Monthly Archives: November 2024
SOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
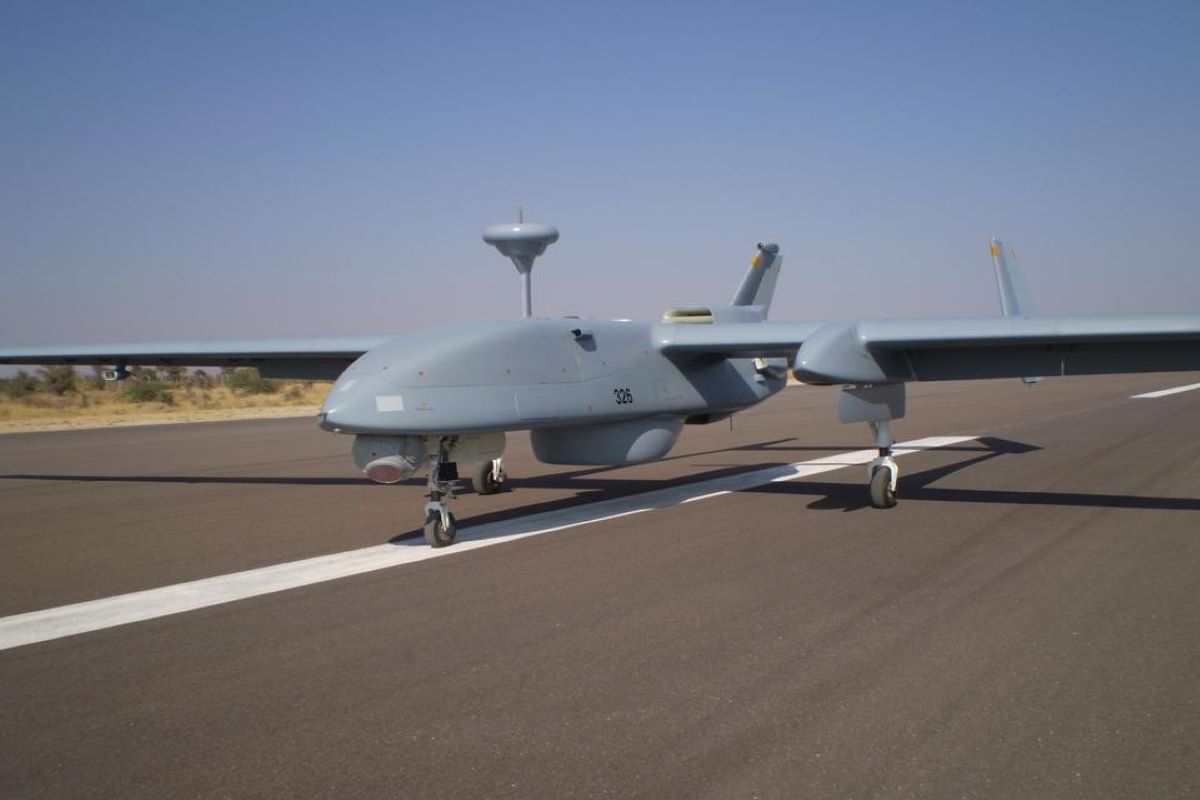


India’s Technology Development Fund (TDF) Scheme is set to play a critical role in enhancing the capabilities of Remotely Piloted Aircrafts (RPAs) by focusing on the design and development of advanced payloads. These new payloads aim to replace the legacy systems currently in use, addressing the increasing demands of modern warfare, surveillance, and reconnaissance operations. The project will significantly enhance the operational capability, efficiency, and mission readiness of RPAs, ensuring their effectiveness in dynamic and complex battlefield scenarios.
The RPAs in use today are equipped with older, legacy payloads that no longer meet the high standards required for contemporary military and surveillance tasks. These payloads have limitations, such as lower resolution, reduced operational range, and insufficient data processing capabilities, which hamper their performance in modern combat and intelligence-gathering roles. The need for upgrading these payloads has become more urgent, particularly as new technologies emerge and the demands of modern warfare evolve.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
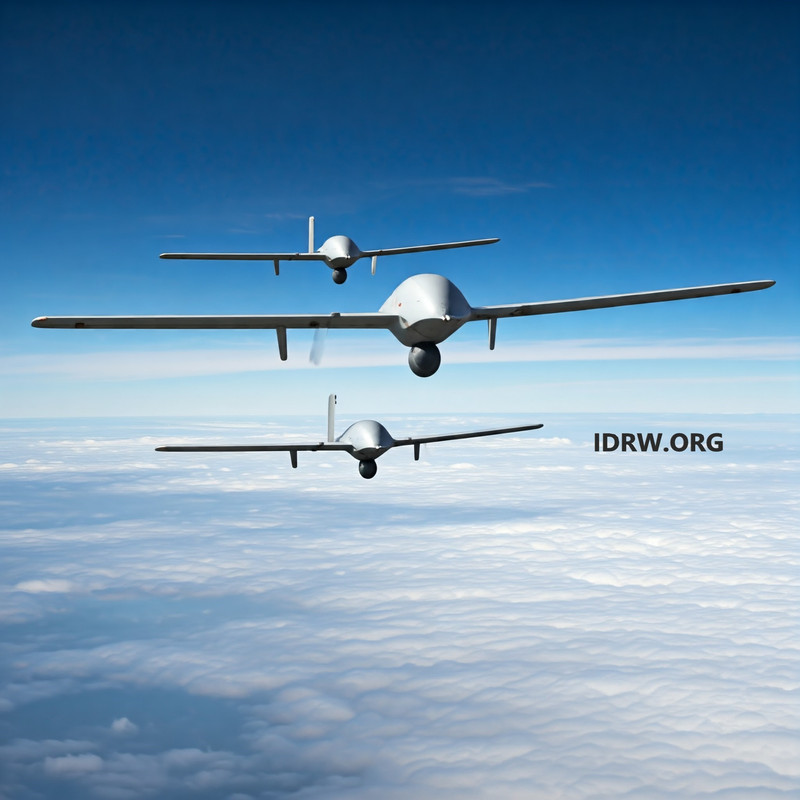


The Indian Army has initiated a search for state-of-the-art unmanned “surveillance copters” capable of operating effectively in extreme and varied terrains, from expansive plains and arid deserts to the high-altitude reaches of mountainous regions exceeding 4,500 meters. These advanced drones, essential to the Army’s modernization efforts, are intended to bolster surveillance and intelligence capabilities along India’s challenging frontiers, especially in regions where conventional surveillance tools face operational limitations.
The Indian Army’s specifications for these drones reflect the unique operational demands of high-altitude regions, emphasizing resilience, versatility, and cutting-edge technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
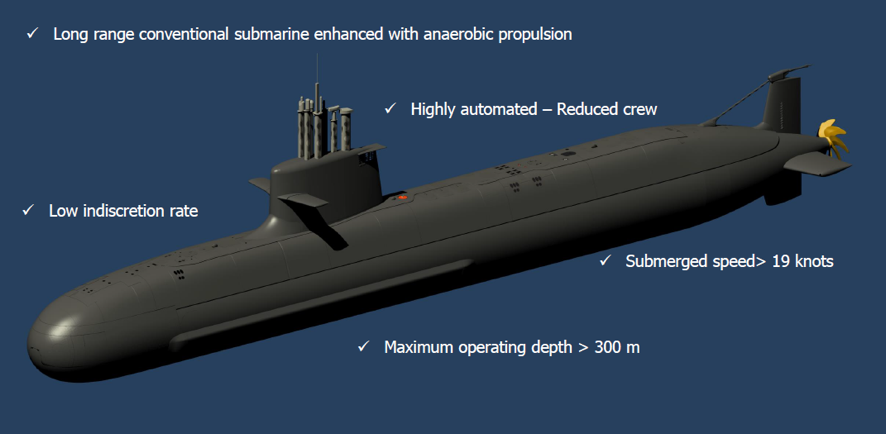

Spain’s state-owned shipbuilder, Navantia, is actively promoting its S-80 Plus submarine with the next-generation Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) system, known as BEST (Bio-Ethanol Stealth Technology), for the Indian Navy’s Project-75I tender, which seeks to procure six advanced submarines. Navantia officials assert that the BEST AIP system offers substantial advantages over conventional AIP fuel-cell technologies, including those used by Germany’s TKMS, whose U-214NG submarine is also a contender in the same project.
Navantia’s BEST AIP system, which utilizes bio-ethanol fuel, provides a clean, efficient, and stealthy alternative to traditional AIP systems. According to Navantia, the BEST system offers superior endurance, allowing submarines to stay submerged for extended periods without surfacing for air. This endurance capability can be particularly advantageous for stealth missions, as it minimizes the submarine’s detectability.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


General Atomics Aeronautical Systems, Inc. (GA-ASI) recently made headlines with a significant contract to supply 31 MQ-9B drones to the Indian Armed Forces. This deal, which allocates 15 of these advanced UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles) to the Indian Navy, strengthens India’s maritime surveillance and reconnaissance capabilities.
However, GA-ASI is also promoting its innovative Mojave Unmanned Aircraft System (UAS) as a potential carrier-capable UAV for the Indian Navy’s evolving requirements. The Mojave, a short takeoff and landing (STOL) demonstrator, was initially developed to operate from unprepared and compact landing sites but has potential applications in carrier-based environments.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
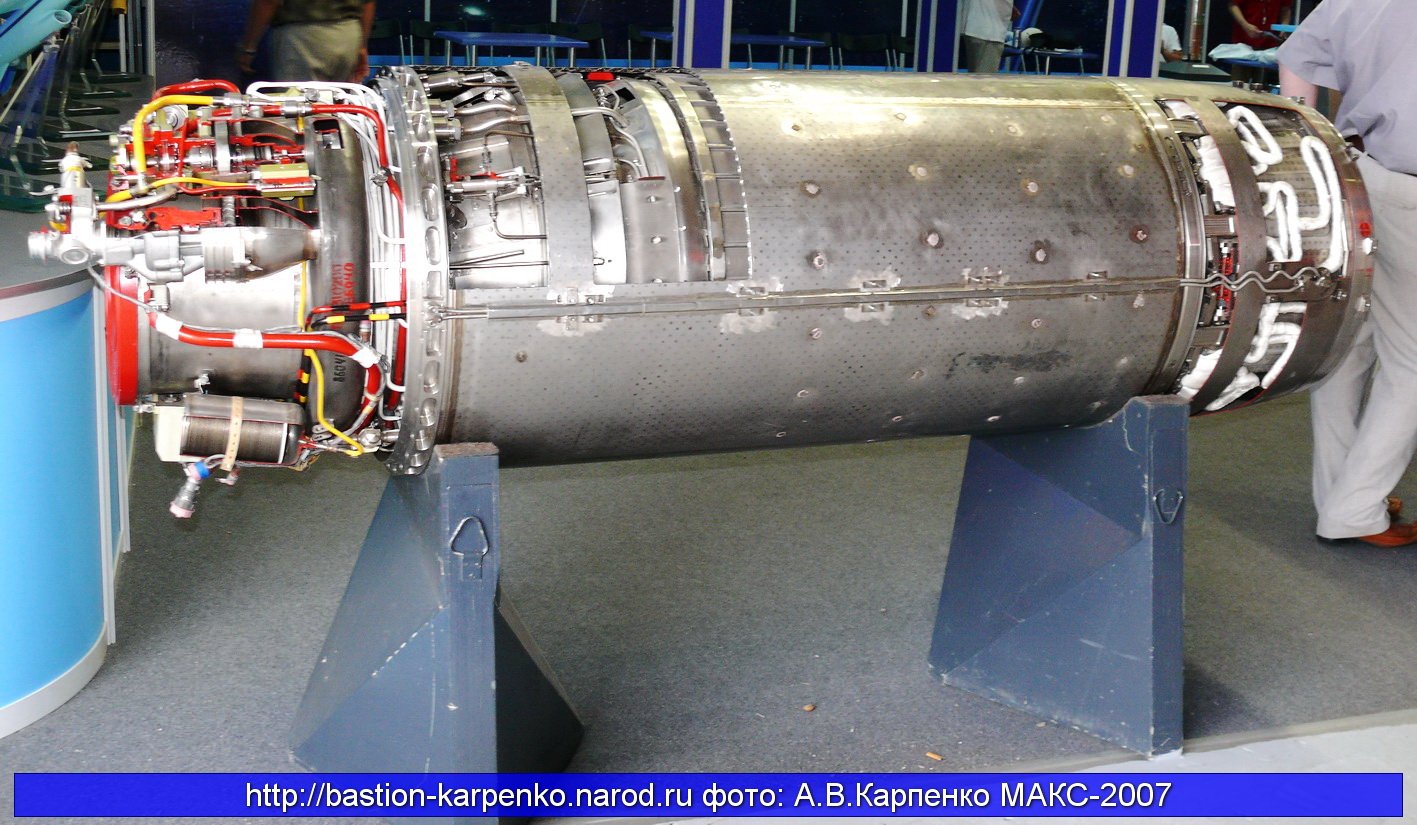


BrahMos Aerospace, the joint venture between India and Russia, is working on significant upgrades to the current ramjet engine used in the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile. The enhancements aim to achieve hypersonic speeds of Mach 5 or above within the next 4-5 years. This marks an exciting phase in the missile’s development, as the company looks to push the boundaries of speed, precision, and strike capability.
The upgraded BrahMos missile will retain the same airframe as the current version but will feature a more powerful ramjet engine capable of achieving hypersonic speeds, with a target of Mach 5. However, it’s crucial to distinguish this from the BrahMos 2K, which is expected to exceed Mach 7 speeds, placing it in the extreme hypersonic category.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
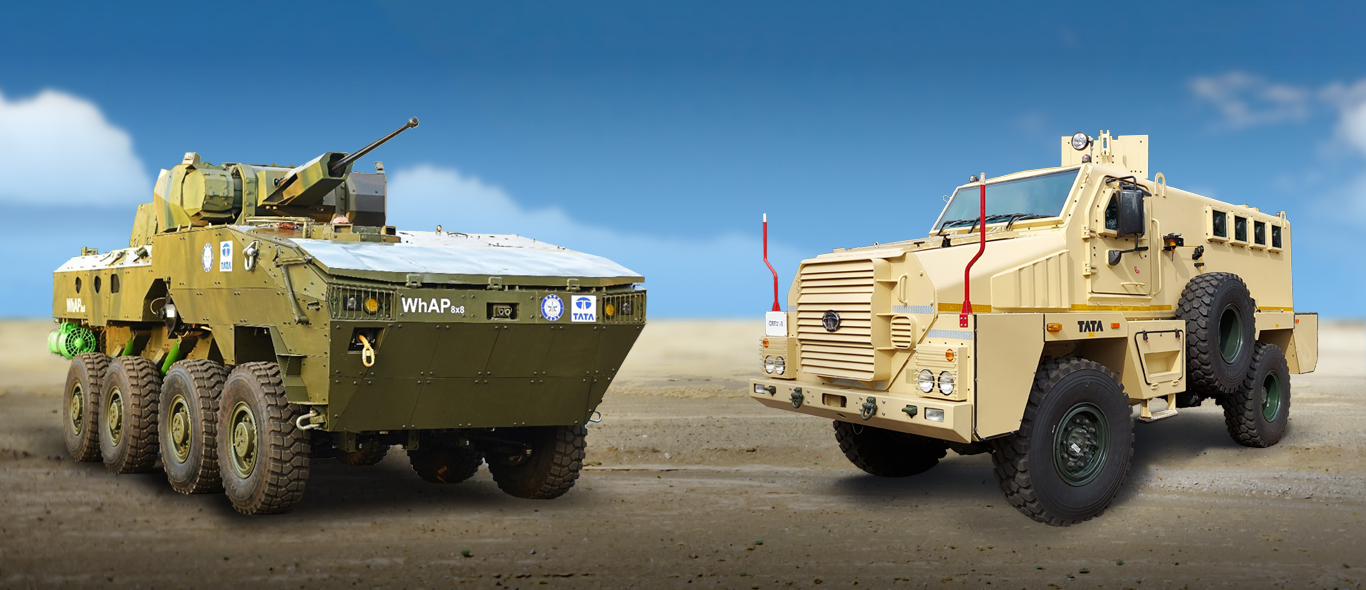


On November 18, 2024, representatives of TATA made an online presentation to the Hellenic Army General Staff (GES), highlighting the company’s cutting-edge military ground weapon systems and transport vehicles. The presentation demonstrated TATA’s commitment to expanding its footprint in the global defense market and its focus on providing versatile and reliable solutions tailored to the needs of modern armed forces.
ATA presented a range of its advanced military platforms, emphasizing the following vehicles WhAP 8×8 (Wheeled Armored Platform) A modular and versatile armored vehicle, the WhAP 8×8 is designed to meet diverse operational requirements, including reconnaissance, troop transport, and infantry support. Developed in collaboration with the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), this amphibious platform boasts impressive off-road capabilities and protection features. It can be equipped with various weapon systems, including machine guns, automatic grenade launchers, and anti-tank guided missiles, making it a formidable addition to any mechanized infantry unit.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
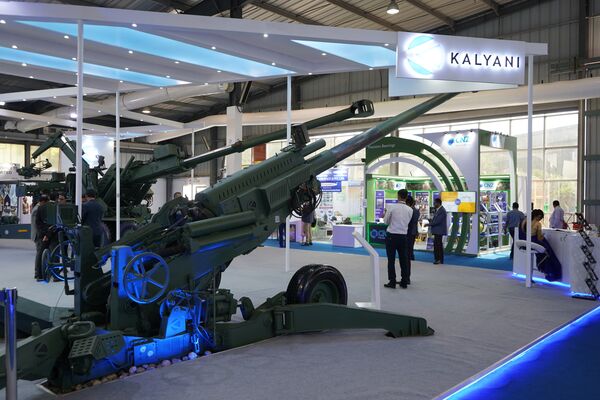


The Indian Army has recently decided to drop plans for procuring more ultra-light howitzers (ULHs) like the M777 or any local offerings from the Towed Gun System (TGS), instead opting to focus on the acquisition of 155/52 calibre artillery guns. This strategic shift stems from several factors, including the Army’s evolving requirements for firepower and the operational advantages offered by the larger 155/52 calibre guns over the smaller 155/39 calibre systems.
The 155/52 caliber guns are increasingly seen as the preferred choice for the Indian Army’s artillery modernization. These guns, capable of firing extended-range ammunition, have significant advantages over smaller caliber systems such as the 155/39 caliber guns, which are typically used for shorter-range engagements.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Indian Army, under the Ministry of Defence, has released a Request for Information (RFI) to procure approximately 5,000 to 10,000 Software Defined Radios (SDR) for vehicular applications. This new communication system aims to enhance tactical vehicular radio communication across a wide range of military vehicles, providing reliable and resilient communication capabilities essential for modern warfare. These SDRs will play a vital role in equipping the Indian Army’s vehicular fleet, from heavily armored tanks to lighter utility vehicles, with advanced, adaptable communication tools.
The SDRs are intended to support vehicular communication for both A and B category vehicles used by the Indian Army. Category A vehicles include heavily armored and specialized vehicles like tanks, while Category B vehicles cover light utility and logistical support vehicles. By equipping both categories, the SDRs will create a standardized communication network across the vehicle spectrum, ensuring secure, reliable, and high-quality communication channels across the battlefield.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Indian Air Force’s (IAF) long-awaited Medium Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender, aimed at acquiring 114 advanced fighter jets, is facing an additional challenge as local production costs are projected to exceed direct procurement prices by $20-30 million per jet. According to an IAF official who spoke to idrw.org, manufacturing these jets locally—an integral part of the Make in India initiative—would incur significantly higher expenses compared to acquiring them directly from the original equipment manufacturers (OEMs).
The MRFA tender includes four twin-engine fighters in consideration: the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Block III, the Eurofighter Typhoon, the Russian MiG-35, and the Dassault Rafale. Additionally, two single-engine options, the Lockheed Martin F-16 Block V (marketed as the F-21) and Saab’s Gripen-E, have also been proposed. While all six fighters present advanced capabilities, the increased costs associated with establishing local production lines, building specialized infrastructure, and training a domestic workforce will push the final price per unit well above what a direct OEM purchase would entail.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


India’s Future Ready Combat Vehicle (FRCV) program is setting an ambitious course for the modernization of the Indian Army’s armoured forces by developing a next-generation main battle tank (MBT) to replace its ageing fleet of T-72 tanks. The program is not only focused on creating a more advanced, capable tank but is also exploring the potential for autonomous, unmanned combat vehicles.
These unmanned MBTs are envisioned to operate autonomously, leveraging direct satellite links for real-time battlefield data exchange, robust communication networks, and advanced firepower capabilities to transform combat operations. Here’s a look into the transformative technology and vision guiding India’s FRCV program.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


Swedish defence giant Saab has presented a compelling proposal to the Indian Air Force (IAF) under its Medium Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender, offering its Gripen-E fighter jet with a comprehensive “Make in India” production strategy. Saab not only plans to set up a production line for the Gripen-E in India but has also offered its expertise to support the production line of India’s indigenous Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. This collaboration would leverage Saab’s experience in digital engineering and fighter jet production to aid India in establishing a modernized manufacturing ecosystem.
Saab officials have highlighted India’s availability of a skilled workforce and the potential for advanced digital engineering techniques, noting that recent projects, such as the Gripen-E, have allowed Saab to refine its high-tech production capabilities. Saab’s proposal goes beyond the MRFA requirements, potentially positioning itself as a key partner in enhancing India’s domestic fighter manufacturing capability, especially for complex, next-generation platforms.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
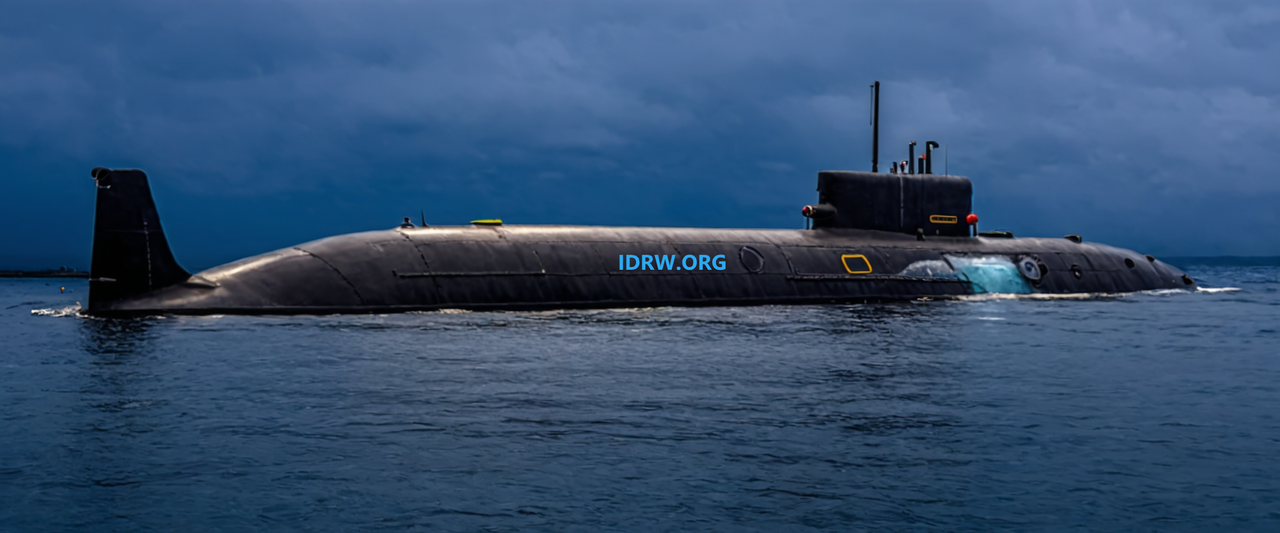


In a significant milestone for India’s nuclear deterrence capabilities, the INS Arihant, India’s first nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN), reportedly conducted its first operational trial of the K-4 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM) yesterday morning. According to a report by the Times of India, this marks a major step forward in integrating long-range SLBMs into India’s underwater strategic forces.
The K-4 SLBM, with a range of approximately 3,500 km, represents a considerable advancement over the K-15 (B-05) missile, which has a range of 750 km. Until now, tests of the K-4 had been carried out from submerged platforms says TOI report, ensuring the missile’s capabilities in realistic underwater launch scenarios. But idrw.org Reports from 2022 indicated that INS Arihant successfully conducted trials of the K-15 SLBM, marking its ability to operationally deploy short-range SLBMs but also K4 trials were also carried out in the same year as two trials were recorded from Arihant, so technically this could be a second test but first full-range test of the K-4 missile.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The indigenously developed Zorawar light tank has arrived in Ladakh for a month-long trial at the Nyoma field firing range. This critical phase of testing, which commenced in mid-November, is scheduled to conclude by mid-December 2024. Developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) in collaboration with Larsen & Toubro (L&T), the Zorawar is poised to play a pivotal role in enhancing the Indian Army’s capability in high-altitude and challenging terrains.
The Zorawar light tank has already successfully completed its internal trials and firing trials, which were jointly conducted by L&T and DRDO. These tests validated the tank’s core systems, including its advanced firepower, mobility, and survivability features. Now, the platform has entered the critical user trial phase, where it will be assessed by the Indian Army under operational conditions.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
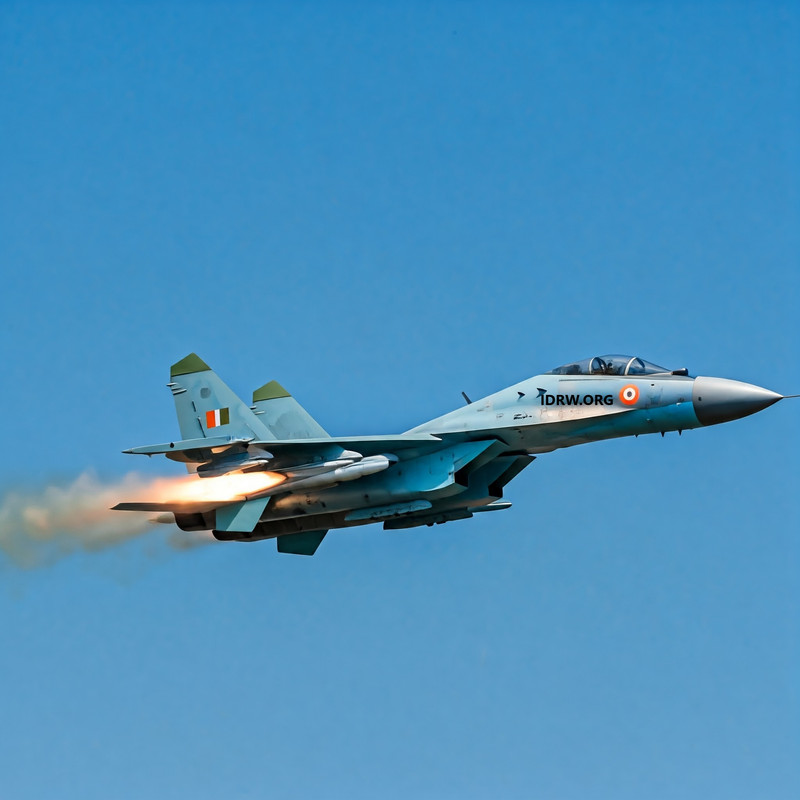


The European consortium responsible for developing the Meteor, one of the world’s most advanced long-range air-to-air missiles, is reportedly not keen on supporting the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) plans to integrate the missile on its frontline fighter jets like the Super Su-30MKI, Tejas Mk1A, and the upcoming Tejas MkII. Currently, only the 36 Rafale jets in India’s arsenal are equipped with the Meteor missile, despite the IAF’s interest in expanding the missile’s integration to other indigenous and Russian-origin platforms.
Besides the Rafale, the Meteor has been integrated with the Gripen-E and Eurofighter Typhoon, which are contenders in India’s Medium Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender for 114 fighter jets. Industrial sources close to idrw.org reveal that the European consortium has reservations regarding the Meteor’s integration on Russian-origin platforms and has shown reluctance to support its deployment on Indian-made jets like the Tejas Mk1A. This stance appears to be a deliberate strategy, with the consortium aiming to position the Meteor missile as a unique selling proposition (USP) for European fighters in India’s MRFA competition. By limiting the Meteor to European platforms, the consortium is possibly creating a competitive advantage for its missile-equipped fighter jets in the tender process.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
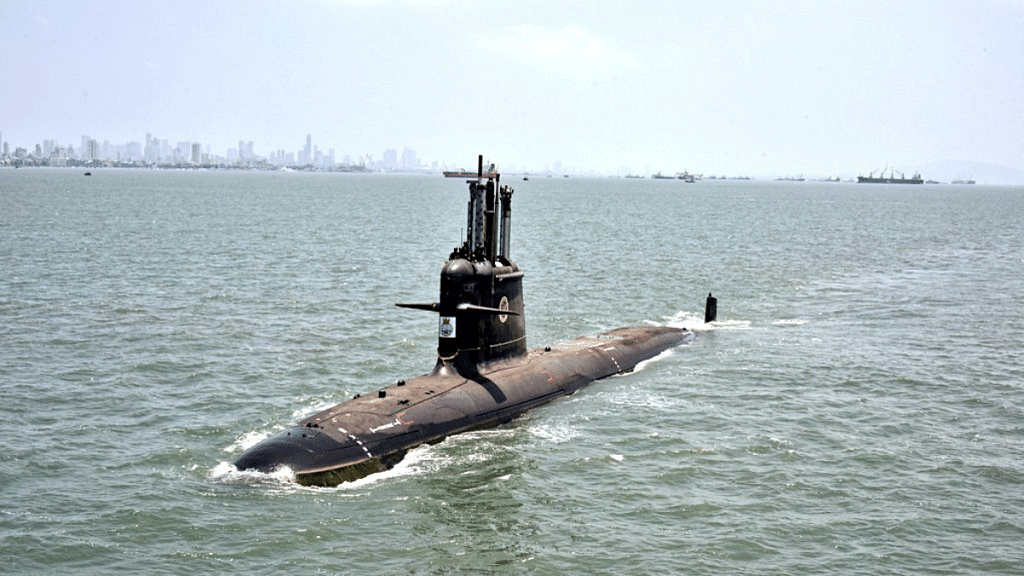


The Defense Research and Development Organisation’s (DRDO) ambitious Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) system, developed specifically for the Indian Navy’s Kalvari-class submarines, appears likely to miss its scheduled 2025 installation target due to delays in ground-based testing. Sources close to the project informed idrw.org that several critical tests for the AIP system are still pending, casting uncertainty over its timeline.
The AIP system, designed to enhance underwater endurance and stealth capabilities, was initially planned for integration into the first of the Scorpène-class submarines, INS Kalvari, during its upcoming refit scheduled for 2025. However, delays in testing mean that the integration may now be pushed to 2026 or to the Second Kalvari Class submarine.
Continue reading