SOURCE: IDRW.ORG
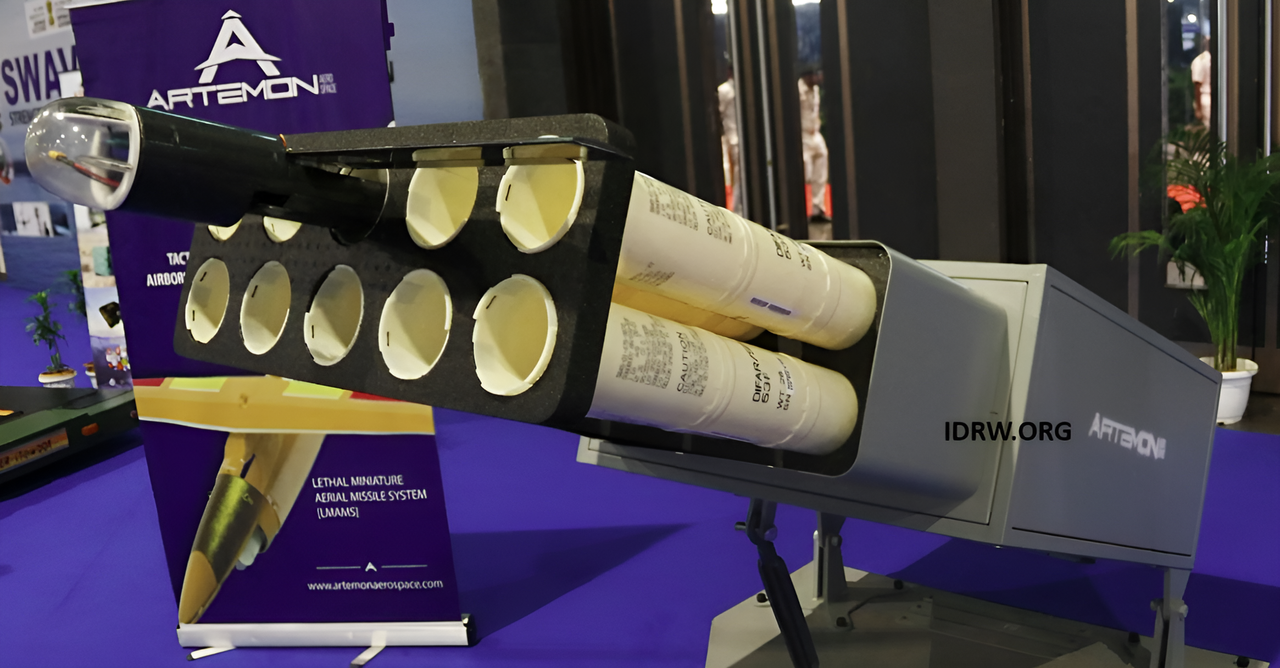


At Swavlamban 2024, Artemon Aerospace introduced a groundbreaking Loitering Munition designed to integrate seamlessly with the Indian Navy’s P-8I maritime patrol aircraft. This innovative system, capable of launching from the P-8I’s sonobuoy tubes, offers a unique combination of surveillance and precision strike capabilities, presenting a new tactical asset for anti-surface and reconnaissance missions over sea.
One of the most striking features of Artemon’s Loitering Munition is its compatibility with the P-8I’s sonobuoy tubes, which allows the aircraft to deploy up to 120 of these units in a single mission. Designed to be launched mid-air from the sonobuoy tubes, the loitering munitions offer an operationally efficient and swift launch process.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


In a strategic move to foster an advanced research ecosystem, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has established the DRDO-Industry-Academia Centre of Excellence (DIA-CoE) at the Indian Institute of Technology Hyderabad (IIT-H). This new centre, known as DIA-CoE, IITH, focuses on developing critical technologies that will bolster India’s defense capabilities across multiple domains, including missile defense, hypersonics, artificial intelligence, and space applications.
The DIA-CoE at IIT Hyderabad marks a key step in DRDO’s broader mission to establish Directed Research Eco-systems across India’s premier academic institutions. By bringing together DRDO laboratories, academia, startups, and industry, the initiative aims to accelerate indigenous development of technologies that will meet the evolving demands of modern warfare and national security. The center at IIT-H is part of DRDO’s nationwide network of Centers of Excellence, each focusing on specialized areas of defense research and development.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
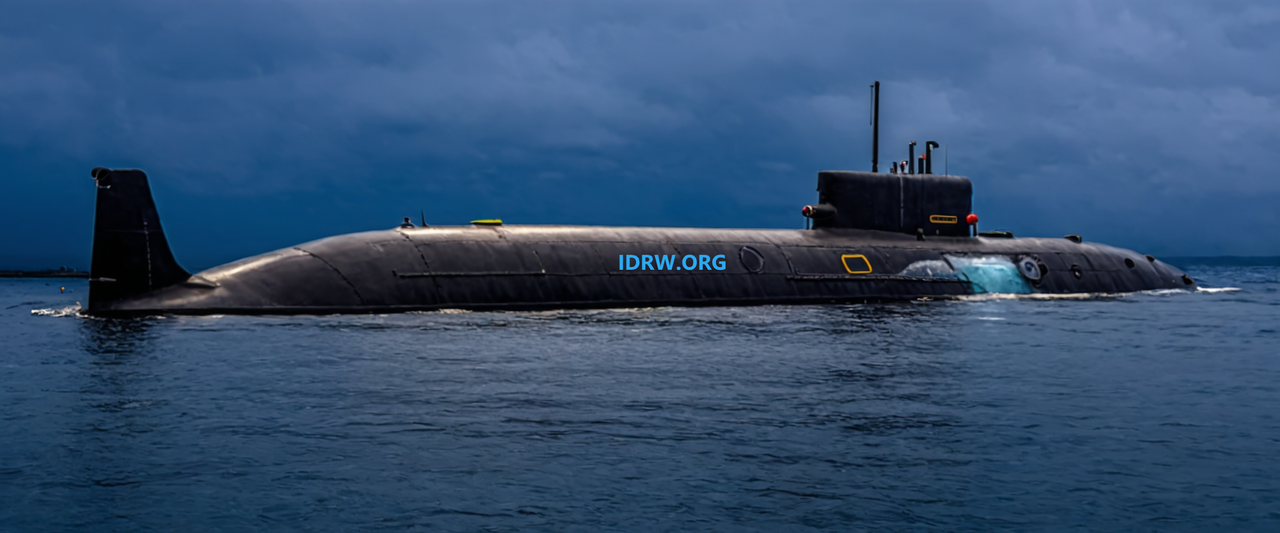


Dr. Mansoor Ahmed, an Honorary Lecturer at the Strategic and Defence Studies Centre of Australian National University, recently discussed India’s nuclear strategic goals on World Echo News with host Syed Muhammad Ali. Dr. Ahmed emphasized India’s growing commitment to bolstering its sea-based nuclear deterrent through an extensive fleet of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs). He suggested that the Indian Navy would likely need an arsenal of around 300 nuclear warheads exclusively for its SSBN fleet by 2035 to establish a credible deterrent.
India currently operates two Arihant-class SSBNs and has two more advanced S4-class SSBNs nearing operational status. The next generation, the S5 class, is expected to consist of three more SSBNs, ultimately expanding the fleet to a formidable six nuclear-capable submarines. The addition of these submarines underscores India’s focus on strengthening its nuclear deterrent with a credible second-strike capability, which will play a vital role in its broader defense strategy.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
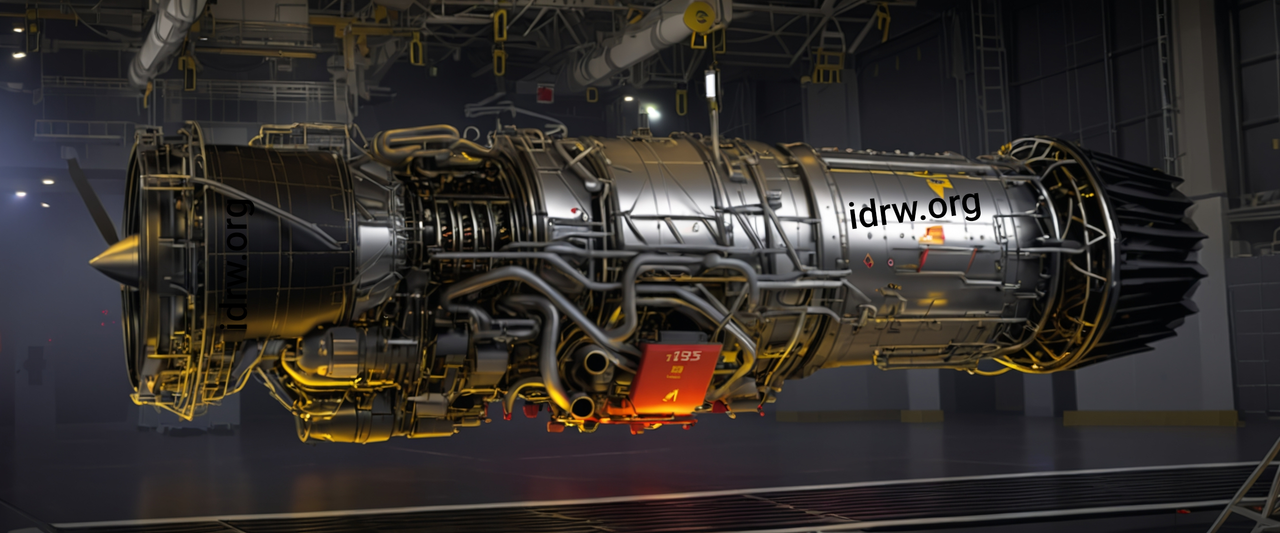

In a significant boost to India’s Indigenous defence capabilities, French aerospace giant Safran has proposed to partner with India’s Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) for the development of a new 110kN engine to power India’s Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA) program. As part of this collaboration, Safran has committed to leveraging Chennai’s growing pool of engineering talent, ensuring that most of the research and development (R&D) for the engine will now take place on Indian soil.
This proposal marks a key milestone in India’s push for self-reliance in defence manufacturing under the “Make in India” initiative, particularly in critical areas like jet engine technology, which has long been a strategic focus for the country.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
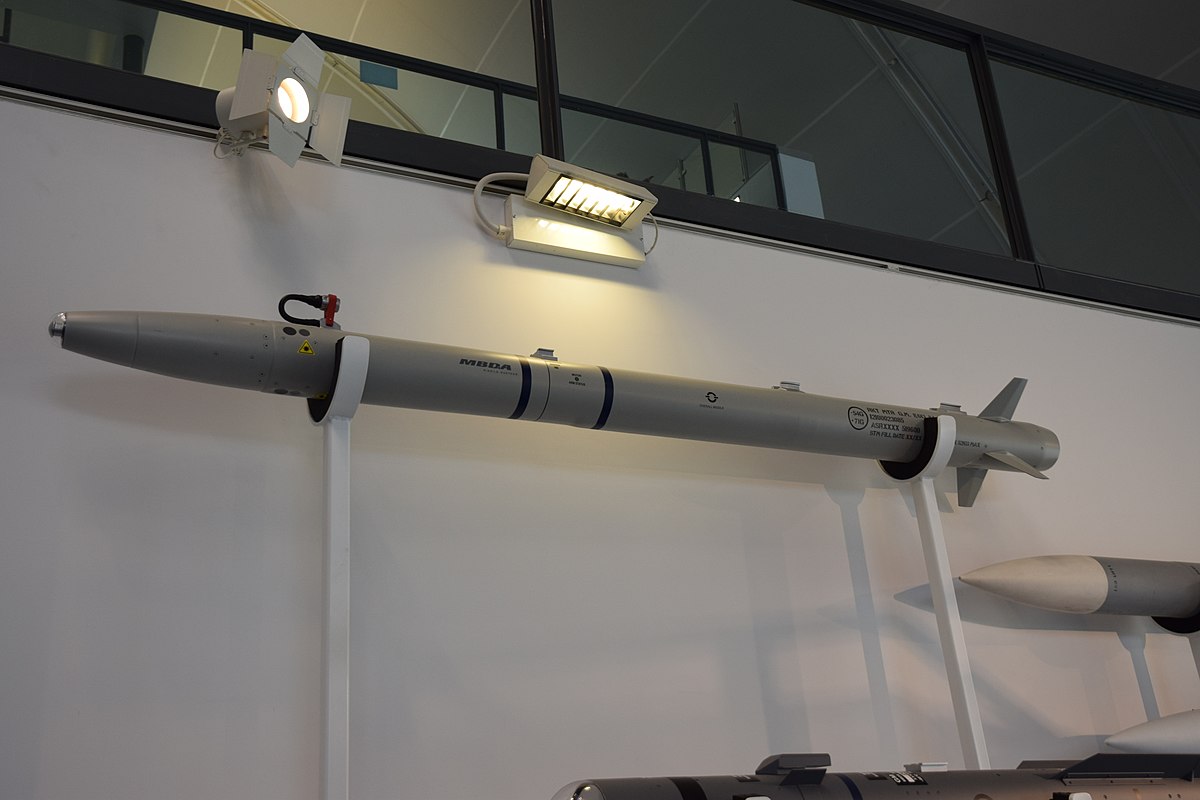


Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), in collaboration with the Indian Air Force (IAF), are looking to integrate Advanced Short Range Air-to-Air Missiles (ASRAAM) into the “Super Sukhoi” upgrade configuration for 84 Su-30MKI jets. This upgrade will replace the current Russian R-73 close-combat missiles in the Sukhoi fleet, enhancing the aircraft’s short-range air-to-air combat capabilities.
The ASRAAM, developed by the European defence manufacturer MBDA, is already operational on India’s Jaguar DARIN-III strike aircraft and the LCA Tejas Mk1A. Its successful deployment on these platforms has encouraged the IAF to push for further integration into the upcoming Tejas Mk2 and HAL’s CATS Loyal Wingman unmanned system, signaling a broader shift towards Western missile systems for close-combat engagements.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Marine Commando Force (MARCOS), the elite special forces unit of the Indian Navy, has initiated testing of the HOVERBEE system, a Portable Reconnaissance System (PRS) developed by Bengaluru-based startup Zulu Defence Systems. Known for their exceptional capabilities in special maritime operations, MARCOS are evaluating HOVERBEE’s potential for enhancing their operations, particularly in maritime environments.
HOVERBEE is a breakthrough innovation in reconnaissance technology, offering advanced situational awareness in a compact and highly portable package. Designed with agility and efficiency in mind, the device can be launched and recovered from the palm of the hand, making it ideal for rapid deployment in high-stakes situations where time and discretion are critical.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG


Chennai-based Space Rickshaw has achieved a significant milestone by securing its first defense contract with the Indian Defence Space Agency through the prestigious iDEX Aditi Challenge. This accomplishment comes just eight months after the company’s inception, showcasing its rapid growth and innovative capabilities.
Space Rickshaw’s deployer, specifically designed for nanosats, is a standout solution in the global market due to its unique design and lightweight nature. Under the terms of the contract, the company will supply its cutting-edge satellite separation systems, which were originally developed for internal use.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
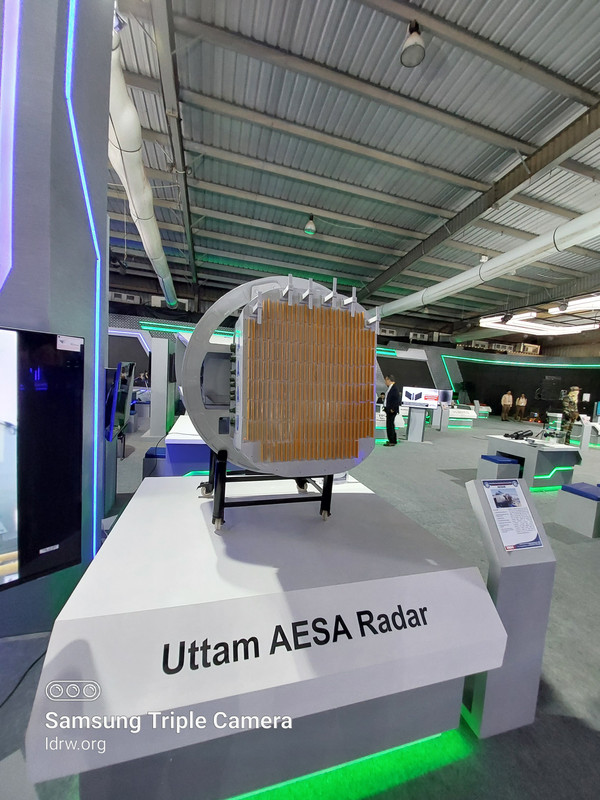


The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO)’s ADA has issued a tender for the supply of an Active Electronically Scanned Array Radar (AESAR), a sophisticated Fire Control Radar (FCR) intended for the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) AF Mk2 platform. This tender aligns with India’s ongoing modernization drive for its indigenous defense aviation capabilities, focusing on outfitting the Mk2 variant of the LCA with a next-generation radar system capable of multiple operational modes across diverse mission requirements.
The AESA radar for the LCA AF Mk2 is designed as a modular, multi-functional system comprising three critical subsystems. Active Array Antenna Unit (AAAU), Exciter Receiver Processor (ERP) and Array Power Supply (APS).
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
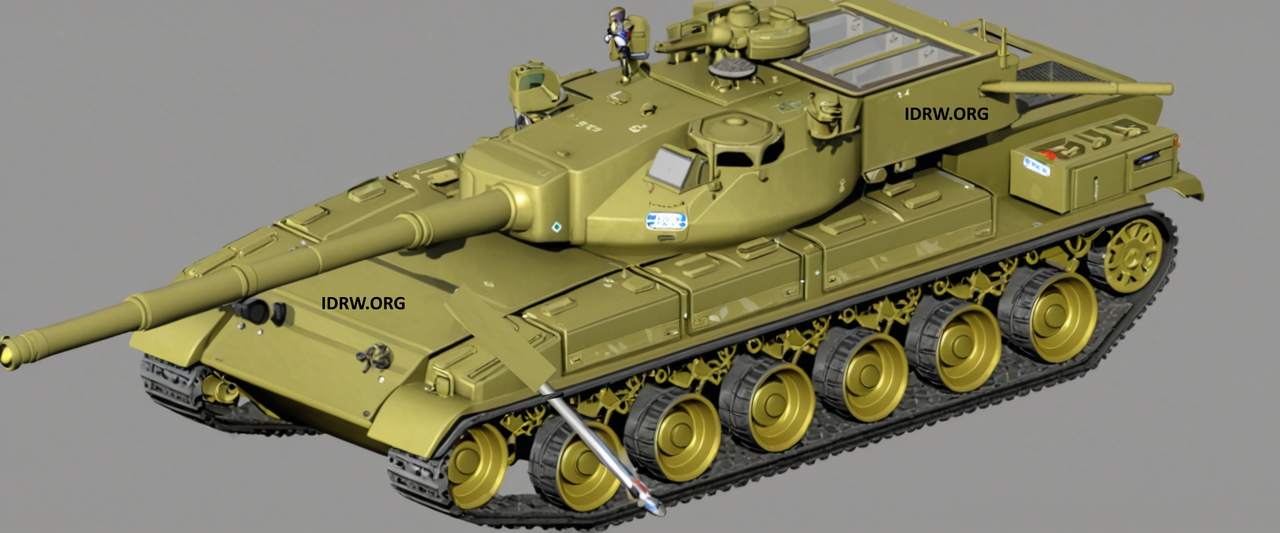


The Combat Vehicles Research and Development Establishment (CVRDE), in collaboration with the Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), Chennai, is advancing the development of a lab prototype for a smart antenna-based sensor, aimed for future use in Active Protection Systems (APS). This initiative signifies a pivotal step in enhancing the defence capabilities of Indian armoured vehicles, ensuring they are better equipped to counter evolving threats on the battlefield.
The smart antenna-based sensor is designed to integrate various modules that contribute to an effective Active Protection System. APS are critical for providing defensive measures against incoming threats, such as anti-tank missiles and projectiles. The development of this technology aligns with India’s focus on indigenizing defence systems and improving the operational readiness of its armed forces.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


As India ramps up its nuclear submarine fleet, the Indian Navy is constructing a strategic Very Low Frequency (VLF) transmitting station in Vikarabad, Telangana, set to become fully operational by 2027. This new infrastructure is critical for enhancing communication with the Navy’s expanding fleet of nuclear-powered submarines (SSBNs and SSNs), ensuring secure and reliable links for submerged vessels.
Located 75 kilometres from Hyderabad in the Damagudam Reserve Forest near Pudur village, the station will feature three imposing 500-meter-tall radio transmitter towers, equivalent to about 165 floors. These towering structures will form the backbone of the Navy’s advanced communication system, specifically designed to transmit messages to submarines operating at depths far below the surface.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.
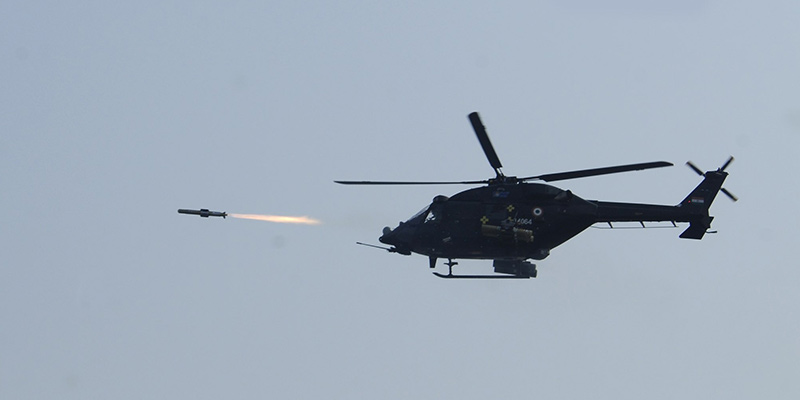


Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL) has officially begun the production process for a small batch of HELINA launchers and associated equipment. This initial order, comprising 20+ launchers and 7 associated items, marks a significant milestone in the development and deployment of this advanced anti-tank missile system.
The HELINA launcher assembly, to be manufactured and supplied by a designated vendor, will be produced in accordance with the specified scope of work and technical specifications. While the gas bottle and cooling system assembly will not be included in this initial batch, they are essential components of the complete HELINA system.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG
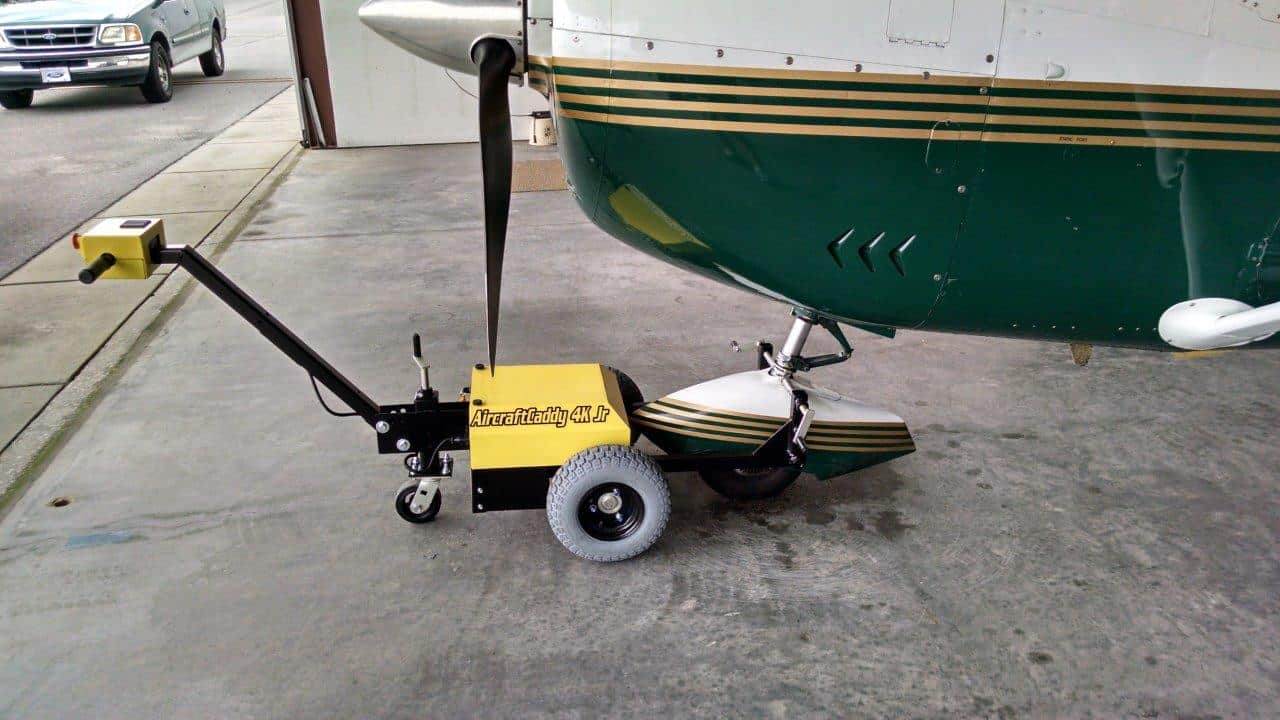


The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) is focusing on indigenizing key systems and equipment to improve operational efficiency and self-reliance. One of the latest initiatives is the indigenization of a Portable Battery-Operated Towing Aggregate (PBOTA), a critical system used for maneuvering helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft. The ICG is inviting private sector companies to participate in the development of an improved version of the PBOTA, which offers enhanced portability, reduced weight, and greater ease of use, specifically for deployment on ships and various operational platforms.
The existing PBOTA systems, currently in use by the ICG, are essential for moving rotary-wing aircraft in and out of hangars on board ships, or across airport aprons. These systems are vital for ensuring the safe and efficient positioning of aircraft, especially in environments where space and mobility are constrained, such as aboard ships or remote airbases.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
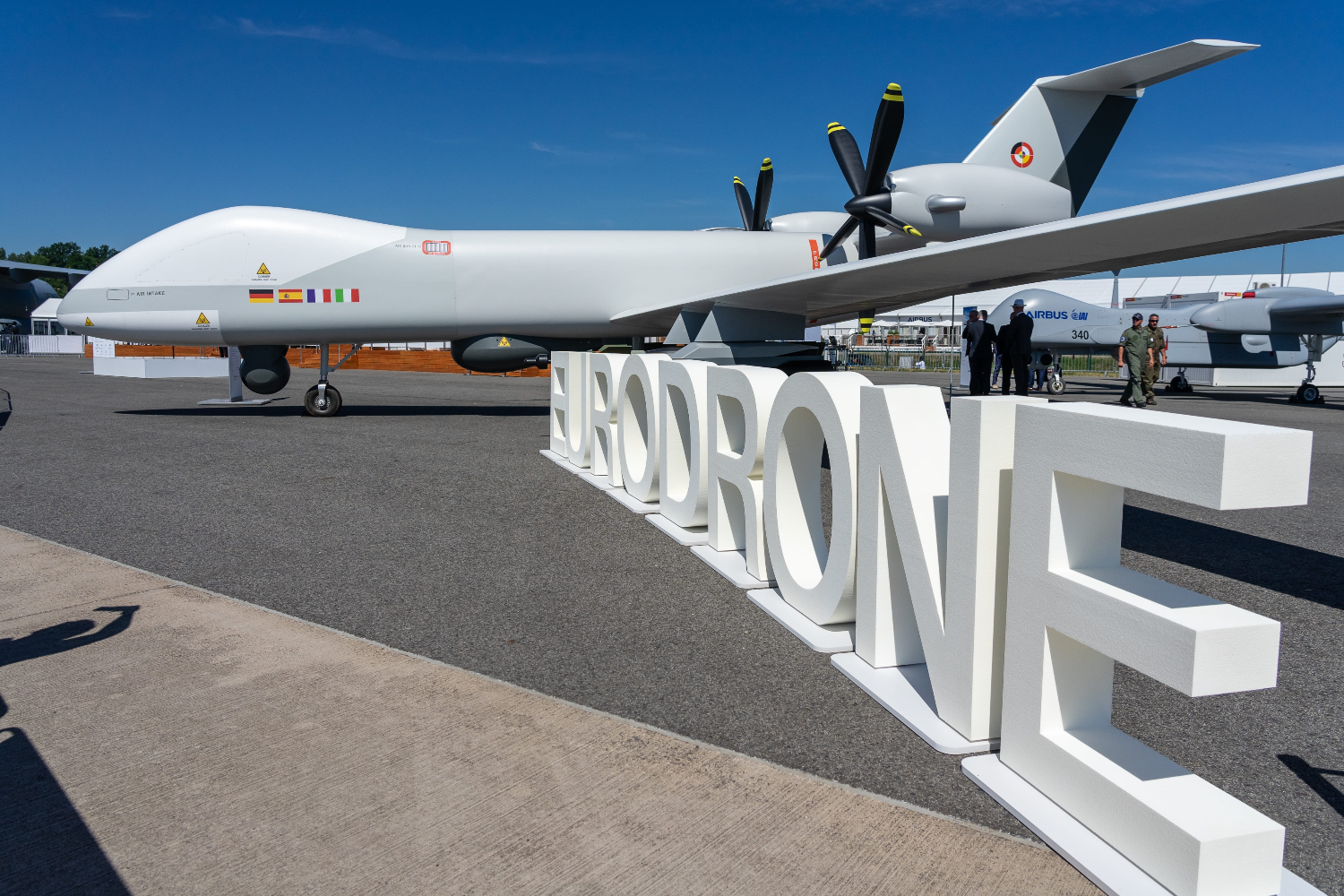


Germany has extended an invitation to India to join the Eurodrone Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance (MALE) UAV program as an observer, allowing India the opportunity to closely monitor the development of one of Europe’s most ambitious unmanned aerial vehicle projects.
The Eurodrone MALE UAV program, officially known as the European Medium-Altitude Long-Endurance Remotely Piloted Aircraft System (RPAS), is being jointly developed by Airbus, Dassault Aviation, and Leonardo for Germany, France, Italy, and Spain. It marks a strategic collaboration within Europe to produce a homegrown UAV capability that is competitive with international alternatives.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
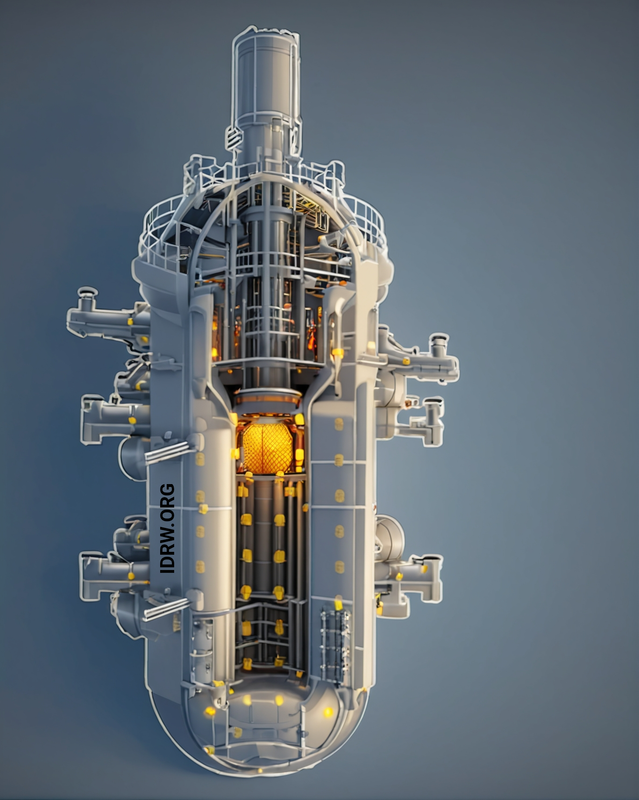


With formal approval granted for the development of two nuclear attack submarines (SSNs) under Project-77 for the Indian Navy, the next phase of India’s nuclear submarine program is well underway. According to a former Bhabha Atomic Research Centre (BARC) official who spoke to idrw.org, work on the second-generation 190-MW nuclear reactor has been ongoing for nearly eight years and will be ready in time to power the upcoming submarines.
The approval for these two SSNs marks a significant step forward in bolstering India’s maritime capabilities. Nuclear-powered attack submarines are critical assets for modern navies due to their ability to remain submerged for extended periods and travel vast distances without surfacing, making them indispensable for surveillance, deterrence, and offensive operations.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Drishti 10 (Hermes 900) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), locally manufactured by Adani Defence at its Hyderabad facility, was procured by the Indian Navy and Army for benchmarking testing purposes. Initially seen as an interim solution, both services acquired two units to assess their performance while awaiting a larger procurement initiative for Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) UAVs. However, as the services continue testing, it seems that further orders for the Drishti 10 might not materialize.
Both the Indian Army and Navy are keen on issuing a tender for the procurement of nearly 76 MALE UAVs, with 60 units designated for the Army, 12 for the Indian Air Force, and four for the Navy. This would allow the forces to acquire modern UAVs capable of meeting their operational requirements, rather than settling on interim solutions like the Drishti 10.
Continue reading