SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


European missile manufacturer MBDA already has deepened its collaboration with India’s defence ecosystem by expanding the manufacturing of 15 major subassemblies for its MICA (Missile d’Interception et de Combat Aérien) missile. The partnership spans complex areas like mechanical, electrical, electromechanical, and pyrotechnic components, underscoring MBDA’s commitment to localizing advanced technology production within India. With the success of this collaboration, MBDA has ambitious plans to further leverage India’s defence manufacturing capabilities in its development of the next-generation MICA NG missile.
Scheduled for delivery starting in 2026, the MICA NG (Nouvelle Génération) is designed as a comprehensive upgrade of the existing MICA missile family, which has been in operational service with the French Armed Forces and 14 other nations. The MICA NG aims to be a seamless replacement, featuring substantial design improvements while preserving the current missile’s aerodynamics, mass, and centre of gravity to maintain compatibility with existing platforms and launchers. This approach will allow easy integration with systems already equipped with MICA, minimizing adaptation costs and requirements.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
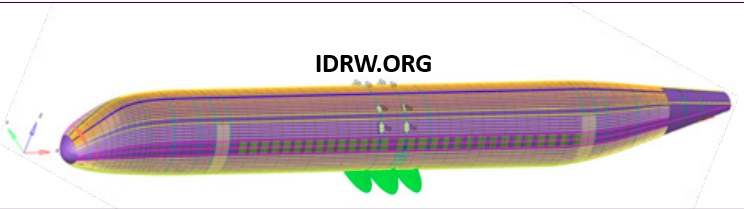

During 2023-24, the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-National Aerospace Laboratories (CSIR-NAL) made significant strides in the development of the RTA-90 regional transport aircraft. Key activities included extensive structural design and analysis, aerodynamic characterization, cockpit mock-up construction, and propulsion system advancements.
The RTA-90’s fuselage underwent detailed structural design and optimization, focusing on critical parameters like weight distribution, material thickness, stress points, deflection contours, and buckling eigenvalues. By simulating various load scenarios and estimating fatigue load spectrums, CSIR-NAL aimed to create a durable fuselage optimized for lightweight and resilient performance. This approach not only enhances the aircraft’s structural integrity but also contributes to fuel efficiency, crucial for regional transport operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


As India’s Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) continues to expand its Beyond Visual Range Air-to-Air Missile (BVRAAM) lineup, the organization is now setting the stage for the development of Astra MkIV, a missile concept tailored to meet the needs of next-generation air combat scenarios. With Astra MkI already operational in the Indian Air Force (IAF) and Astra MkII nearing the end of its development phase, the DRDO is accelerating its roadmap for air-to-air missile systems with Astra MkIII also in the pipeline.
The Astra MkI has solidified its place as a reliable BVRAAM for the IAF, marking India’s first successful indigenous BVRAAM program after over 15 years of research and development. The Astra MkI provides the IAF with an effective weapon to engage hostile aircraft at extended ranges, making it a standard part of the IAF’s armament.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is advancing its capabilities in space technology with Project VEDA, an ambitious program aimed at developing a launch vehicle tailored for low-cost, efficient satellite deployment.
With a focus on enhancing India’s self-reliance in satellite launch technology, Project VEDA’s specifications suggest it will be capable of carrying substantial payloads to low-Earth orbit (LEO).
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) has recently revealed its intent to conduct an open tender for the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) project, aiming to procure 114 jets for the Indian Air Force (IAF). This initiative is poised to be one of the largest defence procurement projects in recent years. As part of this ambitious plan, the MoD is focusing on companies that can assure high delivery rates, potentially targeting 20-24 jets per year. However, achieving this pace comes with certain challenges, particularly concerning localization—a core goal of India’s defence procurement strategy.
Sources familiar with the developments shared insights with IDRW.org, highlighting a primary concern: balancing the high delivery rates with localization requirements. While India’s defence policy emphasizes self-reliance and local production, particularly under the “Make in India” and “Atmanirbhar Bharat” initiatives, implementing these ideals in the MRFA project may necessitate some compromises. High delivery rates generally require a well-established production line and a streamlined supply chain, which can be challenging to achieve if each jet must meet extensive localization targets from the outset.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Indian Navy is evaluating Italy’s “Black Shark” torpedo as a potential solution for its Kalvari-class submarines, marking a re-emergence for this advanced heavyweight torpedo in India’s defense considerations. With a requirement for 48 new torpedoes, the Navy is conducting assessments and exploring options as several international contenders—including companies from Germany and France—vie for the contract. Notably, this interest in the Black Shark comes after the Italian company, which was previously blacklisted, has now re-entered the fray.
The Black Shark torpedo was initially evaluated for the Indian Navy in 2008 when it emerged as the leading candidate to fulfill a demand for 98 torpedoes intended to equip the Navy’s then-upcoming fleet of Scorpene-class submarines. The Black Shark, known for its long-range, high-speed performance, and advanced homing capabilities, seemed like an ideal match. However, the project faced a setback in 2013, when allegations of corruption linked to other defense deals with the same Italian company led to a comprehensive review and eventually a blacklisting by the Ministry of Defence (MoD). As a result, the entire acquisition process was suspended, and the case was subsequently referred to the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI).
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Indian Navy has made significant strides in indigenization by deciding to install indigenously developed Software-Defined Radios (SDRs) on all its aerial platforms. Among the first platforms to benefit from this upgrade are the Navy’s MH-60R Seahawk helicopters, also known as Romeos. This development marks a leap in the Navy’s efforts to enhance encrypted communication capabilities across its fleet.
The SDRs have been co-developed by the Indian Navy in collaboration with Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL). They are already deployed on the Navy’s surface ships, showcasing their reliability and performance. The version installed on aerial platforms like the MH-60R is a miniaturized variant of the surface ship system, optimized for airborne operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a strategic move to enhance the protection of aircraft on the ground, the Indian Navy has announced its interest in the development of a Radar Obscurant Cloak under the iDEX DISC (Defence India Startup Challenge) 13 initiative. The objective of this innovative project is to shield aircraft parked on the ground from detection by enemy radar, offering an additional layer of defense for assets at airbases and other vulnerable locations.
The primary function of this radar obscurant cloak is to minimize the radar signature of grounded aircraft, making it difficult for enemy radars to detect them. This is crucial in modern warfare, where the ability to conceal high-value assets from adversaries can make a significant difference in operational readiness and asset longevity.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


At the recent Indian Armour Symposium, Lt Gen Vivek Kashyap, Director General of the Armoured Corps, outlined the Indian Army’s future plans for a new generation of light battle tanks. Speaking to an audience of defense experts, industry leaders, and military officials, Lt Gen Kashyap revealed that the Army intends to work closely with private industry partners to develop a future light battle tank. These tanks, according to him, will be tailored to meet the evolving needs of the Army, especially in high-intensity and varied operational environments.
The Indian Army is moving forward with plans to identify two private industry partners after a thorough technical evaluation, who will each develop their own variants of the future light battle tank. These tanks will be built to meet specific Army requirements, focusing on mobility, survivability, firepower, and cost-efficiency. Lt Gen Kashyap emphasized that the collaboration between DRDO, L&T, and private industry will be critical in creating a platform that is adaptable, innovative, and future-proof for battlefield conditions.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
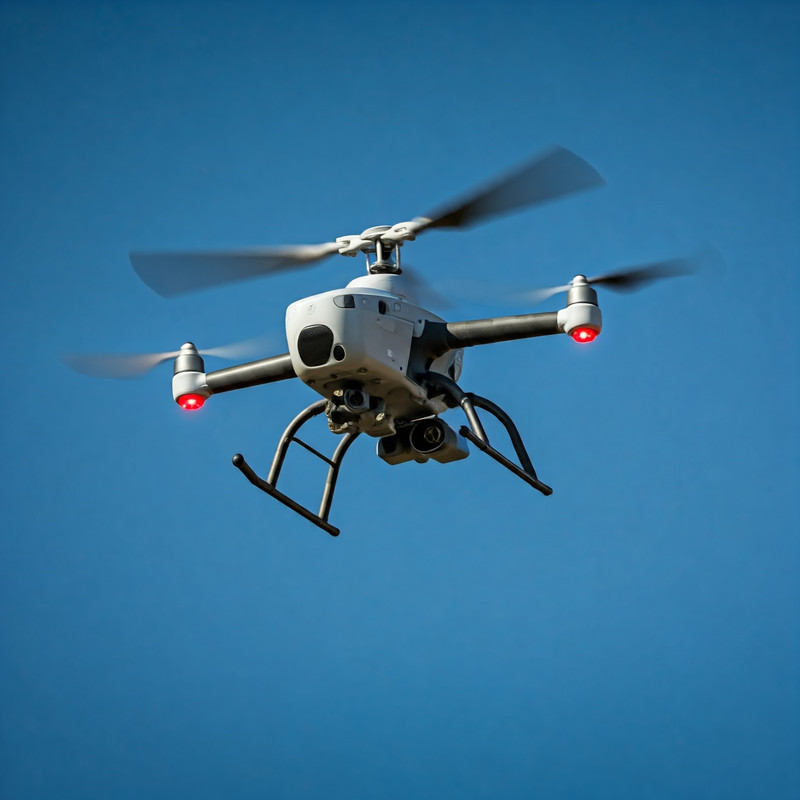


The Indian Army, in alignment with the Ministry of Defence (MoD), has announced its intention to procure advanced Surveillance Copters, including essential accessories, to enhance its situational awareness across diverse terrains. This initiative comes under India’s Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat programs, aiming to boost domestic manufacturing capabilities and reduce dependency on foreign technology in critical defense infrastructure. The issuance of a Request for Information (RFI) for Surveillance Copters marks a step toward defining the system’s specifications, identifying capable Indian vendors, and selecting a procurement category.
The Indian Army has outlined specific technical requirements to guide the development of the Surveillance Copter and its accessories.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) has reported significant advancements in the development of core technologies essential to the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. As India’s ambitious project to produce a fifth-generation stealth fighter, the AMCA program is a vital part of India’s defense self-reliance initiative. Two key areas of development that are progressing well include the test box and air intake-duct assembly using co-cured hybrid composites and the Frequency Selective Surface (FSS) Radome—both critical elements in achieving the AMCA’s stealth and performance goals.
The development of a stealthy fighter like the AMCA demands innovative approaches to both structural strength and radar cross-section (RCS) minimization. NAL’s work on the test box and air intake-duct assembly using co-cured hybrid composites represents a breakthrough in materials technology that will significantly reduce the aircraft’s weight while enhancing its stealth characteristics.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
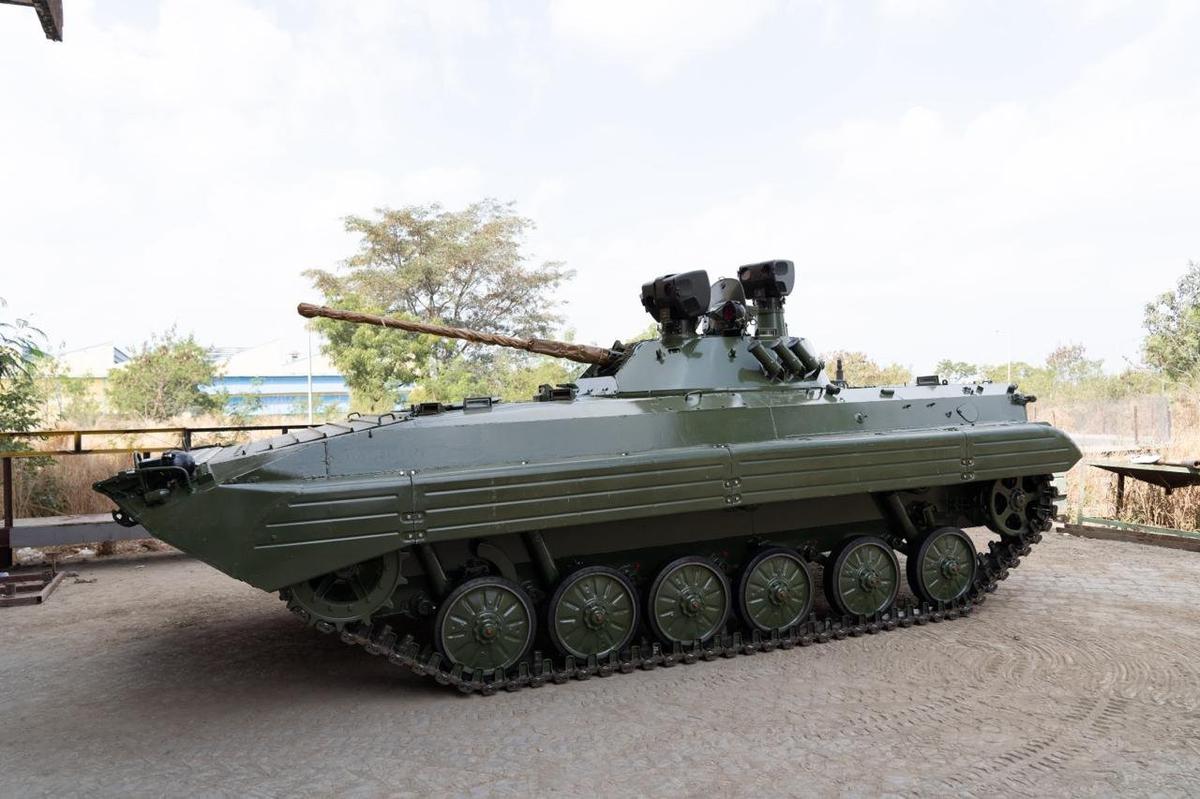


The Indian Army, through the iDEX DISC 12 Challenge, is addressing the critical need for Antiskid Tracks for BMP Infantry Fighting Vehicles operating in High Altitude Areas (HAA) and glaciated terrain. This initiative comes as the Mechanised Infantry is increasingly being deployed in unconventional terrains, including deserts, high-altitude mountains, and glaciated regions, where mobility challenges for heavy equipment like BMPs (Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty) have become more pronounced.
The BMPs, a core component of the Indian Army’s mechanised forces, are designed for manoeuvrability, speed, and firepower in diverse battlefield environments. However, the extreme conditions of high-altitude and snow-covered terrain present significant operational challenges. As these terrains experience severe ice accumulation, particularly on mountain passes and glaciated areas, the metal tracks of the BMPs face deterioration due to prolonged use, leading to reduced friction and increased slipping and skidding during manoeuvres, especially while making sharp turns or braking.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a recent meeting with prospective suppliers for the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, officials from the Indian Air Force (IAF) indicated that the service aims to acquire more than 200 units of the indigenous stealth fighter over the long term. Organized by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA), the meeting was attended by potential suppliers from the private sector and representatives of the IAF, who highlighted the program’s broad potential, both for domestic deployment and possible exports.
The ADA issued an Expression of Interest (EOI) to private sector aerospace component suppliers, seeking companies to join the supply chain for the AMCA program. The EOI covers various elements of the aircraft’s manufacturing, including airframe and structural components, underscoring the AMCA’s need for a robust industrial ecosystem. The program aims to tap into India’s private sector to build advanced manufacturing capabilities, fostering an efficient and high-quality production environment for the AMCA.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a recent discussion with idrw.org, a former Indian Air Force (IAF) navigator, who served on the IAF’s IL-76 transport aircraft, expressed significant concerns about the Indian Air Force’s decision to combine the tender for the Medium Transport Aircraft (MTA) with a replacement program for the IL-76. This strategy, he argues, could create a substantial vacuum in the IAF’s cargo-carrying capabilities, particularly when it comes to fulfilling the distinct roles that these aircraft serve.
The IL-76, a heavy transport aircraft, has long been a workhorse for the IAF, capable of carrying large payloads over considerable distances. Meanwhile, the An-32, a medium transport aircraft, plays a crucial role in supporting operations in challenging terrains and carrying troops and cargo to forward bases. The merging of these two distinct platforms into a single program raises critical questions about operational efficacy.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
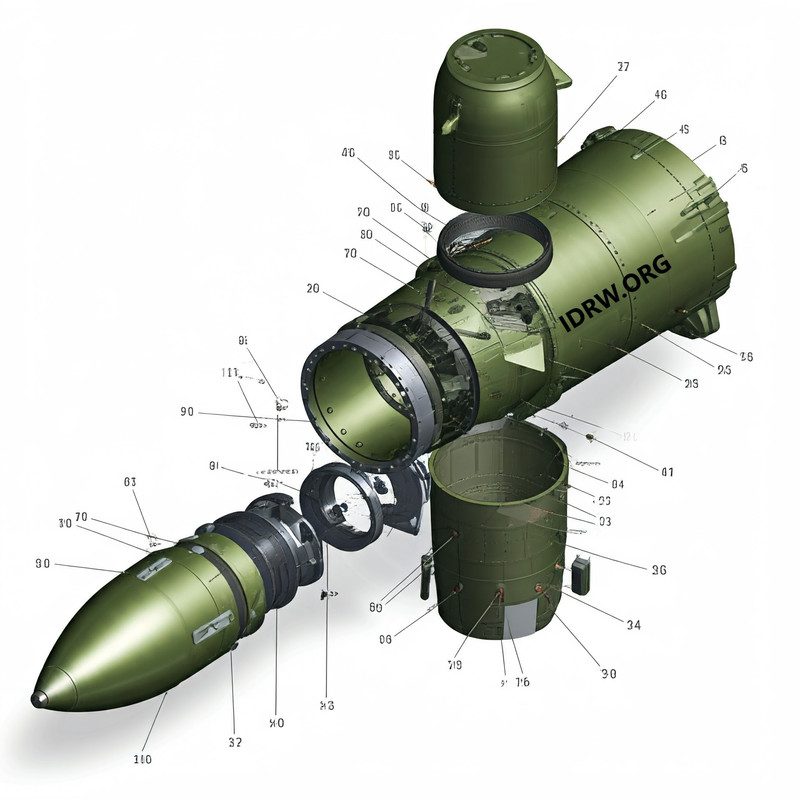

The Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) has embarked on an ambitious project focusing on the development of a 155mm Ramjet projectile. This innovative undertaking aims to enhance artillery capabilities with advanced projectile technology, leveraging the potential of ramjet propulsion systems.
The ARDE’s comprehensive approach encompasses a wide range of activities, from initial design to final manufacturing and quality assurance, ensuring that the project meets the rigorous standards required for defence applications.
Continue reading