SOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


The Indian Navy is looking to bolster its self-reliance in critical technologies by partnering with private steel manufacturers to develop indigenous arrestor wires for its aircraft carriers. Arrestor wires, essential for flight operations on carriers, play a pivotal role in enabling aircraft to land safely on limited deck space by rapidly decelerating them.
This move aligns with India’s overarching goal of reducing dependence on foreign suppliers and strengthening the domestic defense manufacturing ecosystem under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


In recent years, India has been increasingly focused on modernizing its defense capabilities, and one of the more intriguing proposals on the table is the acquisition of Russia’s Tu-160M strategic bombers, often referred to as the “White Swan.” This offer from Russia has sparked considerable interest within the Indian Air Force (IAF), especially following the aircraft’s prominent role in the ongoing conflict in Ukraine. The proposal to acquire these bombers presents both an opportunity and a challenge for India as it assesses its strategic needs, regional security considerations, and its long-standing defense relationship with Russia.
The Tu-160, a supersonic, variable-sweep wing heavy bomber, is one of the most formidable aircraft in the world. The Tu-160M, an upgraded version of the original Tu-160, is capable of carrying a wide range of advanced cruise missiles and nuclear warheads, giving it the ability to strike strategic targets at long ranges. This capability would be a significant addition to the Indian Air Force’s arsenal, enhancing its deterrence posture and strategic flexibility.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Pierre Henri Chuet, a former fighter pilot in the French Navy, widely recognized for his experience with iconic aircraft like the Rafale Marine and Super Etendard, recently shared his thoughts on the crash of an Indian Air Force (IAF) MiG-29UPG fighter that occurred last month. The incident involved the aircraft entering a flat spin, a phenomenon that led to the ejection of the pilot. Chuet, reflecting on the event, emphasized key aspects of aircraft ejection protocols, pilot safety, and the mechanics of handling high-stakes situations in combat aviation.
Chuet began by stressing that twin-engine aircraft, like the MiG-29UPG, inherently possess a lower risk of catastrophic failure compared to single-engine planes. He noted that while twin-engine jets are generally more stable, incidents like flat spins demand immediate action. The MiG-29UPG pilot, in this case, was able to eject after ensuring that the plane was not over populated areas, a crucial decision in preventing civilian casualties.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
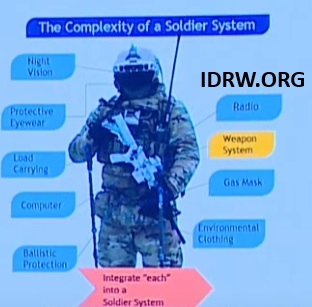

The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has unveiled a groundbreaking Digital Soldier as a System (DSaaS) concept, designed to significantly enhance the capabilities and survivability of soldiers in modern battlefields. The system integrates cutting-edge technologies, making each soldier a networked combatant with advanced situational awareness, communication, and decision-making tools.
The Digital Soldier as a System leverages a Body Area Network (BAN) to seamlessly connect an array of smart devices and sensors, enabling real-time data sharing and enhancing combat efficiency. The components include:
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


A Bengaluru-based company has achieved a significant milestone by winning the iDEX Prime X Challenge of Innovations for Defence Space Agency (DSA). The challenge focused on the development of a 200-Watt Ka-band Solid State Power Amplifier (SSPA), a critical technology for satellite ground stations. This development is expected to strengthen India’s capabilities in space-based communication and defense systems.
The iDEX Prime X initiative, under the Ministry of Defence’s Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) program, seeks to foster innovation and technology development by engaging startups and MSMEs in addressing specific challenges posed by the Indian defense sector. The challenge by the DSA specifically aimed at addressing the need for high-power, efficient, and reliable amplifiers operating in the Ka-band frequency range, which is essential for satellite communications.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


The Central Industrial Security Force (CISF) has issued a tender for the procurement of 613 Submachine Guns (SMGs) chambered in 9x19mm. The procurement will also include holographic sights and other essential accessories.
This move is part of the CISF’s ongoing efforts to modernize its arsenal and enhance the operational capabilities of its personnel. The new SMGs are expected to provide improved firepower and accuracy, particularly in close-quarters combat situations.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


Russia’s Tactical Missiles Corporation (KTRV) and design bureau MKB Raduga are keen to introduce the Kh-69 stealth cruise missile to Indian Air Force (IAF) officials as an advanced strike option for the IAF’s Sukhoi-30MKI fleet.
The scaled model of this missile, initially showcased at Moscow’s Army-2022 military exhibition, highlights its stealth characteristics, precision targeting, and long-range capabilities, positioning it as a formidable tool for modern warfare. Rosoboronexport, Russia’s official arms exporter, aims to underline the missile’s potential to significantly enhance the strike capabilities of India’s Su-30MKI fighters.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


The Indian Navy’s ambitious S5-class of ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs), each set to have a submerged displacement of around 13,000 tons, will be fitted with advanced submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) currently under development. While the Arihant and Arighat SSBNs are already operational with the B05/K-15 and K-4 SLBMs, the future S4, S4* (Star), and S5 submarines will bring enhanced deterrent capabilities, including a new generation of SLBMs.
To match the increased size and strategic role of the S5 class, India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is progressing on an array of SLBMs with significantly extended ranges and payload capacities.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG


For the first time, tender documents have provided a detailed look at the technical specifications of the Active Electronically Scanned Array (AESA) radar antenna, specifically the AESA-AAAU, designed for the Indian Air Force’s Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) AF Mk2. This advanced radar represents a significant technological upgrade aimed at enhancing the capabilities of the LCA Mk2, with its architecture closely following the Uttam AESA radar used in the Tejas Mk1A but featuring several design modifications to suit the Mk2’s requirements.
The AESA-AAAU radar for the LCA AF Mk2 is built around a 912-element array of transmit-receive modules (TRMs), with 896 active elements and 16 receive-only elements. The radar utilizes Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) TRMs with a power output of 10W, similar to those used in the Uttam radar for Tejas Mk1A. This high number of active elements is designed to enhance radar detection range, target acquisition, and tracking capabilities, allowing the LCA Mk2 to perform in complex and high-intensity combat scenarios.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


Larsen & Toubro (L&T), one of India’s leading defense manufacturers, has been working diligently on the development of its Futuristic Infantry Combat Vehicle (FICV), which is currently undergoing an upgradation process to meet the requirements outlined in the Request for Proposal (RFP) issued by the Indian Army. The FICV program is part of India’s ongoing efforts to modernize its armored vehicle fleet and enhance the capabilities of its mechanized infantry.
The FICV is envisioned as a key platform for the Indian Army’s infantry forces, providing superior mobility, firepower, and protection in modern combat scenarios. The vehicle is designed to be a highly versatile combat platform, capable of performing a wide range of roles, including offensive operations, defensive maneuvers, combat support, and surveillance missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


As the global strategic landscape continues to evolve, Italy has emerged as a key partner for India in the field of defense equipment and technology cooperation. With both nations sharing a growing and robust global strategic partnership, Italy views its defense ties with India as an essential area for future collaboration. This burgeoning relationship is exemplified by Italy’s offer of the Falco Xplorer Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV), a cutting-edge platform developed by Leonardo S.p.A., one of Italy’s premier defense and aerospace companies.
The Falco Xplorer stands at the forefront of Italy’s defense technology offerings to India. Capable of performing a wide range of missions, the UAV is engineered to excel in intelligence, surveillance, target acquisition, reconnaissance (ISTAR), and even airstrike capabilities. This versatility makes it a highly attractive asset for India, which faces complex security challenges across its vast and diverse terrain.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI

The National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL), a constituent of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), has achieved a significant milestone in propulsion technology by developing advanced Wankel engines in two power categories: a 10-15 kW hybrid Wankel engine and an 80-100 kW Wankel engine. These engines are poised to play a pivotal role in powering Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and cruise missiles, boosting India’s self-reliance in cutting-edge propulsion systems for strategic and tactical applications.
The 10-15 kW hybrid Wankel engine is designed to combine the best of combustion and electric propulsion systems. The hybrid configuration ensures high efficiency, reduced fuel consumption, and extended operational range, making it suitable for lightweight UAVs that require silent operation during critical missions.
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI


On November 15, 2024, India and Japan took a significant stride in their defense partnership by signing a Memorandum of Implementation (MoI) for the co-development of the UNICORN antenna complex for Indian warships. This marks a historic milestone, signifying the first-ever co-development/co-production of defense equipment between the two nations.
The UNICORN antenna complex, a technological marvel conceptualized by the Japanese Navy and manufactured by NEC Corporation, Japan, is a state-of-the-art composite communication antenna designed to enhance the stealth capabilities of warships. It has been specifically developed for the Future Frigate Multirole (FFM) class of warships, also known as the “Upgraded Mogami.”
Continue readingSOURCE: AFI
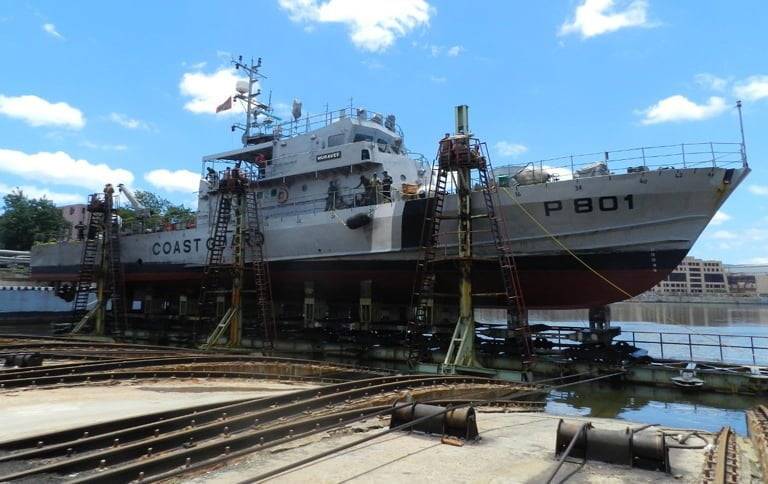


In a demonstration of its commitment to regional security cooperation, the Indian Navy is currently undertaking the maintenance and repair of two important vessels for its neighboring countries: the Maldivian Coast Guard Ship (MCGS) Huravee and the Mauritius Coast Guard Ship (MCGS) Valiant. These refits are being carried out at no cost to the respective governments, highlighting India’s proactive approach to strengthening maritime security in the Indian Ocean region.
Originally commissioned by India in 2016, the MCGS Huravee was formally handed over to the Maldives in 2023. The vessel is currently undergoing a comprehensive refit at the Naval Dockyard in Mumbai. This process involves critical repairs and upgrades aimed at enhancing its operational capabilities, ensuring its continued service in safeguarding Maldivian waters. The decision to refit the Maldivian vessel was made during the state visit of Maldivian President Ibrahim Mohamed Solih to India in October 2023.
Continue readingSOURCE: IDRW.ORG.


India is in the early stages of discussions with Vietnam for the supply of Guided Pinaka Rockets, a move that aims to help Vietnam replace its aging fleet of BM-21 and BM-14 multiple rocket launchers (MRLs), which were originally sourced from the Soviet Union. According to sources close to the negotiations, the talks are in the initial phases, and it could take several months before a formal deal is reached. However, both countries have shown a keen interest in moving forward with the collaboration as Vietnam seeks to modernize its artillery capabilities.
The Guided Pinaka Rocket System, developed by India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), has gained considerable traction in international markets due to its advanced precision strike capabilities. It is part of India’s push to expand its defense exports and offers significant advantages over older, conventional rocket systems. The system’s advanced guidance technology allows it to strike targets with high accuracy, a crucial advantage over the older, unguided rockets such as the Soviet-era BM-21 and BM-14, which are less effective in modern warfare scenarios.
Continue reading