SOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India has issued a Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) indicating an upcoming missile test. The designated airspace for the test covers an area of 1390 kilometres, suggesting that the missile involved could be the Agni-1P, a short-range ballistic missile.
The NOTAM, issued on September 26, 2024, specifies that the missile test will take place on October 3 and 4. The extensive area covered by the NOTAM suggests that the missile’s trajectory will be relatively long, consistent with the range of the Agni-1P.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
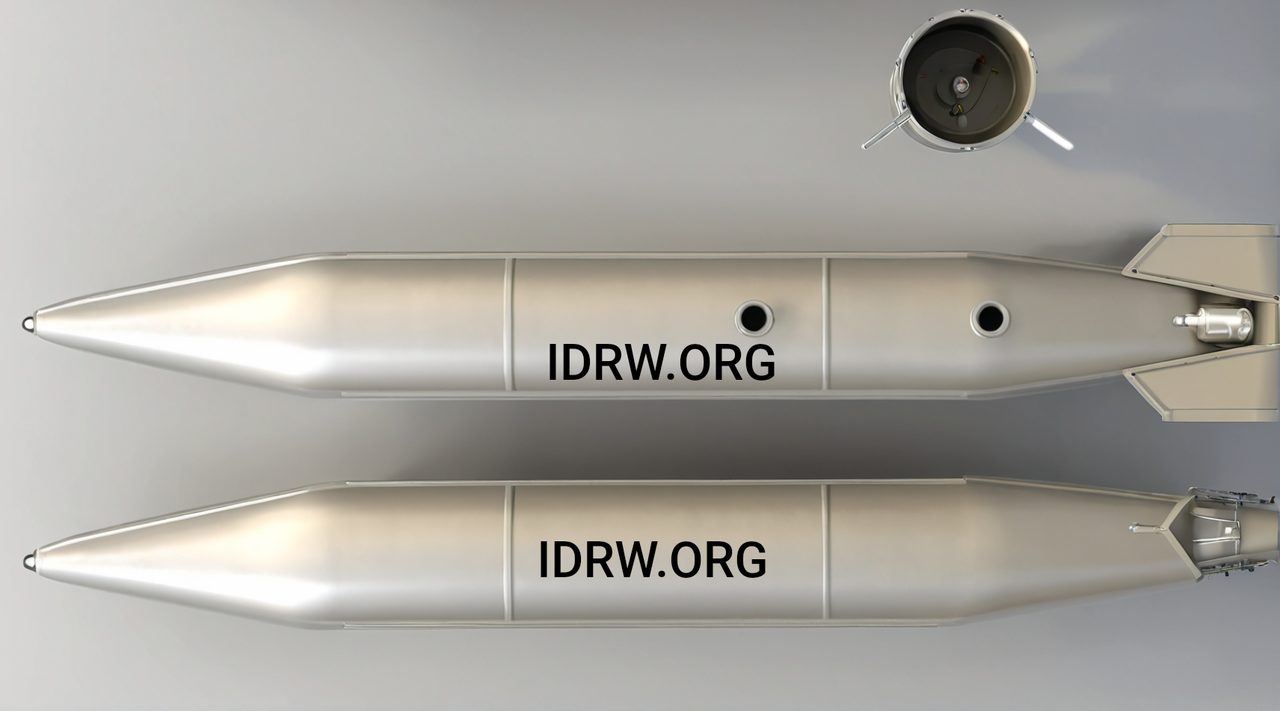

The Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) has initiated development work on external fuel drop tanks for the upcoming Tejas MkII program. As per tender specifications, ADE plans to develop two distinct models: a 1700-litre drop tank and a 1300-litre drop tank.
Initially, ADE will focus on producing two units of each drop tank for testing purposes. However, the final procurement will include six units of the 1700-litre drop tank and three units of the 1300-litre drop tank. These external fuel tanks will be integrated with the Tejas MkII prototypes, which are currently under development.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
The Electronics & Radar Development Establishment (LRDE), a premier lab under DRDO, has embarked on a series of new initiatives in the optoelectronics domain, particularly aimed at revolutionizing radar systems. The focus is primarily on integrating photonics technologies into radar applications, which promises to enhance the performance, accuracy, and efficiency of future radar systems.
The introduction of photonic radar technology marks a significant leap from conventional radar systems. While traditional radar relies on electronic components for signal transmission and reception, photonic radars use light-based technologies, such as lasers, to process signals. This allows for faster data transmission, increased bandwidth, and better signal resolution. LRDE’s efforts to develop photonic modules demonstrate its forward-looking approach to enhancing India’s radar capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

As negotiations for the purchase of 26 Rafale M fighter jets for the Indian Navy progress, the Navy is also planning to procure two Rafale Simulation Centers to train its crew, including pilots.
The proposed deal for the Rafale M includes 22 single-seater and 4 two-seater aircraft. However, the two-seater Rafale M variants are not carrier-capable, meaning they cannot take off or land from aircraft carriers. To address this limitation, the Indian Navy has decided to invest in simulation centres to provide comprehensive training for its pilots.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
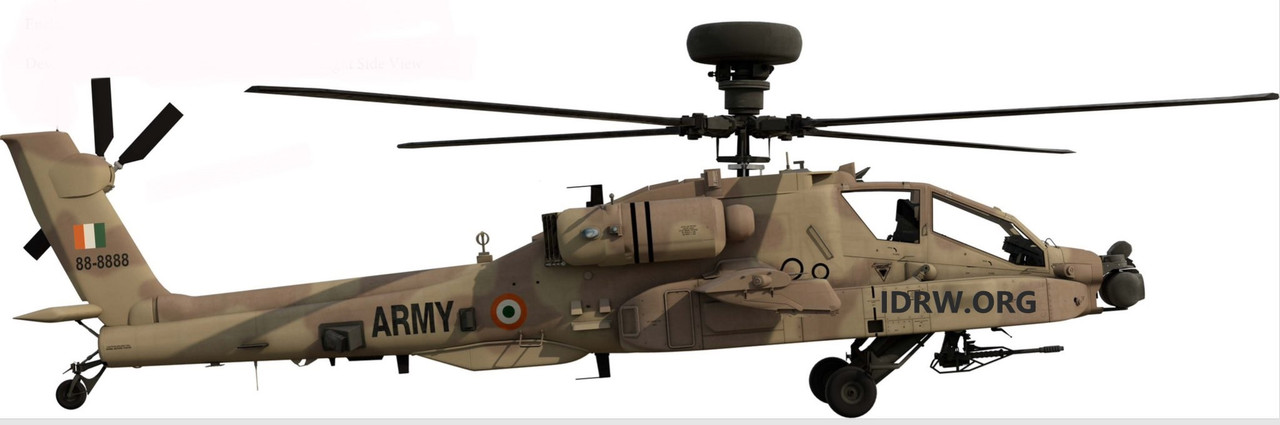

The Indian Army is set to receive the first batch of three AH-64E Apache attack helicopters from Boeing in December 2024, following a delay of over six months. The delays were attributed to global supply chain disruptions, which have affected the manufacturing schedule, according to a report in The Hindu. Initially, the delivery was planned for May, with the next batch scheduled for July. However, the first set of helicopters will now arrive in December, with the remaining three set to follow in the coming months.
The Apache AH-64E attack helicopters will be deployed primarily in the desert regions, significantly enhancing the Indian Army’s capabilities in desert warfare. Known for their lethal firepower, advanced sensors, and precision strike capabilities, the Apaches are considered one of the most formidable attack helicopters in the world. These helicopters will play a critical role in improving the Army’s ability to respond to potential threats along India’s western borders, where the desert terrain can present unique operational challenges.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Bengaluru-based Celeritas Automation LLP has emerged as the winner of the Indian Navy Open Challenge 9.0, securing a contract to develop an advanced Optical Landing System (OLS) for aircraft carriers. The OLS, often referred to as the “meatball,” is a critical piece of equipment that provides pilots with precise glidepath information during the final stages of landing on an aircraft carrier.
The OLS plays a vital role in ensuring the safe and efficient landing of aircraft on aircraft carriers. It consists of a series of lights that project a visual glidepath onto the carrier’s flight deck. Pilots use this information to maintain the correct approach angle and speed for a successful landing.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
General Electric (GE) Aerospace was caught by surprise when the Indian Air Force (IAF) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) placed an order for an additional 83 Tejas Mk1A fighter jets in 2021, necessitating the delivery of nearly 99 more F404-IN20 engines. The F404-IN20 is a variant of the F404 engine developed specifically for the Tejas Mk1 program, providing enhanced thrust and optimized performance for single-engine operations.
The F404-IN20 engine, producing 19,000 pounds of thrust (or 84kN of wet thrust), was custom-designed by GE Aerospace for the Tejas Mk1 program to meet India’s unique operational requirements. It delivers the highest wet thrust among all F404 variants, specifically catering to the demands of India’s indigenous fighter program. Initially, GE Aerospace provided around 75 F404 engines to India over the last two decades, which was seen as a slow pace of supply for the company.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
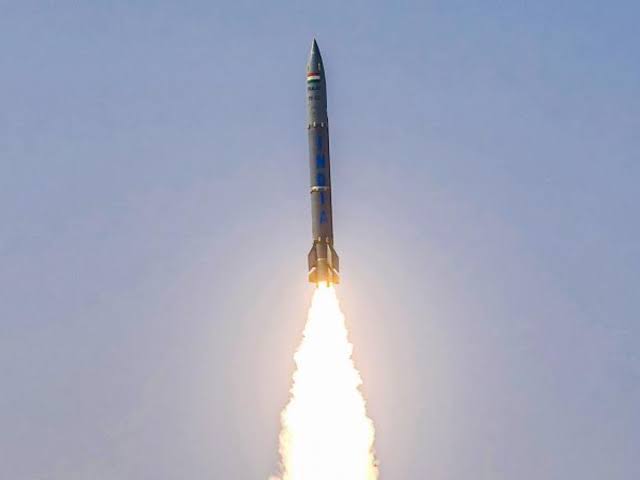

As Reported earlier by idrw.org, India is now considering a request from Armenia to supply the Pralay tactical ballistic missile. This development comes amidst heightened tensions between Armenia and Azerbaijan in the Nagorno-Karabakh region.
idrw.org reported in June that Armenia had approached India seeking to procure the Pralay tactical ballistic missile to counter Azerbaijan’s acquisition of the Israeli LORA long-range surface-to-surface missile system. The LORA system was allegedly used by Azerbaijan against Armenia in October 2020 during a military conflict.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
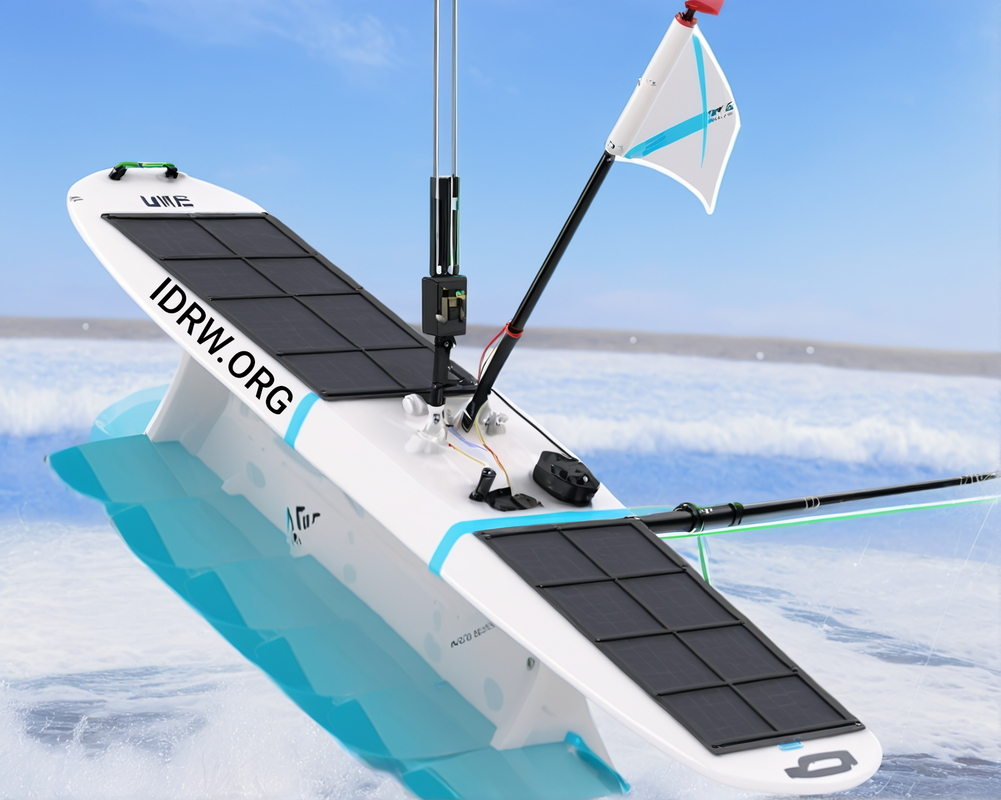

Liquid Robotics, a Boeing company, and India-based Sagar Defence Engineering Private Limited have announced a strategic partnership to co-develop and co-produce scaled Uncrewed Surface Vehicle (USV) systems. This collaboration aims to strengthen maritime security in the Indo-Pacific region and promote defense cooperation between the United States and India.
The Wave Glider, Liquid Robotics’ flagship USV, is an ideal platform for this partnership due to its endurance, reliability, and adaptability. Powered by wave and solar energy, the Wave Glider can operate continuously for months, providing real-time data and communications for various applications.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

An alleged image of India’s K-15 Sagarika Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), also known as B05, going through a sequential launch from an Arihant-class nuclear submarine has recently gone viral. The image reportedly depicts the missile launched at 10-second intervals, stirring excitement and speculation among defence enthusiasts and analysts.
India has been steadily advancing its nuclear triad capabilities, and the K-15 plays a crucial role in the country’s underwater strategic deterrent. The missile, which is designed to be launched from a submerged submarine, is capable of carrying nuclear warheads, providing India with a second-strike capability that is essential for maintaining credible deterrence.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India has revised its Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) for an upcoming missile test, extending the designated danger zone and potentially indicating a more powerful missile than initially planned.
The original NOTAM, issued on September 23, specified a danger zone extending over 1,720 kilometers. However, the revised NOTAM has expanded this area, suggesting that a larger missile may be under consideration.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) is poised to become the world’s first 5.5th generation fighter jet, showcasing features that surpass those of current 5th generation aircraft. Developed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), the AMCA is classified as a 5.5th-generation aircraft due to its late entry into the program, allowing for the incorporation of advanced technologies.
One of the standout features of the AMCA MKII is its Remote Pilot capability. This innovative feature enables the aircraft to be controlled by a remote operator in the event of pilot injury or incapacitation, ensuring mission continuity and enhancing survivability. Additionally, the AMCA MKII will feature Electronic Pilot, an AI program that can take over basic piloting tasks, allowing the human pilot to focus on mission-critical areas.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
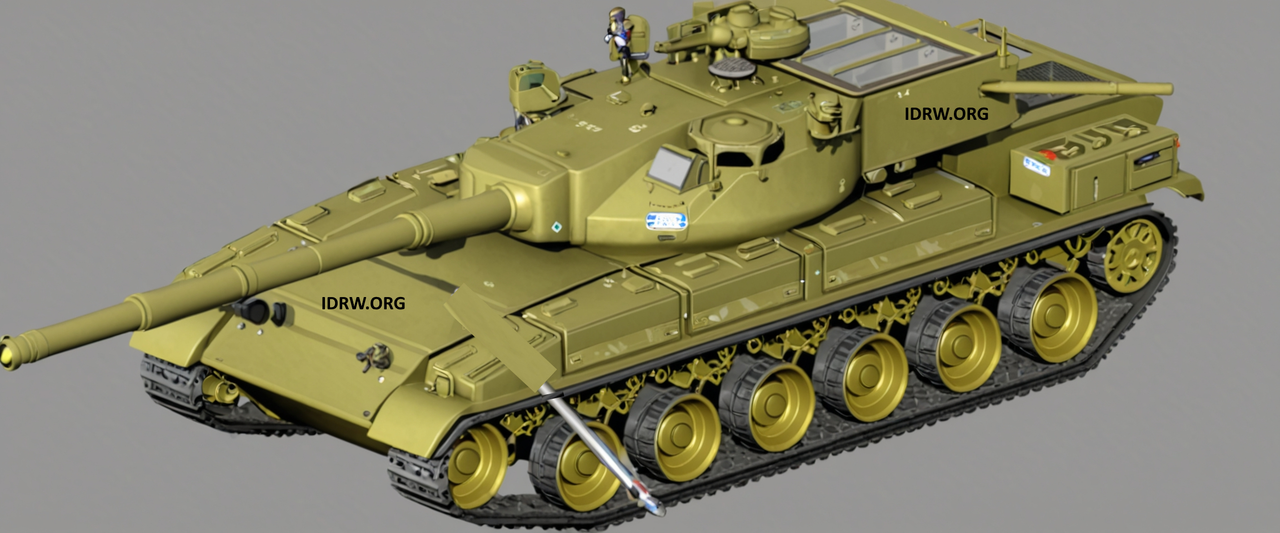

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is steadily progressing towards the completion of the Critical Design Review (CDR) for its Next Generation Main Battle Tank (NGMBT) design, intended for the Indian Army’s Future Ready Combat Vehicle (FRCV) program.
The NGMBT project has been making significant strides since its inception. After undergoing a preliminary design review (PDR) approximately three years ago, the DRDO has been diligently refining the design to meet the specific requirements outlined in the Army’s Request for Information (RFI) tender.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
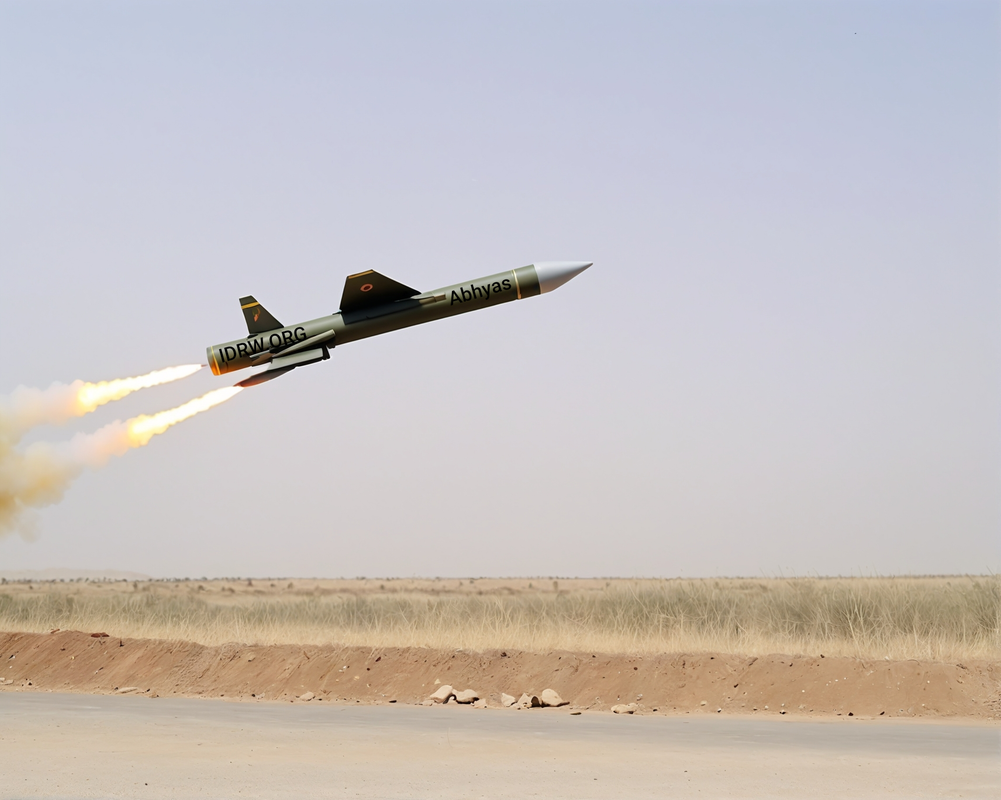

The Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE), a premier lab of India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has been expanding the capabilities of its Abhyas High-speed Expendable Aerial Target (HEAT). Originally designed as an aerial target to simulate enemy aircraft for missile testing, Abhyas is now being developed into more versatile systems, including kamikaze drones and loitering munitions, with potential roles in Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) operations.
Initially developed as a cost-effective solution for training and missile target practice, Abhyas has a range of 100 km, can fly at speeds up to 0.5 Mach, and offers 45 minutes of endurance. However, ADE is now working on new variants that can transform Abhyas from a purely expendable target into a tactical platform capable of performing a variety of critical missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Indo-Russian Rifles Private Limited (IRRPL), the joint venture between India and Russia responsible for producing the Kalashnikov AK-203 assault rifles, is witnessing a surge in inquiries from African and Middle Eastern countries. The Western sanctions imposed on Russian arms manufacturers have created a lucrative opportunity for IRRPL to export its Made in India AK-203 assault rifles to these regions.
Recently, IRRPL successfully delivered 35,000 AK-203 rifles to the Indian Army, marking a significant milestone in the project. The production of these rifles in India is fully aligned with the government’s Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan (Self-Reliant India) initiatives. The project involves technology transfer and aims for 100% localization of AK-203 production.
Continue reading