SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
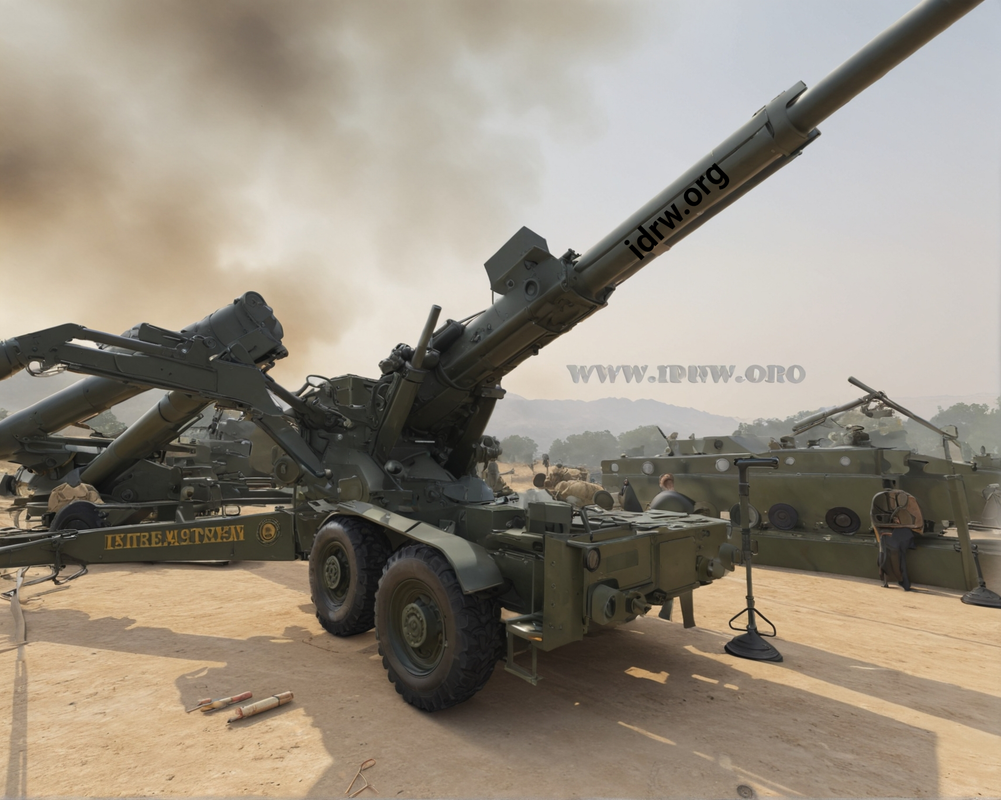


The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is in the process of developing a lighter variant of the Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS) to meet the Indian Army’s requirements for a more mobile, lightweight artillery system.
This new Towed Gun System (TGS) is designed to feature a 23-litre chamber capacity and a lighter barrel, which will bring its weight under the 15-ton threshold mandated by the Army. The TGS is intended to meet the Army’s growing need for agile, high-performance artillery, with plans to procure approximately 1,200 units in the future, starting with an initial order of 400 guns.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
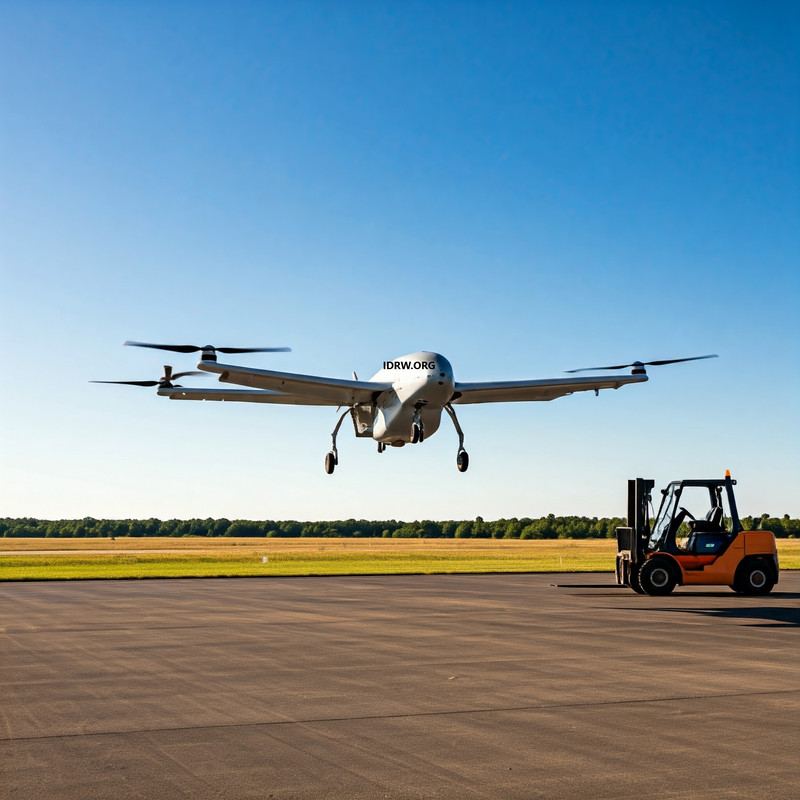


The Indian Army is keen on expanding its fleet of cargo-carrying unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), currently capable of handling payloads ranging from 5kg to 250kg, by introducing much larger UAVs with significantly enhanced lifting capacities. The Army has initiated discussions with several key UAV manufacturers in India, exploring the development of UAVs capable of transporting 1-2 tons of cargo. These UAVs will be instrumental in delivering supplies to remote and difficult-to-access regions, especially in areas where adverse weather conditions make traditional cargo transportation by manned aircraft risky.
The current fleet of cargo-carrying UAVs has been highly effective in transporting light loads, and supporting military operations by ensuring timely delivery of essential supplies in difficult terrains and high-altitude areas. However, with the Army’s increasing logistical demands in remote regions, such as along the Himalayan border, there is an urgent need for UAVs with higher payload capacities. The Army is particularly interested in UAVs capable of carrying 1-2 tons of cargo, significantly increasing operational efficiency and reducing the need for manned helicopters in hazardous conditions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


After experiencing delays in the supply of F-404 engines from GE Aerospace, the Indian government is considering a strategic move to mitigate future supply chain disruptions for the indigenous Tejas Mk1A fighter jet program. With the Indian Air Force (IAF) planning to induct nearly 180 Tejas Mk1A aircraft, powered by F-404 engines, India is expected to request that GE Aerospace expand its local supply chain footprint within India. This request aims to secure a reliable supply of components and services for the F-404 engines and establish a robust, sustainable support network for the next four decades.
Recent delays in the delivery of F-404 engines have impacted the IAF’s production timeline for the Tejas Mk1A, raising concerns about the long-term viability of relying solely on GE’s existing global supply chain. As the Indian defense sector is increasingly prioritizing self-reliance under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative, the need for an uninterrupted and efficient supply chain for critical equipment like engines has become essential. A localized supply chain in India would minimize the impact of global disruptions and streamline support for the growing fleet of Tejas aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL) in Visakhapatnam, a prominent Research and Development Laboratory under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) of the Ministry of Defence (MoD), has issued an Expression of Interest (EOI) aimed at Indian manufacturers. This initiative seeks companies with sufficient experience, expertise, and the willingness to undertake the production of the Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM).
The Multi Influence Ground Mine (MIGM) is a cutting-edge naval mine designed and developed by NSTL, DRDO, with the primary objective of providing the Indian Navy a tactical advantage against modern stealth ships. The MIGM represents a significant advancement in maritime defense technology, incorporating state-of-the-art components that enhance its operational capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a recent discussion with idrw.org, a senior Indian Air Force (IAF) official revealed that the IAF would consider settling for 90 additional Rafale fighter jets under the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender if the Dassault Rafale is selected even though the MRFA tender was for 114 jets.
This move would align with the IAF’s original objective under the Medium Multi-Role Combat Aircraft (MMRCA) program, which initially sought a total of 126 aircraft to fill a critical capability gap.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
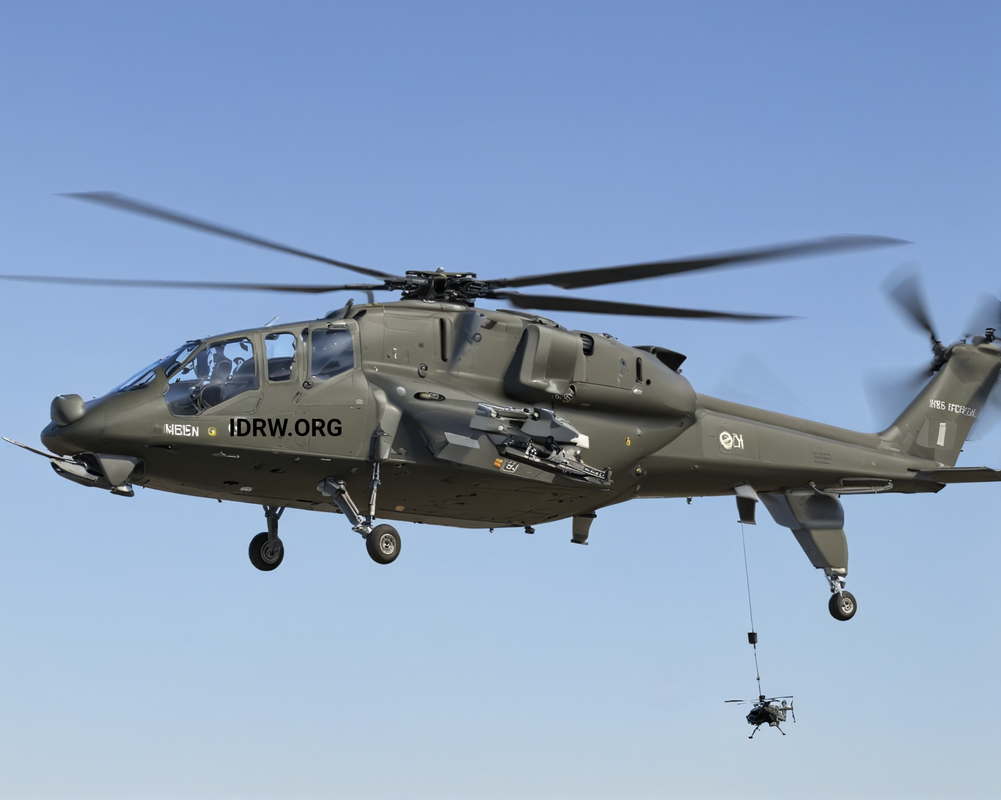


The LCH Prachand, India’s indigenously developed Light Combat Helicopter (LCH), is set to receive a Tactical Video Data Link (TVDL) system, significantly enhancing its network-centric warfare capabilities. This development will enable real-time data sharing across various platforms, improving coordination and battle management.
According to industrial sources close to idrw.org, work has already begun on the development and testing of such a system, designed specifically for the LCH Prachand to provide its crew with a comprehensive visual and data-sharing advantage in the battlespace.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
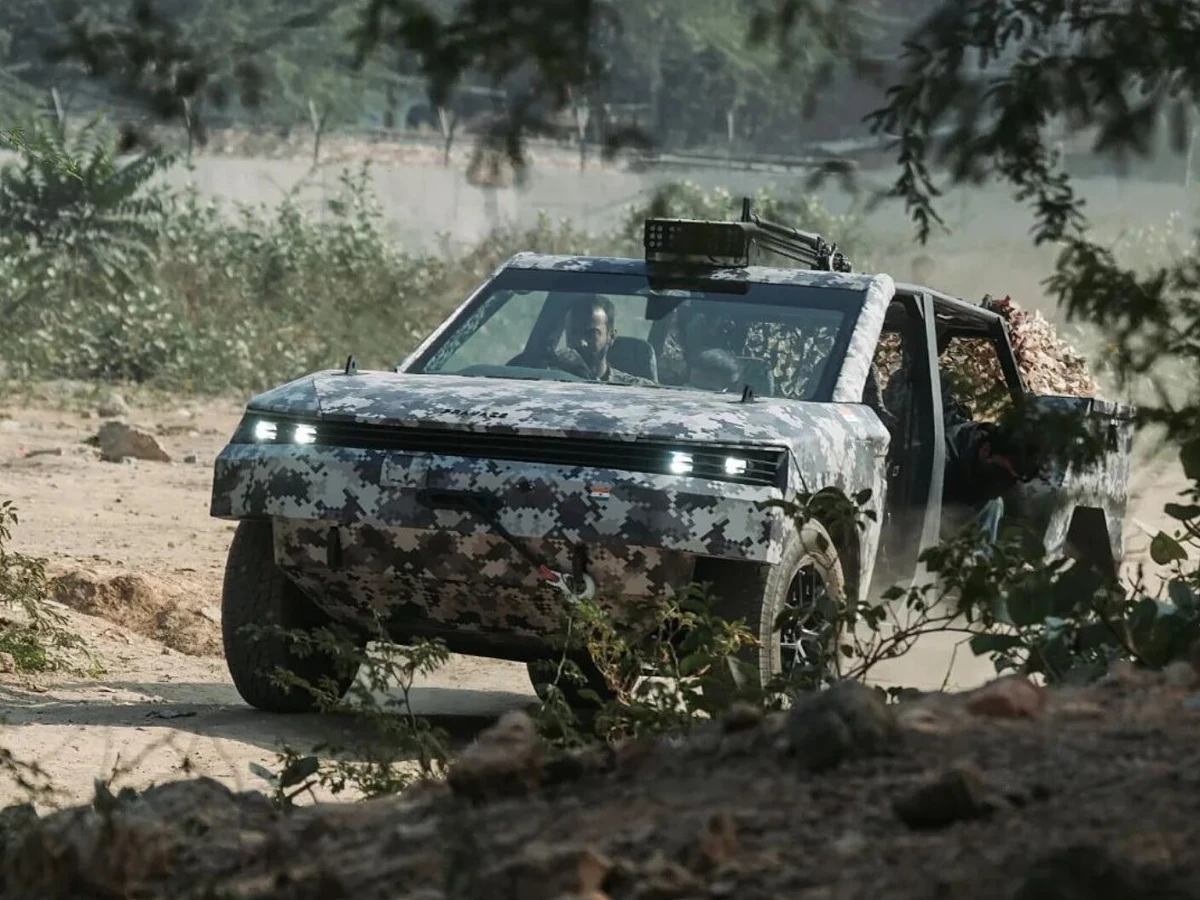


Bengaluru-based start-up Pravaig has achieved a significant milestone with its Veer EV, which completed rigorous trials in Ladakh and other northern high-altitude regions. These trials, conducted by the Indian Army, spanned nearly two months and tested the vehicle’s capabilities across challenging terrains and conditions. The trials are part of the Army’s evaluation for potential use by its Special Forces, and initial results suggest the Veer EV could be an excellent addition to their operational capabilities.
The Veer EV is powered by a dual-motor setup that generates an impressive 408 horsepower and 620Nm of torque. Equipped with a 90.9kWh battery, the vehicle boasts a range of over 500km, making it suitable for extended operations in remote areas. Designed to operate efficiently in harsh environments, the Veer EV was subjected to trials in Ladakh’s difficult terrains, including steep inclines, rocky paths, and extreme temperatures, proving its resilience and operational potential.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


India finds itself in a complex situation regarding the sale of its BrahMos supersonic cruise missile to Indonesia. This missile, developed as a joint venture with Russia, has seen increasing demand from countries looking to bolster their maritime defense capabilities. However, the U.S. has reportedly expressed concerns over the potential sale, adding layers of diplomatic and strategic calculations for India.
The BrahMos missile, known for its pinpoint accuracy, has a range of 300 kilometers and is effective in anti-ship warfare. Capable of hitting both land and sea targets, the missile is highly sought after for its speed and precision. Indonesia, with its vast archipelagic territory, has been interested in acquiring the BrahMos to protect its maritime boundaries, particularly as tensions rise in the South China Sea.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


Ordnance Factory Medak (OFM), one of India’s premier defense manufacturing units under the Ministry of Defence, has recently dispatched advanced Quadrant Fire Control systems and Optical Quadrant KO-60 to Israel. This dispatch reflects India’s expanding technical expertise and strengthening defense ties with international allies, particularly Israel, which has been a strategic partner in technology exchange and defense cooperation.
The Quadrant Fire Control systems produced by Ordnance Factory Medak are precision instruments essential for artillery fire control, enabling accurate targeting by measuring the angle of inclination on various surfaces. The precision of these instruments allows military units to calibrate artillery and other equipment with high accuracy, optimizing performance in tactical and battlefield scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
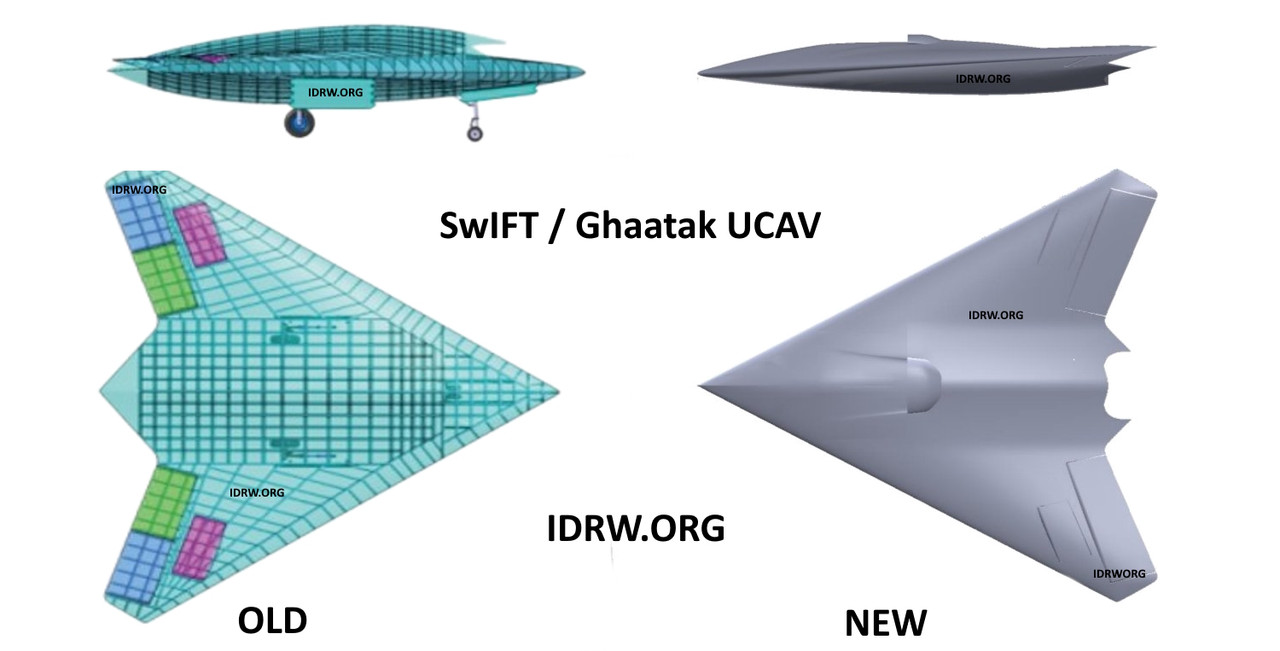

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) are set to begin fabricating a full-scale model of the Ghatak stealth unmanned combat aerial vehicle (UCAV) program. This development follows the infusion of funding for the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) and Ghatak programs, signifying a major milestone in India’s indigenous stealth aircraft capabilities.
The Ghatak is a 12-ton, stealthy unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed to operate in high-threat environments. It is intended to perform deep penetration strikes, surveillance, and reconnaissance missions in contested airspace, where conventional manned aircraft may not survive.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has added a significant advancement to India’s arsenal with the development of TARA, the Tactical Advanced Range Augmentation system. This new glide bomb series, which will include variants based on 250kg, 450kg, and 500kg bomb bodies, marks India’s first indigenous glide weapon system designed to enhance the precision and range of air-delivered munitions.
One of the standout features of the TARA series is its integration of dual CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) / IIR (Imaging Infrared) seekers, providing enhanced target acquisition and guidance. The inclusion of advanced scene-matching algorithms significantly boosts the bomb’s ability to locate and engage targets in complex environments, including under adverse weather conditions or in the presence of countermeasures.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Indian Navy’s ageing Kilo-class submarine fleet, once the backbone of its underwater force, has now dwindled to seven from its original strength of ten submarines. The fleet, officially designated as the Sindhughosh class, has been a critical part of India’s naval capabilities for over three decades. However, with advancements in submarine technology and the increasing challenges posed by modern naval warfare, the Indian Navy is now preparing for the gradual phase-out of these vessels.
The reduction in the Kilo-class fleet began with the retirement of INS Sindhudhvaj in July 2022, a submarine that had served the Navy since 1987. Another significant loss was the tragic sinking of INS Sindhurakshak in 2013, which was caused by an onboard explosion that claimed the lives of 18 sailors. Further, the INS Sindhuvir was transferred to Myanmar in 2020 as part of defence cooperation between the two nations, reducing the fleet size.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


2022 trials at the Indian Navy’s airbase, INS Hansa in Goa, tested two leading fighter jets, Dassault’s Rafale M and Boeing’s F/A-18E/F Super Hornet, both competing for a key role in enhancing the Navy’s carrier-based combat capabilities. Sources familiar with the trials indicate that the Rafale M outperformed the Super Hornet on several critical technical criteria, with one significant differentiator being the lack of an integrated Infrared Search and Track (IRST) system on the F/A-18E/F.
The IRST system is a passive, infrared-based tracking sensor that allows a fighter jet to detect and follow enemy aircraft without emitting radio frequencies, thus remaining undetected by adversaries. By operating exclusively in the infrared spectrum, the IRST system provides the ability to spot airborne threats well beyond visual range. This is particularly valuable in modern combat scenarios, where stealth and the element of surprise are critical.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is set to elevate the capabilities of the Advanced Light-Weight Torpedo (ALWT) with a 100 kW Magnesium-Silver Chloride (Mg-AgCl) battery upgrade, intended to boost its speed from 33 knots to an impressive 47 knots—a significant 42% increase. This enhancement aims to meet evolving anti-submarine warfare (ASW) requirements for the Indian Navy, furthering India’s indigenous defense technology capabilities.
The ALWT is the second generation of the Shyena torpedo, developed by DRDO’s Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), with production managed by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL). Specifically designed for anti-submarine warfare, the ALWT has cleared all trials and has been proposed for production.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
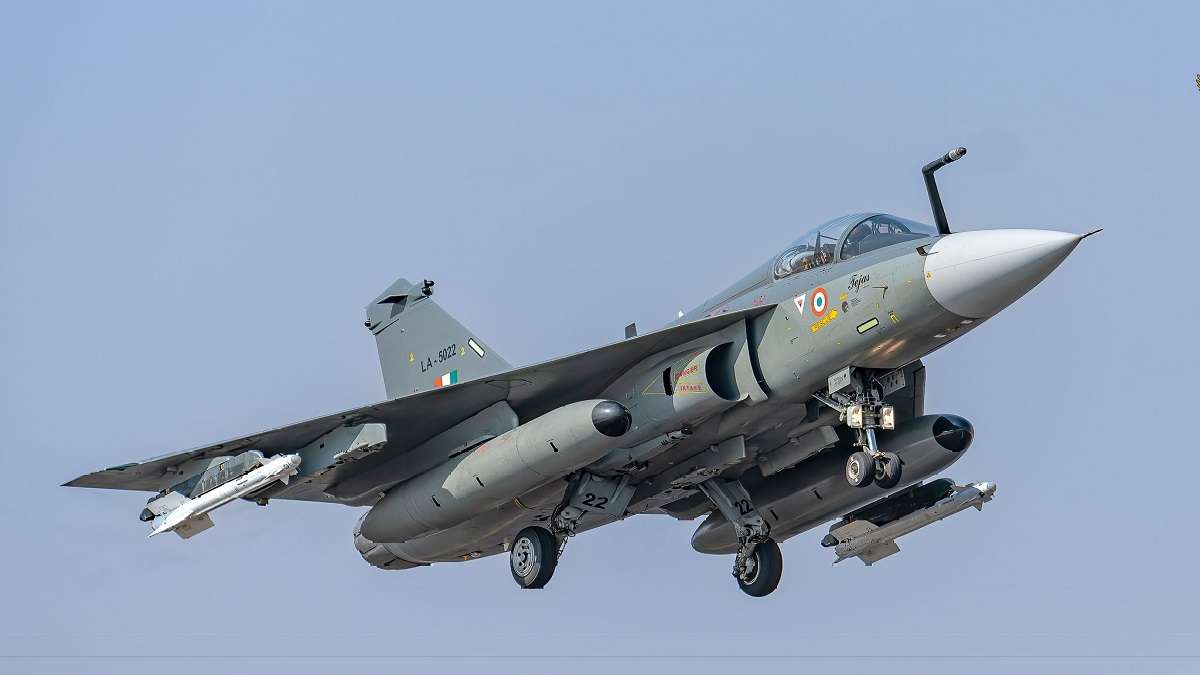


Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), the lead integrator of the indigenous Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (LCA), is facing significant delays in the production of the Tejas Mk1A due to the lack of supply of F-404 engines from GE Aerospace. The setback has affected the planned rollout of the first Tejas Mk1A jet from HAL’s new third production line, located in the MiG complex in Nashik. Originally scheduled for November, the milestone has now been postponed till March 2025, further impacting HAL’s ambitious production targets.
HAL, which currently operates two Tejas LCA production lines in Bangalore, has been manufacturing 16 aircraft per year. However, the lack of F-404 engines has caused production to slow down. HAL had aimed to expand its manufacturing capacity by opening the Nashik plant, with plans to initially produce an additional five Tejas Mk1A jets per year and eventually ramp up to eight. The production boost at Nashik was seen as critical to meeting the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) requirement of 83 Tejas Mk1A jets, which were ordered under a ?46,898 crore contract signed in February 2021.
Continue reading