Idrw Team
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


Ordnance Factory Medak (OFM), one of India’s premier defense manufacturing units under the Ministry of Defence, has recently dispatched advanced Quadrant Fire Control systems and Optical Quadrant KO-60 to Israel. This dispatch reflects India’s expanding technical expertise and strengthening defense ties with international allies, particularly Israel, which has been a strategic partner in technology exchange and defense cooperation.
The Quadrant Fire Control systems produced by Ordnance Factory Medak are precision instruments essential for artillery fire control, enabling accurate targeting by measuring the angle of inclination on various surfaces. The precision of these instruments allows military units to calibrate artillery and other equipment with high accuracy, optimizing performance in tactical and battlefield scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


2022 trials at the Indian Navy’s airbase, INS Hansa in Goa, tested two leading fighter jets, Dassault’s Rafale M and Boeing’s F/A-18E/F Super Hornet, both competing for a key role in enhancing the Navy’s carrier-based combat capabilities. Sources familiar with the trials indicate that the Rafale M outperformed the Super Hornet on several critical technical criteria, with one significant differentiator being the lack of an integrated Infrared Search and Track (IRST) system on the F/A-18E/F.
The IRST system is a passive, infrared-based tracking sensor that allows a fighter jet to detect and follow enemy aircraft without emitting radio frequencies, thus remaining undetected by adversaries. By operating exclusively in the infrared spectrum, the IRST system provides the ability to spot airborne threats well beyond visual range. This is particularly valuable in modern combat scenarios, where stealth and the element of surprise are critical.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is set to elevate the capabilities of the Advanced Light-Weight Torpedo (ALWT) with a 100 kW Magnesium-Silver Chloride (Mg-AgCl) battery upgrade, intended to boost its speed from 33 knots to an impressive 47 knots—a significant 42% increase. This enhancement aims to meet evolving anti-submarine warfare (ASW) requirements for the Indian Navy, furthering India’s indigenous defense technology capabilities.
The ALWT is the second generation of the Shyena torpedo, developed by DRDO’s Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL), with production managed by Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL). Specifically designed for anti-submarine warfare, the ALWT has cleared all trials and has been proposed for production.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Indian Air Force (IAF) has taken a significant step toward preserving its aviation heritage by initiating the revival of two MiG-23UB trainer aircraft. Through its Headquarters Maintenance Command (HQ MC), the IAF has issued an Expression of Interest (EoI) inviting qualified Indian firms to participate in the restoration and maintenance of these historic aircraft. The selected firms must have the technical expertise, financial stability, infrastructure, and experience required to make these MiG-23UB trainers flyworthy once again, and to support their long-term upkeep as part of the IAF’s Heritage Flight.
The MiG-23, an iconic swing-wing fighter developed by the Soviet Union, served in the IAF from the early 1980s and played a crucial role in bolstering the force’s air superiority capabilities. Known for its powerful performance in high-speed intercepts, the MiG-23 fleet included variants like the MiG-23MF, MiG-23BN, and the MiG-23UB, which was specifically designed as a two-seat trainer for pilot training and specialized missions. The MiG-23MF variant was retired in March 2007, followed by the MiG-23BN ground-attack variant in March 2011. However, a limited number of MiG-23UB trainers continued to operate for specialized roles within the IAF, maintaining a connection to the aircraft’s rich legacy within the service.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.

The Technology Development Fund (TDF) has issued a call to Indian Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) to develop a Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG)-based Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) system. The aim of this initiative is to enhance the structural integrity of various vehicles and systems by continuously monitoring their health throughout their operational lifespan, ensuring both safety and economic efficiency.
Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) systems are designed to monitor the health of a structure, ensuring its static strength, durability, and damage tolerance during its specified usage period. The primary goal of SHM is to prevent unexpected structural failures, which can pose safety risks and lead to expensive repairs. By having structures equipped with SHM systems, maintenance teams can receive real-time data on the overall health of the structure based on information gathered from built-in sensors and analyzed by SHM algorithms.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
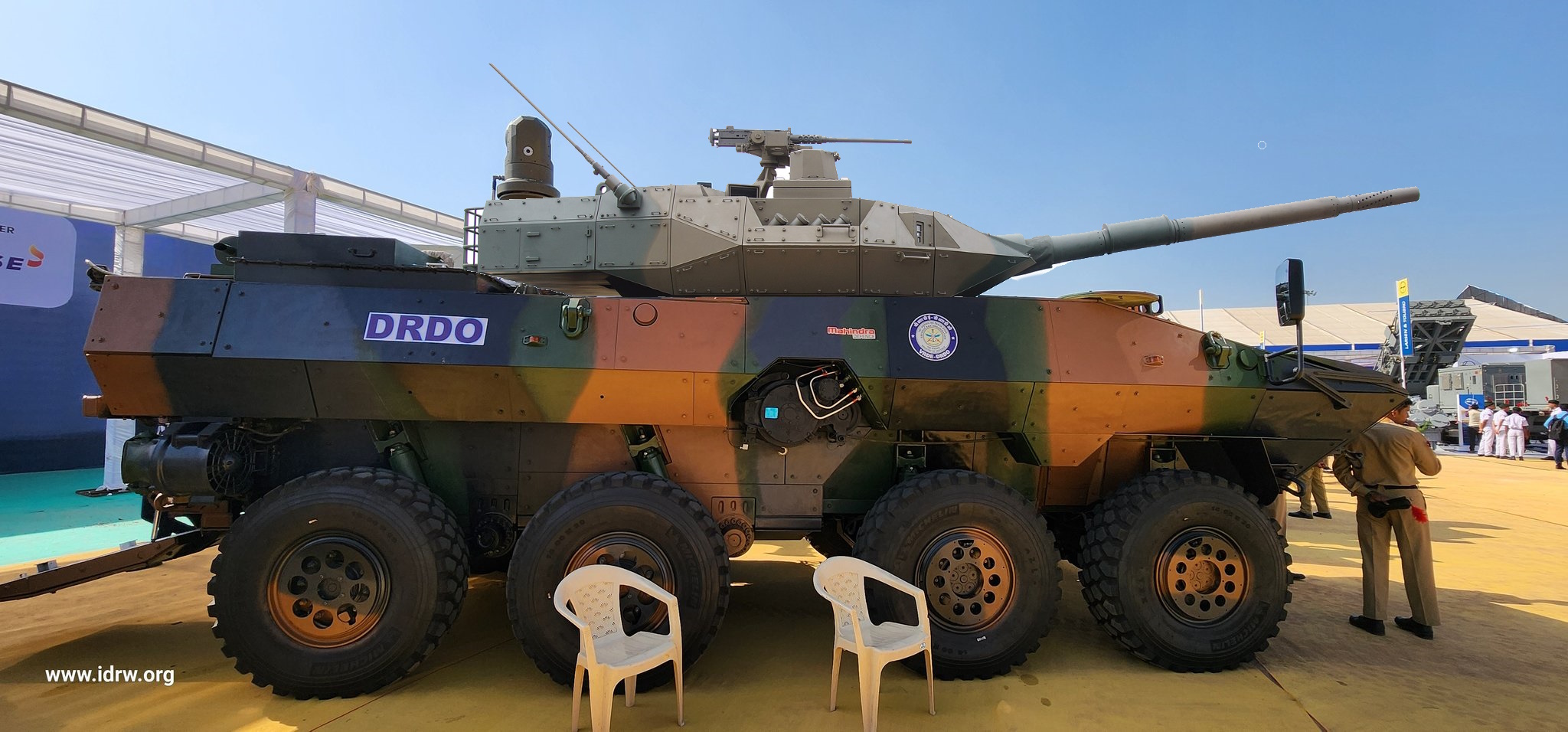


At the recent Marrakech International Air Show, Tata Advanced Systems Ltd (TASL) confirmed a significant contract with the Royal Moroccan Armed Forces to manufacture WhaP 8×8 armoured vehicles. The deal marks a major milestone in the defence relationship between India and Morocco. Tata prepares to deliver over 400 units of this versatile Armoured platform in various configurations to Morocco, with more than 150 being of the WhaP 8×8 type. The vehicles will be manufactured locally in Morocco, in partnership with local industry, strengthening Morocco’s defence manufacturing capabilities.
The Moroccan version of the WhaP 8×8 has been adapted to meet the specific operational needs of the Royal Moroccan Armed Forces. Unlike the amphibious Indian version, the Moroccan WhaP variant has had its amphibious capabilities removed, a modification that not only extends its operational range but also allows for an expanded and optimized troop transport compartment. The redesigned compartment offers improved space and comfort, enabling it to carry more personnel or equipment.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Indian Navy, through the iDEX DISC 12 Challenge, is seeking private sector companies to participate in the design and development of a cutting-edge Underwater Smart Communication Buoy for passive surveillance and data transmission in open sea environments. This innovative initiative aligns with the broader goals of enhancing indigenous defence capabilities under the Atmanirbhar Bharat program, aiming to reduce reliance on foreign technology and promote domestic solutions for critical defence systems.
The Underwater Smart Communication Buoy is being designed for passive underwater surveillance at depths of up to 200 meters. It will surface at regular intervals to transmit critical acoustic data to a base station through satellite communication. The buoy is intended to operate autonomously, collecting and analyzing data while remaining in the open seas for up to 90 days without human intervention.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
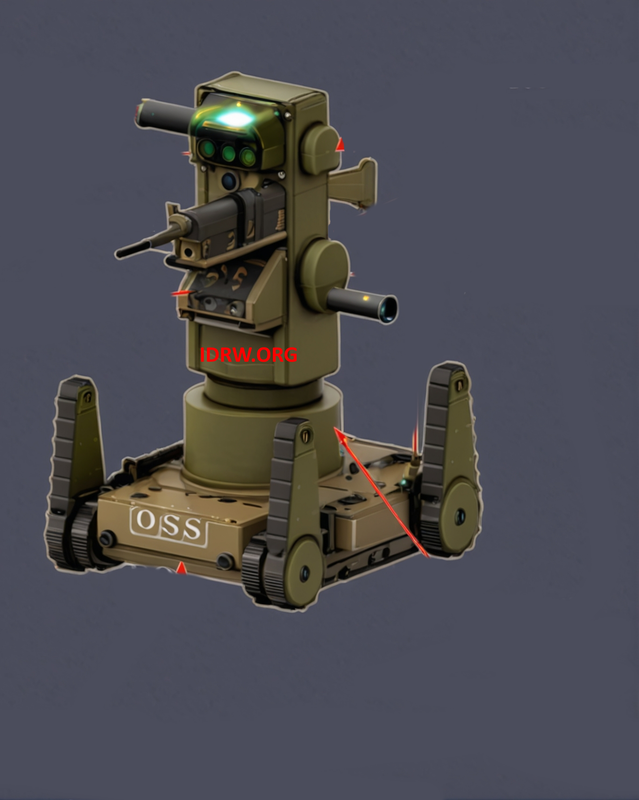


The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is currently working on the development of an advanced system known as the Electro-Optical Soldier System (EOSS). This innovative project is designed to enhance battlefield awareness, providing a comprehensive suite of tools for reconnaissance, surveillance, and combat engagement. The system aims to improve the effectiveness of ground soldiers by enabling remote control and real-time intelligence gathering, which can be crucial in high-risk combat zones.
The EOSS consists of four mobile platforms that are interconnected through a secure wireless networking scheme. These platforms can be operated remotely from a distant control station, offering flexibility and safety for soldiers in challenging environments.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
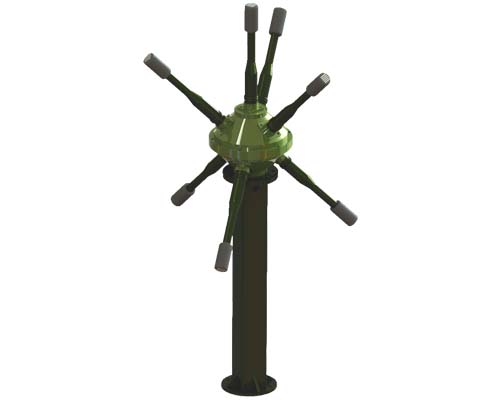


Indian robotics and AI company Gridbots has introduced the Gridbots BAT, an advanced gunshot direction-finding system designed to accurately detect and pinpoint the source of gunfire. This state-of-the-art system offers an exceptional accuracy of ± 5 degrees in both elevation and azimuth, as well as a distance precision of ± 4% FS, making it a crucial tool for security forces, military units, and law enforcement agencies.
BAT stands out for its unique ability to not only detect gunshots but also differentiate between various gunfire types. This selectivity allows operators to focus on specific frequencies or gunshots, filtering out irrelevant noises in complex environments.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


India’s ambitious plan to establish a comprehensive multi-tiered air defense system has taken a significant step forward with the Defense Research and Development Organization (DRDO) commencing the fabrication of M1, M2, and M3 interceptors. These interceptors form the core of Project Khusha, an indigenous air defense program that aims to create a layered shield capable of protecting the country from a wide array of airborne threats, including hypersonic missiles.
According to sources, DRDO has placed an order for the fabrication of 12 units of the three interceptor variants, marking a critical milestone in the development of the defense system. The goal is to deploy the long-range surface-to-air missile (LR-SAM) system under Project Khusha by 2028-2029, with a maximum interception range of 350 km.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


HFCL Limited, a leading Indian technology company, has achieved a significant milestone by indigenously developing electronic fuzes for artillery shells. The company has successfully created electronic fuzes for 130mm and 155mm artillery shells, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of India’s artillery arsenal.
The electronic fuzes developed by HFCL are equipped with two operating modes: Point Detonation Super Quick (PDSQ) and Point Detonation delay. These modes allow for precise control over the detonation of the artillery shell, ensuring accurate targeting and minimizing collateral damage. The fuze function can be programmed between the two modes using a simple switch located on the side of the fuze.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


On February 12th, 2014, a crucial moment in India’s defense history unfolded when the Ministry of Defence (MoD) was jolted from its passive stance by the increasing presence of China’s nuclear-powered submarines in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR). This was the day India realized the growing threat in its own backyard, as the Chinese People’s Liberation Army Navy (PLA Navy) deployed Shang-class (Type 093) nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs) in the IOR for the first time. This deployment was a clear demonstration of China’s intent to project its naval power in the region, marking the start of a new era of maritime strategic competition between India and China.
This move by China highlighted India’s vulnerability in the IOR, spurring the Indian MoD to take decisive action. The Chinese SSN presence effectively underscored the strategic imbalance in the region and prompted India to expedite the development of its own nuclear-powered attack submarines.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Indian Ministry of Defence (MoD) has issued a call to Indian industries, particularly MSMEs and startups, to develop Automatic Defect Recognition (ADR) software for weld radiography inspection, specifically for naval applications. This initiative is crucial as India’s defense forces are heavily involved in the fabrication of steel hulls for various naval vessels, and ensuring the integrity of these welds is critical for safety and performance.
Weld integrity is a vital aspect of naval construction, particularly in the fabrication of steel hulls that form the backbone of ships and submarines. The Indian Navy relies on nondestructive testing (NDT) methods to inspect these weldments, with Digital Radiographic Testing (DRT) being a widely adopted technique. DRT includes digitized film-based and computed radiography (CR)-based approaches that capture high-resolution images of welds for evaluation.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Indian Air Force (IAF) is considering an open tender for its ambitious Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) program, which aims to procure 114 advanced fighter jets. In a significant departure from earlier plans, the IAF is pushing for a high production rate within India, aiming for 24 aircraft per year instead of the previously suggested rate of 10-14 units annually. This proposed increase in production rate could lead to additional costs for the Ministry of Defence (MoD), as a larger-scale manufacturing setup will be necessary to meet the new output requirements.
The IAF’s demand for a higher production rate reflects its urgency to quickly bolster its combat capabilities, addressing current operational demands and strengthening defences across multiple fronts. By accelerating production to 24 jets annually.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
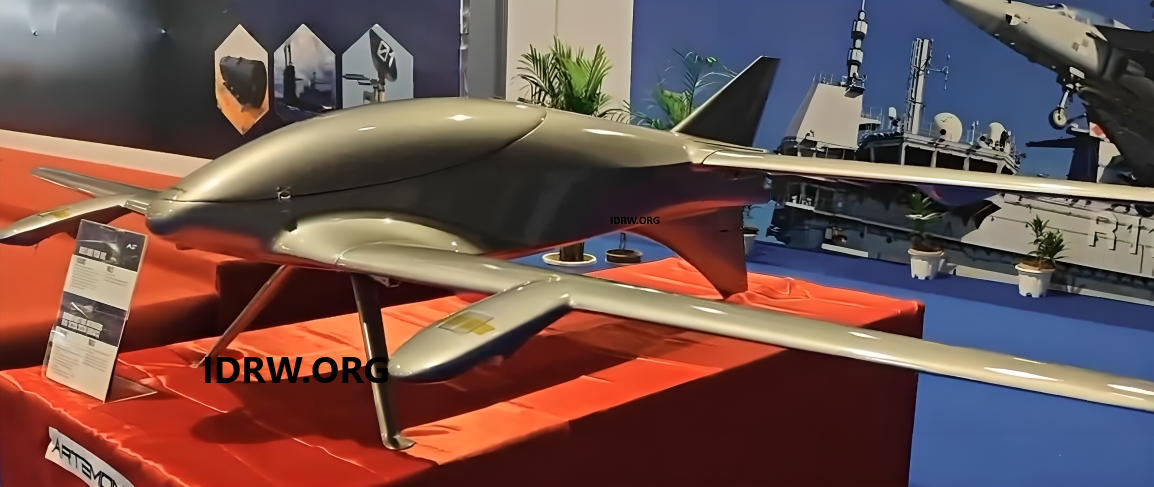


At Swavlamban 2024, Artemon Aerospace unveiled its latest innovation in unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) with the launch of a multi-role VTOL (Vertical Take-Off and Landing) UAV. This new UAV, designed to deliver versatile and high-performance aerial capabilities, can carry payloads up to 35 kilograms, making it a strong contender in both defense and commercial markets where heavy payload transport and precision operation are crucial.
According to officials from Artemon Aerospace, the UAV has been designed for extended endurance, a standout feature for its size class. This enables it to stay in the air longer than typical VTOL UAVs, enhancing its suitability for a variety of extended surveillance and reconnaissance missions. Furthermore, its advanced navigation systems allow it to operate effectively in GNSS-denied environments, making it ideal for deployment in remote or GPS-jammed areas. This capability opens up avenues for both defense and intelligence operations, where GPS-denial is a common tactic.
Continue reading