SOURCE: IDRW.ORG
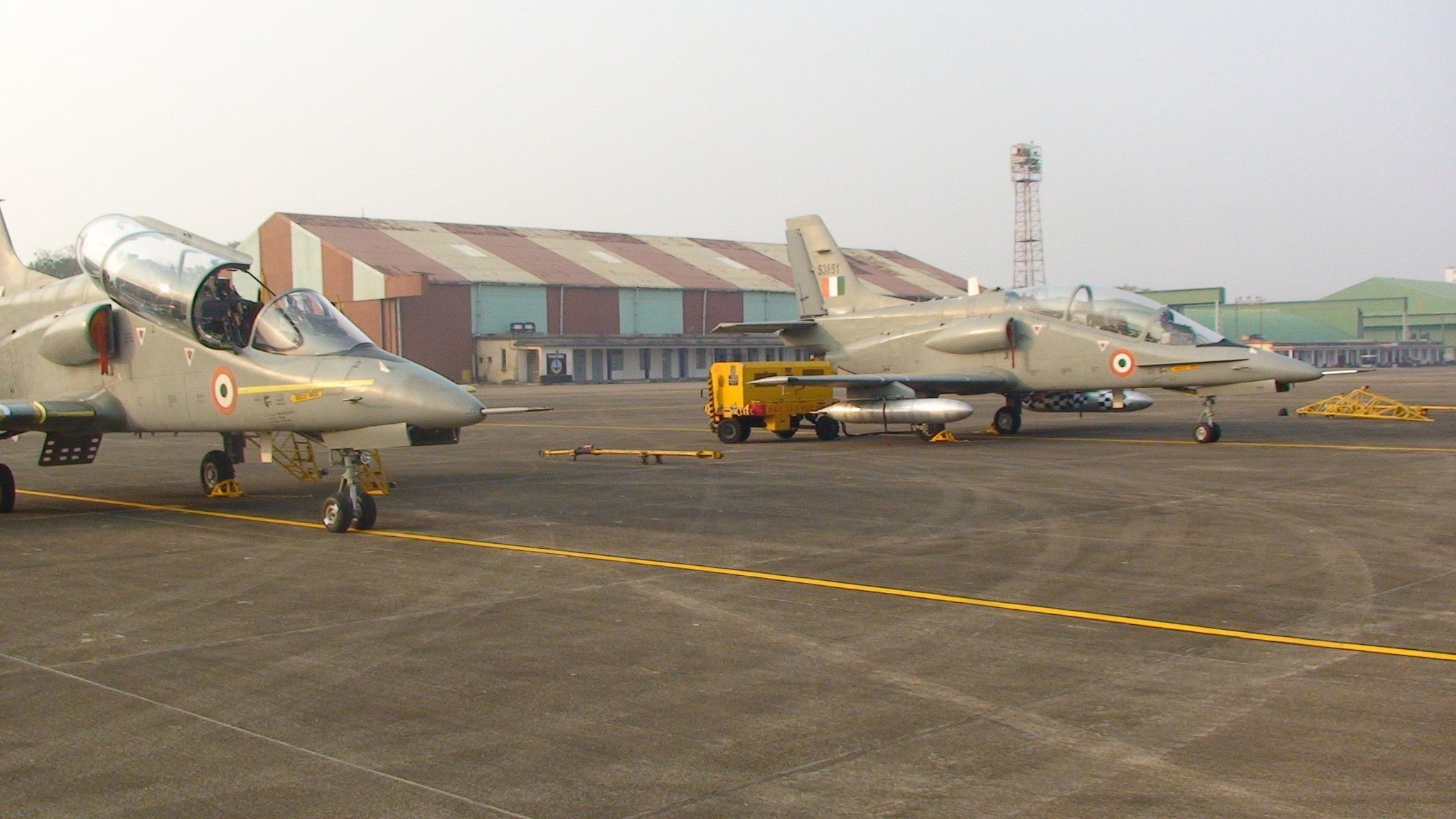

Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) is set to bring back its HJT-36 intermediate jet trainer (IJT), also known as Sitara, for a flying display at the upcoming Aero India 2025 in Bengaluru. This marks a significant comeback for the subsonic trainer, which has been absent from the event for over a decade following technical challenges and developmental delays.
The HJT-36’s appearance at Aero India has been rough for the program, as in 2007, an airshow incident marred its performance. The aircraft veered off the runway after its canopy unlocked during the take-off run, raising concerns about its operational readiness. Subsequently, HAL withdrew the Sitara from Aero India in 2009 due to technical snags, leading to a prolonged hiatus in public demonstrations of the jet.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Bangalore-based aerospace company Q-Alpha Aerospace has announced its work on the development of the QAL-J10, a cutting-edge multi-stage AI-augmented 10 kN turbojet engine. This engine is designed to revolutionize propulsion systems for unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs) and drones, while also paving the way for future hypersonic applications.
The QAL-J10 turbojet engine features an afterburner and exhaust choking system, designed with high precision using advanced scientific and mathematical models. According to Q-Alpha Aerospace, the engine has been specifically engineered for compatibility with TBCC (Turbine-Based Combined Cycle) architecture, making it a potential candidate for hypersonic UCAVs in the future.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a significant stride towards self-reliant defense capabilities, the Solar Group, through its subsidiary Economic Explosives Ltd (EEL), has successfully tested a new counter-drone system named Bhargavastra. This innovative micro-missile-based system, designed to neutralize the threat of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and drone swarms, might just be India’s answer to the much-acclaimed Iron Dome of Israel.
Bhargavastra can detect small incoming drones from over 6 kilometers away and neutralize them with guided micro-munitions. This capability is crucial in an era where drones, both commercial and militarized, pose significant security risks.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a strategic move to enhance its maritime surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities, the Indian Navy has expressed a keen interest in procuring additional Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), emphasizing the need for locally developed solutions. This push comes as the Navy looks to reduce the operational burden on its Boeing P-8I Poseidon fleet, which has been pivotal in monitoring the vast expanse of the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
The Navy’s desire for MALE UAVs stems from a need for sustained surveillance over large maritime areas without over-relying on its P8I aircraft, which, while highly capable, come with significant operational costs and maintenance demands.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Navy has been identified as a key driver behind the development of the Long-Range Anti-Ship Missile (LRAShM) by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). While the LRAShM was initially conceived for coastal defense, its massive size and weight have rendered it incompatible with integration on the Navy’s frontline warships. However, this limitation has not diminished its strategic value; instead, it has led to a unique deployment strategy aimed at enhancing coastal security and deterrence.
The missile employs a hybrid propulsion system, combining rocket boosters for initial launch with a scramjet engine for sustained hypersonic flight. This technology allows LRAShM to travel at speeds exceeding Mach 5, making it incredibly difficult for enemy defenses to counter.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
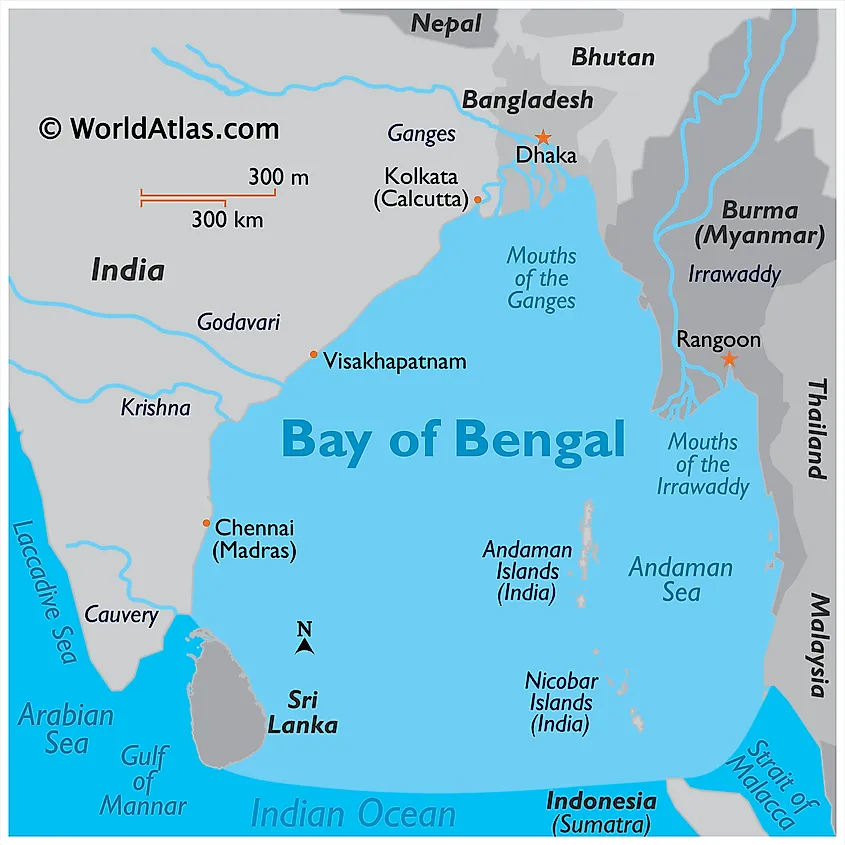
An intense debate has erupted on social media platform X (formerly Twitter) over whether India should rename the Bay of Bengal as the Bay of India. This discussion gained traction after newly inaugurated U.S. President Trump signed an executive order to rename the Gulf of Mexico as the Gulf of America, citing territorial and strategic reasons.
Proponents of the renaming argue that the Bay of Bengal, which is geographically bordered more significantly by India than by any other country, should reflect this dominant presence. Advocates point out that the bay is flanked by India’s eastern coastline, including the states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, and West Bengal, which together form a vast majority of its border.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a significant stride towards self-reliance in defense manufacturing, India appears to be transitioning away from the long-serving Czech Republic-made Tatra Transporter Erector Launchers (TELs) to home-grown alternatives. This change was notably showcased during the Republic Day 2025 rehearsals, where Ashok Leyland’s 12×12 heavy-duty vehicle was seen carrying the formidable Pralay tactical ballistic missiles.
For decades, the Indian military has relied on Tatra trucks, known for their robustness and off-road capabilities, particularly in rugged terrains like the Himalayas and the deserts of Rajasthan. These vehicles have been pivotal in transporting and deploying various missile systems, including the BrahMos and Prithvi. However, the push for indigenous solutions under the “Atmanirbhar Bharat” (Self-reliant India) initiative has catalyzed this shift.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
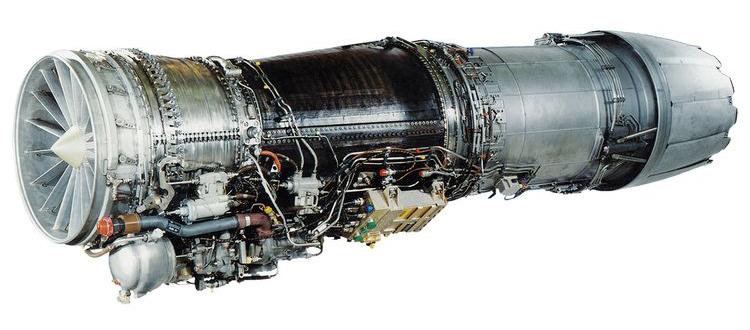
Negotiations between General Electric (GE) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the local manufacturing of the F-414 engines have encountered a significant hurdle. Sources at idrw.org have revealed that GE has demanded an increase in the contract price to incorporate 80% Transfer of Technology (ToT) for the engines.
The price for manufacturing 99 F-414 engines in India, which was earlier agreed upon at $1 billion, has now escalated to approximately $1.5 billion, a difference of $500 million. This sudden price increase has caused delays in finalizing the deal, as price negotiations remain ongoing.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a strategic pivot aimed at optimizing costs while enhancing capabilities, the Indian Army is considering deferring the purchase of high-cost tactical missiles in favor of the domestically developed Guided Pinaka rocket system. The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has recently been authorized to expand the Pinaka family with two new variants, one with a range of 120 kilometers and another extending to 300 kilometers, both incorporating advanced guidance systems.
The 300km variant of the Guided Pinaka, which will utilize a 300mm diameter, has particularly caught the Army’s attention. Its larger size not only allows for an increased payload but also ensures compatibility with existing launch platforms, including those used in high-altitude areas. This development comes as the Army seeks versatile, yet cost-effective solutions for both conventional and, potentially, tactical nuclear strikes, given its strategic positioning along contentious borders.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
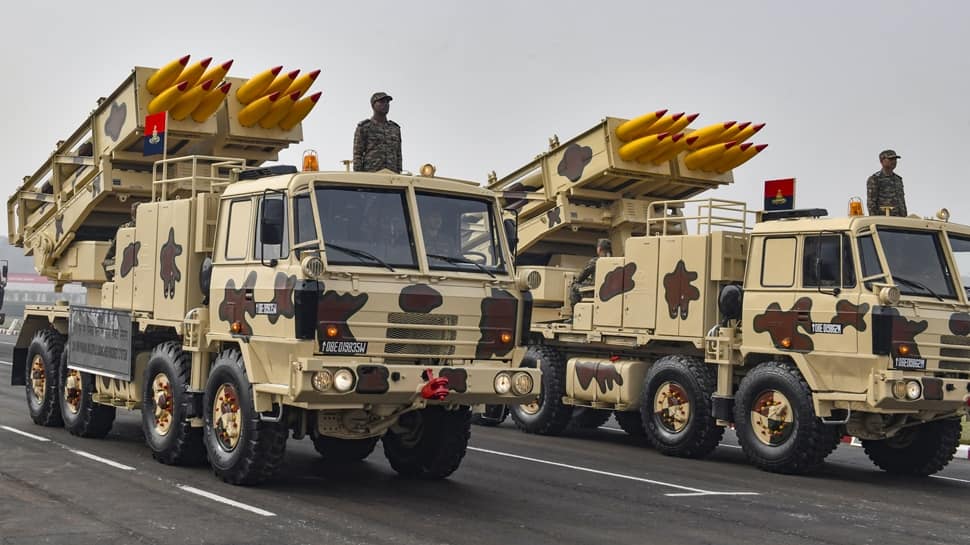

In a significant boost to India’s artillery capabilities, Army Chief General Upendra Dwivedi has announced that two major contracts for the Pinaka Multi-Barrel Rocket Launcher (MBRL) system are slated for signing before the fiscal year concludes on March 31. These contracts, valued at Rs 5,700 crore for high-explosive pre-fragmented ammunition and Rs 4,500 crore for area denial munitions, underscore India’s commitment to enhancing its military’s operational readiness and self-reliance.
This contract, amounting to Rs 5,700 crore, will supply the Indian Army with ammunition boasting a strike range of 45 kilometers. The high-explosive pre-fragmented shells are designed to maximize damage through fragmentation upon impact, making them highly effective against both personnel and light armored vehicles. This upgrade will significantly extend the reach and lethality of the Pinaka systems currently in use.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
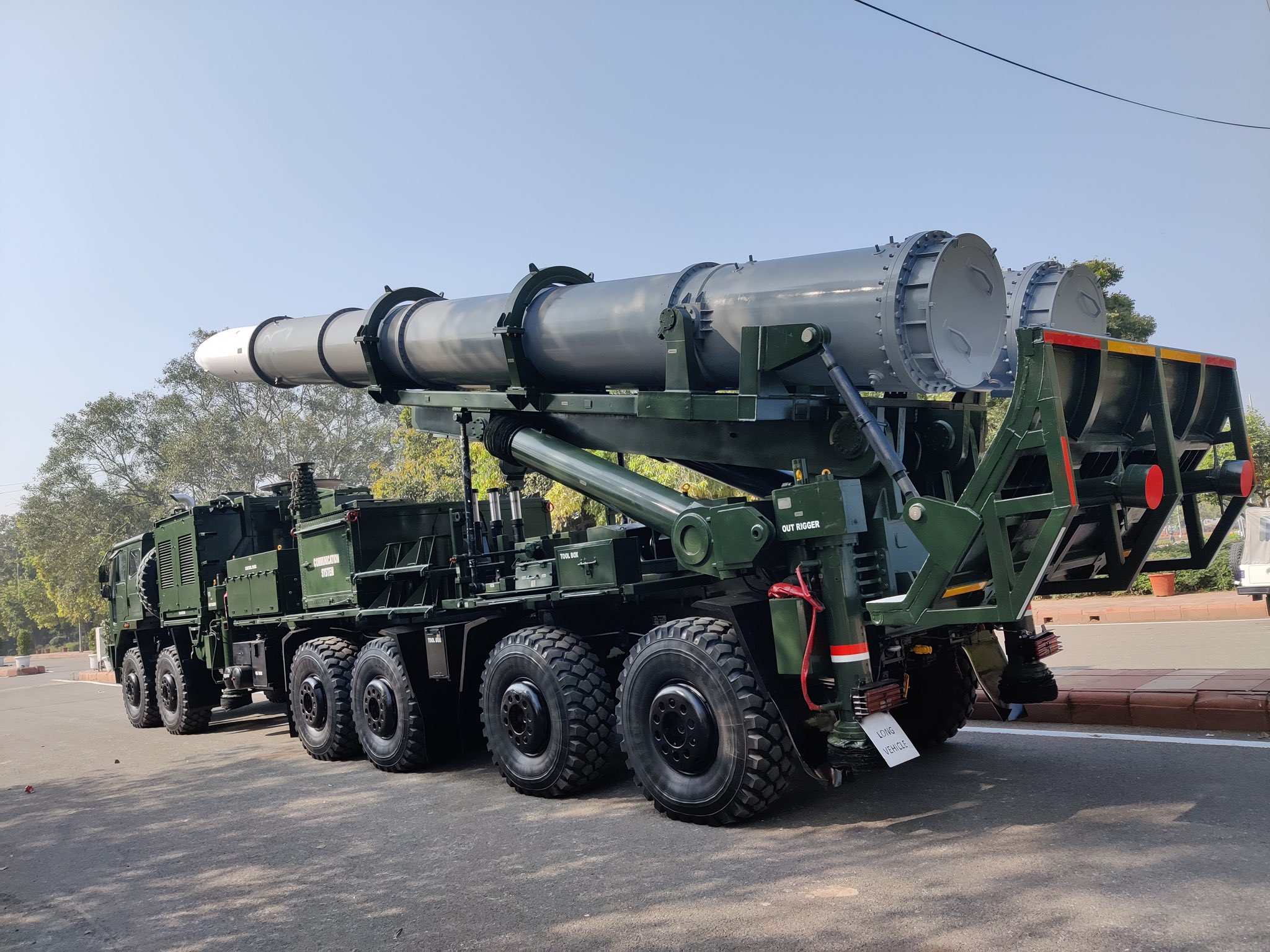

In a momentous display of India’s advancing military might, the Republic Day Parade on January 20, 2025, featured the inaugural showcase of the Twin Launcher for the Pralay ballistic missiles. This event not only underscored the country’s commitment to bolstering its strategic capabilities but also marked a significant milestone in missile technology development under the auspices of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
The Pralay missile, known for its tactical, short-range surface-to-surface capabilities, has been in the spotlight since its successful tests. With a range varying between 150 to 500 kilometers, Pralay is designed for conventional and nuclear roles, offering a versatile asset to the Indian Army’s arsenal. The introduction of a twin launcher configuration signifies an enhancement in deployment speed and efficiency, allowing for rapid, successive strikes on multiple or the same target.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a landmark move for sustainable and innovative manufacturing, PTC Industries has announced the signing of a long-term agreement with AMIC Toho Titanium Metal Company Limited (ATTM) for the supply of Titanium Sponge. This significant agreement was formalized at the prestigious Future Minerals Forum 2025 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, underscoring PTC’s commitment to advancing its capabilities in the aerospace and industrial materials sector.
The agreement with ATTM, a joint venture between Advanced Metal Industries Cluster (AMIC) and Japan’s Toho Titanium, is pivotal for PTC Industries as it guarantees a consistent and sustainable supply of Titanium Sponge. This raw material is crucial for the production of high-quality aviation-grade Titanium Ingots and subsequent products, which are in high demand in the aerospace industry for their lightweight, strength, and resistance to corrosion.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a significant shift in policy, Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd (BHEL), a state-run enterprise known for its extensive range from rail coaches to power generation equipment, is potentially being removed from the list of companies targeted for divestment. This development stems from discussions about categorizing BHEL as a “strategic” public sector unit (PSU), according to sources familiar with the matter.
A source, speaking under the condition of anonymity, revealed that this decision aligns with recommendations from a parliamentary committee which has advocated for BHEL to be recognized as a strategic PSU. “Now that a parliamentary committee has also recommended the tag of strategic PSU for the company, there would be further thought on this,” the source explained, indicating a reevaluation of BHEL’s role within the national framework.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In 2024, India’s strategic defense capabilities have seen significant advancements with the addition of several new missile systems to its already formidable arsenal. Among the notable developments is the introduction of an upgraded version of the Agni-5 Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM), now equipped with Multiple Independently Targetable Re-entry Vehicle (MIRV) technology, marking a substantial leap in India’s nuclear deterrence strategy.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India’s ambitious Phase-III Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD) program is making strides with the development of the ADAH three-stage missile, a next-generation interceptor designed to provide robust protection against advanced ballistic threats. The missile incorporates cutting-edge technologies and complex safety-critical systems that ensure its reliability and effectiveness in high-stakes scenarios.
The ADAH missile boasts a three-stage configuration, each stage designed to perform distinct and critical functions in its trajectory. Key innovations include several pyro-activated mechanisms, which are integral for the missile’s operation and safety. These mechanisms ensure the seamless execution of functions such as.
Continue reading