News Beat
News Beat reporting is an idrw.org initiative to let our Readers to report News Based on Actual facts but some how has not been reported in Main Stream Media .
SOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

In a major leap forward for indigenous defense capabilities, the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has confirmed the successful testing of the Prototype DATRAN 1500hp engine for the Futuristic Main Battle Tank (FMBT). This development, highlighted in the DRDO Year End Review of 2023, showcases India’s commitment to advancing its technological prowess in the field of defense. The engine, a product of collaborative efforts with Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML), is a key component in the quest to enhance the country’s armored warfare capabilities.
Bharat Earth Movers Limited (BEML) has played a pivotal role in the realization of the DATRAN 1500hp engine. Taking on the responsibility of Design, Development, and Supply of these high-powered engines to CVRDE, BEML has demonstrated its commitment to advancing India’s defense manufacturing capabilities. The successful collaboration between DRDO and BEML underscores the synergy between government agencies and private enterprises in achieving strategic defense objectives.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
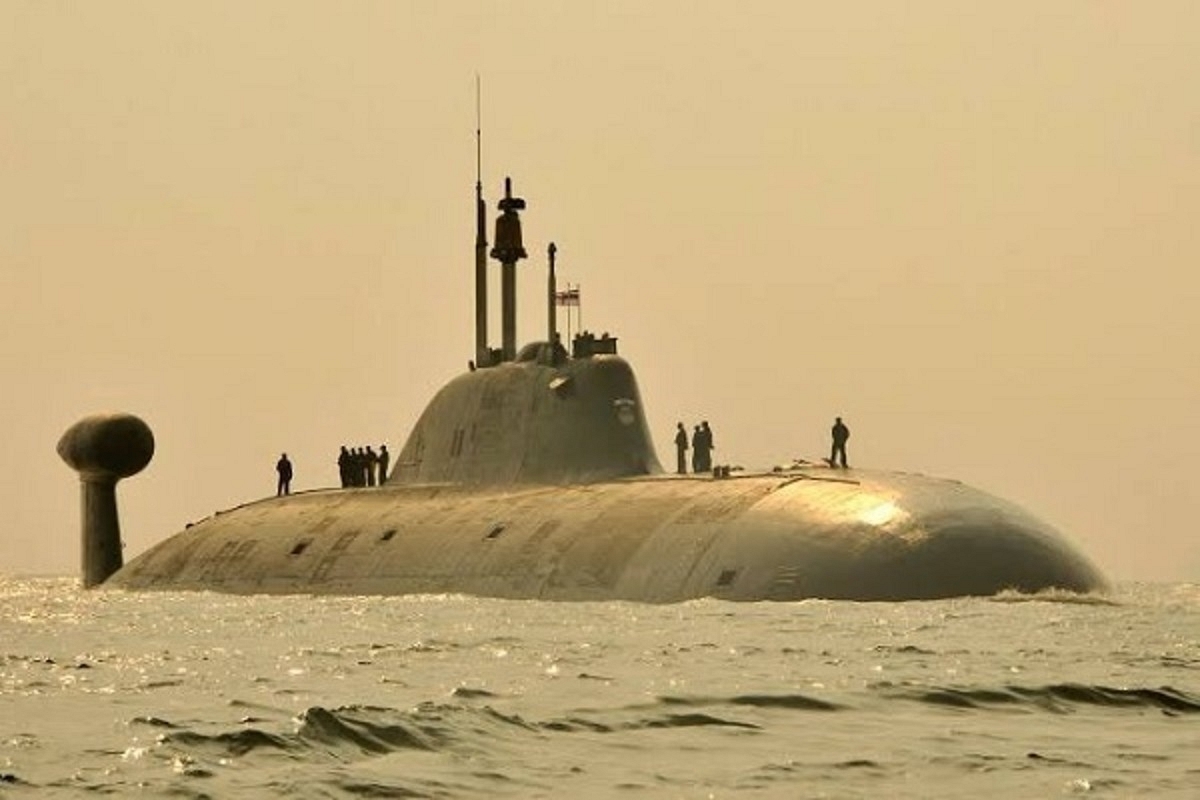

The fate of India’s highly anticipated Akula-class nuclear-powered attack submarine, Chakra-3, hangs in the balance as Russia grapples with delivery delays and India navigates complex financial hurdles. Despite assurances from Russia during External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar’s recent visit, the path towards acquiring this crucial underwater asset remains shrouded in uncertainty.
In 2019, India inked a $3 billion deal with Russia to lease an Akula-class submarine for a decade. This advanced acquisition, known as Chakra-3, was slated to bolster India’s maritime prowess and deter regional adversaries.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
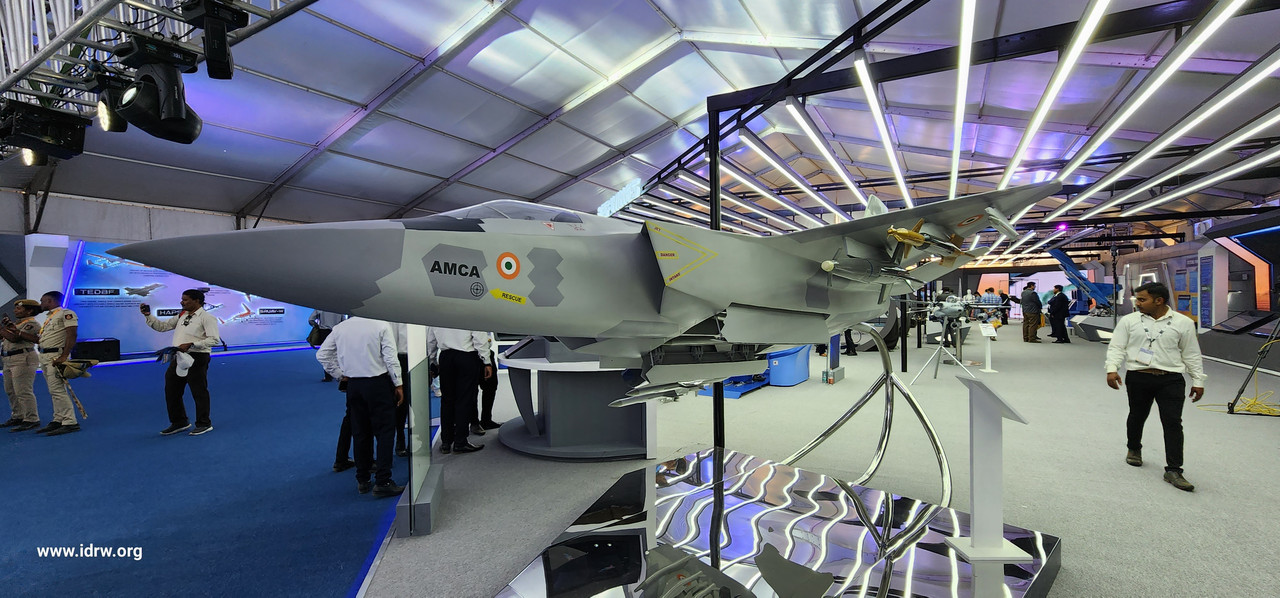

While India might be behind the curve in joining the 5th generation fighter jet club with its Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), it’s already peeking into the future. Former Air Chief Marshal RKS Bhadauria and outgoing ADA chief Girish Deodhare offer exciting insights into the AMCA’s potential, hinting at technologies bordering on the 6th generation.
Deodhare’s description of AMCA as a “5.5 generation” aircraft is intriguing. It signifies the integration of cutting-edge features not yet found in operational 5th gen jets but poised to be core elements of future 6th gen fighters developed by global powers. This puts India on a fascinating path, not just catching up but potentially leapfrogging with next-generation advancements.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
The Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) is developing a new Medium Altitude Long Endurance (MALE) class Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) called the Archer-NG. The UAV is expected to be rolled out in early 2024 with the first flight expected by mid-2024.
The Archer-NG will be equipped with technologies like avionics, software, a Ground Control Station and a Ground Data Terminal developed for the Rustom-2 UAV program. The Rustom-2 program was closed down due to its failure to meet the Indian Armed Forces’ requirement of an altitude of 30,000 ft and an endurance of 24 hours. The Archer-NG is being designed to address these shortcomings.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) has set its sights beyond the atmosphere, proposing a groundbreaking transformation into the Indian Air and Space Force (IASF). This ambitious move aims to propel India into the ranks of major aerospace powers, with a focus on harnessing the strategic potential of space.
At the heart of this vision lies the development of Co-orbital weapons, a controversial yet potentially game-changing technology. These satellites, equipped with explosives, lasers, or other directed-energy weapons, would be maneuvered in orbit to neutralize enemy satellites or even ground targets.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

It’s been over a decade since the Sukhoi Su-57, Russia’s first fifth-generation fighter jet, took to the skies. Yet, despite its impressive capabilities, the aircraft has struggled to find widespread adoption, particularly among its traditional allies like India and China.
India and China have long been major buyers of Russian fighter jets. However, both nations have taken different paths in the era of fifth-generation fighters. China has successfully developed its own J-20, while India, after a failed co-development project with Russia for the FGFA (Fifth Generation Fighter Aircraft) based on the Su-57 airframe, is focusing on its own Tejas and AMCA programs.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) are embarking on a major upgrade program for their fleet of 84 Sukhoi-30MKI fighter jets. This ambitious project will see a significant overhaul of the aircraft’s avionics, systems, and components, with a focus on incorporating Indian-made technologies and weapon systems. While this move towards self-reliance is laudable, it also presents challenges in integrating Western weapons onto a platform originally designed for Russian armaments.
The upgrade program prioritizes Indian-made sensors and avionics, enabling the Sukhoi-30MKI to seamlessly integrate domestic weapons like the Astra air-to-air missile family and Rudram air-to-surface missiles. This not only reduces dependence on foreign arms but also boosts the Indian defence industry. Additionally, the IAF plans to equip the upgraded jets with the MBDA-developed ASRAAM close-combat missile, demonstrating a continued willingness to leverage proven Western technologies where necessary.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
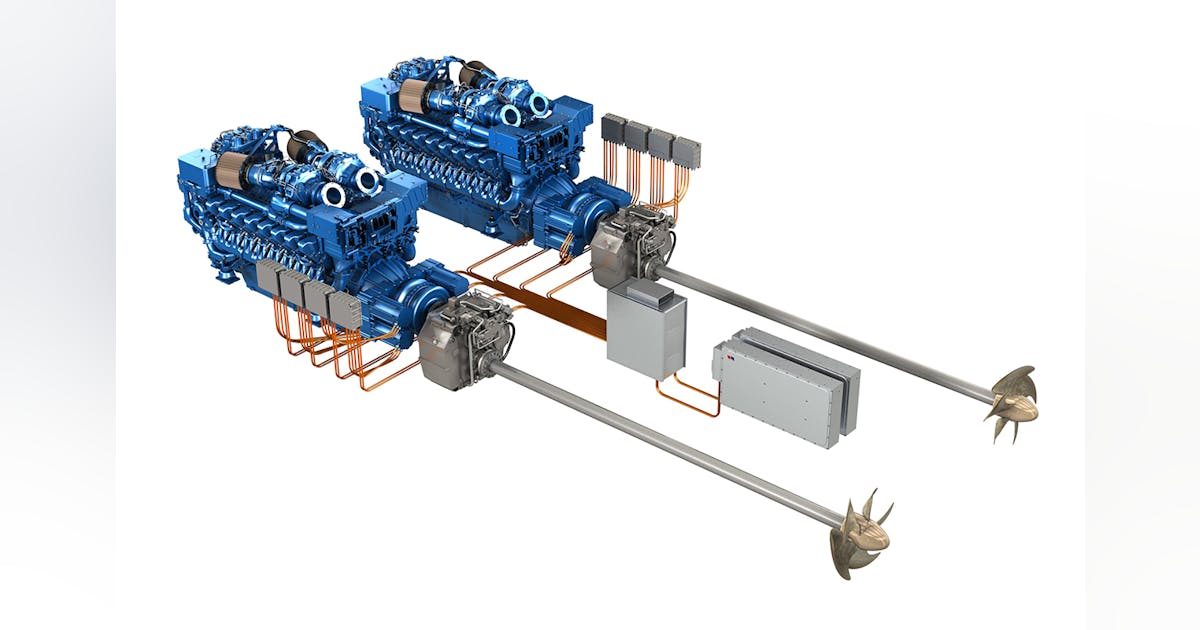
Rolls-Royce, a renowned name in the world of power and propulsion, has thrown its hat in the ring for India’s upcoming Next-Generation Destroyer (NGD) program with a cutting-edge hybrid propulsion solution. This proposal promises not only enhanced operational capabilities but also improved efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
At the heart of the Rolls-Royce solution lies a single, highly reliable gas turbine engine, capable of generating a powerful 36-40 MW of power even in scorching temperatures of 100°F. This engine, likely the Rolls-Royce MT30, will be the workhorse of the hybrid system, propelling the destroyer to full speed in a matter of minutes.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
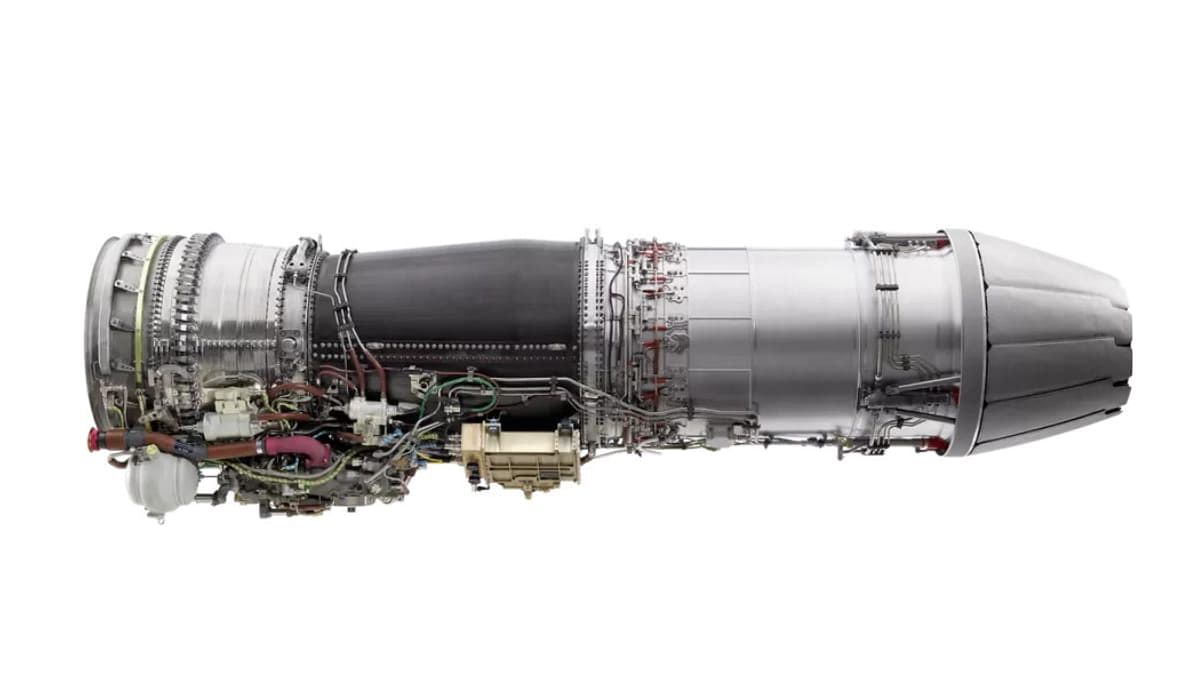
The sale of General Electric’s F-414 engine to India has come under meticulous review by the U.S. government’s Department of Commerce, governed by the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR). This regulatory framework is designed to evaluate critical technology risk and risk mitigation associated with the transfer of advanced defence technology. According to insiders, the deal includes an unprecedented 80% Transfer of Technology (ToT) to India, setting the stage for a comprehensive evaluation process that involves multiple U.S. government departments.
The ITAR process is a crucial mechanism for ensuring that the transfer of sensitive defence technologies, such as the F-414 engine, is conducted with utmost care and adherence to national security interests. It is within the purview of the Department of Commerce to oversee this process, emphasizing a thorough examination of the associated risks and appropriate mitigation strategies.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Air Force (IAF) is undergoing a significant shift in its helicopter procurement strategy, prioritizing domestic production and affordability over additional imports. This comes after the IAF confirmed it will not acquire more Apache attack helicopters, opting instead for the locally-made LCH Prachand. Now, the focus is turning to heavy-lift helicopters, with the IAF reportedly dropping plans for further purchases of the iconic Boeing CH-47F(I) Chinook.
The decision to forego additional Chinooks, despite their impressive capabilities, stems from a desire to support indigenous development and optimize costs. The IAF had previously acquired 15 Chinooks in 2020, but their high operating costs and potential dependence on foreign suppliers for maintenance have led to a reevaluation.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
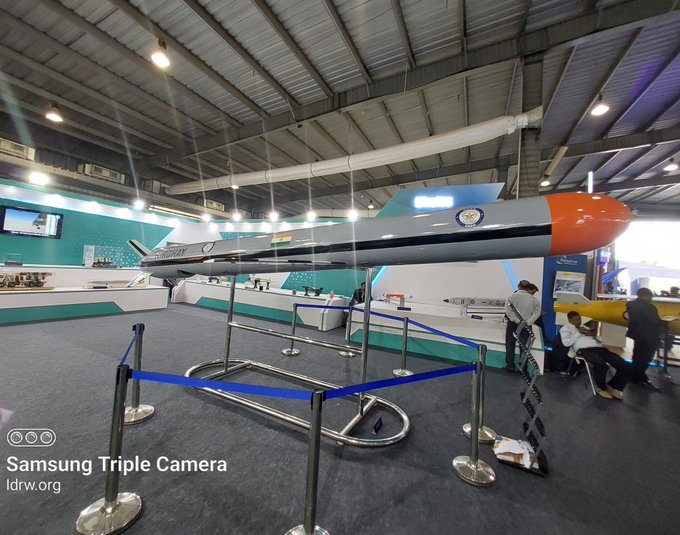

After successfully testing its land and sea-based long-range missiles last year, India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is now setting its sights on the sky. In the next 12 months, the organization plans to conduct carriage trials and potentially test an air-launched variant (ALCM) of its sub-sonic cruise missile, dramatically boosting India’s long-range strike capabilities.
This ALCM variant, stripped of its booster stage for aerial deployment, will be carried by India’s formidable Su-30MKI fighter jets. With a potent payload of 1 tonne and a range exceeding 600km, it will become India’s longest-range air-launched cruise missile, eclipsing the French-made Scalp ALCM currently equipped on the Rafale fleet.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

India’s Aeronautical Development Establishment (ADE) has taken a giant leap forward in its stealth aircraft development with the successful flight of the Stealth Wing Flying Testbed (SWiFT) Technology Demonstrator in its tailless configuration. This milestone marks the beginning of the next chapter for SWiFT, as ADE shifts its focus towards testing an internal weapons bay (IBW) and paving the way for a more advanced Remotely Piloted Strike Aircraft (RPSA).
The IBW is a crucial addition to SWiFT’s capabilities. By carrying weapons internally, the aircraft maintains its low-observable profile, making it even more difficult for enemy radars to detect. This enhanced stealth significantly increases survivability and mission effectiveness.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

The Indian Army has taken a significant step towards the future with the greenlighting of development for unmanned autonomous land robots powered by artificial intelligence (AI). These robots, capable of both offensive and defensive roles, hold immense potential for revolutionizing the Indian military landscape.
The integration of AI into land robots offers a plethora of advantages. These robots can operate in hazardous environments, perform tasks with greater precision and speed, and even engage in combat situations. Their autonomous capabilities allow them to make decisions in real time, adapting to changing situations without human intervention.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG
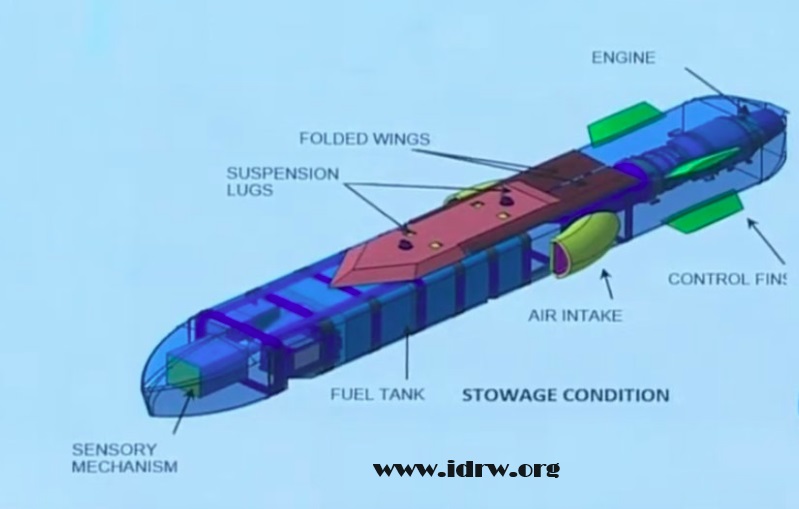
Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), India’s state-owned aerospace giant, has unveiled new details about its next-generation weapon system, the CATS Hunter Air-Launched Cruise Missile (ALCM). This sub-sonic, 700kg behemoth promises to significantly enhance India’s air attack capabilities with its lethal combination of stealth, range, and precision.
The CATS Hunter is designed to be the silent predator of the skies. Launched from a fighter aircraft (“Mothership”), it flies close to the ground or sea, mimicking terrain features to remain invisible to enemy radar. This low-altitude flight, coupled with its stealthy design, makes it a formidable foe for even the most advanced air defense systems.
Continue readingSOURCE: RAUNAK KUNDE / NEWS BEAT / IDRW.ORG

Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), India’s premier aerospace and defense company, has embarked on a critical project to develop a next-generation 4.2kN class turbojet engine. This upgraded version of the PTAE-7 engine, known as the PTAE-7G, marks a significant step forward for Indian aerospace capabilities and is poised to play a crucial role in two key programs: the CATS Warrior Loyal Wingman unmanned jet and the CATS Hunter Air-Launched Cruise Missile (ALCM).
The PTAE-7, originally developed in the 1980s, was a single-spool turbojet engine generating 3.43kN of thrust. While reliable, it lacked the advanced features and performance demanded by modern military applications. The PTAE-7G addresses these limitations by incorporating several key upgrades:
Continue reading