SOURCE: AFI


In a significant leap forward for military aviation, Boeing’s upcoming F-47, developed under the U.S. Air Force’s Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program, is set to reintroduce a feature long absent from fifth-generation fighter jets: the ability to travel at Mach 2 speeds. This capability, seen in third- and some fourth-generation jets, vanished from the fifth-generation lineup due to the challenges of overheating stealth coatings. Boeing appears to have cracked the code, designing a sixth-generation fighter that marries high supersonic speed with advanced stealth technology without compromising either.
Fifth-generation jets like the F-22 Raptor and F-35 Lightning II, while revolutionary for their stealth and sensor fusion capabilities, sacrificed high-speed performance to preserve their low-observable coatings. These specialized materials, critical for evading radar detection, are prone to degradation or damage when subjected to the intense heat generated at speeds exceeding Mach 1.5. As a result, the F-22 tops out at around Mach 2 but rarely sustains it, and the F-35 is limited to Mach 1.6, prioritizing survivability over raw velocity. This trade-off marked a departure from earlier generations, such as the third-generation F-4 Phantom II (Mach 2.2) and fourth-generation F-15 Eagle (Mach 2.5), where speed was a defining attribute.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Azaz Syed, an Islamabad-based Pakistani journalist and author of The Secrets of Pakistan’s War on Al-Qaeda, has made a provocative claim that India’s Research and Analysis Wing (RAW) has placed 16 prominent Pakistani personalities on a targeted hitlist. In a statement that has stirred tensions across the border, Syed named several high-profile militants, including Masood Azhar, the founder of Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), his brother Mufti Abdul Rauf, and Fazal ur Rehman Khalil, the founder of Harkat-ul-Mujahideen (HuM), as key targets. He further cautioned that Pakistan could respond with its own hitlist targeting figures in India if such alleged operations persist, escalating the shadow war between the two nuclear-armed neighbors.
Syed’s assertions, made public on March 22, 2025, come amid a backdrop of heightened Indo-Pak friction, with cross-border militancy and covert operations often dominating the discourse. Masood Azhar, infamous for orchestrating the 2001 Indian Parliament attack and the 2019 Pulwama bombing, has long been a thorn in India’s side, evading capture despite a UN designation as a global terrorist. His brother, Mufti Abdul Rauf, is a senior JeM operative, while Fazal ur Rehman Khalil, a veteran jihadist tied to HuM and allegedly linked to Al-Qaeda, carries his own legacy of militancy from the Afghan-Soviet war era. Syed’s claim that these figures are on RAW’s radar aligns with India’s stated policy of neutralizing threats emanating from Pakistani soil, though no official confirmation has emerged from New Delhi.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
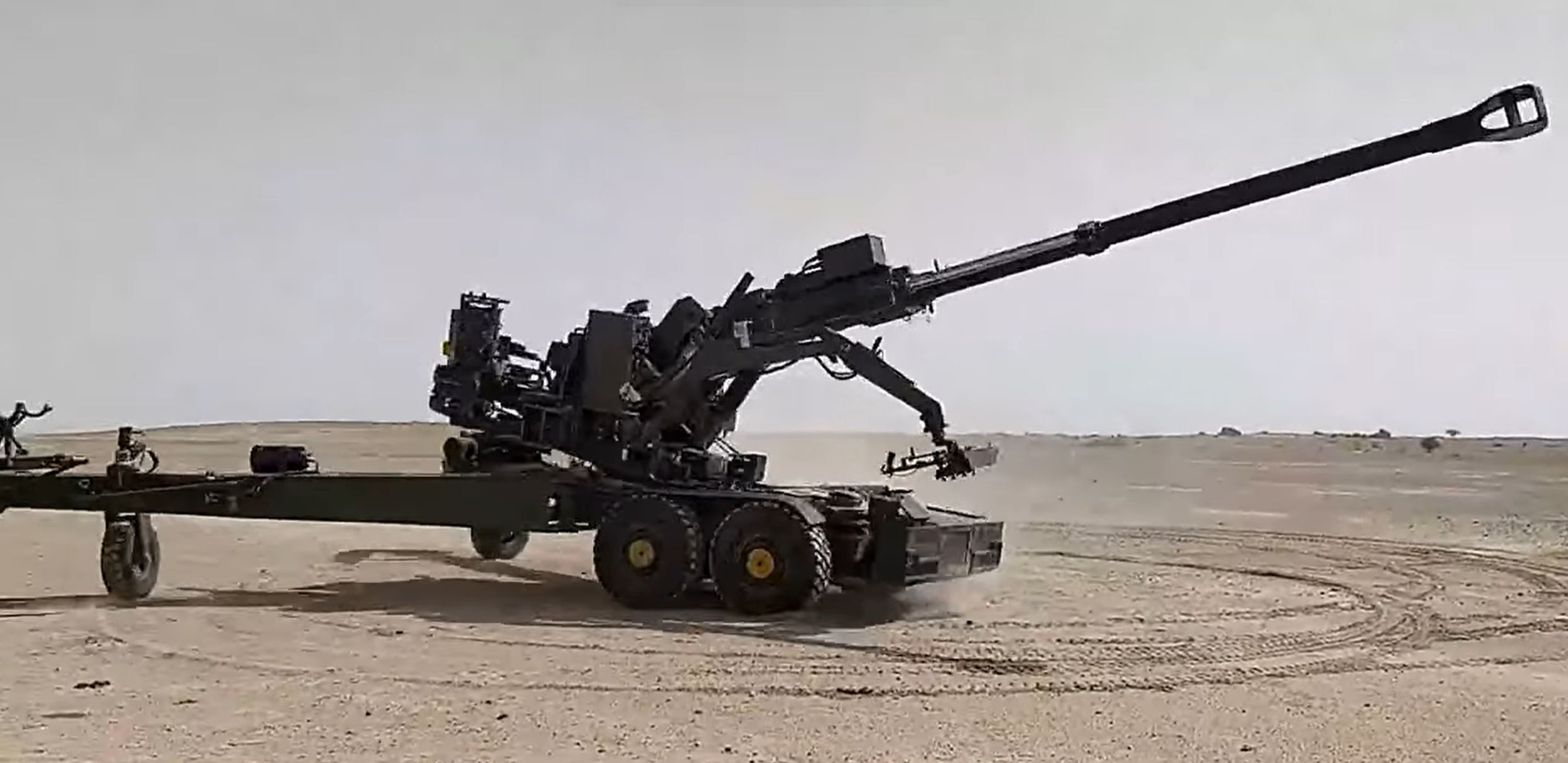


In a significant stride toward self-reliance in India’s defense sector, the Chairman of Kalyani Strategic Systems (KSSL), a subsidiary of Bharat Forge Ltd., has announced that the indigenous content in their weapon platforms, particularly the Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS), will exceed 80%. “Since we are making almost everything in-house, the indigenous content will be in excess of 80%. It will be a purely Indian-developed and Indian-manufactured platform,” the Chairman stated, emphasizing the company’s commitment to minimizing reliance on foreign components.
The ATAGS, a 155mm/52 caliber towed howitzer developed in collaboration with the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has been a flagship project for India’s artillery modernization. Initially, the gun boasted an indigenous content (IC) of around 60%, a commendable figure for a system of its complexity. However, KSSL is now pushing the envelope further, aiming to elevate this to 80% as production ramps up. This increase reflects the company’s focus on in-house manufacturing and its strategic investments in research, design, and supply chain localization.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
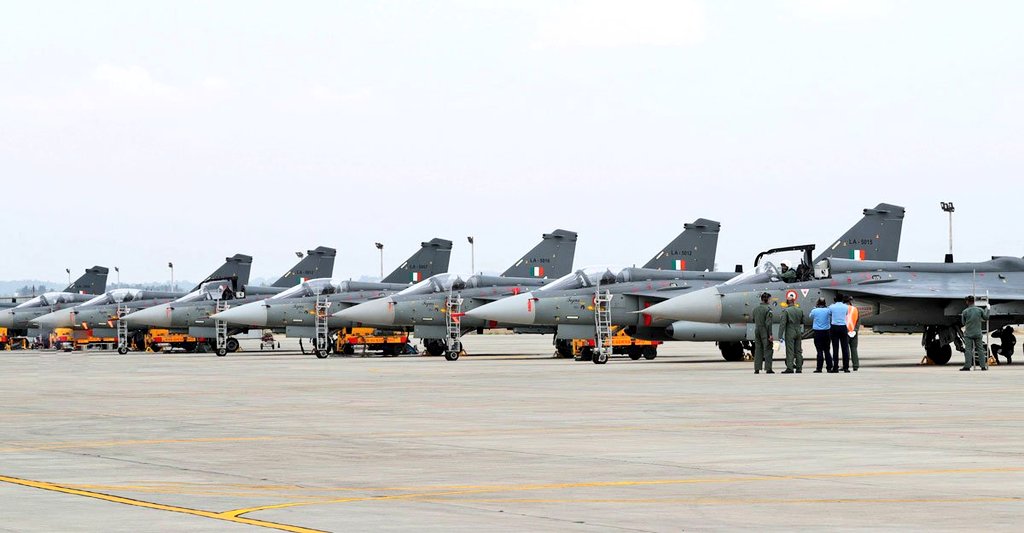


In a pivotal development for India’s indigenous fighter jet program, General Electric (GE) Aerospace has confirmed that the first of its F-404 engines for the Tejas Mk1A is en route to India, expected to arrive before the end of March 2025. This milestone marks the beginning of a revised delivery schedule that promises to accelerate the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) deployment of the advanced Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) variant. With 12 engines slated for delivery in 2025 and a ramp-up to 20 engines annually from 2026 onward, the IAF is poised to raise its first Tejas Mk1A squadrons by year-end, significantly bolstering its combat capabilities.
The F-404-IN20 engine, a critical powerplant for the Tejas Mk1A, has been a bottleneck in the program due to supply chain delays that pushed back initial deliveries from March 2023 to this month. GE’s commitment to deliver 12 engines by December 2025 will enable Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) to complete and hand over at least eight Tejas Mk1A jets—six fighters and two trainers—allowing the IAF to operationalize its first squadron of 18 aircraft (16 fighters and two trainers) by the end of the year. This aligns with the IAF’s urgent need to replace its retiring MiG-21 Bison squadrons and address a dwindling squadron strength, currently at 31 against a sanctioned 42.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The unveiling of artist impressions and official renderings of Boeing’s F-47, the United States Air Force’s (USAF) sixth-generation fighter jet under the Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD) program, has ignited a firestorm of discussion among defense enthusiasts and analysts. The graphics, showcased during and after the NGAD announcement, revealed two distinct design variants—one featuring a canard delta configuration and another without—prompting widespread speculation about the aircraft’s final form, its stealth capabilities, and the intent behind these divergent depictions.
The inclusion of canards—small forewings positioned ahead of the main wings—in one rendering has been the focal point of contention. Traditionally, canards enhance maneuverability, offering superior pitch control and agility, as seen in aircraft like the, Rafale, Tejas MkII, Eurofighter Typhoon, Saab Gripen and even on 5th gen jets like J-20. However, their presence on a sixth-generation stealth fighter like the F-47 raises eyebrows, given the conventional wisdom that such protrusions increase radar cross-section (RCS), potentially undermining the low-observable profile critical to modern air combat. Some remained skeptic, with sentiments like “Don’t go believing the initial PR snaps… canards/forewings are bad for stealth for starters,” reflecting a broader concern that these features clash with the F-47’s promised “state-of-the-art stealth technologies.”
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant development highlighting growing military cooperation, two delegations from the Armenian Army Spetsnaz recently met with representatives of India’s elite 50th Para Brigade. The meeting, held in India, focused on exploring joint tactics, training programs, and potential collaboration in advanced military operations. This engagement is seen as a step forward in the evolving defense partnership between Armenia and India, two nations increasingly aligned in their strategic interests.
The discussions likely centered on key areas of mutual interest, including personnel training, the integration of cutting-edge technologies—both manned and unmanned—and the exchange of operational expertise. The Armenian Spetsnaz, known for their specialized combat capabilities, and the 50th Para Brigade, a highly regarded airborne and special operations unit within the Indian Army, bring complementary strengths to the table. This synergy could pave the way for enhanced interoperability between the two forces.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
)

In a groundbreaking move to bolster India’s defense manufacturing ecosystem, the Uttar Pradesh government is establishing a state-of-the-art military hardware testing facility in Lucknow. This facility, the first of its kind in the state and only the second in the country, is poised to enhance the Uttar Pradesh Defence Industrial Corridor (UPDIC) while reinforcing India’s push toward self-reliance in defense production.
The ambitious project is being developed under the Defence Testing Infrastructure Scheme (DTIS), an initiative launched by the Ministry of Defence (MoD) to promote indigenous defense capabilities. A special purpose vehicle (SPV) named the Advanced Material (Defence) Testing Foundation (AMDTF) will oversee the facility’s development and operations. To ensure the project’s swift progress, the Uttar Pradesh government has approved the allocation of free land, signaling its commitment to making the state a hub for defense innovation.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a landmark achievement for India’s private defence manufacturing sector, Bengaluru-based SSS Defence has clinched a contract to supply 405 units of its indigenous P-72 Assault Rifles, chambered in 7.62x39mm, to the Uttar Pradesh (UP) Police. Emerging as the lowest bidder (L-1) in a fiercely competitive tender, SSS Defence outshone established players, including the public-sector giant Advanced Weapons and Equipment India Limited (AWEIL), by clearing the technical evaluation phase with its modern, versatile rifle.
The P-72 Assault Rifle, developed by SSS Defence, is part of the company’s innovative P-72 family of rifles, designed to meet the evolving needs of military and law enforcement agencies. Chambered in the widely used 7.62x39mm caliber—the same as the iconic AK-47—the P-72 offers a blend of firepower, reliability, and adaptability. Featuring a short-stroke piston operating system, the rifle ensures smoother operation, reduced recoil, and enhanced durability, making it well-suited for the demanding conditions faced by the UP Police in urban and rural security operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The developers of Modern Warships, a popular cross-platform arcade online action game, have announced the imminent arrival of INS Vikrant (IAC-I), an aircraft carrier currently in service with the Indian Navy. This exciting addition, brought to life by Artstorm FZE, Cube Software, and Gaijin Entertainment, promises to inject fresh tactical depth into the game’s dynamic naval battles. Known for its realistic portrayal of modern warships, jets, and drones, Modern Warships continues to expand its roster with this indigenous Indian marvel, blending real-world design with arcade-style action.
INS Vikrant, India’s first domestically built aircraft carrier, commissioned in September 2022, is a symbol of national pride and engineering prowess. In Modern Warships, it joins a lineup of global naval titans, offering players a chance to command a vessel that mirrors its real-world counterpart’s versatility and power. The gameplay mechanics for Vikrant align with the standard tactics of aircraft carriers in the game: deploying its air wing for reconnaissance, air strikes, and enemy suppression. With a capacity to carry up to 36 aircraft—including MiG-29K fighters, Kamov-31 helicopters, and MH-60R multi-role helicopters—Vikrant’s aviation capabilities make it a formidable force for dominating the skies and striking distant targets.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
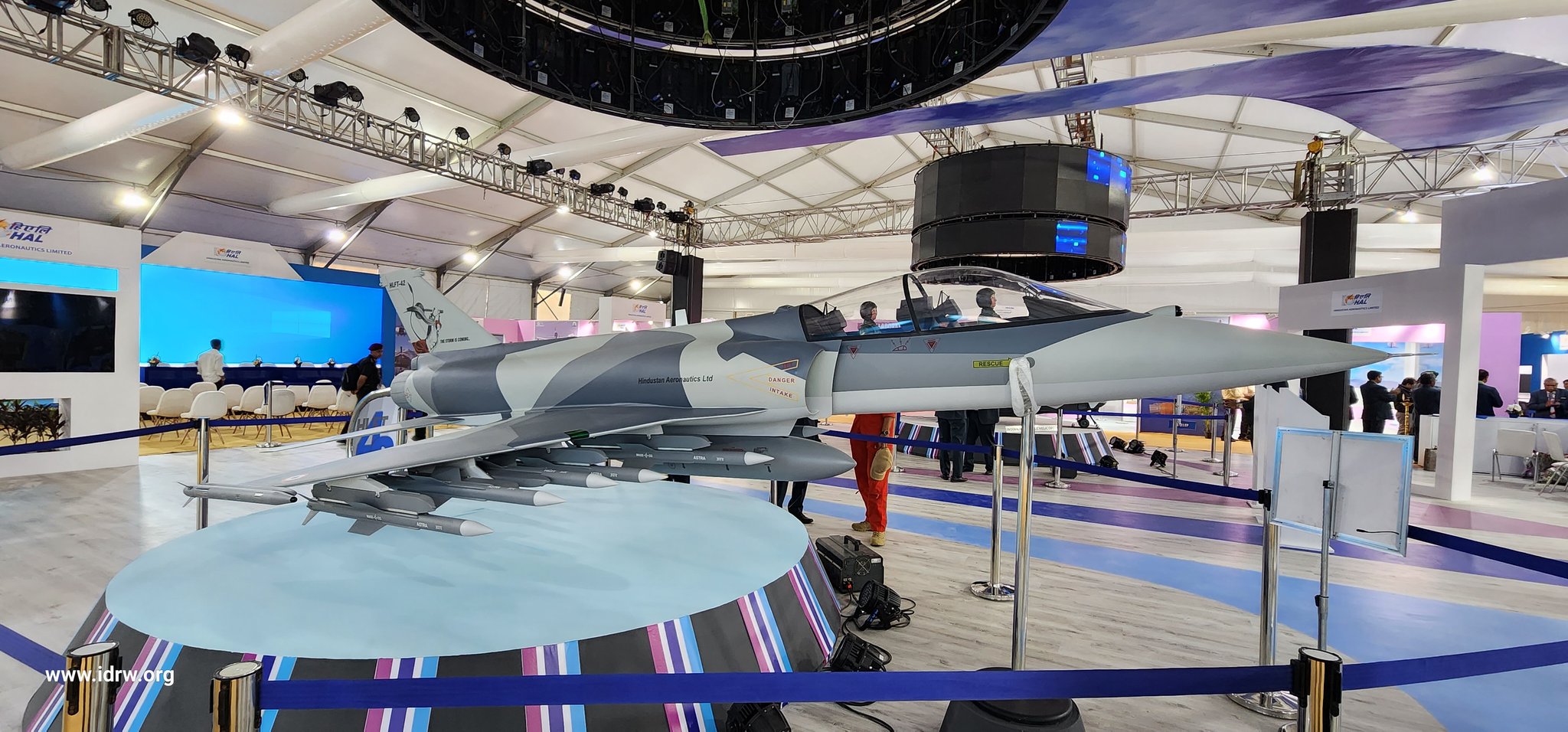


Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has taken a significant step in the development of its Hindustan Lead-in Fighter Trainer (HLFT-42) by issuing a Request for Information (RFI) for a jet engine to power this ambitious supersonic trainer aircraft. Released on March 17, 2025, the RFI outlines stringent performance criteria, calling for an engine with a maximum thrust of 95-100 kN (kilonewtons) and a total technical life of 6,000 hours. This move signals HAL’s intent to equip the HLFT-42 with a powerplant capable of meeting the rigorous demands of modern pilot training while potentially laying the groundwork for India’s broader aerospace ambitions.
According to details emerging from industry sources , the RFI specifies an engine with a maximum thrust of 95-100 kilonewtons (kN) and a total technical life of 6,000 hours. maximum Mach Number at1.8 and will be able to operate at Up to 18 km (60,000 feet).
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
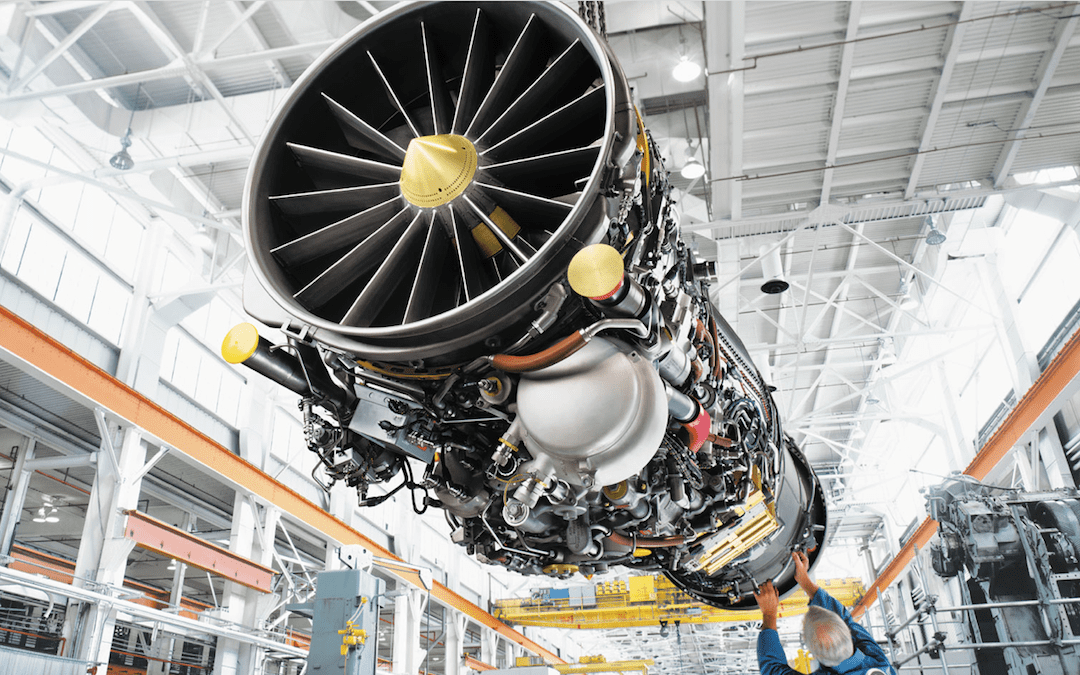

The long-standing uncertainty surrounding the engine supply for India’s Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk1A has finally been resolved, bringing relief to the Indian Air Force (IAF) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL). According to aerospace journalist Anantha Krishnan M, the GE F404 engines, critical to powering the new Mk1A variant—affectionately dubbed “LCA Alpha”—are on their way to India.
This development, detailed in a report by Tarmak Media House (TMH) on March 21, 2025, puts an end to months of speculation, debate, and concern over the “missing power plant” that had threatened to derail the ambitious indigenous fighter program.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has confirmed that its 25-ton Zorawar Light Tank, currently undergoing developmental trials under Project Zorawar, is designed with scalability in mind, paving the way for a potential 32-ton variant if the Indian Army seeks greater firepower and upgrades in the light tank category. This flexibility underscores DRDO’s forward-thinking approach, ensuring the platform can adapt to evolving operational needs while maintaining its core design integrity.
The Zorawar, developed in collaboration with Larsen & Toubro (L&T), was unveiled in July 2024 as a 25-ton light tank tailored for high-altitude warfare, particularly along India’s northern borders in Ladakh and Sikkim. Optimized for agility and air-transportability, it currently features a 105mm turret from Belgium’s John Cockerill and a Cummins engine delivering a power-to-weight ratio exceeding 35 hp/tonne.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
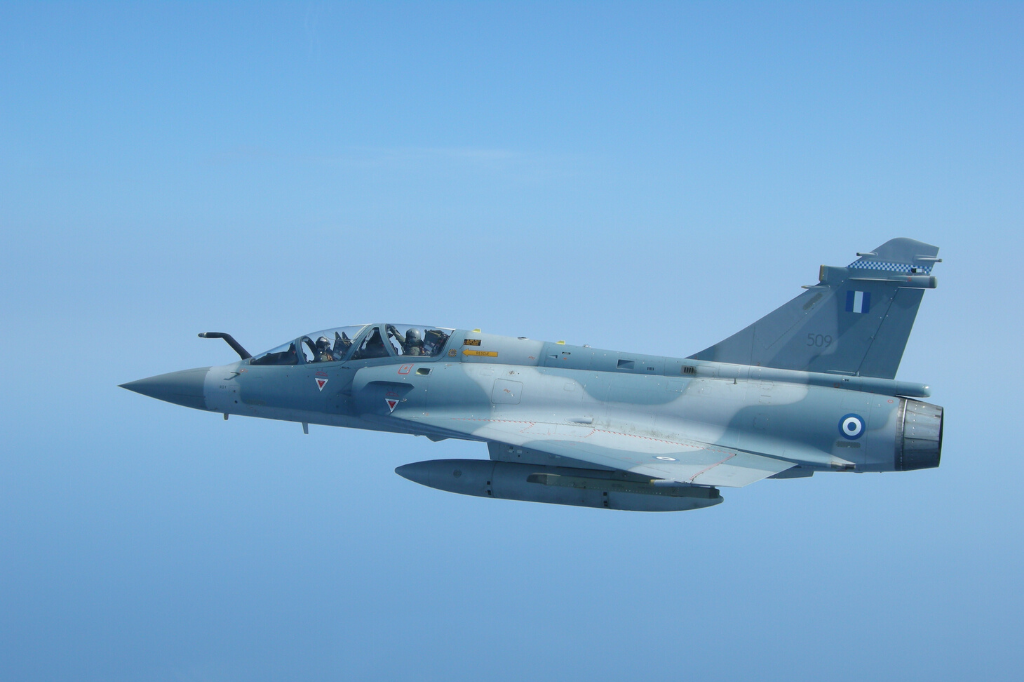


The prospect of Ukraine bolstering its air force with additional Mirage 2000-5 fighter jets remains a topic of active discussion, with French President Emmanuel Macron indicating that these aircraft could be supplied by third countries currently operating them.
This statement comes as France has already pledged a limited number of Mirage 2000-5Fs to Ukraine, signaling a willingness to support Kyiv’s aerial defense capabilities. However, no other nation has publicly committed to transferring their Mirage 2000-5s, leaving the possibility of further deliveries uncertain.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In an unexpected development, the Indian Army has decided to upgrade the engines of its T-90 tank fleet to a new 1350 horsepower (HP) variant, a move that has caught many observers off guard. This decision, confirmed in a recent Standing Committee report and bolstered by the Defence Acquisition Council’s (DAC) approval of eight capital acquisition proposals worth over Rs 54,000 crore on March 20, 2025, signals a significant enhancement in the operational capabilities of one of India’s mainstay battle tanks. However, the specifics of this upgrade—particularly the supplier and the engine’s origins—remain shrouded in ambiguity, sparking curiosity and speculation.
The T-90, a third-generation Russian main battle tank, forms the backbone of the Indian Army’s armored corps, with over 1,100 units in service, primarily the T-90S “Bhishma” variant. The Bhishma, tailored for Indian requirements, is currently powered by the V-92S2 diesel engine, delivering 1,000 HP. This engine, while reliable, has been seen as underpowered for the tank’s 48-tonne combat weight, particularly in the high-altitude regions of Ladakh and along the Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China, where agility and power-to-weight ratio are critical.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Indian Air Force (IAF) is set to enhance the survivability of its frontline airbases by procuring aircraft decoys modeled after its Rafale, Su-30 MKI, and Tejas fighters. These decoys, designed to mimic the visual and radar signatures of the real aircraft, will be deployed at forward runways to deceive enemy forces during a surprise attack, providing a critical layer of passive defense against aerial and missile strikes. The initiative reflects the IAF’s growing emphasis on safeguarding its assets amid rising regional tensions and the evolving threat of precision-guided munitions.
The plan, currently in the preliminary stages, aims to protect key bases along India’s northern and western borders, where aircraft like the Rafale, Su-30 MKI, and Tejas are stationed to counter potential aggression from China and Pakistan. By deploying realistic decoys, the IAF seeks to confuse enemy reconnaissance and targeting systems, drawing fire away from operational aircraft and infrastructure.
Continue reading