SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is on the cusp of a significant upgrade in India’s aerial combat capabilities with the Astra Mk2 (Astra-2) missile, which is poised to become the primary Beyond Visual Range (BVR) weapon in the Indian arsenal. This development does not, however, diminish the importance of the Astra Mk1 (Astra-1), which remains vital for building a robust domestic supply chain for BVR missiles.
The Astra-2 missile is undergoing rigorous developmental trials, with expectations to complete these by 2026, leading directly into production.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a move to bolster the naval air wing’s capabilities, the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS), under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, is poised to formally approve the acquisition of 26 Rafale-M fighter jets from the French manufacturer Dassault Aviation. This significant defense deal, which has already received the nod from the Ministry of Defence, is anticipated to be a key agenda during PM Modi’s upcoming visit to Paris.
The deal, pegged at an estimated $7.2 billion, encompasses the procurement of 22 single-seater Rafale-M jets and four twin-seater Rafale trainers. These aircraft are tailored for naval operations, designed specifically to operate from aircraft carriers, enhancing the Indian Navy’s operational range and combat effectiveness.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

A recent audit by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India has shed light on concerning practices within the Indian Air Force (IAF) regarding the formulation of Aircraft and Systems Qualitative Requirements (ASQRs). Instead of adhering to the spirit of the Defence Procurement Procedure (DPP), which aims for a transparent and competitive procurement process, the IAF has been found to tailor ASQRs based on the technical specifications of already available products in the market.
The audit pointed out that the IAF has been drafting ASQRs by directly copying the technical specifications of products which are already in the commercial domain. Moreover, these requirements have often been based on the inputs provided by vendors in response to the Request for Information (RFI) issued by the IAF. The DPP envisages the RFI as a tool to gather widespread information that would help in crafting broad, inclusive Qualitative Requirements (QRs) to ensure a level playing field among potential suppliers.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
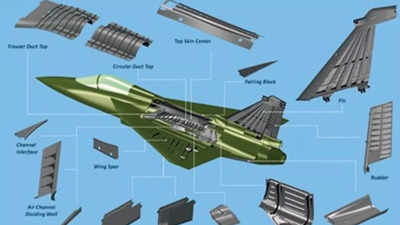
In an ambitious move to bolster its indigenous defense capabilities, India is set to significantly increase the production of composites for its burgeoning fighter jet programs. This initiative is driven by the escalating demand for local manufacturing of advanced materials for aircraft like the Tejas M1A and the upcoming Tejas MkII, with production orders expected to exceed 300 units by 2035.
The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), a key player in aerospace research and development under the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), has been at the forefront of this technology. NAL has pioneered the use of composites in India’s aircraft programs, including the LCA Tejas and the SARAS, where composites make up a significant portion of the aircraft structure. Now, with the Tejas M1A and MkII projects, the focus is on enhancing these capabilities further, leveraging composites for their lightweight, strength, and durability benefits.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

In a significant stride towards enhancing its naval capabilities, the Indian Navy is set to commission INS Nilgiri, the first of its kind among Indian-made warships. This stealth frigate, part of the Project 17A class, will be the inaugural vessel equipped with the Super Rapid Gun Mount (SRGM) system, specifically designed to deploy the advanced DART (Driven Ammunition Reduced Time of flight) ammunition.
The SRGM, a 76/62 mm gun system known for its high rate of fire and accuracy, has been a staple in naval arsenals around the world. However, the integration of this system on INS Nilgiri marks a new chapter in India’s naval armament history. Manufactured indigenously by Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) at its Haridwar plant, this SRGM is not just about firepower; it’s about precision and versatility in naval combat.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

In a significant stride towards self-reliance in defense technology, the Defence Innovation Accelerator (DIA) Centre of Excellence (CoE) at IIT Kharagpur, formerly known as the Joint Centre for Biomedical Engineering and Assistive Technology (JCBCAT), has successfully developed a novel Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) platform. This innovative project, executed in collaboration with the Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute (CSIR-CMERI) and the Vehicle Research and Development Establishment (VRDE) under DRDO, marks a new era in India’s capability to produce advanced, terrain-versatile robotic systems.
The UGV platform, distinguished by its hub motor technology, has been engineered to excel in diverse operational scenarios, from rugged terrains to urban environments. This design choice enhances the vehicle’s maneuverability and efficiency, allowing it to navigate through complex landscapes with ease. The hub motors, integrated directly into the wheels, provide a compact, high-torque solution that minimizes maintenance and maximizes operational uptime.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
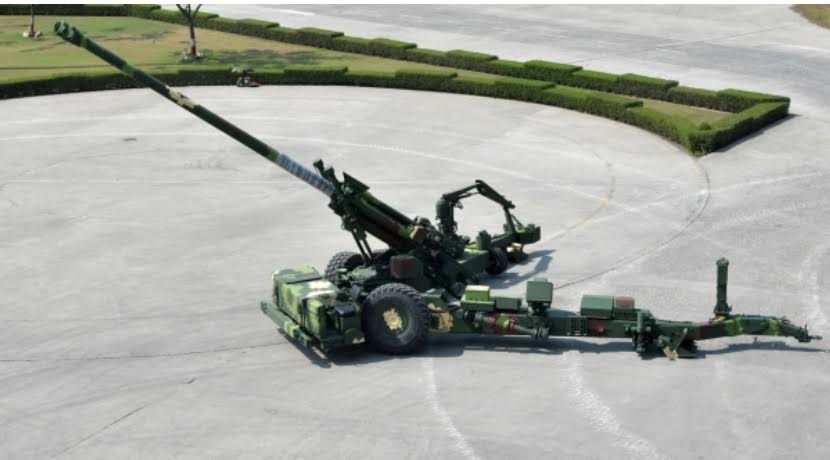

In a significant stride in international defense collaboration, India and France have jointly developed the Trajan 155 mm towed artillery gun system, showcasing a fusion of technological expertise from both nations. This development has now led to Armenia selecting the Trajan system for its armed forces, enhancing its military capabilities with cutting-edge technology.
The Trajan 155 mm towed gun is not just another addition to global artillery; it represents a synergy between French and Indian defense sectors. While France provided the initial design and technology, several key subsystems were developed in India, underscoring the country’s growing prowess in defense manufacturing. These subsystems include advanced communication and navigation systems, which are crucial for modern warfare scenarios where precision and speed are paramount.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Journalist, researcher, and commentator Adnan Aamir from Islamabad has provided insights into the recent U.S. sanctions on Pakistani entities involved in long-range missile programs. According to Aamir, these sanctions are not merely punitive actions but are deeply rooted in Washington’s broader Indo-Pacific security strategy, potentially altering the geopolitical balance in South Asia in favor of India.
Aamir points out that the U.S. has imposed sanctions on several Pakistani organizations, notably those linked to the development of ballistic missiles, which are seen as integral to Pakistan’s defense against perceived threats, primarily from India. These sanctions include freezing any U.S. property belonging to these entities and barring Americans from conducting business with them, effectively aiming to curb the proliferation of missile technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

India is ramping up efforts to position itself as a key player in the global defense maintenance sector by highlighting its Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) facilities, especially for the Rafale fighter jets, to Indonesia. This initiative comes in the context of Indonesia’s substantial military acquisition from France.
In February 2022, Indonesia’s Air Force inked a landmark $8.1 billion deal for 42 French-made Rafale aircraft, as confirmed by Air Vice Marshal Sukadis. He elaborated, “The signing of the Rafale contract also provides training to pilots and technicians of Rafale aircraft so that they can maintain optimal aircraft performance.” This statement underscores the comprehensive nature of the deal, which includes a significant human resource development package centered around pilot crew training and aircraft maintenance.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
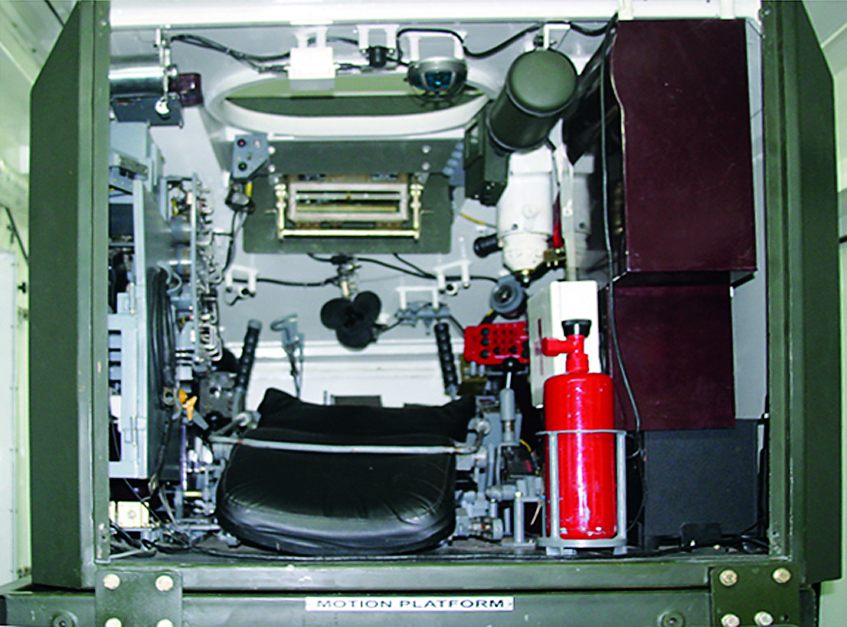

Hyderabad-based Zen Technologies Limited, a leader in providing defense training solutions, has been granted an Indian patent for its innovative “T-72 Containerized Crew Gunnery Simulator System” on January 8, 2025. This marks the eleventh patent awarded to the company in the fiscal year 2024-25, further solidifying its position as a pioneer in military training technology.
The T-72 Containerized Crew Gunnery Simulator System is specifically engineered to enhance the skills of T-72 tank commanders and gunners. This advanced simulator offers an immersive training experience by accurately replicating battlefield scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
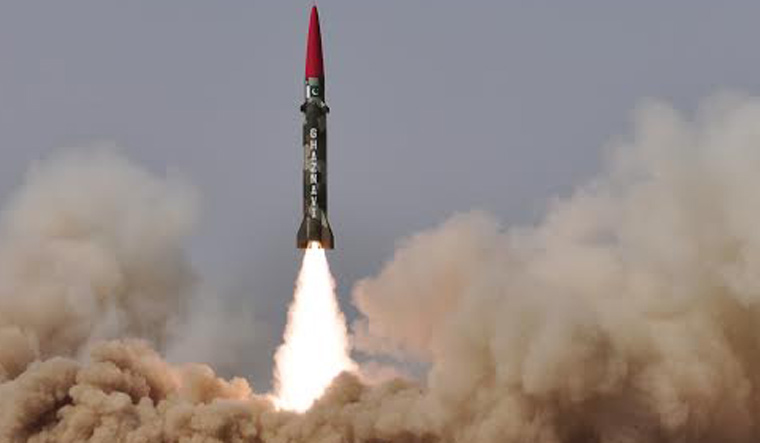

Pakistan’s long-standing practice of naming its ballistic missiles after historical Afghan invaders, intended as a taunt to India, has backfired amidst a new geopolitical spat with Afghanistan. The controversy was sparked by Pakistan’s Defence Minister, Khawaja Muhammad Asif, who in an unexpected turn of events, referred to Mahmud of Ghazni as “merely a plunderer” during a televised interview. This remark has sent shockwaves through Pakistan, where Ghazni is often lionized in educational curricula for his 1026 raid on the Somnath temple in India.
Mahmud of Ghazni, along with other figures like Ahmad Shah Abdali and Muhammad Ghori, have been celebrated in Pakistan for their roles in historical conflicts with Indian forces. Abdali is remembered for his victory in the third battle of Panipat against the Marathas, an event marked by significant bloodshed, while Ghori is noted for his defeat of the Indian king Prithviraj Chauhan. These names — Ghaznavi, Abdali, and Ghauri — adorn Pakistan’s arsenal of missiles, including the Ghaznavi (Hatf-III), Abdali-I (Hatf-II), and Ghauri (Hatf-V), respectively, symbolizing not just military might but also a cultural and historical assertion over India.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE), a key arm of India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has embarked on an innovative project to modify the Small Turbo Fan Engine (STFE) for air-launch applications. This initiative marks a significant stride towards enhancing the versatility and strategic capabilities of India’s indigenous propulsion systems.
The STFE, also known as the Manik engine, has been developed primarily for powering subsonic cruise missiles and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). With a thrust rating of around 4.5 kN, this engine has proven its reliability in various tests, including successful flight demonstrations. However, the new challenge at hand involves adapting this engine for air-launch scenarios, which require unique modifications in terms of fuel management, thrust control, and operational resilience under differing atmospheric conditions.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
The Indian Navy, in its pursuit of enhancing underwater capabilities through the ambitious Project-75I, is currently grappling with significant hurdles concerning the Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) systems of the submarines on offer. The project, aimed at acquiring six advanced diesel-electric submarines, has seen proposals from two major international players: Spain’s Navantia and Germany’s ThyssenKrupp Marine Systems (TKMS). However, the latest developments indicate a level of dissatisfaction from the Navy with the AIP trials conducted by both contenders.
Navantia, which partnered with Larsen & Toubro, presented its AIP solution based on a land-based prototype. This demonstration, although showcasing technological prowess, did not meet the Indian Navy’s requirement for sea-proven AIP technology. The Navy’s insistence on operational trials under actual submarine conditions underscores the critical importance of reliability and performance in real-world scenarios, where land-based tests do not fully replicate the complexities involved.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s Ballistic Missile Defence (BMD) program has entered a pivotal phase with the successful testing of the AD-1 Interceptor missile under Phase II. This development not only marks a significant enhancement in India’s missile defence capabilities but also introduces a new dimension: limited anti-hypersonic interception capabilities. While Phase III is poised to introduce specialized anti-hypersonic interceptors, the current capabilities of the AD-1 offer a glimpse into India’s strategic foresight in countering emerging threats.
The AD-1 is a long-range interceptor capable of neutralizing ballistic missiles with a range of up to 5,000 km. Key features include a Dual-Stage Rocket Motor, Active Radar Seeker, and Capability Against Glide Vehicles.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
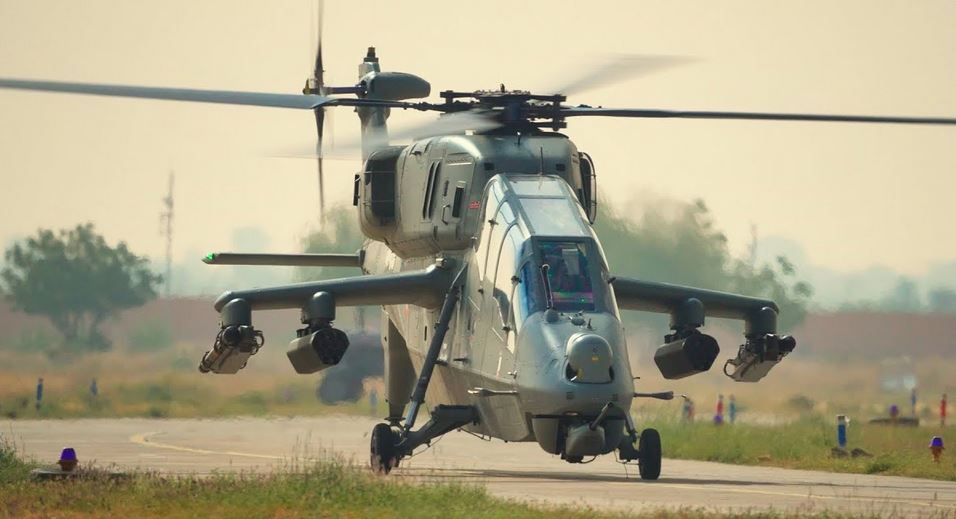

The Ministry of Defence (MoD) of India is set to conclude one of the largest indigenous defense deals by the end of the current financial year, March 2025. The deal involves procuring 156 Prachand Light Combat Helicopters (LCH) from Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), with a total value estimated at ?53,000 crore (approximately $6 billion).
Out of the 156 helicopters, 90 are designated for the Indian Army, while the remaining 66 will strengthen the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) fleet. These helicopters are known for their ability to land and take off at an altitude of 5,000 meters (16,400 feet), making them ideal for operations in some of the world’s most challenging terrains. The Prachand LCH is equipped with an array of modern weaponry, including air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles, enhancing its combat effectiveness.
Continue reading