SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a bid to strengthen its defence ties and expand its footprint in the global arms market, India recently hosted a delegation of Armenian Air Force officials for a detailed briefing on the indigenous Tejas Mk1A and Tejas MkII fighter jets.
The briefing, conducted by representatives from Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA), comes at a time when Armenia is seeking to modernize its ageing and limited air fleet in response to Azerbaijan’s recent acquisition of JF-17 fighter jets from China. The development underscores India’s growing efforts to boost defence exports, particularly to Armenia, which has emerged as one of the largest importers of Indian-made weapons in recent years.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant development for India’s military aviation capabilities, the Ministry of Defence (MoD) on Friday, March 28, 2025, signed a contract with Metrea Management, a private company specializing in air-to-air refuelling services, for the wet leasing of one Flight Refuelling Aircraft (FRA). The agreement stipulates that Metrea will provide a KC-135 aircraft within six months, marking the first time the Indian Air Force (IAF) has opted for a wet-leased FRA. This move is aimed at enhancing the air-to-air refuelling training for pilots of both the IAF and the Indian Navy.
According to an official statement from the MoD, the KC-135, a proven aerial refuelling platform, will bolster the operational readiness of India’s armed forces by providing critical training opportunities. Wet leasing, which includes the provision of the aircraft along with crew, maintenance, and insurance, offers a flexible and efficient solution for the IAF, which has been seeking to augment its refuelling capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a move that appears to signal a strategic shift in its maritime defense posture, the Pakistani Navy (PN) is reportedly planning to procure the Chengdu J-10CE fighter jet from China. This development comes as a potential counter to India’s acquisition of the Dassault Rafale M, a naval variant of the advanced French fighter jet tailored for carrier operations.
The J-10CE, a 4.5-generation multirole aircraft, is being considered as Pakistan phases out its aging fleet of Mirage-III fighters, currently operated by the Pakistan Air Force (PAF) but assigned to the PN for maritime protection roles. However, ambiguity surrounds whether the PN will directly operate these new jets or if the PAF will bolster its own J-10CE fleet to take over maritime surveillance and defense duties over the Arabian Sea.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


As the race to develop sixth-generation fighter jets accelerates, manufacturers and developers remain tight-lipped about the specifics that set these advanced platforms apart from their fifth-generation predecessors. Unlike the well-documented capabilities of fifth-generation jets like the Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor, F-35 Lightning II, Russia’s Su-57, and China’s J-20, the details of sixth-generation designs are shrouded in secrecy, often cloaked under classified programs or vague press releases.
Yet, recent observations from prototype unveilings, industry hints, and expert analyses suggest a clear evolution in design and performance. Here’s what sets sixth-generation fighters apart from their fifth-generation counterparts, based on emerging trends and informed speculation.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant realignment of military resources, the Rashtriya Rifles (RR) Division of the Uniform Force, previously redeployed to Eastern Ladakh, is set to return to its original operational area in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K). This shift comes as the newly established 72 Infantry Division, whose raising has been underway for months, prepares to assume responsibility for securing India’s northern frontiers in Ladakh. The redeployment reflects the Indian Army’s evolving strategy to balance security challenges along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China and the Line of Control (LoC) with Pakistan.
The RR Division, known for its counter-insurgency expertise, was moved to Eastern Ladakh following heightened tensions with China, particularly after the deadly Galwan Valley clash in June 2020. The clash prompted a major reassessment of India’s military posture, leading to an increased focus on bolstering defenses along the LAC. However, this shift left a security gap in Jammu, where Pakistan-based terrorist groups have exploited the reduced troop presence to escalate attacks. The return of the RR Division to J&K aims to address this vulnerability and restore stability in the region.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


Bengaluru-based aerospace startup Nabhdrishti Aerospace has secured $3 million in a seed funding round led by Accel, with participation from IIMA Ventures and other existing investors. Announced in late March 2025, this infusion of capital will propel the company’s mission to develop fuel-flexible gas turbines for power generation and aircraft propulsion, addressing India’s long-standing reliance on imported propulsion systems. Founded by a trio of industry veterans with roots at General Electric (GE), Rolls-Royce, and DRDO-GTRE, Nabhdrishti is poised to redefine aerospace innovation with its cutting-edge technology.
The co-founders—Rohit Chouhan, Arjun Srivatsa, and Antanu Sadhu—bring a wealth of experience to the table. Chouhan, who also worked at the Defence Research and Development Organisation’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (DRDO-GTRE), joins Srivatsa and Sadhu in leveraging their time at GE and Rolls-Royce to tackle one of aerospace’s toughest challenges: propulsion. Graduates of IIT Delhi, IIT Kanpur, and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), respectively, the trio is channeling their expertise into a common-core micro gas turbine platform designed for dual-use applications.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


BEML Limited, a leading public sector undertaking under India’s Ministry of Defence, launched its indigenously designed and manufactured High Mobility Vehicle (HMV) 12×12 at its Palakkad complex in Kerala. Developed in collaboration with the Vehicles Research and Development Establishment (VRDE), a unit of the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), this state-of-the-art vehicle promises to enhance the operational mobility of India’s armed forces while advancing the nation’s “AatmaNirbhar Bharat” vision for self-reliance in strategic military assets.
The formal launch ceremony was presided over by BEML Limited’s Chairman and Managing Director, Shantanu Roy, with G. Ramamohana Rao, Director of VRDE, in attendance, alongside BEML’s functional directors and senior officials from both organizations. The HMV 12×12, engineered to tackle extreme terrains and harsh climatic conditions, represents a significant leap in India’s defence manufacturing capabilities, tailored to meet the rigorous demands of modern military operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), India’s premier defence public sector undertaking, announced on Thursday, March 27, 2025, a significant amendment to its contract for the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk1 Final Operational Clearance (FOC) variant. Originally signed with the Indian Air Force (IAF) on December 23, 2010, the contract’s value has been revised upward from ?5,989.39 crore to ?6,542.20 crore, reflecting adjustments in the delivery timeline.
In a regulatory filing, HAL stated, “We wish to inform that the company has signed today an amendment to the LCA Mk1 FOC Contract dated 23rd December, 2010. The value of the contract has been revised from ?5,989.39 crore to ?6,542.20 crore, on account of revision in the delivery schedule.” While HAL did not elaborate on the specific reasons for the delay, industry observers point to challenges such as supply chain disruptions, integration of new systems, and the need for additional components as likely factors contributing to the rescheduling.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a major boost to its defence portfolio, Force Motors Limited has clinched a landmark contract with the Indian Defence Forces to supply 2,978 Force Gurkha light vehicles, cementing its position as a key player in India’s military logistics ecosystem. The deal, awarded by the Directorate General of Capability Development (CD-13/14) under the General Staff Branch, was announced on March 27, 2025, and underscores the Pune-based automaker’s growing stature in meeting the nation’s security needs.
The contract centers on the Force Gurkha GS 4X4 800 kg Soft Top model, a Light Strike Vehicle (LSV) tailored to the exacting standards of military operations. Known for its rugged design and versatility, the Gurkha has earned a reputation as a reliable workhorse, capable of tackling the harshest environments—be it the arid deserts of Rajasthan, the flooded plains of the Northeast, or the treacherous heights of the Himalayas. This order, valued implicitly through the scale of 2,978 units, represents a significant vote of confidence in Force Motors’ engineering prowess and its ability to deliver mission-critical solutions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


India issued a Notice to Airmen (NOTAM) announcing a missile firing exercise scheduled to take place in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a strategically vital archipelago in the Bay of Bengal. The NOTAM, effective from April 4, 2025, at 9:00 AM IST to April 10, 2025, at 5:30 PM IST, designates a firing range of 465 kilometers, sparking speculation that the Indian armed forces are gearing up to test the air-launched variant of the BrahMos supersonic cruise missile, known as BrahMos-A.
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands, positioned near the Malacca Strait—a critical global maritime chokepoint—have long served as a testing ground for India’s advanced missile systems. The specified range of 465 kilometers aligns closely with the capabilities of the BrahMos-A, an air-launched version of the BrahMos missile, which boasts an extended range of over 450 kilometers following India’s entry into the Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) in 2016. This range extension, up from the original 290 kilometers, enhances the missile’s reach, making it a formidable asset for precision strikes from the air.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On March 26, 2025, Pakistan’s Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission (Suparco) issued a statement predicting that Eidul Fitr would likely fall on March 31, based on scientific parameters indicating a high probability of moon sighting on March 30. What might have been a routine astronomical forecast quickly turned into a lightning rod for ridicule across the border, as Indian social media users seized the opportunity to mock Pakistan’s space agency, reigniting a decades-old rivalry in space exploration.
Suparco’s statement read, “Given scientific parameters, the likelihood of moon sighting on March 30, 2025 in Pakistan was high. Consequently, Ramazan is expected to complete 29 days, and the first day of Eidul Fitr will likely be observed on 31 March 2025.” The agency, tasked with advancing Pakistan’s space research, based its prediction on astronomical models—a task it has performed for years to assist the nation’s moon-sighting committees. But for many in India, the announcement was less about science and more about an opportunity to highlight the disparity between Suparco and its Indian counterpart, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a significant stride toward bolstering India’s strategic underwater capabilities, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) recently unveiled key components of the K-5 Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM), signalling that its development is gaining momentum.
The showcased items—including the missile’s canister, nose cap, torrential air bottle, and TOR gas generator casing—offer a rare glimpse into the advanced engineering behind this next-generation weapon system. With a projected range of 6,000–8,000 kilometres, the K-5 SLBM is poised to place all of China within India’s striking reach, even when launched from the farthest stretches of its coastline. Designed as a three-stage missile, the K-5 is set to arm the advanced S-4* class of submarines, further solidifying India’s nuclear triad and second-strike capability.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
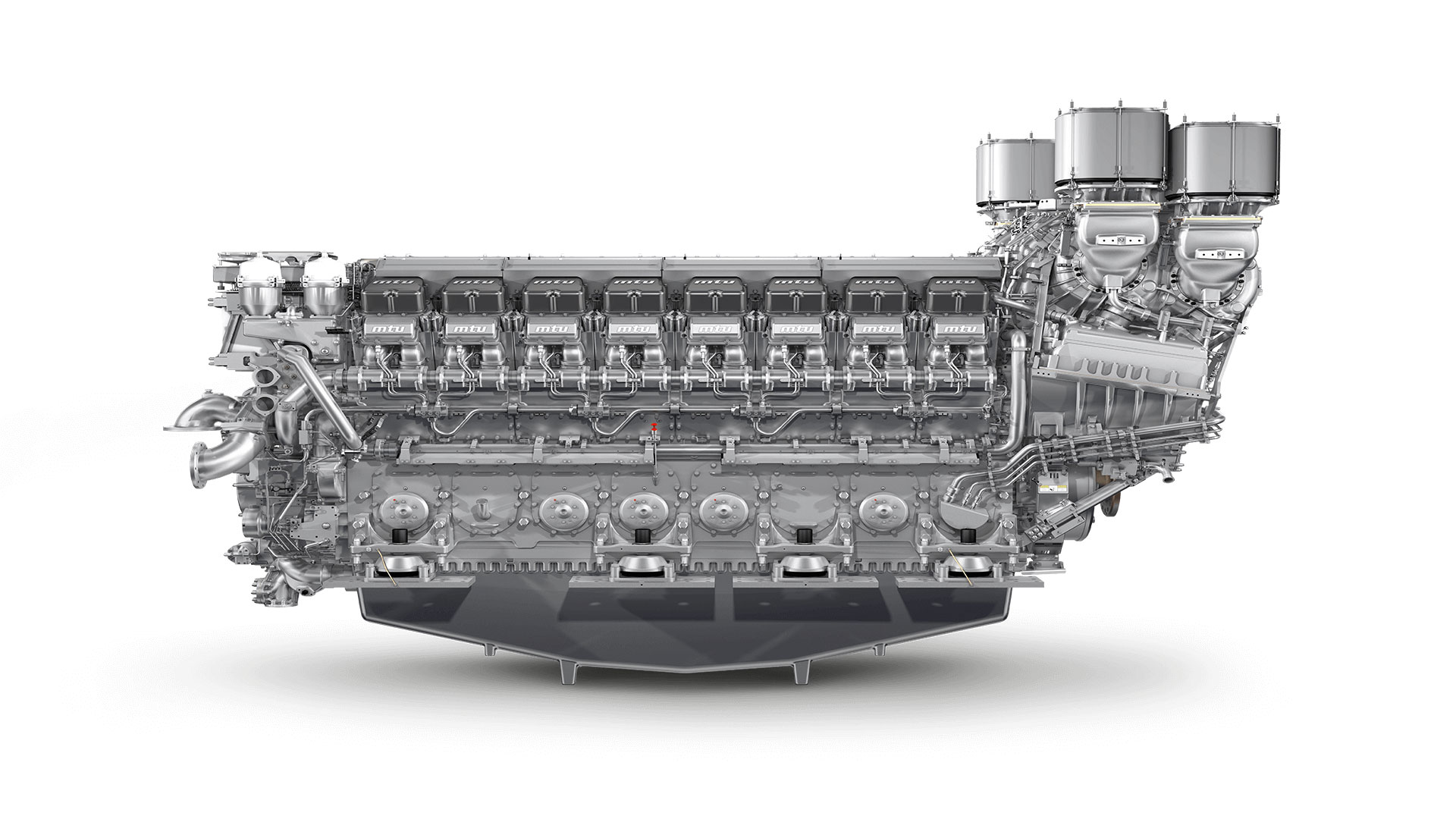

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is gearing up for a pivotal phase in India’s naval modernization with its ambitious Project-76, aimed at designing and developing a new class of indigenous conventional diesel-electric submarines for the Indian Navy. As the program inches closer to Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) approval—expected within the next few months—DRDO is actively planning to collaborate on developing a marine diesel engine, a critical component for the submarines.
DRDO’s mandate to maximize indigenous content—targeting 90-95%—means that relying on imported engines beyond the initial batch is untenable. The organization is thus exploring partnerships to develop a local marine diesel engine, potentially manufactured in India under a Transfer of Technology (ToT) agreement. The engine must not only meet the 3,000+ hp requirement but also integrate seamlessly with the submarine’s AIP and lithium-ion battery systems, a complex engineering feat.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Indian Navy is set to enhance its maritime strike capabilities by incorporating the indigenously developed Naval Anti-Ship Missile-Medium Range (NASM-MR), also known as Medium Range Anti-Ship Missiles (MRAShM), into its fleet of Boeing P-8I Poseidon maritime patrol aircraft. This ambitious plan, which involves collaboration with Boeing, aims to supplement the Navy’s existing arsenal of Harpoon AGM-84D anti-ship missiles, bolstering its ability to tackle surface threats across the Indian Ocean Region.
The NASM-MR, designed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), is already tailored for the Navy’s MiG-29K fighter jets and is slated for integration with the Rafale Marine and the upcoming Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter (TEDBF). Its expansion to the P-8I fleet marks a significant step in unifying advanced weaponry across diverse platforms.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML Ltd), a leading Indian public sector undertaking under the Ministry of Defence, has taken a significant step toward bolstering India’s armored capabilities. On March 26, 2025, the company announced an Expression of Interest (EoI) for a License and Technology Collaboration Agreement (TCA) aimed at the joint development of an Armoured Fighting Vehicle – Future Ready Combat Vehicle (AFV-FRCV) for the Indian Army. This move underscores BEML’s commitment to advancing indigenous defense manufacturing while aligning with the Indian government’s “Make in India” initiative.
The EoI, highlighted in posts on X by @alpha_defense and others, invites prospective technology collaborators from around the globe to partner with BEML Ltd. The TCA will empower BEML to undertake a comprehensive scope of work, including the design, engineering, manufacturing, assembly, testing, supply, field installation, commissioning, repair, service, and retrofitting of the AFV-FRCV. This ambitious project aims to deliver a next-generation combat vehicle tailored to the Indian Army’s evolving operational needs, ensuring it remains future-ready in an era of rapidly advancing military technology.
Continue reading