Monthly Archives: November 2024
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) Chairman and Managing Director, Sunil Kumar, has confirmed that the much-anticipated deal for the procurement of F-414 engines from GE Aerospace is set to take place sometime before Mid 2025, although it is now unlikely to be concluded by the end of this year as initially expected. The deal, which is crucial for the Tejas Mk II program, is expected to be a significant milestone in India’s efforts to boost its domestic aerospace capabilities.
The F-414 engine is the key component for powering the Tejas Mk II, the upgraded variant of the indigenous Tejas Mk I fighter aircraft. The deal with GE Aerospace will involve 99 engines, which will be locally manufactured by HAL with a significant 80% Transfer of Technology (ToT). This represents a major step forward for India’s aviation sector, as the F-414 engines will not only support the Tejas Mk II but also enhance the country’s long-term capability in developing and manufacturing advanced fighter aircraft engines.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
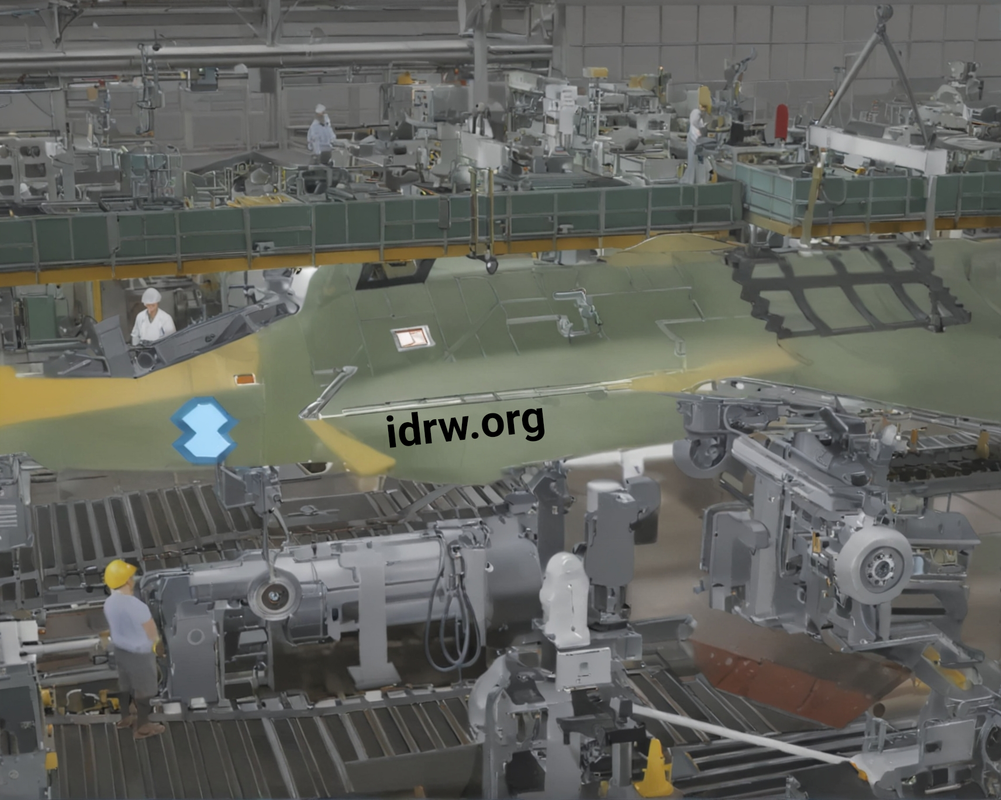

The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) has received enthusiastic responses from over a dozen private sector companies regarding its tender for the manufacturing of aircraft structural assemblies for the upcoming Tejas Mk-2, Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter (TEDBF), and Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) programs. These companies, already involved in the manufacturing of the fuselage for the Tejas Mk1A, are keen to expand their roles in India’s burgeoning defence aerospace sector.
The tender is part of ADA’s strategic initiative to enhance the involvement of Indian private companies in defence manufacturing. The move comes as India aims to bolster its indigenous capabilities and reduce reliance on foreign suppliers for critical military assets. With combined orders of nearly 400 units anticipated over the next two decades, the stakes are high, and the participation of private players will be pivotal.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
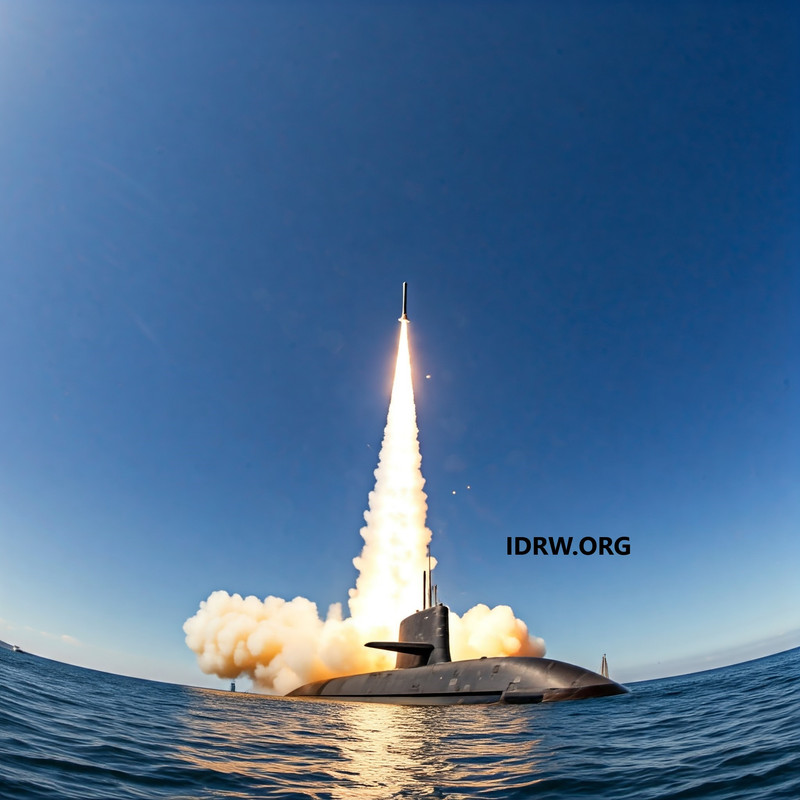

India is making significant strides in its Submarine Shipbuilding Program, particularly with the development of nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs) that will also function as guided missile submarines (SSGNs). This initiative represents a strategic enhancement of India’s naval capabilities, focusing on both land-attack and anti-ship operations.
As the Indian Navy collaborates with the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), a new generation of long-range cruise missiles is set to emerge, effectively doubling the strike capabilities of existing systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is making significant strides in its commitment to the development of the SWiFT stealth UAV (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle) program, a move driven by the performance shortcomings of traditional short- and medium-range UAVs and the operational challenges faced by conventional UAVs, particularly their vulnerability to detection and engagement, have underscored the need for advanced capabilities that can operate effectively in modern warfare environments.
The recent conflicts have demonstrated that traditional UAVs can be easily detected and targeted, relegating them to secondary roles on the battlefield. As such, the IAF’s push for the SWiFT program reflects a strategic pivot towards incorporating stealth technology into its unmanned systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

In a significant development for India’s defense aerospace sector, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Aerospace Laboratories (CSIR-NAL) has initiated the evaluation of control laws for the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Mk2, marking a crucial step in the aircraft’s developmental progress. The evaluation process, undertaken in 2023-24, specifically focused on the control laws governing the aircraft’s take-off phase, with pilots actively participating in the testing loop.
The LCA Mk2, a next-generation iteration of the Tejas Mk1, features numerous enhancements, including a more powerful engine, extended range, and increased payload capacity. Control laws, or “flight control laws,” are algorithms that dictate how an aircraft responds to pilot inputs and environmental factors, playing a critical role in ensuring safe, stable, and efficient flight performance. For the LCA Mk2, these control laws are essential for enabling precise maneuverability and optimal stability across various flight phases.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
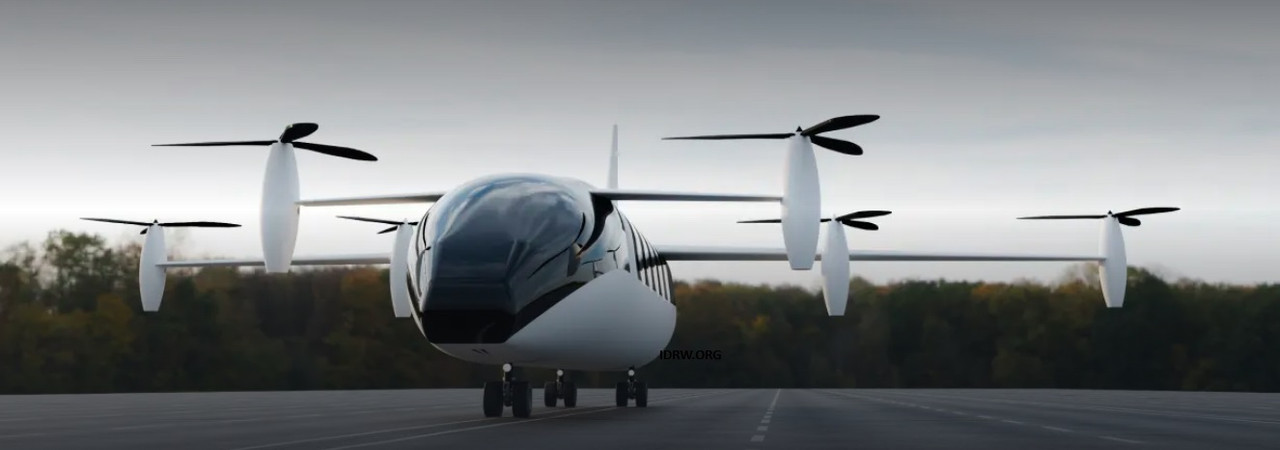

Telangana-based BluJ Aerospace Pvt. Ltd is set to revolutionize urban and regional air transportation with its innovative BluJ Hop vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) aircraft. Powered by hydrogen, the BluJ Hop promises a quieter, cleaner, and safer flying experience while maximizing performance.
Designed for long-range regional travel and high payload capacity, the BluJ Hop aims to redefine the standards for sustainable, commercially viable air transportation. By utilizing hydrogen as a fuel, the aircraft minimizes noise pollution and reduces its environmental footprint, making it an ideal solution for urban and regional areas.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
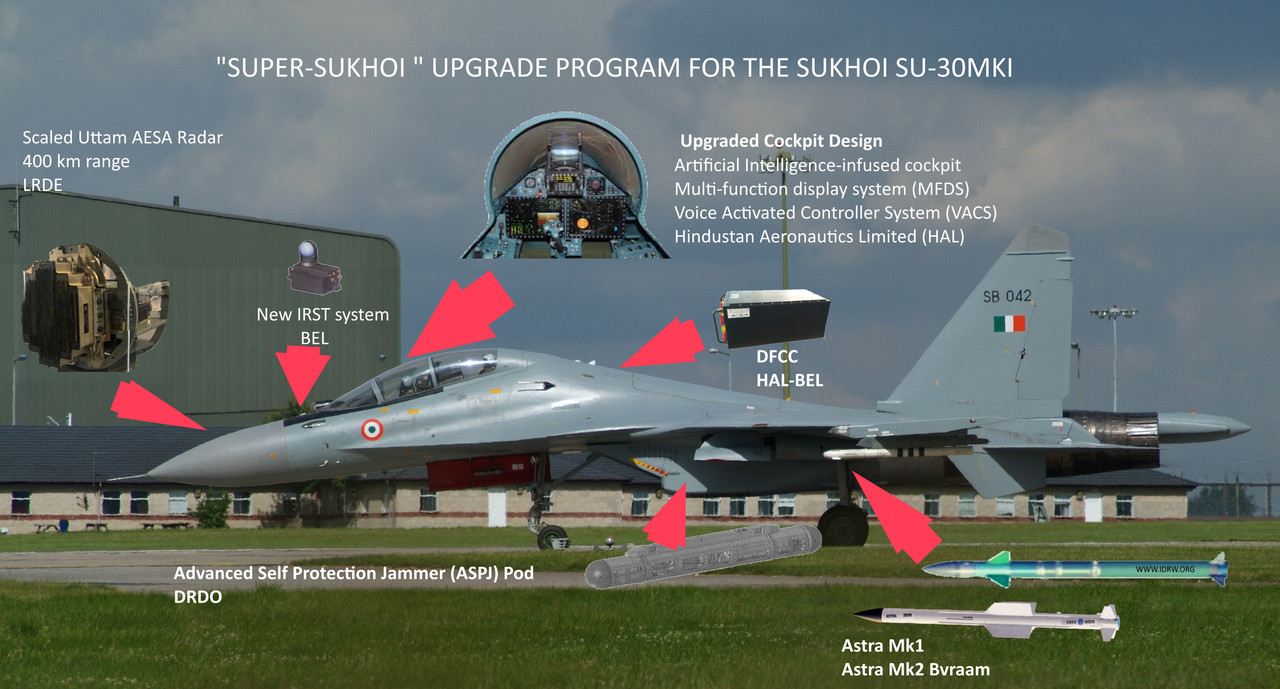
India’s Ministry of Defence is progressing toward finalizing an extensive upgrade plan for 84 of its SU-30MKI fighter jets under the “Super Sukhoi” program, marking a major step in the modernization of the Indian Air Force (IAF). Following the Defense Acquisition Council’s (DAC) approval on November 30, 2023, the draft proposal for the upgrade, valued at approximately ?63,000 crore, is now pending clearance by the Prime Minister-led Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS). This ambitious project aims to enhance the operational capabilities of the SU-30MKI, transforming it into a near fifth-generation platform, though it will lack certain stealth features.
Once the CCS grants approval, a formal contract will initiate the project, with the first upgraded aircraft expected to be rolled out after three and half years. The timeline for the complete development and flight testing process is projected to span seven years. This process includes integrating advanced avionics, new radar systems, enhanced electronic warfare (EW) suites, and more powerful engines. Notably, two test-bed aircraft will be modified to the Super Sukhoi configuration, providing a basis for the comprehensive testing of new systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
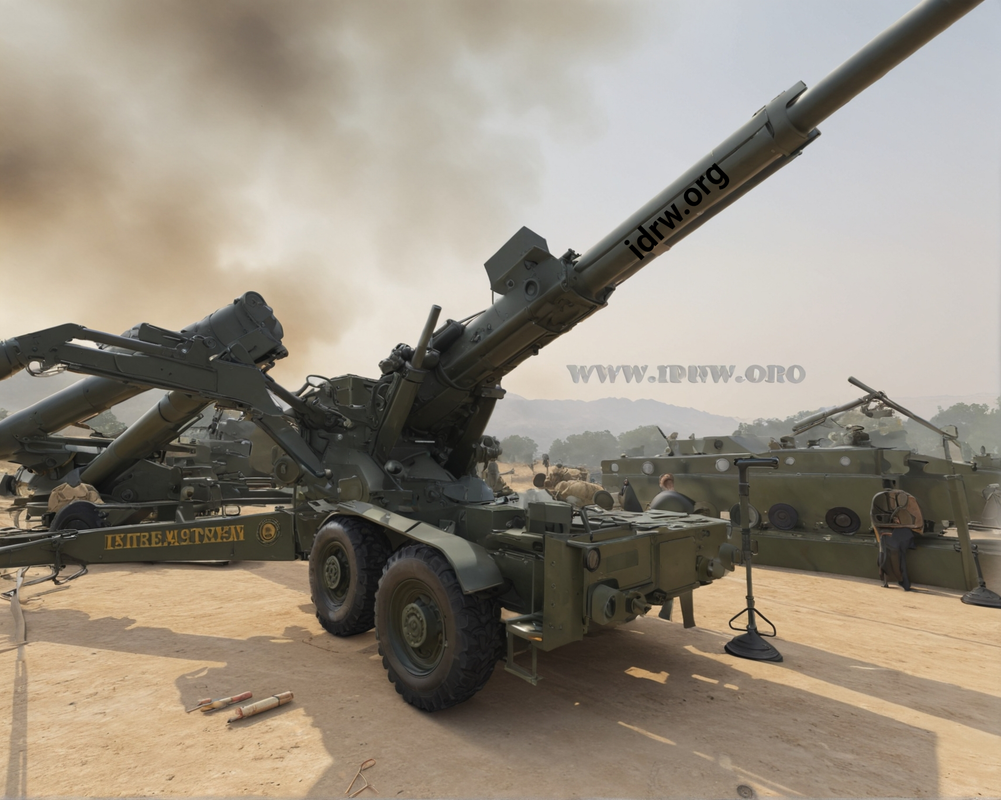

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is in the process of developing a lighter variant of the Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS) to meet the Indian Army’s requirements for a more mobile, lightweight artillery system.
This new Towed Gun System (TGS) is designed to feature a 23-litre chamber capacity and a lighter barrel, which will bring its weight under the 15-ton threshold mandated by the Army. The TGS is intended to meet the Army’s growing need for agile, high-performance artillery, with plans to procure approximately 1,200 units in the future, starting with an initial order of 400 guns.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
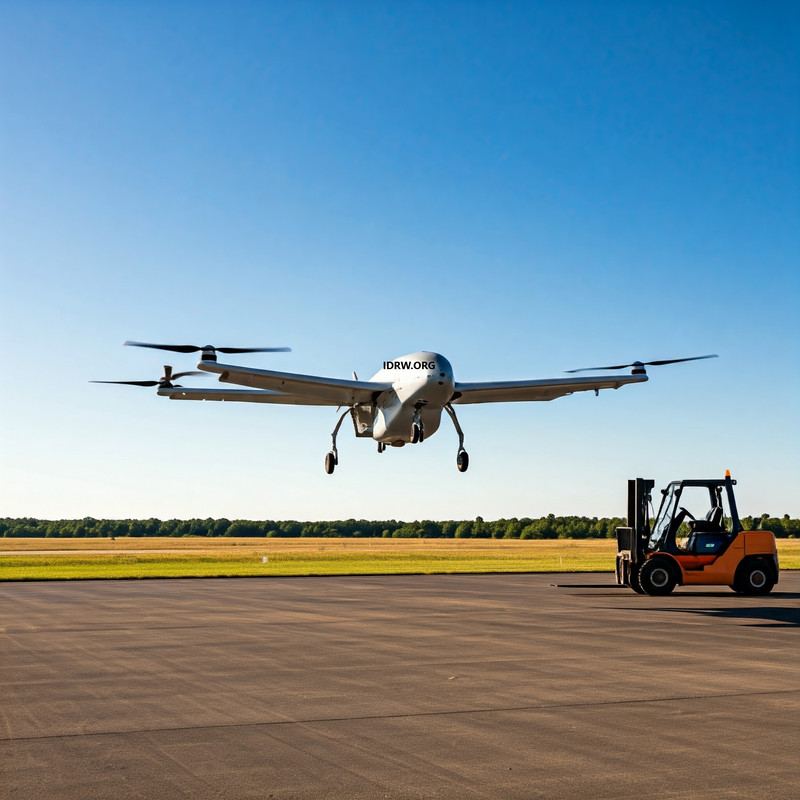

The Indian Army is keen on expanding its fleet of cargo-carrying unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), currently capable of handling payloads ranging from 5kg to 250kg, by introducing much larger UAVs with significantly enhanced lifting capacities. The Army has initiated discussions with several key UAV manufacturers in India, exploring the development of UAVs capable of transporting 1-2 tons of cargo. These UAVs will be instrumental in delivering supplies to remote and difficult-to-access regions, especially in areas where adverse weather conditions make traditional cargo transportation by manned aircraft risky.
The current fleet of cargo-carrying UAVs has been highly effective in transporting light loads, and supporting military operations by ensuring timely delivery of essential supplies in difficult terrains and high-altitude areas. However, with the Army’s increasing logistical demands in remote regions, such as along the Himalayan border, there is an urgent need for UAVs with higher payload capacities. The Army is particularly interested in UAVs capable of carrying 1-2 tons of cargo, significantly increasing operational efficiency and reducing the need for manned helicopters in hazardous conditions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

After experiencing delays in the supply of F-404 engines from GE Aerospace, the Indian government is considering a strategic move to mitigate future supply chain disruptions for the indigenous Tejas Mk1A fighter jet program. With the Indian Air Force (IAF) planning to induct nearly 180 Tejas Mk1A aircraft, powered by F-404 engines, India is expected to request that GE Aerospace expand its local supply chain footprint within India. This request aims to secure a reliable supply of components and services for the F-404 engines and establish a robust, sustainable support network for the next four decades.
Recent delays in the delivery of F-404 engines have impacted the IAF’s production timeline for the Tejas Mk1A, raising concerns about the long-term viability of relying solely on GE’s existing global supply chain. As the Indian defense sector is increasingly prioritizing self-reliance under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, the need for an uninterrupted and efficient supply chain for critical equipment like engines has become essential. A localized supply chain in India would minimize the impact of global disruptions and streamline support for the growing fleet of Tejas aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL) in Visakhapatnam, a prominent Research and Development Laboratory under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of the Ministry of Defence (MoD), has issued an Expression of Interest (EOI) aimed at Indian manufacturers. This initiative seeks companies with sufficient experience, expertise, and the willingness to undertake the production of the Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM).
The Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM) is a cutting-edge naval mine designed and developed by NSTL, DRDO, with the primary objective of providing the Indian Navy a tactical advantage against modern stealth ships. The MIGM represents a significant advancement in maritime defense technology, incorporating state-of-the-art components that enhance its operational capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a recent discussion with idrw.org, a senior Indian Air Force (IAF) official revealed that the IAF would consider settling for 90 additional Rafale fighter jets under the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender if the Dassault Rafale is selected even though the MRFA tender was for 114 jets.
This move would align with the IAF’s original objective under the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) program, which initially sought a total of 126 aircraft to fill a critical capability gap.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
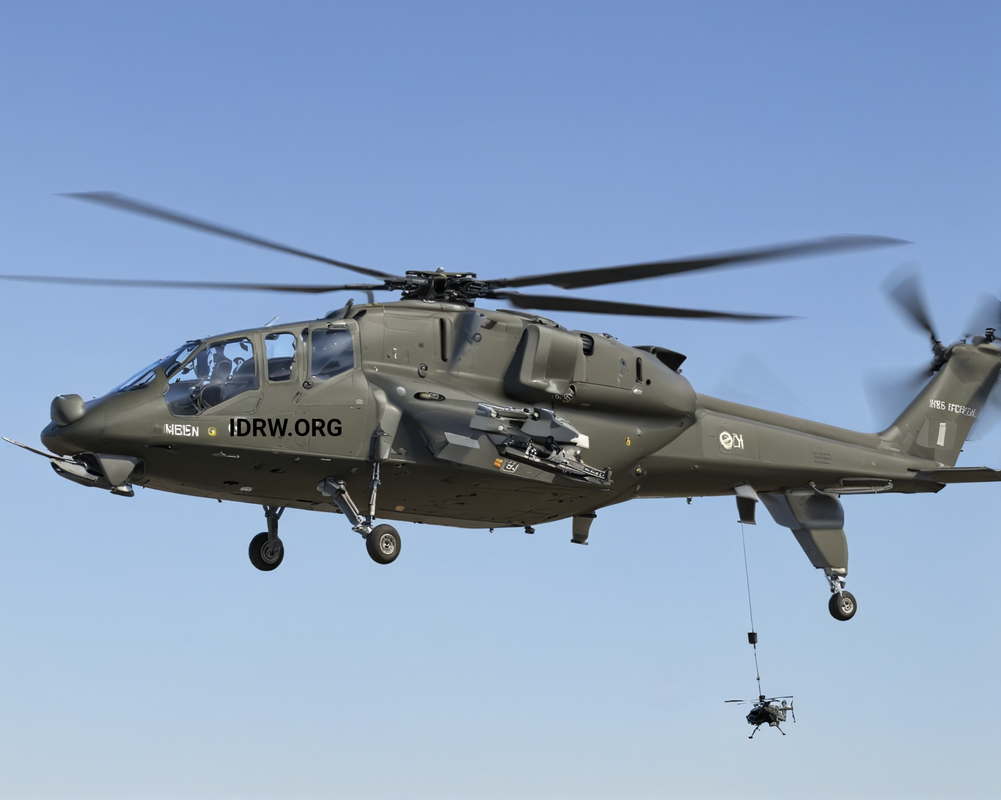

The LCH Prachand, India’s indigenously developed Light Combat Helicopter (LCH), is set to receive a Tactical Video Data Link (TVDL) system, significantly enhancing its network-centric warfare capabilities. This development will enable real-time data sharing across various platforms, improving coordination and battle management.
According to industrial sources close to idrw.org, work has already begun on the development and testing of such a system, designed specifically for the LCH Prachand to provide its crew with a comprehensive visual and data-sharing advantage in the battlespace.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
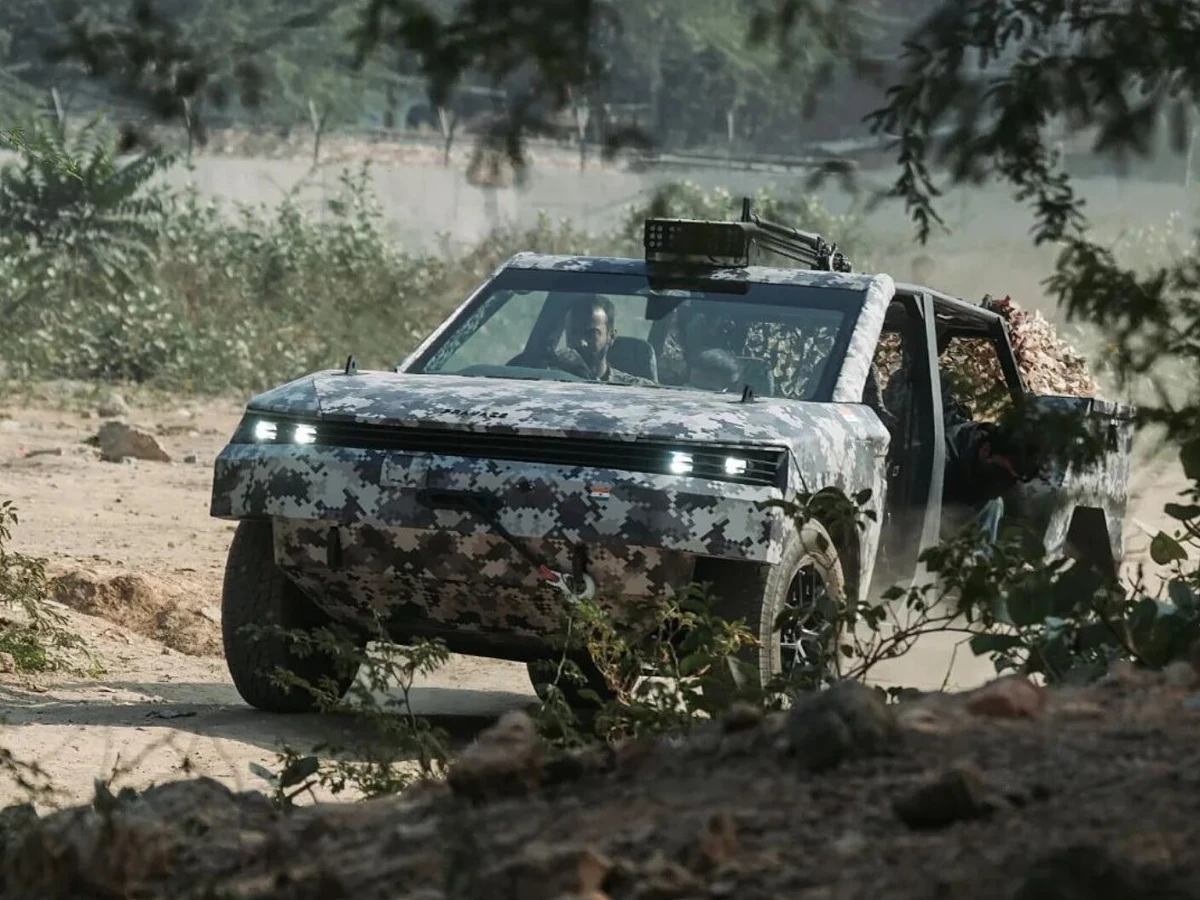

Bengaluru-based start-up Pravaig has achieved a significant milestone with its Veer EV, which completed rigorous trials in Ladakh and other northern high-altitude regions. These trials, conducted by the Indian Army, spanned nearly two months and tested the vehicle’s capabilities across challenging terrains and conditions. The trials are part of the Army’s evaluation for potential use by its Special Forces, and initial results suggest the Veer EV could be an excellent addition to their operational capabilities.
The Veer EV is powered by a dual-motor setup that generates an impressive 408 horsepower and 620Nm of torque. Equipped with a 90.9kWh battery, the vehicle boasts a range of over 500km, making it suitable for extended operations in remote areas. Designed to operate efficiently in harsh environments, the Veer EV was subjected to trials in Ladakh’s difficult terrains, including steep inclines, rocky paths, and extreme temperatures, proving its resilience and operational potential.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

India finds itself in a complex situation regarding the sale of its BrahMos supersonic cruise missile to Indonesia. This missile, developed as a joint venture with Russia, has seen increasing demand from countries looking to bolster their maritime defense capabilities. However, the U.S. has reportedly expressed concerns over the potential sale, adding layers of diplomatic and strategic calculations for India.
The BrahMos missile, known for its pinpoint accuracy, has a range of 300 kilometers and is effective in anti-ship warfare. Capable of hitting both land and sea targets, the missile is highly sought after for its speed and precision. Indonesia, with its vast archipelagic territory, has been interested in acquiring the BrahMos to protect its maritime boundaries, particularly as tensions rise in the South China Sea.
Continue reading