SOURCE: AFI

The Indian Navy has found itself at the center of a controversy after it inadvertently featured an American F-16 fighter jet in one of its promotional videos, instead of the Russian-made MiG-29K, which is actually in service with the Indian naval aviation. The mistake, described by many as an embarrassing oversight, has sparked a wave of criticism and jest on social media platforms and among defense analysts.
The promotional video, meant to showcase the prowess and capabilities of the Indian Navy, included footage of various naval assets. However, eagle-eyed viewers quickly pointed out the inclusion of the F-16, a multirole fighter aircraft designed and manufactured by Lockheed Martin for the U.S. Air Force, which has never been part of the Indian Navy’s fleet.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), one of India’s premier defense electronics companies, has confirmed that it is progressing on schedule with its supply commitments for components destined for the 83 Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk IA aircraft under contract with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). Moreover, BEL expresses optimism regarding securing an additional order for 97 more Tejas aircraft, signaling a robust outlook for the future.
BEL has stated that there are no delays in fulfilling the contract for supplying critical avionics systems, line replaceable units (LRUs), and other electronic components for the LCA Tejas Mk IA. This includes systems like the Digital Flight Control Computers, Air Data Computers, and various sensors crucial for the aircraft’s operation.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

In a significant boost to its defense capabilities, India is set to receive the fourth squadron of the Russian S-400 Triumf air defense missile systems by the end of 2025, according to an exclusive report by Sputnik India. This development underscores the deepening military cooperation between India and Russia, amidst strategic regional dynamics.
The S-400 Triumf, known by NATO as the SA-21 Growler, is one of the most advanced long-range surface-to-air missile systems globally. Capable of engaging aircraft, drones, ballistic and cruise missiles at ranges up to 400 kilometers, the system significantly enhances India’s aerial defense network.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has proudly announced that India’s indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas showcases one of the lowest Radar Cross-Sections (RCS) in its segment, attributing this achievement to the extensive use of composite materials in its construction. This revelation underscores India’s pioneering role in leveraging composite technology for defence applications, significantly enhancing the stealth capabilities of the Tejas, albeit not originally designed as a stealth fighter.
According to DRDO, the LCA-Tejas incorporates 45% composites by weight in its airframe. This is a notable proportion, especially when compared to other contemporary fighters which often use less composite material in their construction.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

Abdul Basit, the former High Commissioner of Pakistan to India, has once again stirred the pot with what many are calling an “outrageous” claim. In his latest statement, Basit asserts that Pakistan’s Nasr (Hatf 9) short-range ballistic missile, with its range of 60-70 kilometers, is “way superior” to India’s Pralay tactical missile, which boasts a range of 150km to 500km. This assertion has sparked both debate and skepticism across defense and diplomatic circles.
Nasr (Hatf 9) Developed by Pakistan’s National Development Complex, the Nasr is explicitly designed as a battlefield weapon system. Its short range is tailored for tactical nuclear deterrence, particularly in response to India’s conventional military doctrines like “Cold Start.” The missile’s primary advantage, according to Basit, lies in its suitability for quick, precise strikes in a battlefield scenario, deterring enemy armor and troop concentrations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The Indian Air Force (IAF) faces a strategic dilemma with American fighter jets, primarily due to the potential for the United States to suspend spares and support during conflicts, especially if those conflicts involve Pakistan or China, two countries with significant geopolitical ties to the U.S. This concern stems from historical precedents where the U.S. has leveraged its supply chain influence in military engagements.
1971 Indo-Pakistani War: During this conflict, the U.S. imposed an arms embargo on both India and Pakistan, though the impact was felt more by India due to its lesser reliance on American military hardware at the time. This embargo highlighted how geopolitical stances could affect military operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

A heated debate has been unfolding on X (formerly Twitter), where netizens and defense analysts clash over the origins of the Fuel Cell-based Air Independent Propulsion (AIP) system intended for India’s submarines. The crux of the debate centers on whether this technology was solely developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) or if it was a collaborative effort with the French Naval Group. Here’s an exploration of the facts to clarify the “actual reality.”
DRDO has publicly stated that the AIP technology was developed by its Naval Materials Research Laboratory (NMRL) with support from Indian industry partners like Larsen & Toubro (L&T) and Thermax. This narrative emphasizes India’s push towards self-reliance in defense technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
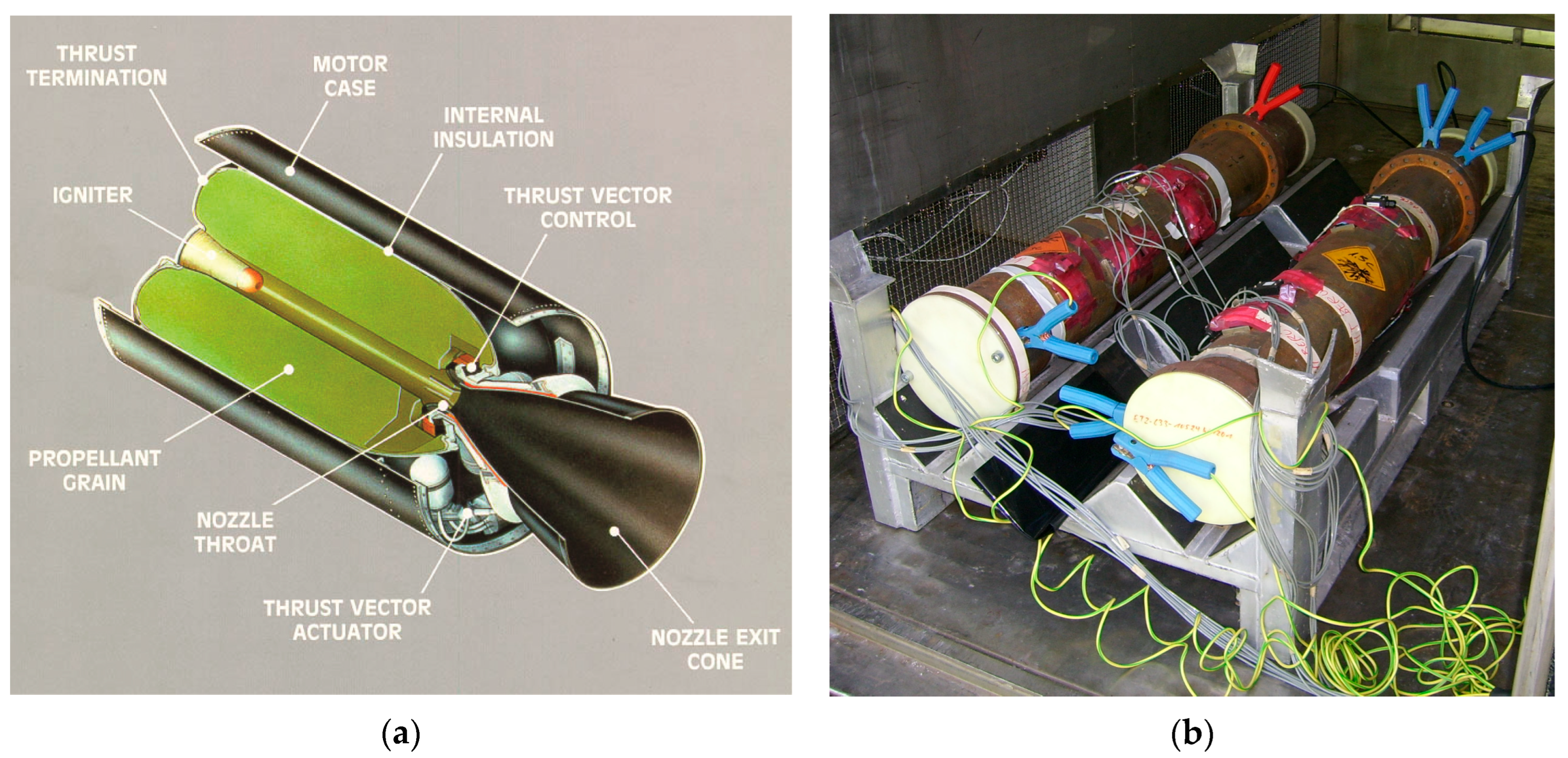
The Technology Development Fund (TDF) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has initiated the ‘Dare to Dream 5.0’ Challenge specifically for the Individual Category, calling for innovative solutions in the realm of rocket motor design using Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). This challenge focuses on enhancing the design, health monitoring, and service life prediction of Solid Rocket Motors (SRMs), which are crucial for various missile systems.
Solid rocket motors are designed for long-term storage and are meant for one-time use, making the assessment of their longevity and reliability paramount. The propellant used in these motors is a particulate composite material that exhibits viscoelastic behavior, meaning its mechanical properties change with both time and temperature, particularly under the stresses of thermal cycling and operational chamber pressure.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a significant move, Russia has confirmed that it will showcase the Su-57E, the export variant of its fifth-generation stealth fighter, at Aero India 2025. The aircraft will not only be displayed but will also participate in aerial demonstrations, offering a glimpse into its advanced capabilities.
Additionally, sources have revealed to idrw.org that Russia also plans to exhibit the Su-75 Checkmate, its single-engine stealth fighter currently under development. Unlike the Su-57E, the Checkmate will be presented as a static non-flying prototype, highlighting its design and features for potential customers.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
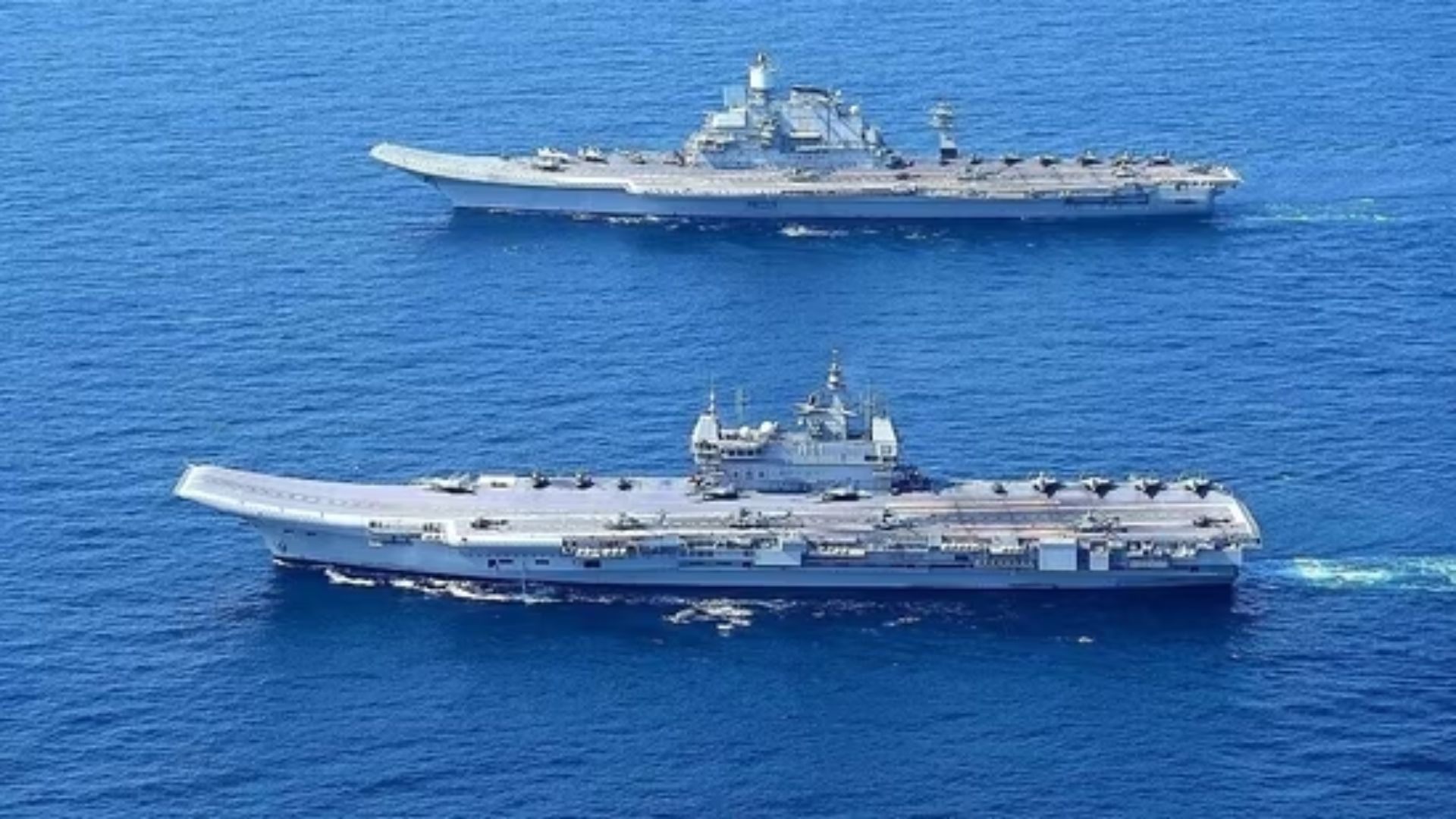

In a significant strategic pivot, the Indian Navy has decided to abandon its plans for a third aircraft carrier, opting instead to focus on the development of the second Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC-2) as a replacement for the aging INS Vikramaditya. This decision recalibrates the Navy’s operational structure to maintain two aircraft carriers, a move that has sparked discussions on India’s naval capabilities and strategic priorities.
The government has overruled the Navy’s long-standing argument for operating three aircraft carriers simultaneously, which was seen as crucial for ensuring continuous carrier presence in both the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal, even when one carrier is under maintenance.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
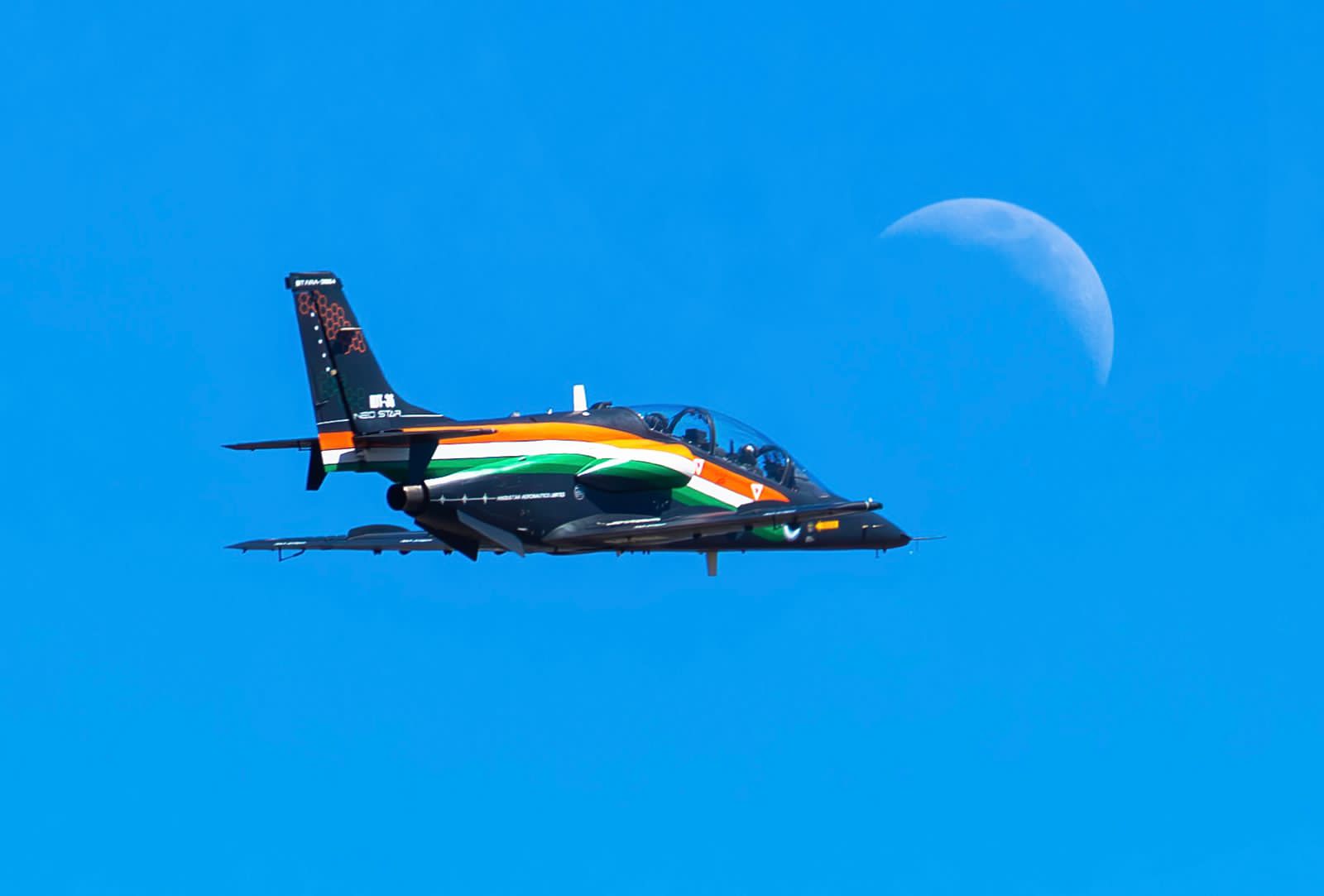

Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) is set to make waves at Aero India 2025 by presenting the revamped Intermediate Jet Trainer (IJT-36) “Sitara” Neo Star, which has undergone significant upgrades, particularly in its avionics suite. According to idrw.org, the aircraft will not only be displayed with an eye-catching new color scheme but also feature cutting-edge technology to meet modern training requirements.
The “Sitara” Neo Star has been fitted with the latest avionics, ensuring that it keeps pace with current technological advancements in aviation training. This upgrade includes advanced navigation systems, digital flight controls, and enhanced communication capabilities, all aimed at providing a more realistic combat training experience.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
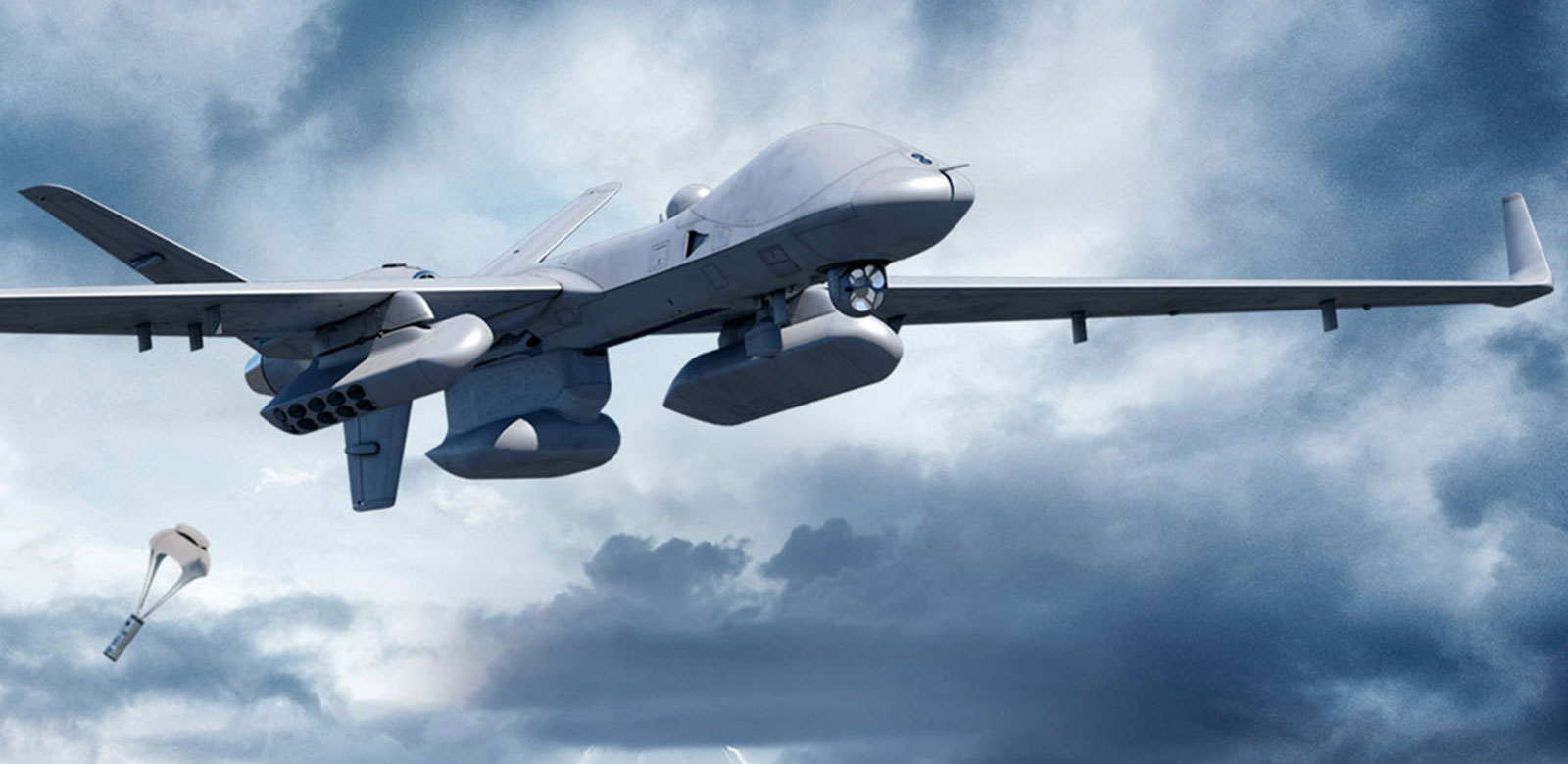

In a swift response to an operational mishap, U.S. defense firm General Atomics has replaced the MQ-9B SeaGuardian remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) that crashed into the Bay of Bengal on September 18. The incident was attributed to a power failure, leading to the drone being declared unsalvageable and written off.
A technical glitch involving a power failure was the reason behind the controlled ditching of the drone, preventing any reset in flight. The drone, while on a routine surveillance mission, was safely maneuvered to a designated spot over the sea off the coast of Chennai before it was intentionally ditched.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The online community in India has found a new source of amusement on X, where users are humorously dubbing the Chinese CH-YH1000 unmanned transport aircraft the “Fat Potato” due to its bulky appearance. This playful mockery comes in the wake of the drone’s recent successful taxiing tests, signaling its potential to take to the skies, an event that has sparked a wave of memes, witty comments, and satirical posts among Indian users.
The CH-YH1000, developed by Aerospace CH UAV Co Ltd, completed a full-load taxiing test at Zhanghe Airport, indicating significant progress towards its maiden flight. However, its unique, somewhat ungainly design has not escaped the sharp wit of the Indian netizens. Posts on X have been filled with humorous comparisons, likening the drone to various improbable flying objects, questioning its aerodynamic efficiency in jest.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a significant boost to India’s military aviation, the government has allocated Rs 48,614 crore under capital expenditure specifically for aircraft and aero engines in the upcoming fiscal year’s defense budget. This substantial investment reflects a strategic focus on modernizing the Indian Air Force’s capabilities, enhancing both its combat and transport fleets.
The emphasis on aero engines highlights an intent to not only procure advanced aircraft but also to foster indigenous development or co-development of engine technology, aligning with the broader ‘Make in India’ initiative.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a remarkable testament to India’s growing prowess in defense manufacturing and exports, the fiscal year 2023-24 has seen the United States, France, and Armenia emerge as the top three destinations for Indian military hardware. This development marks a significant milestone in India’s journey towards self-reliance in defense and showcases the country’s expanding influence in the global defense market.
India’s defense exports hit an all-time high, reaching ?21,083 crore ($2.6 billion) for the fiscal year 2023-24. This figure represents a substantial increase from previous years, underlining the success of initiatives like “Make in India” and “Aatmanirbharta” (self-reliance), which have been pivotal in boosting domestic production and export capabilities.
Continue reading