long been a flashpoint in Sino-Indian relations, with China claiming it as part of “South Tibet.” The airbase’s location offers the PLAAF a forward operating hub, enhancing its ability to project airpower over Arunachal Pradesh and monitor Indian military movements along the LAC.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a groundbreaking stride toward modernizing its warfighting capabilities, the Indian Army’s Trishakti Corps has successfully validated Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) at the tactical level during Exercise Sarvshakti. Conducted in early 2025 under the Eastern Command, this exercise marks a pivotal moment in integrating next-generation technology with frontline tactics, showcasing India’s readiness to adapt to the evolving nature of warfare. The Trishakti Corps, headquartered in Siliguri and tasked with guarding the strategically vital eastern sector along the Line of Actual Control (LAC), has demonstrated how human ingenuity and cutting-edge systems can converge to enhance combat effectiveness.
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) is a revolutionary concept that pairs human-operated platforms—such as fighter jets, helicopters, or ground units—with unmanned systems like drones or robots. This synergy leverages the strengths of both: the decision-making prowess and situational awareness of human operators, combined with the precision, endurance, and expendability of autonomous machines. At its core, MUM-T aims to amplify battlefield awareness, extend operational reach, and reduce risk to personnel—all while delivering a decisive edge over adversaries.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
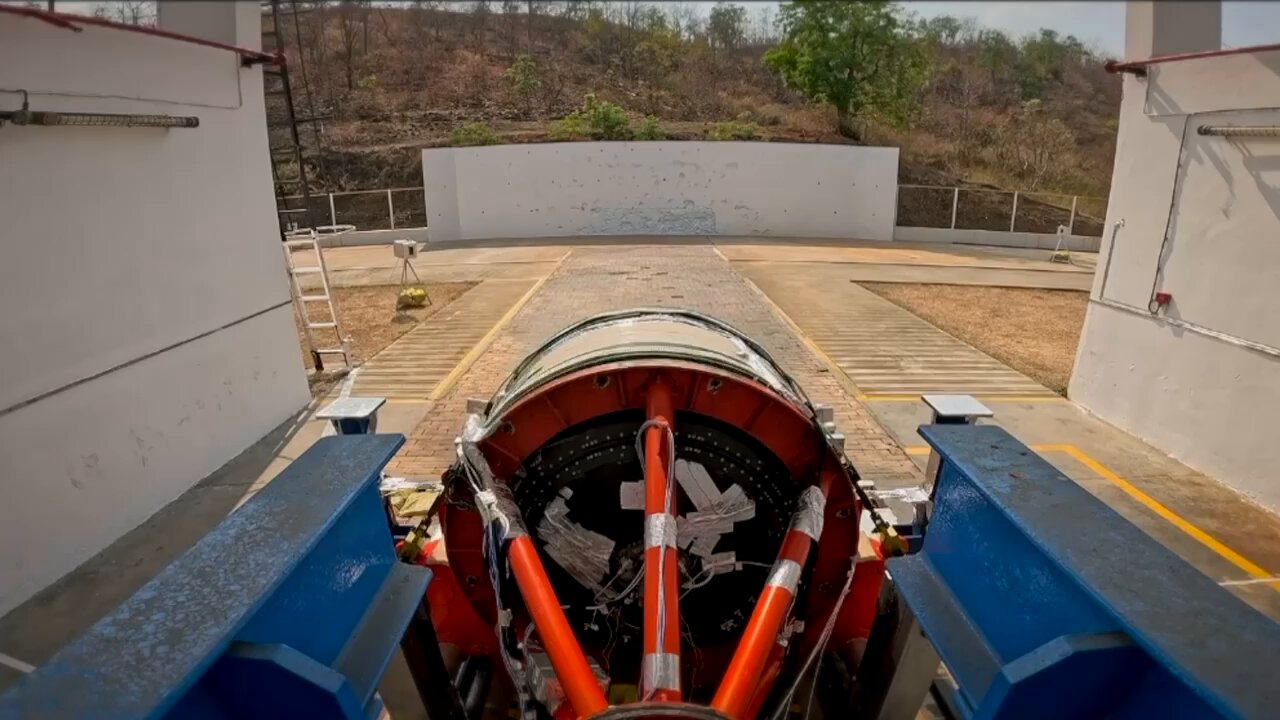


In a significant milestone for India’s private aerospace sector, Solar Defence and Aerospace Limited (SDAL), based in Nagpur, has successfully developed and manufactured the propulsion system, including its igniter and the third-stage rocket motor, for the Vikram-1 Satellite Launch Vehicle. This achievement underscores SDAL’s growing role in advancing India’s space ambitions and highlights the increasing contribution of private industry to the nation’s aerospace ecosystem.
The Vikram-1, developed by Hyderabad-based Skyroot Aerospace, is poised to become India’s first privately built orbital rocket, with its maiden launch targeted for late 2025. SDAL’s contribution to this ambitious project—a robust third-stage rocket motor—marks a critical step toward realizing that goal. With a propellant mass of 2400 kg and a maximum thrust of 75,000 N (approximately 7.65 tons), this rocket motor is a testament to the precision and innovation driving India’s space technology advancements.
Continue reading