SOURCE: AFI


In a significant stride towards bolstering India’s self-reliance in defense manufacturing, Gurugram-based Kohli Enterprises has been awarded the Limited Authorization Transfer of Technology (LA ToT) for the production of brake parachutes for the Indian Air Force’s Su-30 MKI aircraft. The technology transfer, facilitated by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) under the Ministry of Defence, Government of India, marks a pivotal moment in integrating private industry into the nation’s defense production ecosystem.
The formal handover took place during an event organized by DRDO on the sidelines of Aero India 2025, held in Bengaluru from February 10-14, 2025. Kanav Kohli, Managing Director of Kohli Enterprises, received the LA ToT document from Raksha Rajya Mantri Shri Sanjay Seth, Minister of State for Defence, in the presence of senior officials from the Ministry of Defence, DRDO, and the Indian Air Force (IAF). This transfer underscores India’s ongoing “Aatmanirbhar Bharat” initiative, aimed at reducing dependence on foreign suppliers and fostering indigenous innovation.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant step forward for India’s aerospace and propulsion industry, DG Propulsion has announced the successful completion of its first test turbine wheels, marking a pivotal moment in the company’s journey to refine its manufacturing processes. The initial batch, described as “phenomenal” by the company, has passed visual inspections with flying colors, setting a promising tone for the next stages of production.
DG Propulsion, a rising player in the global propulsion technology sector, conducted this trial run to fine-tune its methods and ensure the highest standards of quality and precision. “This was a trial run to refine our process and methods, and so far, the results speak for themselves,” the company stated in an official release. The turbine wheels, a critical component in jet engines and other high-performance propulsion systems, are a testament to DG Propulsion’s commitment to innovation and excellence.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In a significant step towards strengthening India’s defense and surveillance capabilities, Paras Defence and Space Technologies announced on Thursday, April 3, 2025, that it has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with MicroCon Vision Ltd, an Israel-based subsidiary of the Rafael Group. The agreement focuses on the supply of advanced cameras for drones, positioning Paras Defence as a key player in India’s growing unmanned aerial systems market.
The collaboration aims to enhance the indigenous content in drone cameras and Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance (ISR) payloads, aligning with India’s push for self-reliance in defense manufacturing. By integrating locally developed components, Paras Defence expects to significantly reduce costs, making advanced drone technology more accessible for both military and commercial applications. This move underscores the company’s commitment to the ‘Make in India’ initiative while leveraging global expertise to meet domestic needs.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
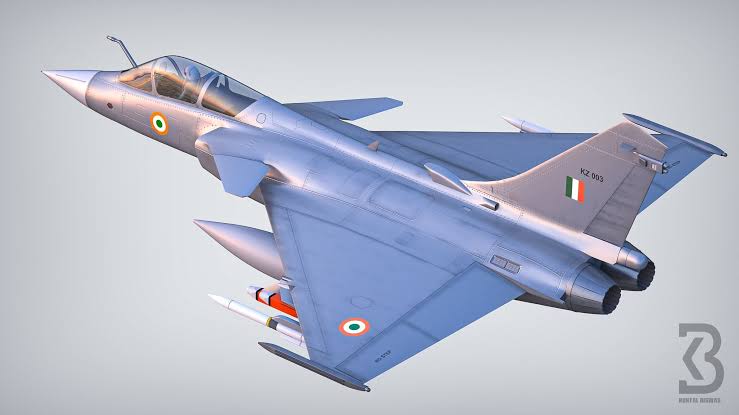


Kuntal Biswas, one of India’s most prominent 3D military system and defense animation experts, has once again captured the imagination of aviation enthusiasts and defense analysts with his latest creation: a twin-engine variant of the Tejas MkII. This conceptual design, powered by twin Kaveri engines each generating 75kN of thrust, showcases the potential of India’s indigenous aerospace capabilities and positions the Tejas MkII in the same league as global heavyweights like the Dassault Rafale. With a Maximum Take-Off Weight (MTOW) of approximately 24 tons, this innovative design aligns closely with the Rafale’s capabilities, powered by the Snecma M-88 engine, which also delivers 75kN of thrust.
Biswas, renowned for his detailed and visionary 3D renderings of military hardware, has evolved the Tejas MkII—originally conceived as a single-engine, medium-weight fighter—into a twin-engine multirole combat aircraft. His design incorporates canard-delta wings, an indigenous Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar, and a fully homegrown weapons suite, blending cutting-edge technology with India’s push for self-reliance in defense manufacturing. The twin-Kaveri engine configuration not only boosts the aircraft’s thrust but also enhances its versatility, making it a formidable contender in air superiority, ground attack, and reconnaissance missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Indian Air Force (IAF) has received a significant boost in its quest to enhance airborne surveillance capabilities, with recent clearance to procure six Embraer EMB-145 aircraft for the Netra Mk1A program. This approval, anticipated to be formalized soon by the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC), marks a critical step in modernizing the IAF’s Airborne Early Warning and Control (AEW&C) fleet. With production of the EMB-145 having ceased years ago, Brazilian aerospace giant Embraer, the aircraft’s original manufacturer, will now scout the secondary market for operational units, partnering with India’s Adani Defence and Aerospace to bring the Netra Mk1A vision to fruition.
The Netra Mk1A is an advanced iteration of the existing Netra AEW&C system, which is built on the EMB-145 platform and equipped with indigenous radar technology developed by the Centre for Airborne Systems (CABS) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The IAF currently operates three Netra systems, providing 240-degree radar coverage with a range of approximately 450 kilometers. The Mk1A variant promises enhanced operational capabilities, including upgraded mission suites and minor equipment modifications, to meet evolving threats along India’s borders with China and Pakistan. The addition of six more aircraft will nearly triple the IAF’s AEW&C capacity, addressing a shortage felt acutely during the 2019 Balakot aerial engagement.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Indian Air Force (IAF) has initiated a proposal to develop a Part Task Trainer (PTT) for its Mirage 2000 aircraft, a critical asset in its fighter fleet, to enhance pilot training and operational readiness. The IAF’s requirement focuses on creating a high-fidelity training system that replicates the Mirage 2000’s cockpit environment, allowing pilots to practice basic flying, simulate various modes of operation, and familiarize themselves with the aircraft’s controls and displays in a controlled, cost-effective setting. This move underscores the IAF’s commitment to leveraging advanced simulation technology to maintain the proficiency of its pilots, particularly as the Mirage 2000 continues to play a pivotal role in India’s air defense strategy.
The IAF’s proposal for the Part Task Trainer emphasizes the need for an accurate replica of the Mirage 2000’s cockpit, with a particular focus on the stick and throttle, which are critical for simulating the aircraft’s handling characteristics. The trainer will also feature Multifunctional Displays (MFDs), Head-Up Displays (HUDs), and other cockpit displays, which will be replicated using modern LCD, TFT, or OLED display panels with touch-screen functionality. This approach allows for a cost-effective yet realistic simulation of the Mirage 2000’s avionics, enabling pilots to interact with the displays as they would in the actual aircraft.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
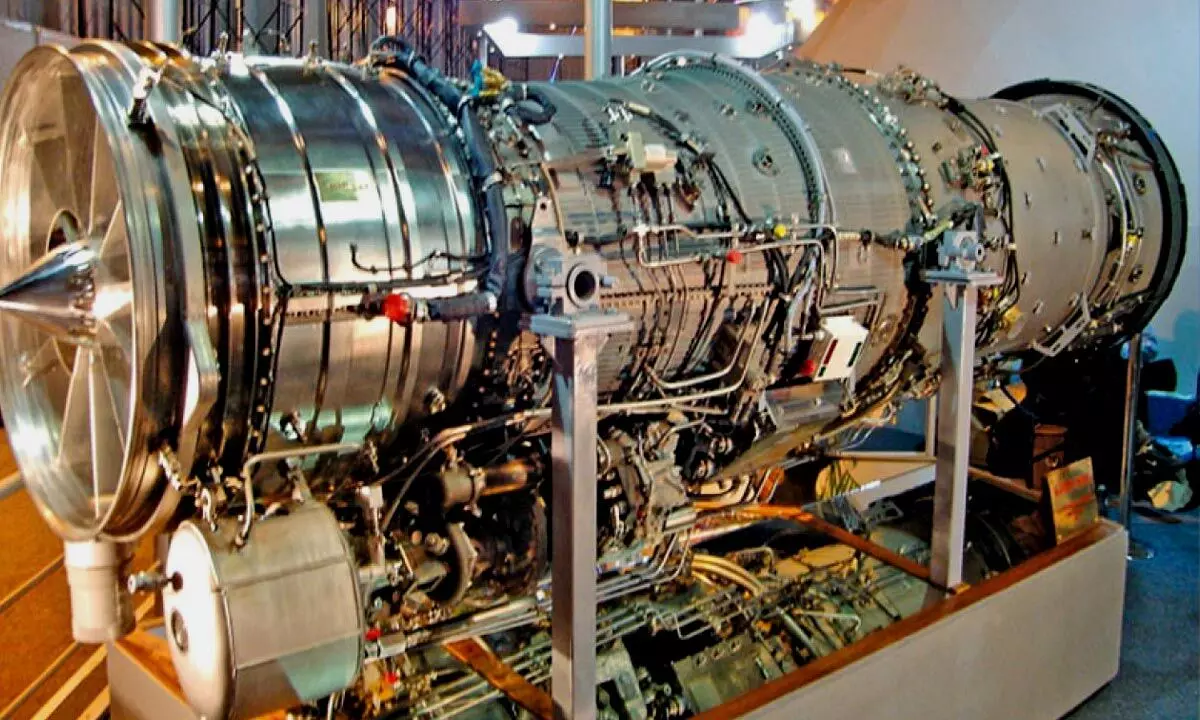

In a significant milestone for India’s aerospace and defense sector, Godrej Aerospace has confirmed the delivery of the first two modules of the Kaveri derivative engine to the Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE). The company, a key player in precision manufacturing, also announced that six additional modules are slated for delivery later this year, fulfilling a critical order placed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
The order, secured by Godrej Aerospace in September 2022, involves the production of eight modules for a specialized Kaveri derivative engine. Unlike the original Kaveri engine, which was developed for fighter aircraft, this variant is a 48 kN dry engine without an afterburner. Sources indicate that this engine is intended for use in autonomous air vehicles, marking a step forward in India’s indigenous unmanned aerial technology.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

In a candid conversation with Snehesh Alex Phillip of The Print, Lt Gen PR Shankar (Retd), former Director General of Artillery, dropped a bombshell about the Indian Army’s experience with the Russian-made Smerch multiple rocket launcher system. According to Shankar, the Smerch that was ordered in 2005 and inducted into service by 2008, yet the Indian Army (IA) was unable to fire it until 2012 due to persistent technical issues. The statement, delivered with a mix of incredulity and frustration, has left defense enthusiasts and analysts questioning the procurement process and the prolonged delay in resolving the problem. “Did I hear it right?” quipped a Indian defence analysts, echoing the disbelief many might feel about this operational hiccup.
The Smerch, a 300mm rocket system with a range of up to 90 kilometers, was acquired from Russia to bolster India’s long-range artillery firepower. Touted as one of the most powerful multiple launch rocket systems (MLRS) in the world, it was intended to give the IA a decisive edge in precision strikes and area saturation against enemy targets. The initial order, part of a broader modernization drive, came at a time when India sought to counter growing threats along its borders, particularly from Pakistan and China. The deal, reportedly worth over $500 million, included launchers, rockets, and support systems, with deliveries beginning in 2007-2008.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On April 2, 2025, an Indian Air Force (IAF) Jaguar fighter jet crashed near Suvarda village, just 12 kilometers from Jamnagar in Gujarat, during a routine training sortie. The twin-seater aircraft, which departed from Jamnagar Air Force Station, suffered a critical technical malfunction around 9:30 PM, leading to its disintegration in an open field. One pilot, Flight Lieutenant Siddharth Yadav, lost his life in the incident, reportedly staying with the aircraft to steer it away from populated areas, while the second pilot ejected safely and is under treatment at GG Hospital. The IAF has launched a Court of Inquiry to investigate, with early indications pointing to a mechanical failure.
Yet, as Indian authorities focus on the technical realities of the crash, a wave of bizarre and baseless narratives has emerged from Pakistan. ISI-backed X handles and several verified Pakistani accounts have flooded social media with claims that the Jaguar was not lost to a malfunction but was instead shot down by the Pakistan Air Force (PAF). These conspiracy theories, ranging from plausible-sounding to outright absurd, highlight a mix of propaganda and technical ignorance.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


India’s aerospace ambitions have been steadily gaining momentum with programs like the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Mk2, the Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter (TEDBF), and the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA). These projects represent India’s push toward self-reliance in defense manufacturing and its pursuit of cutting-edge 5th and 6th generation fighter jet technologies. What sets India apart in this highly competitive domain is the remarkably low cost of its programs compared to similar efforts by global powers.
While nations like the United States, the UK, Japan, Turkey, and South Korea are investing tens of billions of dollars into their next-generation fighter programs, India is achieving comparable goals at a fraction of the cost. Let’s break it down.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
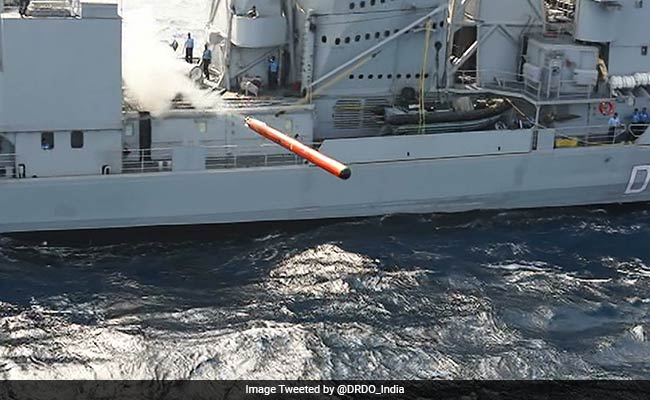


The Indian Navy is steadily enhancing its underwater warfare capabilities with the induction of additional quantities of the Varunastra torpedo, an indigenously developed ship-launched anti-submarine heavyweight torpedo (HWT). On March 20, 2025, the Defence Acquisition Council (DAC), chaired by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh, accorded Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for the procurement of Varunastra torpedoes in their combat variant, marking a significant step toward strengthening the Navy’s arsenal.
Developed by the Naval Science and Technological Laboratory (NSTL) under the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and manufactured by Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL), the Varunastra torpedo represents a pinnacle of India’s indigenous defense technology. Named after the mythological weapon of Varuna, the Hindu god of the oceans, Varunastra is a ship-launched, electrically propelled heavyweight torpedo designed to target quiet and stealthy submarines in both deep and shallow waters, even under intense countermeasure environments.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


On April 2, 2025, a significant milestone in India’s defense manufacturing journey was marked with the metal cutting ceremony of the Advanced Armoured Platforms (AAP)—Wheeled and Tracked—at the Pune premises of the Kalyani Group, a key Development cum Production Partner (DcPP) for the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The ceremony, officiated by Dr. Samir V. Kamat, Secretary of the Department of Defence Research and Development (DDR&D) and Chairman of DRDO, highlighted the collaborative efforts between DRDO and industry partners like the Kalyani Group, Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL), and Bharat Forge Limited (BFL) to design, develop, and manufacture critical defense systems. The event also served as a platform for the Kalyani Group to showcase its AAP-Tr (Tracked), a contender for the Indian Army’s Futuristic Infantry Combat Vehicle (FICV) program aimed at replacing the aging BMP-II fleet.
The AAP-Tr, a tracked variant of the Advanced Armoured Platform, is being positioned by the Kalyani Group as a modern, indigenous solution for the Indian Army’s FICV tender, which seeks to replace over 1,750 BMP-II vehicles currently in service. The BMP-II, a Soviet-era infantry combat vehicle inducted in the 1980s, has long been due for replacement due to its outdated technology and inability to meet the demands of modern warfare, particularly in terms of firepower, protection, and mobility. The Indian Army’s FICV program, estimated to be worth over ?60,000 crore, has been a long-standing priority, with the goal of inducting a new generation of vehicles equipped with advanced electronics, enhanced survivability, and modular weapon systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


Hyderabad-based VEM Technologies, a key player in India’s private defence sector, is set to deepen its involvement in the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program, the country’s ambitious fifth-generation stealth fighter project. Having successfully manufactured the full-scale engineering model of the AMCA showcased at Aero India 2025, the company has now been tasked with contributing to the Tier-II manufacture of the aircraft’s fuselage for its prototype. This development marks a significant step in VEM’s growing footprint in India’s aerospace and defence ecosystem.
The full-scale model unveiled at Aero India 2025 held from February 10-14 at Yelahanka Air Force Station in Bengaluru, drew widespread attention as a tangible representation of India’s push for self-reliance in advanced fighter jet technology. Constructed using indigenously sourced materials from Mishra Dhatu Nigam Limited (MIDHANI) and other private firms, the model highlighted VEM Technologies’ engineering capabilities and its ability to collaborate with both public and private sector entities. Building on this success, VEM has now been entrusted with manufacturing specific sections of the AMCA fuselage for the initial 4-5 prototypes, company officials confirmed in an interview with idrw.org.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In a groundbreaking development for India’s aerospace sector, Godrej Aerospace, a division of Godrej & Boyce under the Godrej Enterprises Group, has announced its readiness to manufacture a 5th-generation jet engine, a move that could significantly reduce India’s reliance on foreign technology.
Maneck Behramkamdin, Executive Vice President and Business Head of Godrej Aerospace, shared this milestone in an interview with The Economic Times, highlighting the company’s progress and its pivotal role in India’s quest for self-reliance in defense and aerospace manufacturing. The announcement, made on April 2, 2025, underscores Godrej Aerospace’s growing influence in the global aerospace ecosystem and its commitment to the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Indian Navy is poised to take a significant leap in its maritime defense capabilities with the Next Generation Missile Vessels (NGMV), a new class of high-speed warships expected to be the first to integrate the indigenously developed Vertical Launch Short Range Surface-to-Air Missile (VL-SRSAM). This development, spotlighted during recent discussions at Aero India 2025 and reinforced by successful test firings, marks a milestone in India’s pursuit of self-reliance in defense technology and underscores the Navy’s commitment to enhancing its layered air defense systems.
The NGMVs, currently under construction by Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL) following a ?9,804 crore contract signed in March 2023, represent a cutting-edge addition to the Indian Navy’s fleet. Designed as agile, weapon-intensive platforms, these vessels are tailored for offensive and defensive operations, including maritime strike, anti-surface warfare, and sea denial at strategic choke points. With a maximum speed of 33 knots and a crew of 80 personnel, the six NGMVs are slated for delivery starting in March 2027, with subsequent ships following at regular intervals.
Continue reading