SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
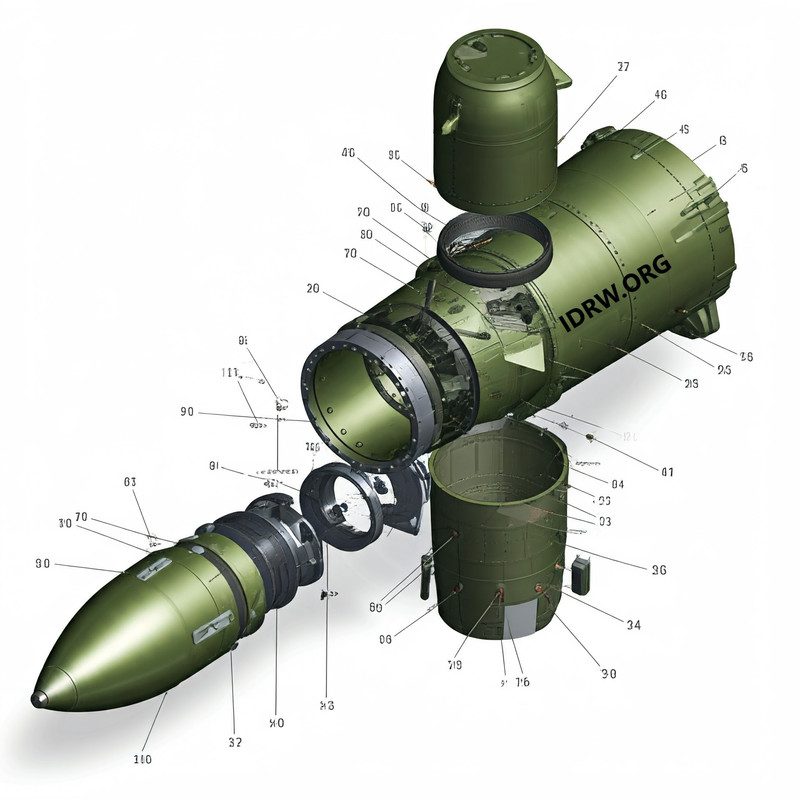

The Armament Research and Development Establishment (ARDE) has embarked on an ambitious project focusing on the development of a 155mm Ramjet projectile. This innovative undertaking aims to enhance artillery capabilities with advanced projectile technology, leveraging the potential of ramjet propulsion systems.
The ARDE’s comprehensive approach encompasses a wide range of activities, from initial design to final manufacturing and quality assurance, ensuring that the project meets the rigorous standards required for defence applications.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
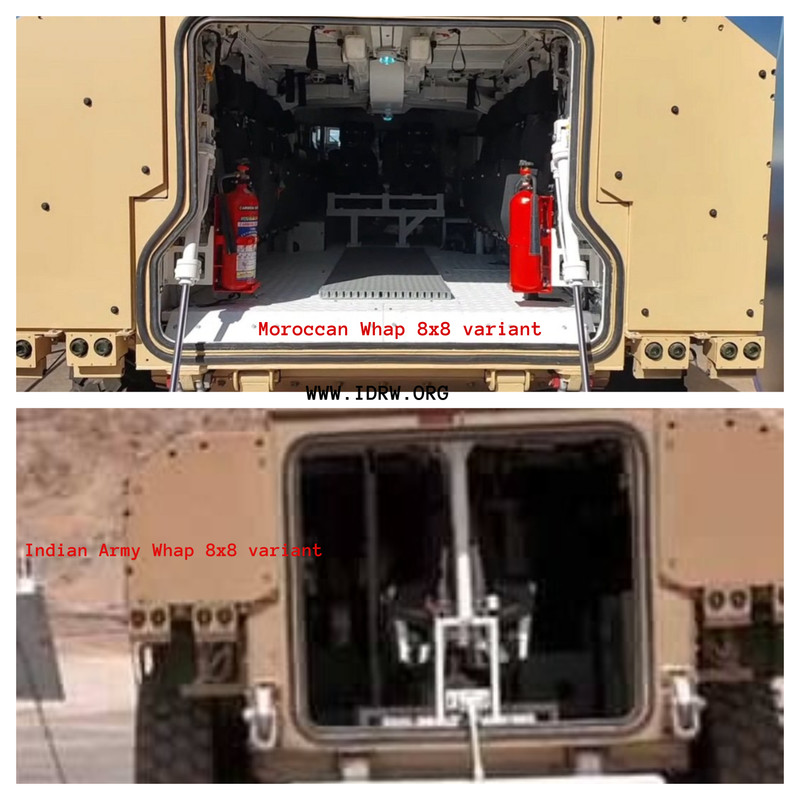


At a recent defense exhibition in Morocco, Tata Advanced Systems Limited (TASL) showcased a customized version of its Wheeled Armoured Platform (WHAP) 8×8, revealing several major changes from the Indian Army variant. The modified WHAP 8×8, tailored to Moroccan requirements, reflects both structural and functional adaptations designed to enhance operational suitability for the Moroccan Armed Forces.
The WHAP 8×8 is a multi-role armored vehicle developed by TASL in partnership with the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and tailored initially for the Indian Army’s requirements. The platform is versatile, capable of fulfilling various roles from reconnaissance to infantry transport and potentially even as an anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) carrier.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


In a significant stride towards enhancing India’s defense capabilities, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has inaugurated the DRDO-Industry-Academia Centres of Excellence (DIA-CoEs) at premier academic institutions, including the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore and the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay. This initiative aims to create a Directed Research Ecosystem that fosters collaboration among DRDO laboratories, academia, startups, and industries, paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in defense technology.
The establishment of DIA-CoEs is a strategic response to the growing need for innovation and indigenous development in the defense sector. By bridging the gap between academia and defense research, DRDO aims to leverage the expertise and resources of leading educational institutions to accelerate the development of cutting-edge technologies that meet the needs of the Indian Armed Forces.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) has recently issued two Requests for Information (RFI) to design, develop, and supply advanced radar systems tailored for its upcoming Dual Band Multirole Helicopter (DBMRH) platform. This RFI specifically seeks to equip two DBMRH variants with radar capabilities tailored for diverse operational roles: an Airborne Early Warning (AEW) radar for the DBMRH-AEW variant and a Surveillance radar for the DBMRH-S Special Operations variant.
The project aims to establish the design and development (D&D) activities and production facility within 60 months from the program’s inception (T0+60). The AEW radar system is set to be ready for integration on the DBMRH prototype by June 2027, while the surveillance radar is expected to be available by March 2027.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


India’s state-owned Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) is set to revive its Nashik plant operations to manufacture 12 Sukhoi Su-30MKI fighters, a production order valued at $1.3 billion approved in September 2023. This move aims to replace Indian Air Force (IAF) losses while bolstering domestic production. The facility, initially a dedicated manufacturing site for the Su-30MKI, will now resume operations to address this immediate order, with deliveries expected to contribute significantly to India’s air capabilities.
HAL is also rekindling its proposal to the IAF for an additional 72 Su-30MKI fighters, which, if accepted, could bring the total fleet to over 344 aircraft, adding four new squadrons by 2029-30. These additional units, valued at an estimated $5 billion, are part of HAL’s broader initiative to modernize and augment the IAF fleet with advanced indigenous technology and capability. However, sources report that budgetary constraints have so far limited the IAF’s response to this proposal.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


Recently, a collaboration among TridenTech Pvt. Ltd, IIT Madras, Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), RAL, and BILVA Technologies culminated in successful tests of a locally developed 80mm Multi-Mode (MM) rocket. This significant achievement marks a notable step forward in India’s defence capabilities, particularly in enhancing the armament of its Light Combat Helicopter (LCH). The 80mm rocket is set to undergo further testing and is expected to be integrated into the LCH, which currently utilizes a 70mm rocket system.
The LCH, a highly versatile and agile platform, is already equipped with 70mm rockets, developed through a partnership between Adani Defence & Aerospace and the Thales Group. The upcoming integration of the 80mm rocket will offer enhanced operational capabilities, providing the Indian Armed Forces with a more effective and versatile aerial weapon system.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
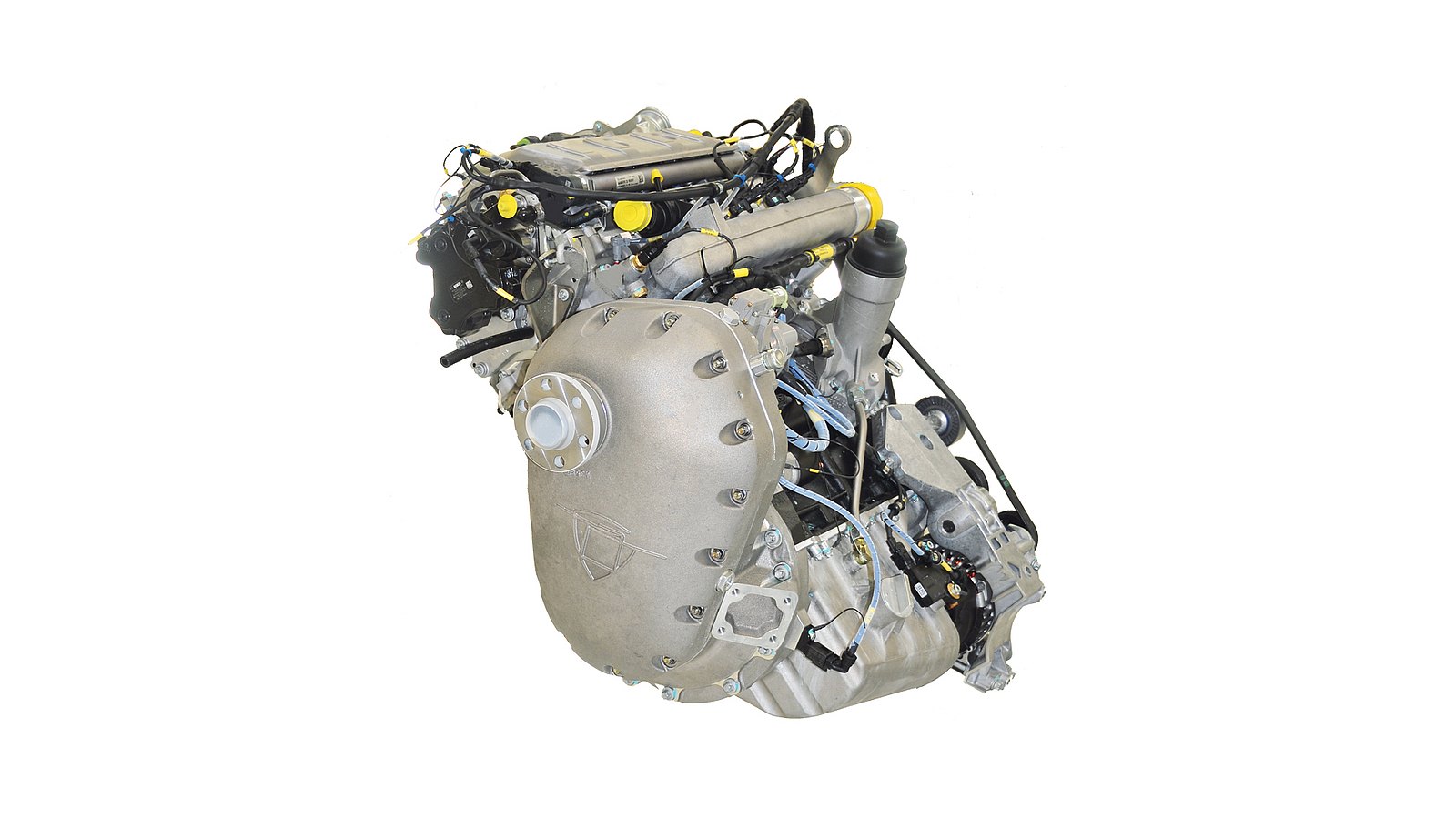


Defense analyst Angad Singh has raised concerns about the Austro 330EP engine, currently being used in India’s Archer-NG Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) UAV prototype, due to its ownership link with China. The engine’s manufacturer, Austro Engine, was acquired by China’s Wanfeng Aviation Industry in 2017, when Wanfeng took over Diamond Aircraft Industries, the parent company of Austro Engine. This connection has raised questions about the engine’s long-term viability in an indigenous defense platform like the Archer-NG, especially given the sensitive nature of UAV technology. However, Singh noted that this foreign engine might only be used in the early development stages of the Archer-NG program.
To mitigate reliance on foreign sources, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has taken proactive measures by developing an indigenous engine with the Vehicles Research and Development Establishment (VRDE) in collaboration with Jayem Automotives. This engine, which produces 180 horsepower, offers superior capabilities tailored to India’s operational requirements and is designed to provide consistent power up to 11,000 feet—a critical feature for operating in mountainous regions.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


In a recent interaction between the Philippine Marine Corps (PMC) and the United States Marine Corps (USMC), the Philippine military provided a detailed briefing on its advanced BrahMos anti-ship cruise missile system. The exchange of information took place during Exercise KAMANDAG, a joint military exercise aimed at enhancing cooperation and interoperability between the two nations’ forces. The exercise, which brings together Filipino and American troops, offers a platform for sharing expertise, discussing operational strategies, and strengthening defense relations between the two countries.
The BrahMos missile, jointly developed by India and Russia, is one of the most potent anti-ship cruise missiles in the world, known for its speed, precision, and devastating impact on naval targets. The Philippine military’s acquisition of this advanced missile system represents a significant step in enhancing its coastal defense capabilities, particularly in securing its maritime borders against external threats.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


In response to the Indian Army’s requirement for 90 Carrier Air Defence Tracked (CADET) systems, with a minimum of 50% indigenous content, South Korea’s Hanwha Aerospace has put forth its Hybrid BiHo system as a leading solution. Designed to address India’s evolving air defense needs, the Hybrid BiHo system is positioned as a highly adaptable and capable platform that could significantly bolster the Army’s mechanized columns across various terrains, including high-altitude areas up to 5,000 meters. As India seeks to strengthen its defense infrastructure with modern, locally-produced solutions, Hanwha Aerospace, in collaboration with India’s Larsen & Toubro (L&T), aims to meet these demands by establishing a robust domestic production line.
The Hybrid BiHo system distinguished itself in 2018 when it emerged as the Indian Army’s preferred choice following rigorous trials. Known for its dual-layered defense capabilities, the BiHo combines direct-fire guns with longer-range missiles, offering a versatile approach to tackling a wide range of low-altitude threats, from aircraft to drones. This unique multi-layered capability equips the system to swiftly engage and neutralize threats within close range, while the missile system provides an extended engagement envelope, enhancing the defensive reach of deployed forces.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
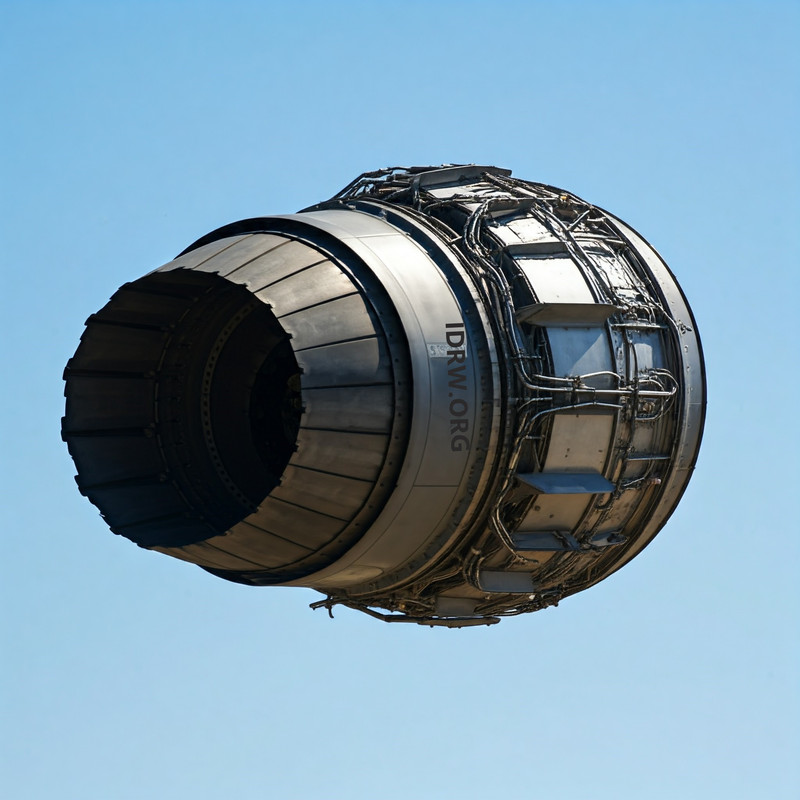


India is gearing up to finalize a significant partnership with a foreign aerospace major for the co-development of a new engine tailored for the fifth-generation Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. Sources close to idrw.org indicate that the deal is expected to be inked by mid-2025, with plans to conduct prototype engine testing by 2029. This initiative marks a crucial step in India’s ambition to bolster its Indigenous defence capabilities and advance its aerospace technology.
The new engine aims to achieve an impressive thrust capability, generating 75 kN of dry thrust, which could translate into approximately 110 to 130 kN of wet thrust when the afterburner is engaged. This thrust range is vital for ensuring optimal performance in various combat scenarios, enhancing the AMCA’s agility and operational effectiveness.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The delivery of India’s fourth S-400 squadron from Russia, originally scheduled for 2025, may now be delayed until early 2026, with the fifth squadron expected to arrive by mid-2026, according to recent media reports. Last month Indian Air Force (IAF) Chief, Air Chief Marshal Amar Preet Singh, acknowledged the delay, attributing it to disruptions stemming from the ongoing Russia-Ukraine conflict. This announcement came despite earlier indications of an accelerated delivery timeline, adding new challenges to India’s air defence upgrade plans.
In 2018, India signed a $5.43 billion contract with Russia for five S-400 air defense squadrons to strengthen its aerial defence capabilities. The deal positioned India as one of a select group of nations equipped with Russia’s advanced S-400 missile systems, known for their long-range precision and versatility in intercepting aircraft, UAVs, and ballistic and cruise missiles. With three squadrons already deployed by the IAF, the remaining two squadrons are highly anticipated to complete India’s comprehensive, multi-layered air defense network.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
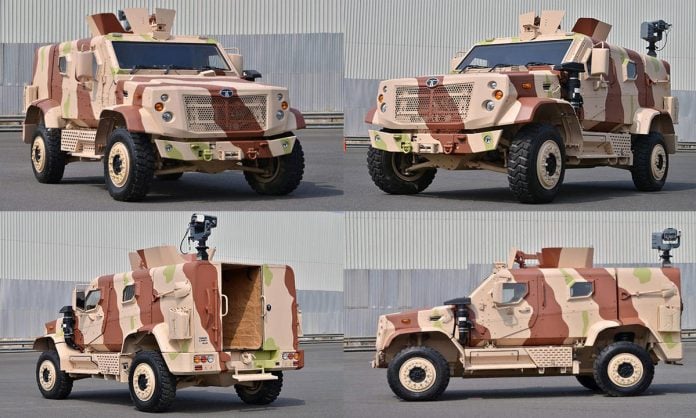


After securing an impressive order for 150 WHAP (Wheeled Armored Amphibious Platform) 8×8 vehicles from the Royal Moroccan Army, Tata Advanced Systems has captured further attention with its Light Armoured Multipurpose Vehicle (LAMV). This versatile, agile, and highly protected vehicle is generating key interest within the Royal Moroccan Army and has reportedly been offered for trials to explore its suitability for diverse operational requirements. With capabilities well-suited for reconnaissance, utility, and tactical operations, the LAMV is positioned to meet Morocco’s defense needs amid growing regional security challenges.
The Tata LAMV is designed to offer exceptional mobility and adaptability across various mission types, combining advanced protection features with state-of-the-art situational awareness systems. Built to withstand a wide range of battlefield threats, the LAMV provides the versatility that modern armed forces demand in light armored vehicles.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


The Indian Army has officially inducted the AARAV_ENX6D surveillance drone, developed by VTOL Aviation India Pvt. Ltd. This cutting-edge Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) brings advanced reconnaissance capabilities to the battlefield, designed with a modular airframe that offers enhanced durability, efficiency, and flexibility. The induction of this Indigenously Designed, Developed, and Manufactured (IDDM) system aligns with the Army’s goal of modernizing its surveillance and intelligence-gathering operations, especially in challenging terrains.
The AARAV_ENX6D features a modular airframe, which facilitates easy part replacement and maintenance. Its compact design allows for transportation in a single box or a backpack, making it highly portable and deployable in various terrains.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Ministry of Defence (MoD) has recently decided against the Indian Air Force’s (IAF) proposal to involve private sector companies in manufacturing the Tejas MkII fighter jets, citing cost efficiency and optimized utilization of current production facilities. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), the state-owned aerospace and defence company, has been designated as the primary manufacturer of the Tejas MkII, ensuring continuity in production and avoiding unnecessary expenditure.
HAL, which is currently leading the Tejas Mk1A production line with an order of 83 jets for the IAF, is expected to secure an additional 97 orders for the Tejas Mk1A variant. This expansion of orders could keep the Mk1A production line operational until 2032, a notable extension beyond the previously planned 2028 deadline. This shift allows HAL to continue fulfilling Mk1A orders, even as the MkII production line gradually ramps up.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


Following the induction of the C-295M transport aircraft into its fleet, the Indian Air Force (IAF) is evaluating the same platform to replace its ageing fleet of Soviet-era An-32 transporters. While the C-295M was initially introduced to replace the Hawker Siddeley HS 748 aircraft, its operational capabilities and size make it a viable option for replacing the An-32 as well. However, the C-295M may require modifications to meet the specific demands of high-altitude operations—capabilities that were purpose-built into the An-32 when it was developed for the IAF.
The An-32, an improved variant of the An-26, was specially tailored for high-altitude operations and rugged conditions. The IAF has relied on the An-32 for decades to transport cargo and personnel to remote, mountainous regions, a role that any replacement will need to fulfil effectively. As the C-295M begins operations in similar terrains, initial observations and performance feedback will be essential for determining what adjustments may be required to fully meet the IAF’s needs in higher altitudes and challenging environmental conditions.
Continue reading