SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is reigniting its quest for mid-air refuelling (MAR) platforms, aiming for a significantly larger fleet than previously envisioned. This renewed effort comes after securing approvals for the indigenous Airborne Warning and Control System (AWACS) program under the Netra Mk1A, MkII, and MkIII variants.
Previously, the IAF sought to acquire six mid-air refuelers. However, the current plan seeks to double that number, bringing the total fleet to 18. This expansion will bolster the IAF’s ability to extend the operational range and flexibility of its fighter jets, particularly crucial in a multi-front scenario.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) has issued a tender for the refurbishment of the LCA Tejas Technology Demonstrator 2 (TD2), which was the second aircraft in the Tejas Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) program’s technology demonstration phase.
The TD2 aircraft, after being stripped of its operational components and systems, now weighs around 6 tons and is slated to be used as a static display on a raised platform at the ORANGE Facility at the Research Centre Imarat (RCI) in Hyderabad. This facility is renowned for its Outdoor Radar Cross Section (RCS) testing capabilities, serving as a test facility for various aircraft and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs).
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Defence Minister Rajnath Singh is set to travel to Russia in early December to commission INS Tushil, the first of two advanced stealth frigates being constructed at the Kaliningrad-based Yantar Shipyard under a $2.5 billion contract. This significant milestone marks a crucial step in the strengthening of the Indian Navy’s maritime capabilities, as INS Tushil is the first of the two frigates being built under a follow-on agreement to the Talwar-class vessels.
In 2016, India and Russia signed an inter-governmental agreement for the construction of four frigates. The agreement was formalized in 2018, with two frigates to be built at Yantar Shipyard in Kaliningrad, and the remaining two at Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL) in India. The construction of these frigates was part of a strategic plan to bolster India’s naval fleet, and the new ships are an advanced iteration of the Talwar-class frigates, based on the Russian Krivak III-class design.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

India’s state-owned engineering giant, Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL), is inviting private sector participation in the design and development of a hydraulically operated Main Winch for the Arjun Armoured Recovery and Repair Vehicle (ARRV). The initiative is part of the larger goal to enhance the indigenous development of defense technologies under the Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India) initiative.
The proposed winch system, with a 50-ton single-line pull capacity, will be a crucial component for the Arjun ARRV, enabling it to perform critical recovery operations in the field. The double capstan-type winch design will offer operational flexibility and control, particularly in high-load recovery scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

With a renewed emphasis on the creation of India’s Rocket Force, the Ministry of Defence (MoD) is set to significantly ramp up the production of the Pralay Short-Range Ballistic Missile (SRBM). The Pralay, a mobile, canister-based surface-to-surface missile with a range of 150-500 km, has garnered increasing attention from both the Indian Air Force (IAF) and the Indian Army. Orders for 120 units were placed by each service branch, with an additional order for another 120 missiles currently in the pipeline. As India prepares to strengthen its missile capabilities, production rates are expected to increase substantially over the coming years.
The current production rate of the Pralay SRBM remains in the single digits per year, according to sources close to idrw.org. However, this number is set to rise gradually into double digits as the MoD expands its missile production capacity. The establishment of the Rocket Force, which is expected to require 1,000 Pralay missiles, has created a demand that will drive further production scale-ups. To meet these ambitious targets, outsourcing to private sector companies is being planned, to achieve double-digit production rates by 2027. If necessary, this could eventually increase to triple digits per year.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Armenia is seeking to bolster its air defence capabilities through a potential two-pronged approach with India. The first involves upgrading its existing fleet of four Su-30SM fighter jets to an Indian “Super-30” configuration.
This upgrade would see the integration of advanced Indian weaponry and technology, including the Astra Mk1 beyond-visual-range air-to-air missile, RudraM air-to-surface missiles, Uttam active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar, and an Indian mission computer. Replacing the original Russian PESA radar with the Uttam AESA radar would significantly enhance the detection and targeting capabilities of the Armenian Su-30SMs.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
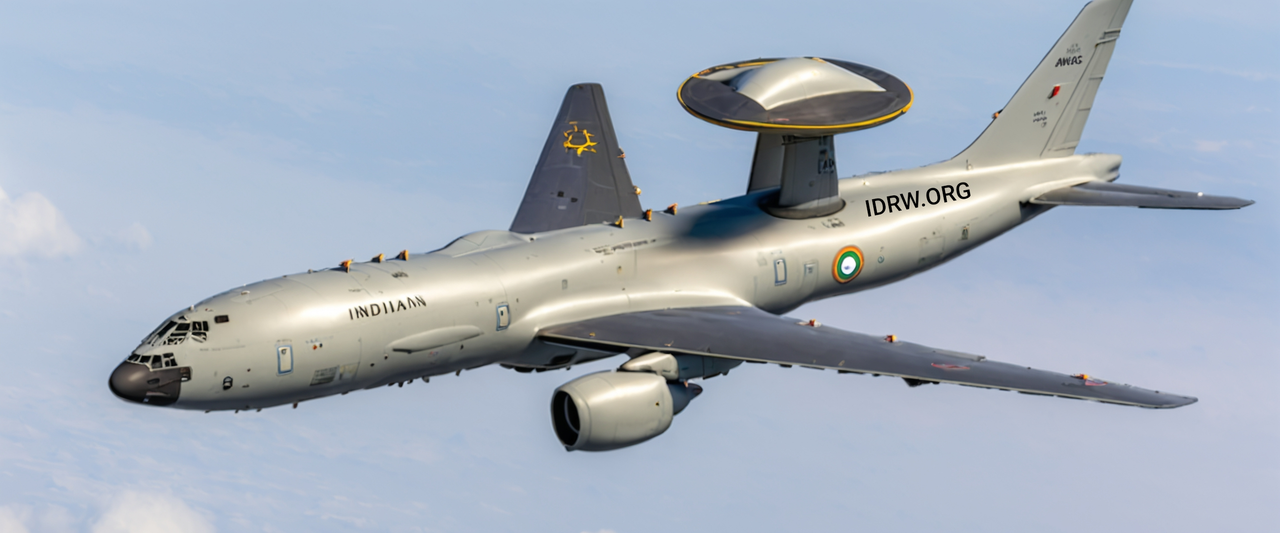

The recent Request for Information (RFI) issued by the Indian Air Force (IAF) for six Airborne Early Warning and Control Systems (AEW&CS) has generated considerable interest and confusion. To clarify the situation, we at idrw.org will explain the different AEW&CS programs currently in development, including the Netra Mk1A, Netra MkII, and the long-term Netra MkIII project. While the RFI for six AEW&CS units involves advanced 360-degree surveillance technology, it is distinct from the ongoing Netra programs.
The IAF has received clearance for the procurement of six Netra Mk1A AEW&CS units, which will be based on the ERJ 145 airframe, a proven and reliable platform. The Netra Mk1A will feature an Active Electronic Scanned Array (AESA) radar, similar to the one used in the Netra Mk1, but with enhanced capabilities and upgrades. This radar allows for better detection, tracking, and surveillance, but its limited size on the ERJ 145 platform means that it covers a reduced range compared to future systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
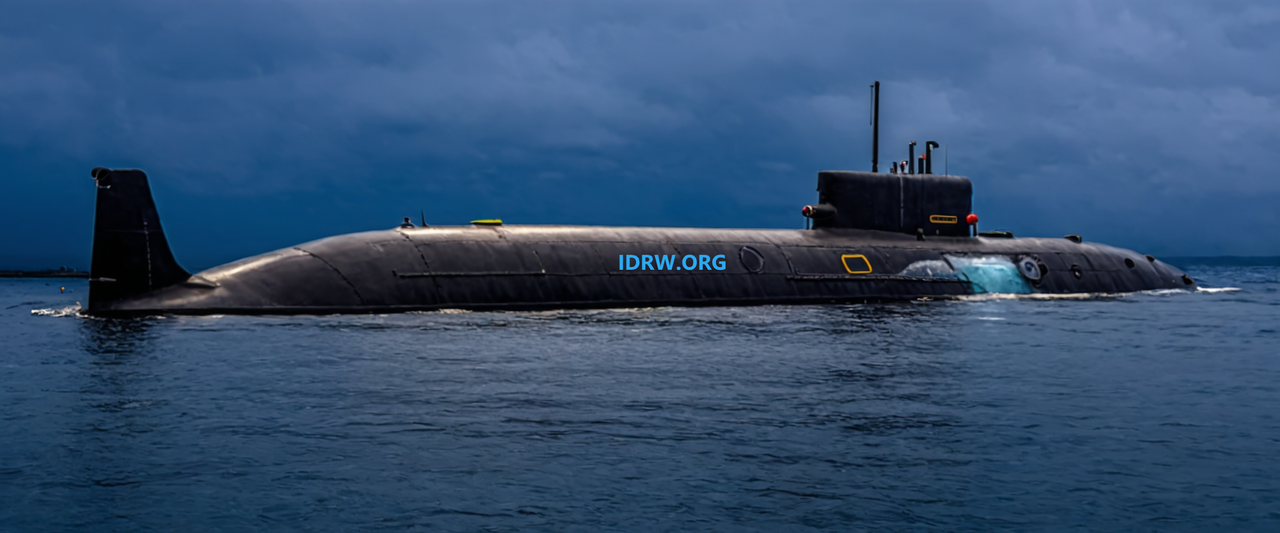

India has quietly achieved another significant milestone in its strategic defense capabilities by launching its fourth nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN), codenamed S4 (Star), according to a recent report from Hindustan Times. The submarine was launched on October 16, 2024, a day after Defence Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated the Very Low-Frequency (VLF) Naval Station, underscoring India’s growing naval prowess.
The S4 (Star) is a sister ship of INS Aridhaman (S4), part of India’s second generation of SSBNs, designed to improve upon the capabilities of the Arihant-class submarines. With a displacement of approximately 7,000 tons, S4 (Star) is 1,000 tons heavier than the earlier Arihant-class submarines, offering more space for enhanced capabilities, including a larger missile payload.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG

Earlier this month, the Supreme Court of India dismissed a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) that sought to halt the export of Indian defense equipment to Israel, citing allegations of war crimes by Tel Aviv in Gaza. The court’s refusal to intervene was rooted in the fact that foreign policy is not within its jurisdiction, deferring the matter to the executive. However, the issue raised by the PIL transcends Israel and touches on a broader debate critical to India’s aspirations to become a major defense exporter.
The question of whether a country should regulate its defence exports based on the actions of its buyers in global conflicts is a normative one. It requires India to balance its moral standing with its strategic and economic ambitions in the global defence market. This debate has gained importance as India seeks to transition from one of the world’s largest arms importers to a competitive exporter of weapons and military systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
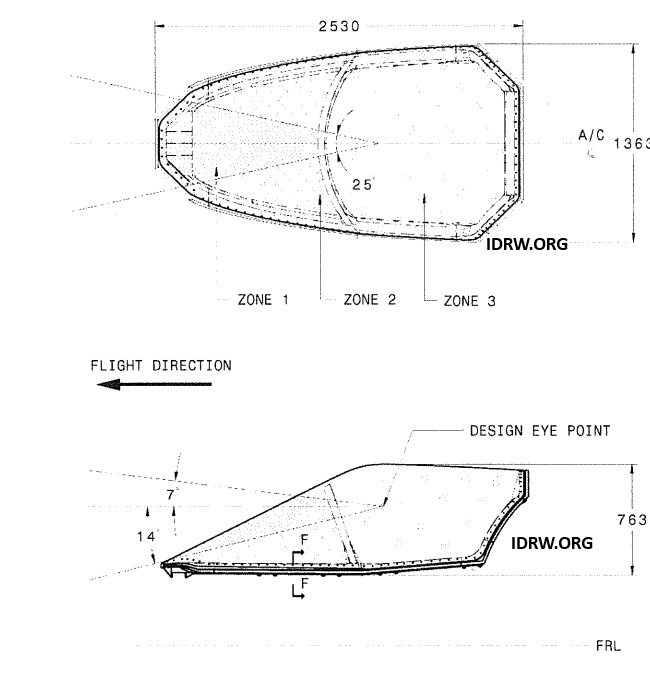
The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) has released a tender for the supply of stretched acrylic canopy systems for India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. The tender specifically calls for six canopy bubbles that adhere to MIL-W-81752A and MIL-C-81590 specifications, which are standards for military aircraft windshields and canopies. This marks a significant step in the development of India’s indigenous 5th-generation fighter jet, which requires advanced components to meet the demanding requirements of modern air combat.
The tender outlines that the canopy bubble is to be manufactured from stretched acrylic laminated material, known for its high durability and optical clarity. This bubble will be mounted on a metal frame using fasteners, and the entire assembly, referred to as the Canopy System, is expected to meet stringent performance and safety criteria.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Major General Rajiv Narayanan, a Professor of Practice at IIT Madras, has announced an innovative project aimed at revolutionizing armored warfare. Collaborating with IIT Madras and Lieutenant General Shankar, Maj Gen Narayanan is working on the development of a tank-fired ramjet-based Fin Stabilized Armour Piercing Discarding Sabot (FSAPDS) ammunition. This groundbreaking project seeks to significantly enhance the lethality and effectiveness of tank munitions against modern armored threats.
With the advancement of armor technology in modern Main Battle Tanks (MBTs), the need for more effective ammunition has become critical. Traditional FSAPDS rounds are already recognized as the most lethal kinetic energy ammunition available, capable of penetrating all known tank armor within a direct shooting range of up to 3000 meters. However, the limitations in range and velocity present challenges, particularly against advanced Active Protection Systems (APS) that are designed to intercept incoming projectiles.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
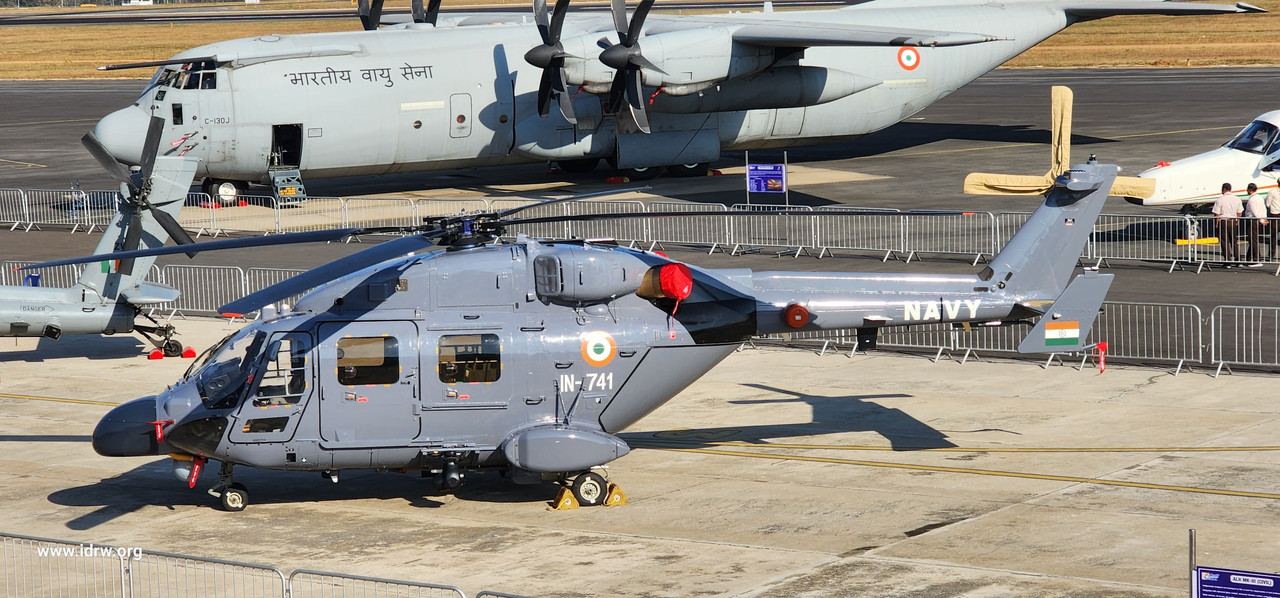

The Indian Navy is set to embark on a significant milestone with the first test flight of the Utility Helicopters-Maritime (UHM), an optimized variant of the Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Dhruv. Scheduled for May 2025, this test flight represents a crucial step in enhancing the operational capabilities of the Indian Navy’s aviation fleet. Sources indicate that the build process for the test aircraft is currently underway, with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) rigorously testing and certifying various systems on a separate test helicopter.
While the UHM is based on the proven design of the ALH Dhruv, officials have emphasized that extensive modifications and structural changes are being implemented, making the UHM akin to the development of a new helicopter. This innovative approach ensures that the UHM will meet the specific operational requirements of the Indian Navy, particularly in maritime environments.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
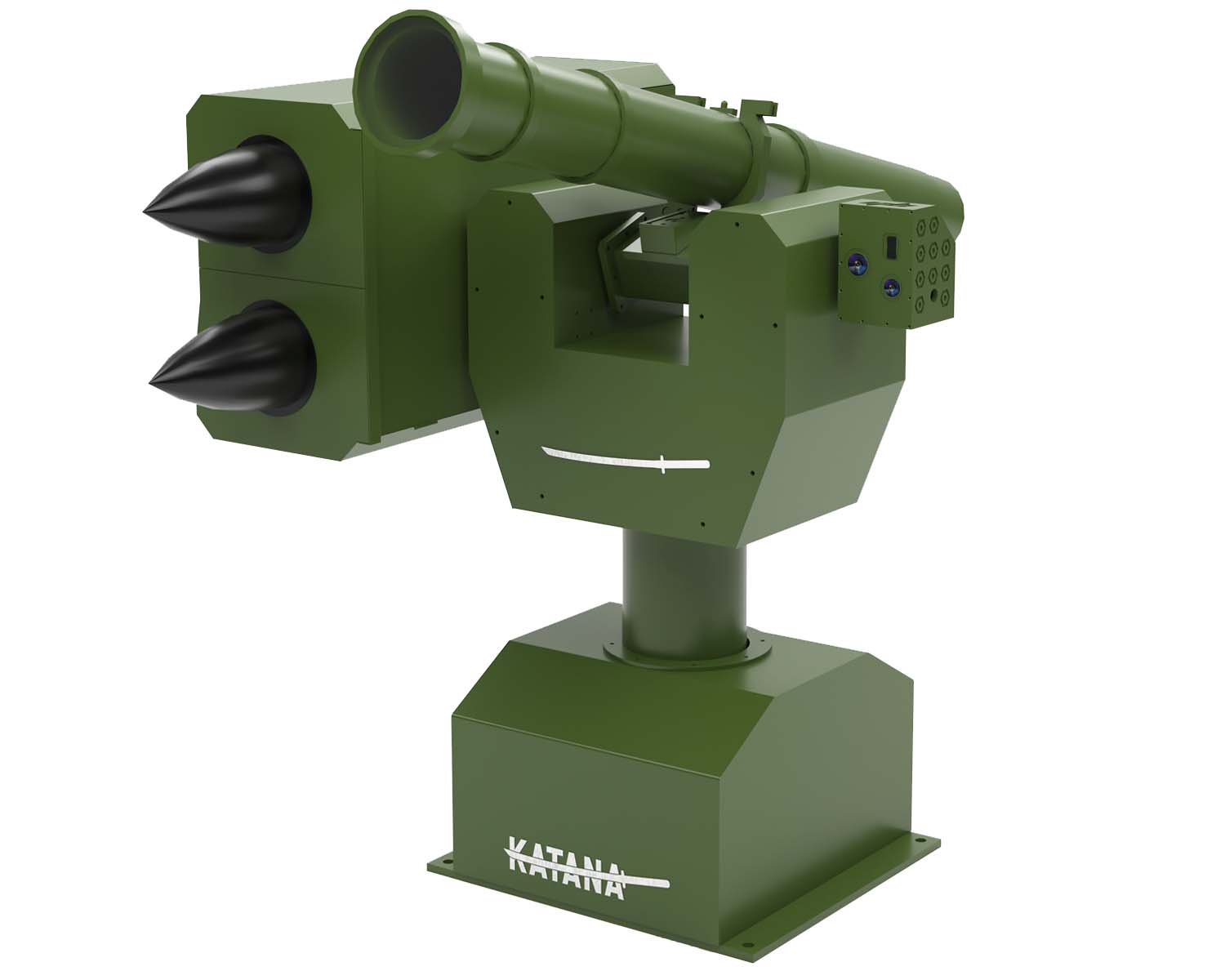

Indian robotics and AI company Gridbots has developed a state-of-the-art autonomous weapon station named KATANA, designed to enhance the situational awareness and defensive capabilities of homeland security units and unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs). The KATANA Autonomous Weapon Station represents a major technological leap, integrating advanced AI systems to track, lock onto, and eliminate multiple threats in seconds, providing a fully autonomous defense solution.
KATANA’s integration of AI and deep learning technologies sets it apart from traditional weapon stations. The system’s AI not only tracks and identifies targets but also learns from previous engagements, allowing it to become more efficient over time. This capability ensures that KATANA can detect, identify, and neutralize threats faster and more accurately than systems relying solely on manual operation.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
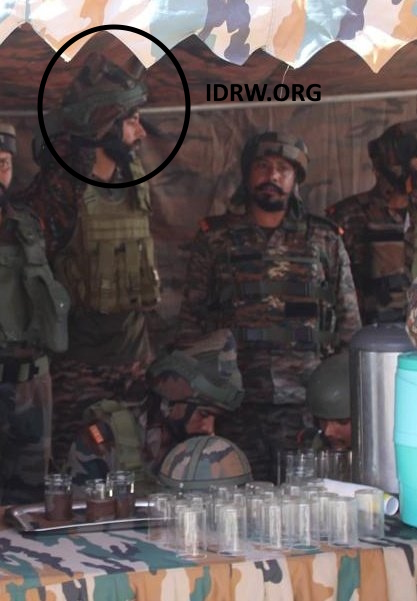

A significant development in the Indian Army’s equipment modernization has seen Sikh soldiers sporting the Kavro SCH 111 T ‘Veer’ helmet, designed specifically for Sikh soldiers. The helmet, developed by Indian firm MKU Limited, is designed to be worn over a cloth patka or turban, providing all-around ballistic protection across the head.
The Indian Army began receiving these helmets last year, and they offer NIJ Level IIIA protection, capable of resisting 9 mm bullets. MKU emphasizes the helmet’s lightweight, anti-allergic, all-weatherproof, and chemical-safe properties, along with its excellent shock absorption capabilities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Dassault Aviation is set to offer its latest Rafale F4 variant to the Indian Air Force (IAF) as part of the Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA) tender for 114 jets. With the production line now transitioning to the F4 standard by 2025 following the delivery of the first aircraft in 2023 and the second in 2025, Dassault is positioning the Rafale F4 as a highly advanced option for the IAF.
Officials from Dassault, speaking to idrw.org, emphasized that the Rafale F4 brings numerous upgrades over the Rafale F3R jets currently operated by the IAF, among them are Thales software-defined radio, satellite communications and other improvements on RBE2 AESA radar, Talios targeting pod, front sector optronics system, and helmet-mounted display capabilities. New capabilities for the F4 include the Thales Scorpion Helmet Mounted Display, MBDA’s MICA NG (Next-Generation) air-to-air missile and the 1,000-kilogram variant of Safran’s AASM (armement air-sol modulaire) “Hammer” precision-guided munition.
Continue reading